SAI GR-7 Imam Ardashir: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| name = SAI G-7 Imam Ardashir | | name = SAI G-7 Imam Ardashir | ||
| image = [[File:GR7 on the tarmac.png|300px]] | | image = [[File:GR7 on the tarmac.png|300px]] | ||
| caption = A SAI G-7/ | | caption = A SAI G-7/ECM variant on the tarmac | ||
| alt = | | alt = | ||
}}{{Infobox aircraft type | }}{{Infobox aircraft type | ||
Revision as of 23:38, 4 February 2020
| SAI G-7 Imam Ardashir | |
|---|---|

| |
| A SAI G-7/ECM variant on the tarmac | |
| Role | Attack aircraft |
| National origin | Zorasan |
| Manufacturer | Soltanabad Aeronautic Industries |
| Designer | Soltanabad Aerospace Design Institute |
| First flight | 1970 |
| Introduction | 1975 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | |
| Produced | 1974-1990 |
| Number built | 266 |
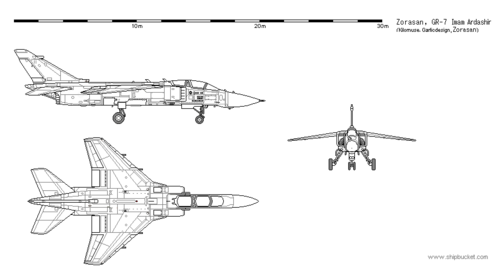
The SAI GR-7 Imam Ardashir (Pasdani: امام اردشیر گر-۷) is a twin-seat attack aircraft used by the Zorasani Irfanic Revolutionary Army Air Force in the close air support role.
Initially designed as a medium-range interceptor, the final design was radically altered to meet the requirements of a domestically produced fighter-bomber, where the ZIRAAF had historically been lacking. Considerable effort was placed into the design and production of the first domestic supersonic capable turbofan engine, this was ultimately achieved with the inception of the Badyar-1352. The final design also saw a strengthened airframe and more hardpoints, to grant the aircraft a significantly larger payload than originally intended.
The GR-7 has seen extensive operational service, proving highly vauled in the Irvadistan War by the ZIRAAF, but also saw action in the Al-Thawra Rebellion, Al-Hizan Uprising, the Kexri Conflict and the 2003-2004 Amardo-Zorasani Standoff. Despite the purchase of 40 Shengkong JK-10 fighter-bombers in 1999, the GR-7 has remained in service, with significant upgrades to its avionics, engine and fuel tank since its introduction in 1974.
Design and development
Design
Overview
Engine
Avionics
Operational history
Zorasan
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 20.13 m (66 ft)
- Wingspan: 8.69 m (28.6 ft)
- Height: 4.89 m (16.1 ft)
- Empty weight: 7,000 kg (15,432 lb)
- Loaded weight: 10,954 kg (24,149 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 15,700 kg (34,613 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Badyar-1352 afterburning turbofan
- Dry thrust: 22.75 kN (5,110 lbf) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 32.5 kN (7,300 lbf) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.1 (at sea level) (1,350 km/h (840 mph, 730 kn; at sea level)
1,699 km/h (1,056 mph; 917 kn) Mach 1.6 at 11,000 m (36,000 ft)) - Combat radius: 800 km
815 km (506 mi, 440 nmi) hi-lo-hi (internal fuel)
575 km (357 mi; 310 nmi) lo-lo-lo (internal fuel)
1,408 km (875 mi; 760 nmi) hi-lo-hi (with external fuel)
908 km (564 mi; 490 nmi) lo-lo-lo (with external fuel ()
- Service ceiling: 13,500 m (44,291. ft)
Armament
- Guns: 2× MTs-23 autocannon, 120 rounds each
- Hardpoints: 9 in total (6× under-wing, 2× wing-tip, 1× under-fuselage) with a capacity of 9,000 kg (20,000 lb) external fuel and ordnance, and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets:
- UB-32 rocket pods
- B-8M rocket pods for S-8 rockets
- S-13
- S-24
- S-25
- Missiles:
- Bombs:
- Other: ECM protection pods, Reconnaissance Pod, laser/electro-optical targeting pods, external drop tanks for extended range/loitering time
- Rockets:
Avionics
QR-10A