Husna
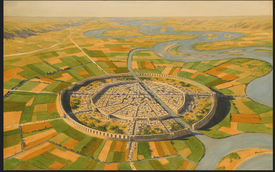
A benteng (ᨅᨙᨊᨈᨙᨊᨁ; Estmerish: fortress) was a large type of fortified settlements found throughout Terangau beginning in the 2nd millennium BCE through the 18th century CE. The benteng emerged with the Pali culture, but became widespread over the island with the Butari and Neo-Butari Empires in the 4th century through 1200s CE. At the start of their history, bentengs were essentially city-states in their own right, controlling large amounts of people. Over the centuries, their economic and cultural power would wane as more centralized forms of governments rose. By the time of the Neo-Butari Empire in the 900s CE, the benteng had been reduced to little more than a noble estate.
Despite their comparison to castles by Euclean historians and anthropologists, the benteng was functionally quite different and there are some key difference between the two that make direct comparisons difficult. The biggest difference between the benteng and Euclean castle, was the entire population of a benteng would live within the confines of the fortress. The movement of the population in and out of a benteng was heavily monitored to ensure the benteng would always have a healthy male population for the defense of the city. Likewise, all economic activity of the benteng was structured around the military to ensure the survival of the benteng. Because of the inclusive nature of the benteng, strong cultural identities developed unique to each one. As Terangau centralized as a polity, these cultural identities have often become a source of tension, particularly between groups of people from historically rival bentengs.
History
Origin
The origins of the benteng are muddled and several conflicting theories on their inception exist. The most widely accepted theory by Euclean anthropologists and archaeologists is early bentengs originating as small congregations of extended family groups, ranging in upwards of 30 households and having a population of anywhere from one hundred to five hundred people. In time, these family groups gradually expanded and incorporated more families, who commonly banded together to ease resource consumption and allocation, as well as common defense.
The first documented benteng comes from the 1000s BCE when a series of earthworks were constructed around the perimeter of the Pali city of Sintok. The earthworks stretched approximately 26 km from the perimeter of the city into its rural area. It is estimated that construction of this wall began in the 9th century BCE and was completed in the 7th century. By the 5th century, the original earthworks, which consisted of little more than ditches and 6 meter high walls, had expanded to a 12-meter high defensive wall and the ditches had been filled with trees. The defensive wall had expanded to include much of the rural area of Sintok, with all entry points having strong wooden gates. Several conflicts between Sintok and its neighbors eventually led to the removal of all but one of the gates, and in 307 BCE, the Datu of Sintok, Sugriwa III, issued an edict forbidding its inhabitants from leaving the city. By 250 BCE, 50 years after the Sintok Declaration, sixteen other bentengs are recorded to have be built. By the turn of the millennium, every major Pali city had been turned into a benteng.
Early Benteng
Following the collapse of Pali culture at the turn of the millennium, the benteng became the primary political unit during the Warring States period of Terangauni history. Over the four centuries between the the collapse of the Pali and the subsequent rise of the Butari Empire, the intrusive nature of the benteng resulted in the formation of unique cultural identities specific to each individual benteng. Along side the development of unique culture endemic to each benteng, the inhabitants would become fiercely loyal to the lord of the benteng. This side effect is theorised to be the primary driving force for the widespread adoption of the benteng, as the loyalty of the inhabitants far surpassed those in ordinary towns and cities.