Invasion of Jungg'o: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
'''The Jungg'o Invasion''', also known as the ''Invasion of Jungg'o'' or the ''Jungg'o Reclamation'' (By Neo-Korea) was an armed conflict between [[Neo-Korea]], the [[Jungg'o Federal Republic]] and its supporters, and (after the collapse of the JFR) the warlord/provisional states which emerged in the aftermath of aforementioned collapse and their supporters. Active hostilities began with [[Zumen-Onyx]] (Plan Onyx), a series of border transgressions with the objective to seize key military locations, carried out early in the morning of October 10th, which would act as the prelude to a direct invasion by the Combined Field Army Grouping. The primary rationale for the war would be, aside from public announcements of reunification between the two "Inherently conjoined states", a desire to end the large-scale rationing which had been in action until this point through the seizure of key agricultural territories from Jungg'o, alongside fears among the leaders of the Neo-Korean State that continued economic development in Jungg'o would begin to rapidly surpass Neo-Korea's own economic development which had occurred throughout recent decades. | '''The Jungg'o Invasion''', also known as the ''Invasion of Jungg'o'' or the ''Jungg'o Reclamation'' (By Neo-Korea) was an armed conflict between [[Neo-Korea]], the [[Jungg'o Federal Republic]] and its supporters, and (after the collapse of the JFR) the warlord/provisional states which emerged in the aftermath of aforementioned collapse and their supporters. Active hostilities began with [[Zumen-Onyx]] (Plan Onyx), a series of border transgressions with the objective to seize key military locations, carried out early in the morning of October 10th, which would act as the prelude to a direct invasion by the Combined Field Army Grouping. The primary rationale for the war would be, aside from public announcements of reunification between the two "Inherently conjoined states", a desire to end the large-scale rationing which had been in action until this point through the seizure of key agricultural territories from Jungg'o, alongside fears among the leaders of the Neo-Korean State that continued economic development in Jungg'o would begin to rapidly surpass Neo-Korea's own economic development which had occurred throughout recent decades. | ||
The Jungg'o invasion can be argued as the ultimate culmination of the longstanding relationship between Jungg'o and | The Jungg'o invasion can be argued as the ultimate culmination of the longstanding relationship between Jungg'o and the Kāichrén state-entities, with the independence (fiscally or otherwise) of one fundamentally being tied to the exploitation or conquest of the other (owing to the resources of Jungg'o and the Sea Access of the Korean Peninsula alongside said region's greater industrial investment), with border skirmishes having occurred repeatedly throughout the decades of continued joint-existence before the conflict. | ||
Despite the slightly-greater economic strength of, and greater foreign support given to Jungg'o, a lack of military unity caused by a long-term state of defacto disunity in the goals of the provinces and their associated militaries would result in [[Neo-Korea]] making rapid progress, seizing the vast majority of urban areas in one year, while the state as a whole would defacto collapse two years into the conflict. Despite these victories, the Neo-Korean Ground Forces would be tied down in counter-insurgency operations until 2010, when they would enact [[Zumen-Bunri]] (Plan Separation), a plan which forced/concentrated the majority (generally believed to be around 2,000,000+ members of) the rural population into urban centers such as [[Lushun]] and [[Harbyin]], alongside several cities constructed in the south of Jungg'o for the purpose (the "[[Bunri-Cities]]") to prevent them giving continued support to partisan forces. This has been declared an act of genocide by several states, including [[Jin Yi]] and [[Janpia]], although [[Neo-Korea]] denies these claims. | Despite the slightly-greater economic strength of, and greater foreign support given to Jungg'o, a lack of military unity caused by a long-term state of defacto disunity in the goals of the provinces and their associated militaries would result in [[Neo-Korea]] making rapid progress, seizing the vast majority of urban areas in one year, while the state as a whole would defacto collapse two years into the conflict. Despite these victories, the Neo-Korean Ground Forces would be tied down in counter-insurgency operations until 2010, when they would enact [[Zumen-Bunri]] (Plan Separation), a plan which forced/concentrated the majority (generally believed to be around 2,000,000+ members of) the rural population into urban centers such as [[Lushun]] and [[Harbyin]], alongside several cities constructed in the south of Jungg'o for the purpose (the "[[Bunri-Cities]]") to prevent them giving continued support to partisan forces. This has been declared an act of genocide by several states, including [[Jin Yi]] and [[Janpia]], although [[Neo-Korea]] denies these claims. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
===Jungg'o - Neo-Korean Relations=== | ===Jungg'o - Neo-Korean Relations=== | ||
Jungg'o and Neo-Korea had possessed negative relations since the end of the [[ | Jungg'o and Neo-Korea had possessed negative relations since the end of the [[Kāichrén Civil War]], owing to mutually opposed unification/[[Pan-Hiakemirism|Pan-Hiakemirian]] sentiments targeting the other. Both sides would attempt to seize border territories from the other, although generally these efforts were not successful. | ||
By the time of the war, the most recent border dispute not associated with it was over a small village set somewhat south of the border which had attempted to join Jungg'o during the civil war. | By the time of the war, the most recent border dispute not associated with it was over a small village set somewhat south of the border which had attempted to join Jungg'o during the civil war. | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
===Agricultural Rationing in Neo-Korea=== | ===Agricultural Rationing in Neo-Korea=== | ||
Throughout the aftermath of the [[ | Throughout the aftermath of the [[Kāichrén Civil War]], the Neo-Korean State lacked the capability to maintain the population it currently possessed without the economic and agricultural capabilities possessed by Jungg'o, which maintained the necessity for rationing throughout the period from 1961 until the end of the war. This continued rationing represented one of the major sources of discontent with the Neo-Korean State during its early establishment, and would linger as a source of discontent until the conflict started. | ||
The Neo-Korean State had, by the mid 70’s, already made the decision that an occupation of Jungg’o or other such form of alignment would be necessary to fix this issue without rendering Neo-Korea dependent on foreign trade or sending segments of the population abroad. Under the [[Hikaru Sakuma]] regime, agricultural drives and a temporary promotion of “backyard farming” would be used as a means to hold over the population until such time as he believed the NKGF was capable of winning a conflict- a date which would never come, owing to the botched assassination which put him into a coma. | The Neo-Korean State had, by the mid 70’s, already made the decision that an occupation of Jungg’o or other such form of alignment would be necessary to fix this issue without rendering Neo-Korea dependent on foreign trade or sending segments of the population abroad. Under the [[Hikaru Sakuma]] regime, agricultural drives and a temporary promotion of “backyard farming” would be used as a means to hold over the population until such time as he believed the NKGF was capable of winning a conflict- a date which would never come, owing to the botched assassination which put him into a coma. | ||
This belief would hold despite the growth of agricultural imports throughout the CGC period - with the rationale for war changing from ensuring the survival of the population to establishing the conditions which could allow for independence from foreign requirements for the population. This would be the same rhetoric utilized by [[Beom Dae]] to ensure a domestic moral high ground for the actions to be taken throughout the war. | |||
===Appointment of Beom Dae to Paramount Leader=== | ===Appointment of Beom Dae to Paramount Leader=== | ||
[[Beom Dae]] would | [[Beom Dae]] would ascend to the role of Paramount Leader in 1995, having successfully leveraged his personal popularity and friendship with [[Muraoka Shig]] to establish himself as the Paramount Leader of the state. In service to his desire to both enact large scale economic reform under the auspice of military necessity, and the desire to secure his own power to the maximal extent possible, he would begin preparations for an invasion of Jungg'o despite his previous support for some level of reconciliation. | ||
It can be argued that this seizure of power is the primary cause of Neo-Korea’s willingness to delve into the militarization of the population during this time, the necessity of propagating a rally-around-the-flag effect creating a situation wherein ceasing the conflict would lead to the failure of the government. | It can be argued that this seizure of power is the primary cause of Neo-Korea’s willingness to delve into the militarization of the population during this time, the necessity of propagating a rally-around-the-flag effect creating a situation wherein ceasing the conflict would lead to the failure of the government. | ||
===Jungg'o Military Preparedness=== | ===Jungg'o Military Preparedness=== | ||
While Jungg'o, on-paper, possessed a greater number of both soldiers and aircraft, the nature of the federation concept inherent to Jungg'oan governance (as a means to prevent a similar situation to the lacking of rights under the Kaesong-KDS period of rulership) meant that these forces were far inferior to what they hypothetically would be on paper. Additionally, many of the aerial vehicles possessed by Jungg'o were modernized craft from the 60's-70's period, making them far outdated in comparison to the craft operated by Neo-Korea. An additional issue was systematic corruption near the border - an issue shared by both parties, but which affected Jungg'o to a greater extent owing to the offensive strike being initiated by Neo-Korea. | |||
With this said, Jungg'o was in possession of an effective general staff under the direction of Juma Kusen, and had they been given a greater amount of both time and economic material to prepare with, it is highly likely the war would not have gone in the direction it eventually did. An addittional benefit possessed by Jungg'o was foreign support, which would be crucial to enduring for the period they managed to accomplish. | |||
===Neo-Korean Military Preparations=== | ===Neo-Korean Military Preparations=== | ||
Neo-Korea would be in possession of both initiative and a technological advantage in the earliest stages of the war - owing to both a greater understanding of modern war gathered through international observation and to a general capacity to stockpile greater amounts of equipment than Jungg'o was capable of - this was generally collated with a logistical advantage owned by NK for much of the war. Additionally notable was the greater capacity of Neo-Korea to mobilize the population - with an existing desire for war being able to cover many of the issues inherent in the starting of the invasion, and the recently begun [[1995 Economic Reforms]] allowing for the state to prevent the growth of protestors in a far more effective fashion than Jungg'o was capable of. | |||
==Course of the War== | ==Course of the War== | ||
| Line 146: | Line 152: | ||
===International Response=== | ===International Response=== | ||
{{flag|Janpia}} - Since the start of the war, [[Janpia|the Janpian Union]] had sent military attachés to [[Jungg'o Federal Republic]] under the | {{flag|Janpia}} - Since the start of the war, [[Janpia|the Janpian Union]] had sent military attachés to the [[Jungg'o Federal Republic]] under the direction of [[Khirelya "Karmiya" Mariyuvisch]]—the People's Marshal at the time, to help train the Jungg'o forces in conducting protracted warfare, urban operations, and field fortification engineering. It was additionally reported that they had sent various forms of political, industrial, and military support to the Jungg'o People's Front after the collapse of the Federal Republic. Among the military aid which was provided were weapons such as the [[SKR-7 Assault Rifle | SKR-7 Assault Rifle]] and the [[ZTG-7| ZTG-7 anti-tank grenade launcher]]. Crews that received specialized platforms such as the [[JP-1| JP-1 tank]] were trained by Janpian advisers for Jungg'o service. | ||
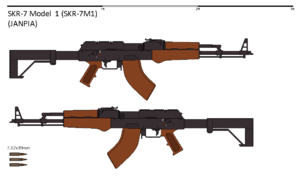
[[File:SKR-7M1 Assault Rifle.png|thumb|The Janpian Union | [[File:SKR-7M1 Assault Rifle.png|thumb|The Janpian Union provided an approximate 20,000 to 60,000 M1 SKR-7 assault rifles to the forces of Jungg'o during the conflict]] | ||
Following the death of Marshal Karmiya in 2010, the stance of the Janpian Union under the newly elected People's Marshal, [[Yorischa Juneschen]], | Following the death of Marshal Karmiya in 2010, the stance of the Janpian Union on the conflict under the newly elected People's Marshal, [[Yorischa Juneschen]], remained the same as her predecessor. During her administration, the [[Union of Party Members Committee]] declared the invasion as an act of genocide, and claimed that various human right violations against the Jungg'o people had occurred over the previous decade. To this day, the Janpian Union still claims that genocide and the violation of human rights have persisted, and continue to be perpetrated against the population of Jungg'o. | ||
Although unofficial, it is estimated that over 500 to 3,000 Janpian volunteers | Although unofficial, it is estimated that over 500 to 3,000 Janpian volunteers actively participated in the conflict starting in 1995 until the early 2000s, mostly acting to fill in the gaps along the frontlines. Minimal air support was also provided by the [[Janpian Union of Revolutionary Airforce|JURAF]] to provide cover for Jungg'o forces, as well as to engage in air interception against the Neo-Korean air force. Active Janpian participation began to subside around the summer of 2000s, as the People's Marshal soon began restricting any Janpian partisans from participating, not wishing to turn the war into a larger engagement with the Neo-Koreans. Although no official list of casulties was ever gathered, it was estimated that around 40 to 600 Janpians died or went missing in action during the 5 years in which participation occurred, with more than 500 dying in the conflict that followed until the official end of Janpian involvement in the conflict in 2010 under the directions of PM [[Yorischa Juneschen]]. | ||
==Aftermath== | ==Aftermath== | ||
| Line 170: | Line 176: | ||
[[Neo-Korea]], having already been in a process of rationing, was in a greater domestic position to perpetuate the war in that regards- with the general population of Neo-Korea not being effected in regards to sustenance by the conflict, and, in fact, gradually started receiving greater amounts of rationed material as the conflict proceeded, owing to both the acquisition of agricultural land and the direct seizure of food from areas which were believed to be hotbeds of insurgent activity, a practice which would be noted to contribute to the continued issues with establishing functional control over areas not immediately surrounded by urban territory. | [[Neo-Korea]], having already been in a process of rationing, was in a greater domestic position to perpetuate the war in that regards- with the general population of Neo-Korea not being effected in regards to sustenance by the conflict, and, in fact, gradually started receiving greater amounts of rationed material as the conflict proceeded, owing to both the acquisition of agricultural land and the direct seizure of food from areas which were believed to be hotbeds of insurgent activity, a practice which would be noted to contribute to the continued issues with establishing functional control over areas not immediately surrounded by urban territory. | ||
The war would be used as a means to expand [[Beom Dae]]'s control over the state, with the enduring insurgency being used as an excuse to mitigate or remove those individuals who had originally installed him from the halls of power. This process would involve the shattering of [[Hikaru Sakuma]]'s personality cult through a greater focus on a "Cult of the People" (as described by exile philosopher [[Maurice Shibuya]]), based around the principles of social militarism and the rallying of the population around the concepts of victory over and general "reunification" with Jungg'o. The [[White Guard]], Neo-Korea's own internal youth militia, would be removed from [[Central Intelligence Service]] control during the war, instead being made independent- both as a means to make the organization more independent of former CIS Director [[Pyoyter Nakiovich]] and to allow it to assume new roles of promoting contributions to the conflict such as blood drives, public works to assist in infrastructural construction in Jungg'o (including the [[Bunri-Cities]]), and other efforts domestically. | The war would be used as a means to expand [[Beom Dae]]'s control over the state, with the enduring insurgency being used as an excuse to mitigate or remove those individuals who had originally installed him from the halls of power. This process would involve the shattering of [[Hikaru Sakuma]]'s personality cult through a greater focus on a "Cult of the People" (as described by exile philosopher [[Maurice Shibuya]]), based around the principles of social militarism and the rallying of the population around the concepts of victory over and general "reunification" with Jungg'o. The [[White Guard]], Neo-Korea's own internal youth militia, would be removed from [[Central Intelligence Services|Central Intelligence Service]] control during the war, instead being made independent- both as a means to make the organization more independent of former CIS Director [[Pyoyter Nakiovich]] and to allow it to assume new roles of promoting contributions to the conflict such as blood drives, public works to assist in infrastructural construction in Jungg'o (including the [[Bunri-Cities]]), and other efforts domestically. | ||
===Jungg'o Federal Republic=== | ===Jungg'o Federal Republic=== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:58, 4 November 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Invasion of Jungg'o/Jungg'o War | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
| Neo-Korea | Jungg'o Federal Republic (until 2000) | Non-Recognized Combatants in the Jungg'o Invasion (2000-2010) | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||
|
|
Northern Provincial Government: Red and Black Army: Jungg'o People's Front: | ||||||
| Strength | ||||||||
|
Combined Field Army Grouping:
Neo-Korean Air Force:
|
Combined Armies (1995-2000):
Federal Airforce:
|
Northern Provincial Government:
Red and Black Army:
Jungg'o People's Front:
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
|
Combined Field Army Grouping:
Neo-Korean Air Force:
|
|
Northern Provincial Government:
Red and Black Army:
Jungg'o People's Front:
| ||||||
The Jungg'o Invasion, also known as the Invasion of Jungg'o or the Jungg'o Reclamation (By Neo-Korea) was an armed conflict between Neo-Korea, the Jungg'o Federal Republic and its supporters, and (after the collapse of the JFR) the warlord/provisional states which emerged in the aftermath of aforementioned collapse and their supporters. Active hostilities began with Zumen-Onyx (Plan Onyx), a series of border transgressions with the objective to seize key military locations, carried out early in the morning of October 10th, which would act as the prelude to a direct invasion by the Combined Field Army Grouping. The primary rationale for the war would be, aside from public announcements of reunification between the two "Inherently conjoined states", a desire to end the large-scale rationing which had been in action until this point through the seizure of key agricultural territories from Jungg'o, alongside fears among the leaders of the Neo-Korean State that continued economic development in Jungg'o would begin to rapidly surpass Neo-Korea's own economic development which had occurred throughout recent decades.
The Jungg'o invasion can be argued as the ultimate culmination of the longstanding relationship between Jungg'o and the Kāichrén state-entities, with the independence (fiscally or otherwise) of one fundamentally being tied to the exploitation or conquest of the other (owing to the resources of Jungg'o and the Sea Access of the Korean Peninsula alongside said region's greater industrial investment), with border skirmishes having occurred repeatedly throughout the decades of continued joint-existence before the conflict.
Despite the slightly-greater economic strength of, and greater foreign support given to Jungg'o, a lack of military unity caused by a long-term state of defacto disunity in the goals of the provinces and their associated militaries would result in Neo-Korea making rapid progress, seizing the vast majority of urban areas in one year, while the state as a whole would defacto collapse two years into the conflict. Despite these victories, the Neo-Korean Ground Forces would be tied down in counter-insurgency operations until 2010, when they would enact Zumen-Bunri (Plan Separation), a plan which forced/concentrated the majority (generally believed to be around 2,000,000+ members of) the rural population into urban centers such as Lushun and Harbyin, alongside several cities constructed in the south of Jungg'o for the purpose (the "Bunri-Cities") to prevent them giving continued support to partisan forces. This has been declared an act of genocide by several states, including Jin Yi and Janpia, although Neo-Korea denies these claims.
Background
Jungg'o - Neo-Korean Relations
Jungg'o and Neo-Korea had possessed negative relations since the end of the Kāichrén Civil War, owing to mutually opposed unification/Pan-Hiakemirian sentiments targeting the other. Both sides would attempt to seize border territories from the other, although generally these efforts were not successful.
By the time of the war, the most recent border dispute not associated with it was over a small village set somewhat south of the border which had attempted to join Jungg'o during the civil war.
Agricultural Rationing in Neo-Korea
Throughout the aftermath of the Kāichrén Civil War, the Neo-Korean State lacked the capability to maintain the population it currently possessed without the economic and agricultural capabilities possessed by Jungg'o, which maintained the necessity for rationing throughout the period from 1961 until the end of the war. This continued rationing represented one of the major sources of discontent with the Neo-Korean State during its early establishment, and would linger as a source of discontent until the conflict started.
The Neo-Korean State had, by the mid 70’s, already made the decision that an occupation of Jungg’o or other such form of alignment would be necessary to fix this issue without rendering Neo-Korea dependent on foreign trade or sending segments of the population abroad. Under the Hikaru Sakuma regime, agricultural drives and a temporary promotion of “backyard farming” would be used as a means to hold over the population until such time as he believed the NKGF was capable of winning a conflict- a date which would never come, owing to the botched assassination which put him into a coma.
This belief would hold despite the growth of agricultural imports throughout the CGC period - with the rationale for war changing from ensuring the survival of the population to establishing the conditions which could allow for independence from foreign requirements for the population. This would be the same rhetoric utilized by Beom Dae to ensure a domestic moral high ground for the actions to be taken throughout the war.
Appointment of Beom Dae to Paramount Leader
Beom Dae would ascend to the role of Paramount Leader in 1995, having successfully leveraged his personal popularity and friendship with Muraoka Shig to establish himself as the Paramount Leader of the state. In service to his desire to both enact large scale economic reform under the auspice of military necessity, and the desire to secure his own power to the maximal extent possible, he would begin preparations for an invasion of Jungg'o despite his previous support for some level of reconciliation.
It can be argued that this seizure of power is the primary cause of Neo-Korea’s willingness to delve into the militarization of the population during this time, the necessity of propagating a rally-around-the-flag effect creating a situation wherein ceasing the conflict would lead to the failure of the government.
Jungg'o Military Preparedness
While Jungg'o, on-paper, possessed a greater number of both soldiers and aircraft, the nature of the federation concept inherent to Jungg'oan governance (as a means to prevent a similar situation to the lacking of rights under the Kaesong-KDS period of rulership) meant that these forces were far inferior to what they hypothetically would be on paper. Additionally, many of the aerial vehicles possessed by Jungg'o were modernized craft from the 60's-70's period, making them far outdated in comparison to the craft operated by Neo-Korea. An additional issue was systematic corruption near the border - an issue shared by both parties, but which affected Jungg'o to a greater extent owing to the offensive strike being initiated by Neo-Korea.
With this said, Jungg'o was in possession of an effective general staff under the direction of Juma Kusen, and had they been given a greater amount of both time and economic material to prepare with, it is highly likely the war would not have gone in the direction it eventually did. An addittional benefit possessed by Jungg'o was foreign support, which would be crucial to enduring for the period they managed to accomplish.
Neo-Korean Military Preparations
Neo-Korea would be in possession of both initiative and a technological advantage in the earliest stages of the war - owing to both a greater understanding of modern war gathered through international observation and to a general capacity to stockpile greater amounts of equipment than Jungg'o was capable of - this was generally collated with a logistical advantage owned by NK for much of the war. Additionally notable was the greater capacity of Neo-Korea to mobilize the population - with an existing desire for war being able to cover many of the issues inherent in the starting of the invasion, and the recently begun 1995 Economic Reforms allowing for the state to prevent the growth of protestors in a far more effective fashion than Jungg'o was capable of.
Course of the War
Zumen-Onyx
Zumen Onyx, or Plan Onyx, would be the series of maneuvers which would begin the war- a series of border incursions which attempted to seize stockpiles and capture key military figures who may have been relocated to the area owing to the recent uptick in border conflicts. The Airforce would launch surprise strikes on 15+ airfields with strike aircraft, failing to damage infrastructure but damaging a majority of the fighter presence Jungg'o had available, although only in areas near the border this was successful- lacking the capability to strike deeper into Jungg'o owing to the limited range of Neo-Korea's aircraft. One hour after this was carried out, a declaration of war was given, followed by the border troops being reinforced by the Combined Field Army Grouping.
Attempts at retaliation later in the day were generally foiled by recently developed Surface-to-Air Missile systems placed near the border, although damage would be done to the northern city of Sinŭiju, alongside the military base near it. Neo-Korea's recently developed helicopters would prove effective in blunting a response by the ground forces in Jungg'o, slowing its armored forces by hours or, in some limited cases, even days. Provincial armies near the border would engage in combat with several Neo-Korean divisions which had been sent ahead in an attempt to seize several southern cities, with both sides sustaining casualties and the Neo-Korean push being blunted.
Early Combat
Shattering of the Combined Armies
Seizure of Key Urban Centers
Battle of Harbyin
Intervention by Chilokver
Carrier Operations
Collapse of the JFR
Remnant Factions
Beginning of Insurgency
Rising War-Weariness
The continuing insurgency, and the casualties caused by such, would begin fermenting public lack of support for the rationing, economic effects of the conflict, and similar issues which could not be entirely suppressed by the mood of social militarism. These feelings would eventually begin to turn into an overt anti-war movement, which represented a severe threat to the continued Neo-Korean war effort, and as such the Beom Dae government would attempt to prevent such from growing stronger- through entering negotiations with the leading figures of these movements and attempting to fulfill those demands they found reasonable- including beginning a gradual troop draw-down as the Zumen-Bunri began implementation.
This conciliatory mood also allowed for the restoration of former soldiers to civilian roles, which bolstered the economy in this lesser stage of the conflict- this most likely being the reason for the surprising tone the state took towards these efforts.
Zumen-Bunri
Zumen Bunri, also known as Plan Separation, was a tactic created by Grand Marshal Naito Keiji, created to bring an end to the war through the internment of populations suspected of assisting insurgent activities- into a series of Bunri-Cities and major urban areas such as Lushun and Harbyin. Around 2 million individuals would be interned in these cities, the exits and perimeters of said areas guided by both conventional military groupings and the CIS, who would also provide benefits to individuals- and the families of said individuals- willing to inform on any activities made in attempts to escape.
This would prove itself effective, according to the Neo-Korean Ground Forces General Staff, which declared that the campaign would be responsible for the end of the war two years after it was implemented, although doubt remains over this narrative, owing to already present slowing in the campaigns of insurgent forces due to losses caused by conventional forces. Conditions in these cities were generally satisfactory for survival, if poor in regards to luxuries or access to electricity, with rations being roughly equivalent to those the domestic population in Neo-Korea was receiving by this point, although communication to individuals outside of them was prevented via the attempted seizure of all communication devices within them.
Official End of the War
Annexation
Incorporation of JFR Power Structures
Emptying of the Bunri-Cities
International Response
![]() Janpia - Since the start of the war, the Janpian Union had sent military attachés to the Jungg'o Federal Republic under the direction of Khirelya "Karmiya" Mariyuvisch—the People's Marshal at the time, to help train the Jungg'o forces in conducting protracted warfare, urban operations, and field fortification engineering. It was additionally reported that they had sent various forms of political, industrial, and military support to the Jungg'o People's Front after the collapse of the Federal Republic. Among the military aid which was provided were weapons such as the SKR-7 Assault Rifle and the ZTG-7 anti-tank grenade launcher. Crews that received specialized platforms such as the JP-1 tank were trained by Janpian advisers for Jungg'o service.
Janpia - Since the start of the war, the Janpian Union had sent military attachés to the Jungg'o Federal Republic under the direction of Khirelya "Karmiya" Mariyuvisch—the People's Marshal at the time, to help train the Jungg'o forces in conducting protracted warfare, urban operations, and field fortification engineering. It was additionally reported that they had sent various forms of political, industrial, and military support to the Jungg'o People's Front after the collapse of the Federal Republic. Among the military aid which was provided were weapons such as the SKR-7 Assault Rifle and the ZTG-7 anti-tank grenade launcher. Crews that received specialized platforms such as the JP-1 tank were trained by Janpian advisers for Jungg'o service.
Following the death of Marshal Karmiya in 2010, the stance of the Janpian Union on the conflict under the newly elected People's Marshal, Yorischa Juneschen, remained the same as her predecessor. During her administration, the Union of Party Members Committee declared the invasion as an act of genocide, and claimed that various human right violations against the Jungg'o people had occurred over the previous decade. To this day, the Janpian Union still claims that genocide and the violation of human rights have persisted, and continue to be perpetrated against the population of Jungg'o.
Although unofficial, it is estimated that over 500 to 3,000 Janpian volunteers actively participated in the conflict starting in 1995 until the early 2000s, mostly acting to fill in the gaps along the frontlines. Minimal air support was also provided by the JURAF to provide cover for Jungg'o forces, as well as to engage in air interception against the Neo-Korean air force. Active Janpian participation began to subside around the summer of 2000s, as the People's Marshal soon began restricting any Janpian partisans from participating, not wishing to turn the war into a larger engagement with the Neo-Koreans. Although no official list of casulties was ever gathered, it was estimated that around 40 to 600 Janpians died or went missing in action during the 5 years in which participation occurred, with more than 500 dying in the conflict that followed until the official end of Janpian involvement in the conflict in 2010 under the directions of PM Yorischa Juneschen.
Aftermath
Casualties
Economic Impacts
Iminchaebol Presence in Military Development
Strategic Innovations
Domestic Situation During the Conflict
Neo-Korea
Neo-Korea, having already been in a process of rationing, was in a greater domestic position to perpetuate the war in that regards- with the general population of Neo-Korea not being effected in regards to sustenance by the conflict, and, in fact, gradually started receiving greater amounts of rationed material as the conflict proceeded, owing to both the acquisition of agricultural land and the direct seizure of food from areas which were believed to be hotbeds of insurgent activity, a practice which would be noted to contribute to the continued issues with establishing functional control over areas not immediately surrounded by urban territory.
The war would be used as a means to expand Beom Dae's control over the state, with the enduring insurgency being used as an excuse to mitigate or remove those individuals who had originally installed him from the halls of power. This process would involve the shattering of Hikaru Sakuma's personality cult through a greater focus on a "Cult of the People" (as described by exile philosopher Maurice Shibuya), based around the principles of social militarism and the rallying of the population around the concepts of victory over and general "reunification" with Jungg'o. The White Guard, Neo-Korea's own internal youth militia, would be removed from Central Intelligence Service control during the war, instead being made independent- both as a means to make the organization more independent of former CIS Director Pyoyter Nakiovich and to allow it to assume new roles of promoting contributions to the conflict such as blood drives, public works to assist in infrastructural construction in Jungg'o (including the Bunri-Cities), and other efforts domestically.
Jungg'o Federal Republic
Pre-Collapse
Post-Collapse
Legacy and Memory
![]() Janpia - A fountain and a memorial was erected at Strukuschena Plaza in Kalingrad, in memory of the Janpian volunteers as well as the Jungg'o people that served in the conflict. The Janpian Union also uses it to highlight its ongoing claims of genocide in Jungg'o perpetrated by Neo-Koreans. A Janpian animation film titled "Red Skies" was also based in this conflict, which follows a story of a Janpian pilot during the war.
Janpia - A fountain and a memorial was erected at Strukuschena Plaza in Kalingrad, in memory of the Janpian volunteers as well as the Jungg'o people that served in the conflict. The Janpian Union also uses it to highlight its ongoing claims of genocide in Jungg'o perpetrated by Neo-Koreans. A Janpian animation film titled "Red Skies" was also based in this conflict, which follows a story of a Janpian pilot during the war.