Tokhari language: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Infobox language | name = Tokhari | altname = Tokhari Persian, Loulanese Persian | nativename = تخاری | acceptance = | image...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category:Languages of Loulan]] | |||
{{Infobox language | {{Infobox language | ||
| name = Tokhari | | name = Tokhari | ||
Revision as of 03:57, 7 May 2019
| Tokhari | |
|---|---|
| Tokhari Persian, Loulanese Persian | |
| تخاری | |
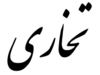 | |
| Pronunciation | [ to̞χɒˈɾiː ] |
| Native to | Loulan |
| Ethnicity | Tokharis |
Native speakers | ~18.3 million (2017) |
Indo-European | |
Early form | |
| Dialects | |
| Persian alphabet | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | prs |
Tokharī (تخاری [ to̞χɒˈɾiː ]) or Tokhari Persian (فارسی تخاری [fɒːɾsije to̞χɒˈɾiː ]) is a variety of the Persian language spoken in Loulan; for this reason it is also known as Loulanese Persian in Western sources.
As defined in the Constitution of Loulan, it is one of the two official languages of Loulan; the other is Mandarin. Tokhari is the most widely spoken language in Loulan and the native language of about 63.4% of the population. It is largely mutually intelligible with the other major varieties of Persian, with the largest similarities existing between Tokhari and Dari. Besides the rather conservative phonology, which it shares with Dari, differences are mostly found in vocabulary, as Tokhari borrows much more extensively from the Indo-Aryan languages, particularly Sanskrit and Pali due to the influence of Buddhism rather than Islam in the region.
By way of Early New Persian, Tokhari, like Western Persian, Dari, and Tajiki, is a continuation of Middle Persian, the official religious and literary language of the Sasanian Empire, itself a continuation of the Old Persian spoken in the courts of the Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE).