Eastarland: Difference between revisions
| Line 165: | Line 165: | ||
==Health== | ==Health== | ||
==Education== | ==Education== | ||
[[File:Usuniversitetas (18).jpg|300px|thumb|right|Višau, Eastarland's oldest university in Fanuburg]] | |||
Education in Eastarland is compulsory from 3 to 16 years old. From 2020, studies between the ages of 16 and 18 will be compulsory (this can be education, employment or civil service). The basic principles of Eastarlandian education are: freedom of teaching (public and private institutions), free education, neutrality of education, secularism, non-religious education. | Education in Eastarland is compulsory from 3 to 16 years old. From 2020, studies between the ages of 16 and 18 will be compulsory (this can be education, employment or civil service). The basic principles of Eastarlandian education are: freedom of teaching (public and private institutions), free education, neutrality of education, secularism, non-religious education. | ||
<br> Eastarlandian legislation guarantees its citizens a universal secondary education (school attendance is not a prerequisite, and about 1200 children are homeschooled).<br> | <br> Eastarlandian legislation guarantees its citizens a universal secondary education (school attendance is not a prerequisite, and about 1200 children are homeschooled).<br> | ||
| Line 171: | Line 172: | ||
The child goes to the school closest to home, but there is a tendency among parents to send their children to educational institutions that are more prestigious from their point of view. If the school is more than two and a half kilometers away, then according to the law, the student (up to the 6th grade) must be brought back and forth by taxi at the expense of the municipality. The school gives out textbooks and all stationery free of charge and teaches the Eastarlandian language, mathematics, natural science, and home economics. Education in the basics of religion (Protestantism or Catholicism) occurs only with parental consent and in accordance with the religion. Atheists have the right to allow secular ethics to be taught to a child, and if objected, children are exempt from any of the courses. The library shelves are in the hallway and are freely accessible. | The child goes to the school closest to home, but there is a tendency among parents to send their children to educational institutions that are more prestigious from their point of view. If the school is more than two and a half kilometers away, then according to the law, the student (up to the 6th grade) must be brought back and forth by taxi at the expense of the municipality. The school gives out textbooks and all stationery free of charge and teaches the Eastarlandian language, mathematics, natural science, and home economics. Education in the basics of religion (Protestantism or Catholicism) occurs only with parental consent and in accordance with the religion. Atheists have the right to allow secular ethics to be taught to a child, and if objected, children are exempt from any of the courses. The library shelves are in the hallway and are freely accessible. | ||
[[File:1231435.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Kuršovsk State University]] | |||
There are no grades in the lower grades; verbal gradation is used: excellent, good, changeable and “training required”. Starting from the 4th grade, grades are put in the range from 4 to 10 points. There are also grades for behavior - the ability to work in a group and alone, good breeding, and the desire to influence others for the better. | There are no grades in the lower grades; verbal gradation is used: excellent, good, changeable and “training required”. Starting from the 4th grade, grades are put in the range from 4 to 10 points. There are also grades for behavior - the ability to work in a group and alone, good breeding, and the desire to influence others for the better. | ||
<br>From grade 3, the first foreign language is added to the subjects - English. A foreign-speaking child (for example, from an immigrant family) is entitled to learn his native language from the first grade.<br> | <br>From grade 3, the first foreign language is added to the subjects - English. A foreign-speaking child (for example, from an immigrant family) is entitled to learn his native language from the first grade.<br> | ||
<br>In the lower grades, subjects are combined (chemistry with physics and biology, language with literature) and home economics is taught to everyone, regardless of gender. They write a lot in the school: all kinds of essays are designed to teach the child to have his own opinion on each issue and to express it in literary language.<br> | <br>In the lower grades, subjects are combined (chemistry with physics and biology, language with literature) and home economics is taught to everyone, regardless of gender. They write a lot in the school: all kinds of essays are designed to teach the child to have his own opinion on each issue and to express it in literary language.<br> | ||
[[File:18797582 401.jpg|300px|frameless|right]] | |||
After graduating from school, a young person can continue his studies at a gymnasium, where his studies end with an examination for a matriculation certificate, or enter a secondary vocational educational institution. | After graduating from school, a young person can continue his studies at a gymnasium, where his studies end with an examination for a matriculation certificate, or enter a secondary vocational educational institution. | ||
<br>As of 2013, 358 higher educational institutions operated in Eastarland: 174 universities, 180 specialized institutes (they study technology, business and economics, art), and 4 military academies.<br> | <br>As of 2013, 358 higher educational institutions operated in Eastarland: 174 universities, 180 specialized institutes (they study technology, business and economics, art), and 4 military academies.<br> | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 30 January 2021
Kingdom of Eastarland Heastarštates Kōninrīek | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Loyalty to the Crown and Fatherland" ("Krileštva un Kronai lojalitāte") | |
| Anthem: "Forward and only forward, Eastarland!" ("Preikos un to preikos, Heastarštate!") | |
| Capital | Fanuburg |
| Largest city | Kuršovsk |
| Official languages | Eastarlandic |
| Recognised national languages | Eastarlandic |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | Eastarishmen (91%) Lusivecians (4.7%) Ykanjoans (2.1%) Scousers (1.4%) Other (0.8%) |
| Demonym(s) | Eastarlandian |
| Government | Unitary Constitutional Parliamentary Monarchy |
• King | Edward XI |
• Prime Minister | Josef Kalter |
• Сhairman of the Senate | Herbert Speer |
• Сhairman of the Kōninstag | Emilia Orenstein |
• Chief of Justice | Friedrich Weiß |
| Legislature | States General |
| Senate | |
| Kōninstag | |
| Foundation | |
• The beginning of the statehood of the Union of Provinces of Eastarland | 1579 |
• Unification of the Kingdom of Eastarland | 1827 |
• Constitution | May 17, 1853 |
| Area | |
• Total | 612,097 km2 (236,332 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 2.1% |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 97,428,353 |
• 2015 census | 95,117,901 |
• Density | 159.2/km2 (412.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 4.971 trillion |
• Per capita | 51,022 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 3.783 trillion |
• Per capita | 38,829 |
| Gini (2020) | 29.6 low |
| HDI (2020) | 0.934 very high |
| Currency | Ducat (D) (EAD) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (East Time) |
| Date format | yyyy,dd,mm |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +370 |
| ISO 3166 code | ETL |
| Internet TLD | .etl |
Eastarland (Heastarštate [əistarʃtate]), officially the Kingdom of Eastarland (Heastarštates Kōninrīek [əistarʃtates kœninri: k]) is a country on the eastern continent of Anteria. The area of the territory is 612,097 km2. The population as of December 31, 2020 is 97,428,353.
Located in the center of the eastern continent, it is washed by the waters of the World Ocean in the west, the Castarilian sea in the east and has an inland sea of Brennoš. It shares borders with Land2020 in the north, Castarilia in the east, Ykanjo in the south.
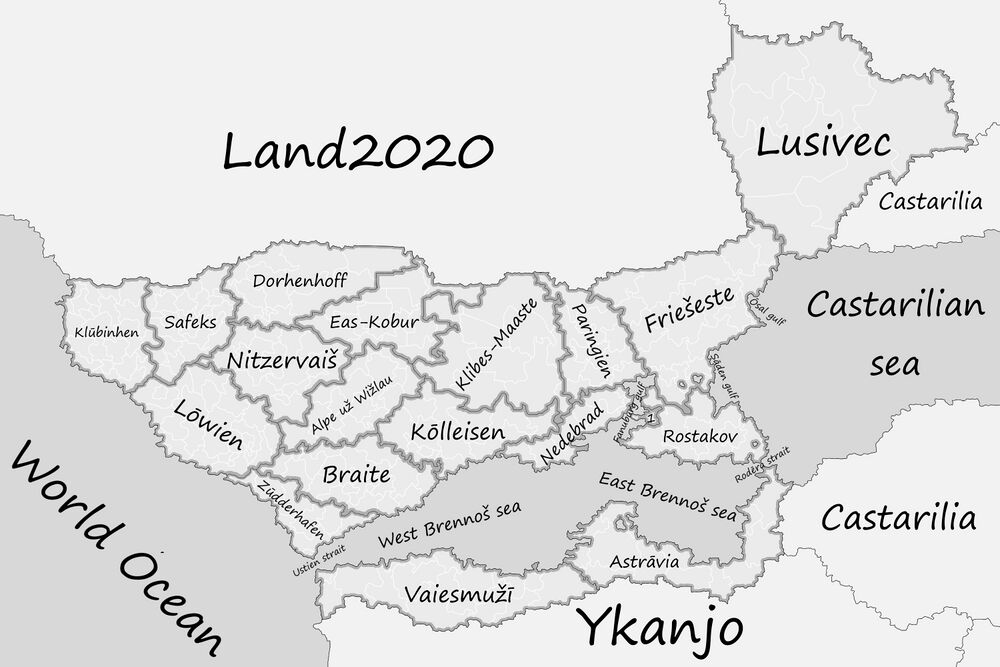
According to the state structure, it is a unitary state, it consists of 19 Crown lands (Fanuburg (metropolitan region), Safeks, Lōwien, Friešeste, Astrāvia, Eas-Kobur, Paringien, Klibes-Maaste, Braite, Zūdderhafen, Nitzervaiš, Klūbīnhen, Dorhenhoff, Kōlleisen, Vaiesmužī, Lusivec, Nedebrad, Rostakov, Alpe už Wižlau). The form of government is a constitutional parliamentary monarchy. The King of Eastarland since 3 August 2016 is Edward XI from the Kataringen-Faerzollen dynasty, since 26 April 2017 Josef Kalter has been the Prime Minister and Head of Government.
The capital is Fanuburg. The largest city is Kuršovsk. The state language is Eastarlandian.
Eastarland is a country with a dynamically developing economy. GDP for 2020 was 4.971 trillion ducats (about 51.022 ducats per capita). The monetary unit is the Eastarlandian ducat.
Etymology
The etymology of the word "Eastarland" is not exactly known, but there are many versions, none of which has received universal recognition. The root "heas" and its variants "es" and "eis" admit different interpretations both. So, for example, there are consonant toponyms on the territory of Ykanjo "Estyrland"' and San Calia "Istlanau", known from the XI-XII centuries. According to some, the toponym is formed from the ancient name of the river Heasta (Iestàu from east. Heistai "pour"). The feudal principality, through the lands of which this river flowed, eventually took a leading position and the name was extended to the entire state.
History
Geografy
Relief
The northern part of Eastarland is a low-lying plain formed during the Ice Age (North Eastarland Plain, lowest point Nahtt Slidas, 6.31 m below sea level). The surface of the lowland has preserved traces of ancient glaciation - chains of low moraine ridges and hills. The western part of the lowland is occupied by swampy lowlands, the formation of which is caused by the subsidence of the platform. In the central part of the country, forest-covered foothills adjoin the lowlands from the south. The highest point is Ustaš Mountain, 3243 m.
Rivers and lakes
A large number of rivers flow through the territory of Eastarland, the largest of which are: Osterkat, Killien, Goder. The largest lake in Eastarland is Gōeldehir, with an area of 1140 km² and a depth of 630 m. The lake is connected by a narrow Astieos strait in the west with the Amber Sea, and in the east with the Stober strait with the Castarilian Bay.
Climate
In general, the climate is temperate, maritime, characterized by cool summers and rather warm winters. The average temperature in July is + 16 ... + 17 ° C, in January - about + 2 ° C on the coast and slightly colder inland. The absolute maximum air temperature (+ 38.6 ° C) was recorded on August 10, 1954 in Drasau, the absolute minimum (−27.4 ° C) was recorded on January 29, 1962 in Litburg. In winter, when anticyclones arrive, the temperature drops below 0 ° C, snow falls, and channels and lakes are covered with ice. Although there is an average of 650 to 750 mm of precipitation per year, rarely a day goes by without rain. There are often fogs, sometimes it snows in winter. Truly extreme natural events (severe droughts, tornadoes, storms, severe frost or heat) are relatively rare.
Demographics
Religion
Religion
According to the 2011 census, 34.5% of citizens do not identify themselves as belonging to any religion or church. In a 2019 survey, only 27% of respondents said they believe in God, 50% said they believe in some kind of natural or spiritual power, and 30% that they don't believe in any of this. The largest number of believers are Catholics (but only 17.4% of the total population as of 2019), the next largest group is Protestants (6.3%).
According to the amendment to the Constitution of the Kingdom of Eastarland, the Kingdom of Eastarland is a secular state with secular values and views. The church is separated from the state, and the schools from the church. There is also a ban on secondary education in parish schools.
In the Crown Land of Lusivec, the Orthodox Church is extremely widespread among a deeply religious fanatical population. It is the official religion of the region, but is semi-official in the Kingdom, meaning it does not receive any government funding. This led to the fact that over the past 130 years the number of Orthodox churches and cathedrals has decreased from 318 at the time of the annexation of the region, to 72 at the moment.
According to universal law, any kind of discrimination based on affiliation with any religion, incitement to wrongdoing, incitement to hatred, causing physical, psychological or financial harm is prohibited to freedom of religion, and is punishable.
Ethnicity
Ethnicity
The population for 2020 is 97,428,353 people. The largest cities are Kuršovsk (8,836,187 people), Fanuburg (7,870,613 people), Lapož (5,699,700 people), Kobur (5,120,059 people). The average life expectancy is 78 years for men, 86 for women. Age composition: from 1 to 17 years old - 21.1%, from 18 to 66 - 65.2%, over 67 - 13.7%. 20 million students. More than 40 million families. 55 out of 100 families own their own houses. Eastarlandic is spoken throughout the country, although a small proportion of the population living in Lusicivec also speaks Lusivecian. Many Eastarlanders are also fluent in English, especially in large cities and young people who are learning English in schools.
With an area of 612,097 km², according to data for 2020, Eastarland has a population density of 159.2 people per square kilometer. The most densely populated are 3 western provinces: Lōwien, Zūdderhafen and Braite (the average population density is 440 people / km2 and more; the maximum indicators are observed in urbanized areas - over 600 people / km2). Largely due to this, Eastarland is one of the countries with the most developed transport and information infrastructure. 90.5 million people, or 93% of the country's population, use the Internet. Eastarland had over 10 million fixed telephones and 12.5 million mobile telephones in 2002-2003. More than 320 radio stations and 37 television stations (as well as 31 repeaters) operate in the country.
Ethnically, the population of Eastarland is very mono-ethnic. The largest ethnic minority in Eastarland are the Lusivecians, but of the total population of the country, their number is 4.7%, which is just over 4.5 million people. This nationality is located entirely in the northern Crown Land of Lusivec. The annexation of this region was preceded by a war between the Kingdom of Eastarland and the Principality of Lusivite. However, in the Kingdom they not only do not have a special status, but are also non-citizens (they have a passport of a non-citizen of Eastarland, which deprives them of the right to all political activities, such as creating or joining political parties, voting in elections at any level, participating in referendums).
Language
Eastarlandian state language (self-name - Heastarštates vālstaios runa [əistarʃtates v: alstajos runa]) is one of the East Anterian languages that have survived to this day. The Eastarlandian language is the only official language of the Eastarland, about 104 million people speak Eastarlandian (most of them live in Eastarland).
Divided into three dialects: Upper Eastarlandian, Middle Eastarlandian, and Ligon. The modern literary Eastarlandian language is based on the Middle Eastarlandian dialect.
The first written monuments appeared in the 6th century. The modern Eastarlandian Latin-based alphabet contains 31 letters.
The stress is fixed on the first syllable. By morphological structure, is an inflectional and synthetic language. The syntax is characterized by a relatively free word order, the basic one being the SVO order. The vocabulary is mostly primordial, Germanisms prevail among the borrowings.
Health
Education
Education in Eastarland is compulsory from 3 to 16 years old. From 2020, studies between the ages of 16 and 18 will be compulsory (this can be education, employment or civil service). The basic principles of Eastarlandian education are: freedom of teaching (public and private institutions), free education, neutrality of education, secularism, non-religious education.
Eastarlandian legislation guarantees its citizens a universal secondary education (school attendance is not a prerequisite, and about 1200 children are homeschooled).
The school year lasts 188 days and the municipalities distribute them independently between the autumn and spring semesters; most often, the first half of the year lasts 89 training days, and the spring - 98. Classes begin in August and end at the end of May. Schools pay attention to ensuring the safety of children and the educational process.
The child goes to the school closest to home, but there is a tendency among parents to send their children to educational institutions that are more prestigious from their point of view. If the school is more than two and a half kilometers away, then according to the law, the student (up to the 6th grade) must be brought back and forth by taxi at the expense of the municipality. The school gives out textbooks and all stationery free of charge and teaches the Eastarlandian language, mathematics, natural science, and home economics. Education in the basics of religion (Protestantism or Catholicism) occurs only with parental consent and in accordance with the religion. Atheists have the right to allow secular ethics to be taught to a child, and if objected, children are exempt from any of the courses. The library shelves are in the hallway and are freely accessible.
There are no grades in the lower grades; verbal gradation is used: excellent, good, changeable and “training required”. Starting from the 4th grade, grades are put in the range from 4 to 10 points. There are also grades for behavior - the ability to work in a group and alone, good breeding, and the desire to influence others for the better.
From grade 3, the first foreign language is added to the subjects - English. A foreign-speaking child (for example, from an immigrant family) is entitled to learn his native language from the first grade.
In the lower grades, subjects are combined (chemistry with physics and biology, language with literature) and home economics is taught to everyone, regardless of gender. They write a lot in the school: all kinds of essays are designed to teach the child to have his own opinion on each issue and to express it in literary language.
After graduating from school, a young person can continue his studies at a gymnasium, where his studies end with an examination for a matriculation certificate, or enter a secondary vocational educational institution.
As of 2013, 358 higher educational institutions operated in Eastarland: 174 universities, 180 specialized institutes (they study technology, business and economics, art), and 4 military academies.
Higher education, like primary education, is completely free for citizens of the country, as well as exchange students. For other groups of students, paid tuition has been introduced since 2016, the cost of which will be ~ 4 thousand ducats per year.
Largest Cities
Largest cities or towns in Eastarland
Royal Committee of Statistics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | County | Pop. | Rank | County | Pop. | ||||
 Kuršovsk  Fanuburg |
1 | Kuršovsk | Zūdderhafen | 8,836,187 | 11 | Karlsburg | Alpe už Wižlau | 2,632,331 |  Lapož  Kobur |
| 2 | Fanuburg | Capital City | 7,870,613 | 12 | Lučižec | Rostakov | 2,520,596 | ||
| 3 | Lapož | Rostakov | 5,699,700 | 13 | Tarršēvsk | Braite | 2,037,828 | ||
| 4 | Kobur | Eas-Kobur | 5,120,059 | 14 | Klaipož | Lusivec | 2,019,594 | ||
| 5 | Krokšākau | Alpe už Wižlau | 5,000,167 | 15 | Rakot | Safeks | 1,676,493 | ||
| 6 | Liedava | Lōwien | 4,489,359 | 16 | Elblaigs | Paringien | 1,419,219 | ||
| 7 | Karaport | Zūdderhafen | 4,030,065 | 17 | Cērhoff | Dorhenhoff | 1,204,111 | ||
| 8 | Nargard | Nedebrad | 3,928,763 | 18 | Rucipēš | Kōlleisen | 1,149,892 | ||
| 9 | Vēspilos | Nitzervaiš | 3,116,851 | 19 | Īštran | Klibes-Maaste | 1,123,502 | ||
| 10 | Paernau | Friešeste | 2,879,265 | 20 | Šiauvai | Vaiesmužī | 1,107,875 | ||
State structure
Administrative division
| Crown Lands | Coat of Arms | Administrative centre | Population | Leader | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
7,870,187 | Governor of the Fanuburg | ||||||
 |
16,124,430 | Governor of Züdderhafen | ||||||
Government
Executive power
Legislature
Judicial branch
Political parties
Migration policy
After a series of terrorist acts in the world, the government has consistently tightened immigration laws. Anti-immigration measures have significantly reduced the inflow of certain categories of migrants to Eastarland. In particular, in 2018, 4198 entry permits for family reunification were issued, which is 70% less than in 2013, and 1038 people were granted political asylum (82.5% less). At the same time, over the period 2013-2018, the number of those who received a study visa increased from 10 to 28.4 thousand people (an increase of 2.8 times), and those who entered on a work visa - from 5.9 to 12.8 thousand people (an increase 100%). In 2019, the measures were further tightened - in particular, a point system was introduced for spouses of immigrants wishing to enter the country.
Economy
Industry
Extraction of iron and uranium ores, bauxite is carried out. Leading manufacturing industries are mechanical engineering, including automotive, electrical and electronic (TVs, washing machines, etc.), aviation, shipbuilding (tankers, sea ferries) and machine tools. Eastarland is one of the world's largest manufacturers of chemical and petrochemical products (including synthetic rubber, plastics, mineral fertilizers, pharmaceuticals and others), ferrous and non-ferrous (aluminum, lead and zinc) metals. Eastarlandian clothing and footwear, jewelry, cheeses are well known in the world market (about 700 varieties are produced).
Agriculture
Eastarland has a highly productive agriculture. It occupies a leading position in the world in terms of agricultural production, grain production, livestock products and milk. Eastarland is a land of predominantly small family farms. Agricultural production efficiency is very high. At the same time Eastarland lags behind in the average yield of corn and sugar beet. In the agro-industrial complex, agriculture plays a subordinate role.
Livestock breeding provides about 70% of marketable agricultural products. Cattle breeding is the main branch of animal husbandry, it provides more than 2/5 of all marketable agricultural products, with the main part being milk (about ¼). Pig breeding is in second place. The country's self-sufficiency in milk and beef systematically exceeds 100%, but in pork it is less than 4/5.
Dairy and beef cattle breeding is most typical for well-moistened coastal areas, rich in meadows and pastures, as well as for the periphery of urban agglomerations. Due to the rather cold winter, stall keeping is common. Pig breeding is developed everywhere, but especially in areas close to the ports of import of imported feed, areas of sugar beet, potato and fodder root crops cultivation. Broiler production, production of eggs, veal, and pig breeding are concentrated in large livestock farms, the location of which depends little on natural factors. There are much more fodder crops than food crops, since a large amount of fodder grains, especially corn, are imported. However, the country ranked (2014) seventh in the world in terms of wheat exports (8.2 million tons). Of great importance is the cultivation of fodder root crops (fodder beets, etc.), corn for green fodder and silage, alfalfa, clover and other fodder grasses. Of the oilseeds, the most important is rapeseed, the crops of which are more than 10 times higher than those of sunflower.
In areas with high natural soil fertility, the main crops are wheat, barley, maize and sugar beets. The poorer soils of the Northern Lowland and the middle-altitude mountains are traditionally used for sowing rye, oats, potatoes and natural forage crops. The traditional nature of Eastarlandian agriculture has significantly changed technological progress. Today, the so-called light soils are valued more, due to their suitability for machine cultivation, using artificial fertilizers; for example, corn is now widely cultivated in the Northern Lowlands, where it replaces potatoes.
Viticulture surpasses, in marketable products, fruit growing and vegetable growing combined. Vineyards are located mainly in the valleys of Osterkat, Godera and other rivers.
Tourism
Attractions
Extractive industry
Forests make up more than 20% of the territory. There are 79 tree species in the Eastarland.
Eastarland has significant reserves of iron ore, uranium ores, bauxite, potash and rock salts, coal, zinc, copper, lead, nickel, oil, timber. The main coal mining regions are Safeks and the Eas-Kobur coal basins. Eastarlandian proven brown coal reserves were 40.5 billion tonnes. Since 1994, imports of coal have exceeded production. Gas production does not exceed 3 billion m³. One of the largest Eastarland gas fields is Olger in Loffier. "East Oil&Gas" is one of the largest gas and oil companies in Eastarland. The main activities of the company are exploration, production, marketing and distribution of natural gas and oil.
Transport and Energy
Transport
Railway transport Eastarland rail transport is highly developed. Local and overnight trains, including high-speed trains, connect the capital with all major cities in the country, as well as with neighboring countries. The speed of these trains is 320 km / h. The railway network is 51,850 km long and is one of the longest railway networks. Rail links exist with all neighboring countries. Metro is available in Fanuburg, Kuršovsk, Litauburg, Ūstimaa, Pilsava. In Feriar - partly underground light rail.
Automobile transport
After winning the 2016 elections in Koninstag, and forming a majority coalition with the Peasant Union, the Green Party banned all non-electric cars. Also, the cost of roads was reduced, but more attention was paid to public transport, railways, etc. The road network does not cover the entire territory of the country. The total length of highways is 610,500 km.
The main roads are divided into the following groups:
Motorways - The name of the road is made up of the letter A followed by the road number. Permissible speed - 130 km / h, obligatory filling stations every 50 km, concrete dividing strip, absence of traffic lights, pedestrian crossings. National roads - prefix N. Permissible speed - 90 km / h (if there is a concrete dividing strip - 110 km / h). Department roads - prefix D. Permissible speed - 90 km / h. In cities, the permissible speed is 50 km / h. The use of seat belts is mandatory. Children under 10 years old must be transported in special seats.
Air transport Eastarland has about 475 airports. 325 of them have asphalt or concrete runways, and the remaining 150 are unpaved (data for 2017). The largest airport is the «Fanuburg» located in the suburbs of Phanuburg. The national Eastarlandian airline «EastarAir» operates flights to almost every country in the world.
Energy
About 99% of the country's population is supplied with electricity. National electricity needs are met almost entirely at the expense of our own capacities; a small part of the electricity produced is exported.
Most of the electricity - 67.79% - is generated at thermal power plants, including 44.9% using coal, 26.5% - oil and 15.8% - natural gas. Hydroelectric power plants account for 20.35% of production, while nuclear power plants account for 11.80%. Solar energy accounts for about 0.03%. Less than 0.01% comes from wind farms.