Zamorodna
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Zamorodnian Hetmanate Замородинський гетьманство | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital | Kostyanopol |
| Official languages | Zamorodnian |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Zamorodnian |
| Government | Confederal minarchist elected autocracy |
• Hetman | Oleh Bohdanuk Petrenko |
• Koshovyy Otaman | Volodymyr Matvyyuk Nesterenko |
| Legislature | Starshyna Rada |
| Establishment | |
• Great Kozak Migration | 1332-1426 CE |
• Unification of the Hosts | 1538 CE |
• Independence from Suvarova | 1672 CE |
| Area | |
• Total | 147,136 km2 (56,810 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 6.8 |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 14,293,012 (2021) |
• Density | 97.14/km2 (251.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $178.6 billion (2021) |
• Per capita | $12,494.43 |
| Gini | medium |
| HDI | medium |
| Currency | Hrish (₴) (ZHR) |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +443 |
| Internet TLD | .zam |
The Zamorodnian Hetmanate (Zamorodnian: Zamorodyns'kyy Het'manstvo), also known as Zamorodna or Zamorodina, is a small, landlocked nation in northern Belisaria. Zamorodna is the homeland of the Kozak peoples, who migrated westward from the Altunid and Ikdemid Khanates in the high middle ages, settling in a harsh, swampy region in the western hinterlands of Suvarova. The Great Kozak Host was an autonomous nation under the Crown of Suvarov, but gained independence in 1672.
In the present day, Zamorodna is a culturally integrated but politically disunified entity. The various constituent polities of the Hetmanate, the tovarystva, have varying degrees of authoritarian or democratic and capitalist or socialist elements. As such, the tovarystva can often be isolationist, particularly from very different neighbours. However, the unified culture, language, and traditions of the Kozaks tie the tovarystva together.
Economically, Zamorodna is self-sufficient but only moderately-to-poorly industrialized. Approximately one-third of the population are traditional pastoralists. Mining and other resource extraction are growing industries and leading sectors in the export economy. Domestically, economic figures can be difficult to ascertain due to limited governmental oversight and a widespread informal economy.
Name
The name of Zamorodna is inconsistently associated with the Kozak peoples who inhabit it. The term originally referred to the land before the Kozak hosts arrived and occupied it. Since then, however, it has come to refer more specifically to both the ethnic Kozaks living on the land and their language. The Zamorodnian language is distinct from that which was spoken by the first migrant Kozaks, having been heavily influenced by Slavic speakers in the region that they settled but retains Turkic influences.
The etymology of Zamorodna can be broken down into three components. The first component, "zam" or "sam", means "on its own", or "independent". The second component "o" is a linking element between the first and third components. The third component is etymologically uncertain and may stem from "rodna" or "rodina" and either means "fertile" or "of nature", or "of family". Read together, "Zamorodna" has the sense of either "fertile wilderness" or "free families". The former is likely descriptive of the harsh marshes and swamps of the region, while the latter has been widely accepted as referring to the independent Kozaks or the previous inhabitants of the land. There is no academic consensus on which interpretation is more likely the original.
History
Pre-migration
Early hosts
Autonomous nation
Independence
Modern era
Geography
Government and politics
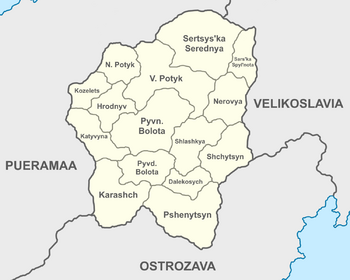
The Zamorodnian Hetmanate is, in effect, a confederation of different Kozak polities descended from the hosts that migrated to occupy the present area of Zamorodna. These 15 polities are referred to collectively as the tovarystva (singular: tovarystvo) but belong specifically to one of two categories. The first and most numerous of the rovarystva are the osavulstva (singular: osavulstvo), or "chiefdoms". The second and less common tovarystva are the sovyetstva (singular: sovyetstvo), or "council realms".
At the upper level of the Hetmanate's government, is the Starshyna Rada, or "Elder Council". The Starshyna Rada is composed of the 15 elders of the tovarystva. The process for appointing an elder varies according to the tovarystvo. The Starhyna Rada meets at Kostyanopol at least yearly, and every three years it appoints a Koshovyy Otaman ("Domestic Executor") who in turn appoints a Hetman ("Chief Executor") to act as the head of state of the Hetmanate. Both candidates are then subject to ratification by a popular referendum. Traditionally, an individual is limited to two terms as either Koshovyy Otaman or Hetman, though this rule is not always observed in practice by the Starhyna Rada. Some conflict between the incumbent executors and the Starshyna Rada has occurred in the past and the peaceful transfer of power is not universal. The elders of the Starshyna Rada remain, effectively, the chief representatives of their respectively tovarystva and can withhold the military power from the Hetman if they deem it necessary.
Each of the executors has different roles and responsibilities. The Koshovyy Otaman appoints members of federal courts, acts as supreme justice, manages land division between the tovarystva, manages federal lands, and exercises taxation and budgeting. The annual tax and budget plan, however, must be approved by the Starshyna Rada. The Hetman is charged with managing foreign relations, the organization of the military, public education, and any residual responsibilities of a federal nature. The tovarystva are otherwise free to manage affairs of a local nature, land division and management within the borders of the tovarystvo, and the budgeting and taxation of their own programs.
Laws and justice
The legal system of the Zamorodnian Hetmanate is a common law system with no written constitution. Courts apply principles established in time immemorial to cases presented before them. Most of these principles come from the Kozak peoples but a limited number of principles of land division are derived from Starzamian traditions. Courts are also, in a way, the major legislative bodies. Rather than a parliament or an individual Rada drafting or proposing legislation, any Zamorodnian is entitled to put an issue before the courts, even a hypothetical issue. The court is only obligated to hear cases that directly affect an individual's rights or property but may grant leave to hear hypotheticals or create their own hypotheticals to be heard. Thus, the court may render preemptive decisions on how the common law principles of Zamorodna may apply to a given hypothetical and any future cases. The ultimate legal distinction between the osavulstva and the sovyetstva is that the former is managed by a singular executor who appoints the courts, while the latter is often a group of judges who are popularly elected and also manage executive tasks.
Administrative subdivisions
| Name | Capital | Flag | Population | Type | Starshyy |
| Sertse Serednya | Kostyanopol | 2,803,735 | Sovyetstvo | Ondrey Premysluk Shumeyko | |
| Pyvnychne Bolota | Barabanopol | 1,963,452 | Osavulstvo | Petr Tymofyyuk Syrko | |
| Zahydne Karashch | Doshchovysto | 1,519,499 | Sovyetstvo | Olha Vasylchuka Zhdanyva | |
| Shchytsyn | Svyatyy Mayklhorod | 1,496,952 | Osavulstvo | Bondar Ylyuk Federenko | |
| Verhnye Potyk | Shumhorod | 1,264,517 | Osavulstvo | Mykyta Mykytanuk Belesarenko | |
| Pshenytsyn | Pshenytsopol | 1,075,923 | Sovyetstvo | Bohdan Oleksandruk Melnyk | |
| Katyvyna | Katyhorodka | 758,832 | Osavulstvo | Martyn Volodymyruk Koval' | |
| Nyzhnye Potyk | Eshchyn | 713,605 | Osavulstvo | Yevgenya Antonuka Huperyvna | |
| Shlashkya | Petrohorod | 662,648 | Osavulstvo | Prokop Yvanuk Nosach | |
| Pyvdenne Bolota | Kosutyn | 542,421 | Osavulstvo | Les' Lavrynuk Gryshenko | |
| Hrodnyv | Hrodnyv | 456,727 | Osavulstvo | Fyodor Fylonuk Fyodoryvych | |
| Nerovya | Nero Zamok | 371,660 | Osavulstvo | Oleksandr Olehuk Pototsky | |
| S'hydne Karashch | Ypelnych'horod | 262,923 | Osavulstvo | Yvan Petruk Vygyvsky | |
| Dalekosych | Myshche Zurychy | 215,966 | Sovyetstvo | Vyacheslyv Dmytryuk Nykonyv | |
| Sarsky Spyl'nota | Sarsky Myr | 187,151 | Osavulstvo | Lukyan Maksymuk Barabash |
Osavulstva
Of the 15 tovarystva in the Zamorodnian Hetmanate, 11 are osavulstva, or "chiefdoms". An osavulstvo is a polity governed by an osavul. The process for appointing or electing an osavul can vary, but typically the osavul is either a hereditary position or it falls to the eldest of the community. In two cases, Nerovya and Sparsky Spyl'nota, the osavul is an elected position. Regardless, after assuming the role, an osavul governs for life or until they step down. The other key aspect of an osavulstvo is the independent judiciary. Judges are appointed by the osavul but otherwise, act independently. The osavul has the power to govern the osavulstvo in all local matters but does not have the right to make unilateral decrees. Any decree that an osavul wishes to make must be considered by the local judiciary. The osavul is also the starshyy of their osavulstvo, though they may elect to delegate this responsibility to a subordinate.
Sovyetstva
Despite being outnumbered by the more autocratic osavulstva, the sovyetstva generally count among the more populous and powerful tovarystva in Zamorodna. The sovyetstva, or "council realms", are characterized by more democratic governance in addition to a blended legislative, judicial, and executive system. At the centre of a sovyetstvo is the sovyet ("council"). The members of the sovyet are collectively elected by their communities for fixed terms as judges. During the first meeting of a new sovyet, executive roles are distributed by consensus. Legislative functions are effectively undertaken by the members as well though the legal reference system. In sufficiently large communities, the sovyet may delegate most of its criminal and civil judicial functions to a certain number of its members while the rest abstain from adjudicating legal matters in order to more effectively conduct their other functions. The starshyy of a sovyetstvo is typically appointed at the beginning of a new sovyet, though occasionally the role will be left vacant until shortly before the Starshyna sovyet is convened.

