JCh-6
| JCh-6 | |
|---|---|
 The three JCh-6 service variants using the "G turret," plus the Sije-Chalyang 808 prototype. | |
| Type | main battle tank |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2004-present |
| Used by | |
| Wars | Ummayan Civil War Innominadan Crisis |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Design Bureau of the Jinjŏng Chŏlgang-Nodongja Vehicle Plant |
| Designed | 1992-2002 |
| Produced | 2003-present |
| No. built | at least 16,000 |
| Variants | JCh-6G, JCh-6N, JCh-6D, JCh-6R, JCh-6M, JCh-5/6 |
| Specifications (JCh-6G) | |
| Weight | 50.2 metric tonnes |
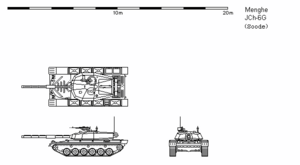
| Length | 9.68 m overall 7.23 m hull only |
| Width | 3.77 m including side armor |
| Height | 2.27 m to turret roof |
| Crew | 3 (driver, gunner, commander) |
| Armor | welded steel base Composite armor (turret face and hull glacis) |
Main armament | 125mm L/48 smoothbore gun |
Secondary armament | 12.7mm GCh-75Ch HMG (commander) 7.62mm GCh-77 MMG (co-axial) |
| Engine | Taekchŏn D130 diesel 858 kW (1,150 hp) |
| Power/weight | 22.9 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | torsion-bar |
| Ground clearance | 43 cm |
Operational range | 800 km (internal fuel) |
| Speed | 65 km/h (road) |
The JCh-6 (formal designation: 6호 주력 전차 / 六號主力戰車, Ryuk-ho Juryŏk Jŏncha, "No.6 Main Battle Tank;" short designation: 전차-6 Jŏncha-ryuk) is a main battle tank designed and built in Menghe. Mass production began in 2003, with service deliveries early the following year. It is sometimes accompanied by the nickname Sŏnbong (선봉 / 先鋒), meaning "Vanguard," though this is more of a marketing device than an actual designation. The JCh-6 is currently the most common main battle tank among the Menghean Army's active forces, though the JCh-5 outnumbers it in the reserves and as of 2018 the JCh-8 has begun replacing it in some front-line units.
Compared to the JCh-5 before it, the JCh-6 incorporates a number of new features, most notably a belt autoloader in the turret bustle. This allows the use of single-piece ammunition rounds, in contrast to the two-piece ammunition used by its predecessor and earlier tanks designed in Letnia. This, in turn, gave it considerably better armor penetration. In its early variants, however, it suffered a number of shortcomings, some of which were corrected in subsequent variants.
Development
Although the JCh-5 MBT had been considered fairly advanced during its early years in service, by the early 1990s concerns about its inadequacy were growing. In addition to constant complaints about the poor reliability of its engine and autoloader, there was a growing perception that the JCh-5's armor and armament were being outpaced by advances in armor technology elsewhere in the world.
The former problem, that of protection, could fairly easily be addressed with applique armor blocks and explosive reactive armor, but that of armament was more complex. Because the JCh-5's autoloader followed an in-hull carousel design, its 125mm rounds had to be broken up into two pieces, one containing the projectile and the other making up most of its propellant charge. While this made storage of rounds easier, it inherently limited the overall length of the APFSDS projectile, which had to fit entirely within the first stage of the ammunition.
The first official records of a solution date from 1992, when the design bureau of the Jinjŏng Chŏlgang-Nodongja tank plant proposed a radical re-design of the JCh-5's turret, with a small bustle autoloader carrying one-piece rounds fitted onto the rear. Under this early proposal, the bustle would only hold rounds of the new APFSDS type, with the remaining HEAT, HE, and ATGM rounds stored within the hull. This approach was soon dismissed as needlessly complex, but in January 1993 JChN was given a state order to develop its bustle autoloader concept into an entirely new Main Battle Tank. In the process, it was hoped that they would address many of the JCh-5's other issues. Work on the new project officially started in 1994.
Early on in the development process, it was decided that the JCh-6's armament would consist of a 125mm gun, the same caliber as the JCh-5. This was mainly intended to ensure reverse compatibility with existing stocks of 125mm two-piece ammunition, which can still be loaded and fired by the autoloader and gun. It also eliminated the need to develop new HEAT, HE, and ATGM ammunition in parallel with the new one-piece round.
For several years period during development, the gun was designated JChP-127/48, and its ammunition used -127 indicators, leading to speculation that the tank used a 127mm main armament. Subsequent reports published in 2002 clarified that the main armament was indeed 125 millimeters in caliber, and that the 127mm designation had been a provisional attempt to ensure that logistical personnel did not mistakenly deliver 125mm single-piece ammunition to Tank Battalions operating the JCh-5, which could not load them. Instead, single-piece APFSDS rounds for the JCh-6 were given the suffix TB (for 특별 / 特別, Tŭkbyŏl, "special"), later replaced with HJG (홑조각, Hotjogak, "single-piece") indicating that they could only be used on tanks with bustle autoloaders.
The first prototype vehicle, designated Sije-Chalyang 808, began trials in 2000. Its main competitor was the Sije-Chalyang 804, a modification of the JCh-5 tank with a bustle autoloader attached to the turret rear. While the 804 prototype had performed well on trials before then, the 808 was superior to it in all relevant categories, including mobility, protection, and ease of maintenance. For this reason, the Sije-Chalyang 808 was selected for the official designation JCh-6, though its competitor would eventually serve as the basis for the JCh-5/6.
Design (JCh-6G)
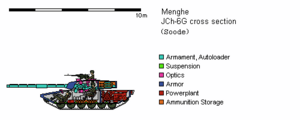
The JCh-6 follows a highly conventional main battle tank layout, with the driver in the front of the hull, the rest of the crew in the turret, ready ammunition in the turret bustle, and the engine and transmission in the rear. It uses a bustle autoloader rather than a human loader, and was designed with greatly improved protection in mind, though combat experience in the Ummayan Civil War revealed serious shortcomings.
Like its predecessor and successor, the JCh-6 has a three-man crew in all variants. The driver is seated in the center of the hull, and the gunner and commander are seated on either side of the gun breech, to the left and right respectively. Because the tank has three crew members rather than four, it is more compact than some of its contemporaries, allowing it to maintain the same armor protection at a lighter weight. Most notable is its low profile, slightly taller than the notoriously cramped JCh-5 but still fairly short at 2.27 meters to the turret roof. This makes the tank harder to detect at long ranges, and more difficult to hit.
The JCh-6G also introduced a new cupola design, with periscopes all around except on the very front, as opposed to two side-facing periscopes. As on the JCh-5, the entire cupola can rotate in place, and in front there is a larger optic system with greater magnification. On subsequent variants, this was replaced with an electro-optical sight. Crews who have served on both tanks report that the JCh-6 offers considerably better visibility and situational awareness to the commander.
Like the JCh-5, the JCh-6 incorporates a folding bulldozer blade on the lower half of the hull front. This can be angled downward at the driver's control by means of hydraulics under the tank. It allows the JCh-6 to prepare a small hull-down firing position in open terrain during the period before an enemy attack.
Protection
During its development, the JCh-6G was designed to resist contemporary 120mm APFSDS ammunition across the frontal arc without the use of explosive reactive armor, which could endanger nearby infantry and would leave openings in the tank's protection after being struck. For this purpose, it relied on a base layer and outer shell made of hardened steel, with composite armor of an unknown composition sandwiched in between. Areas with composite armor include the turret face and turret sides, as well as the hull glacis plate, though the latter relies primarily on sloping.
The tank's sides and rear are protected by hardened steel armor in various thicknesses. It is reportedly resistant to 30mm APFSDS ammunition from all angles at ranges above 1 kilometer, as well as shrapnel from nearby shell impacts. The hull sides use applique armor skirts, variously described as spaced or composite armor, which are designed to induce yaw in APFSDS ammunition approaching at an angle and prematurely detonate HEAT charges.
A unique distinguishing feature of the JCh-6 is the shape of its turret bustle, which grows narrower toward the rear, at an angle of about 12.5 degrees from the horizontal. This was intended to reduce the likelihood of an enemy projectile striking the stowed ammunition. Over the 30-degree frontal arc, the bustle itself is either not visible, or is visible at such a narrow angle that HEAT warheads would fail to detonate and APFSDS rounds would deflect off of the surface. The tank's designers predicted from exercises that in a conventional engagement in open terrain most incoming fire would come over the 60-degree frontal arc, and that the dispersion could be narrowed even further if crews rotated the turret to face a threat. If struck at a wider angle, however, the turret bustle would be protected by nothing more than 60 millimeters of hardened steel.
The autoloader is separated from the rest of the turret by a 12-centimeter-thick steel bulkhead, and an armored cover passes over the ramming hole when rounds are not being loaded. In the event that an enemy round penetrates the turret bustle, this bulkhead is meant to prevent the internal cookoff from injuring the crew or damaging other internal systems; the resulting pressure is instead vented upward through a large blowoff panel. The turret bustle also contains the hydraulic pumps for traversing the turret and elevating the guns; testing with the JCh-5 found that if these systems burst, they could project heated, flammable fluid into the tank, injuring the crew.
For protection against guided munitions, the JCh-6G carries smoke grenade projectors capable of quickly laying a multi-spectral smokescreen in front of the tank's turret. This system can be used to disrupt the guidance systems on certain anti-tank guided missiles, or to break the launch platform's lock on the target, during which time the JCh-6 can either prepare to engage the launch platform or retreat to safety. As the smoke grenades are activated manually by the commander upon spotting the incoming missile, it is debatable whether this constitutes a softkill active protection system, though it has some functional similarities. All JCh-6 variants can also inject diesel fuel into the engine exhaust, generating a thick smokescreen behind the tank in order to cover mechanized units advancing behind it or conceal its retreat.
In the event that the battlefield is contaminated by chemical, biological, radioactive, or nuclear weapons, the tank can be sealed against its environment, with an air filtration system ensuring an adequate supply of oxygen. While the main gun's breech is open, a combination of airflow from the bore evacuator and overpressure from the air filter prevent contaminants from entering via the gun barrel. The airtight seal is also breached for roughly one second during the firing cycle, as a panel above the breech opens to eject the spent stub at the end of the round's combustible casing. Overpressure can partially prevent the inflow of foreign air, but testing with the JCh-6 found that trace amounts of contaminated air could still enter the tank during this period, and the feature was eliminated on the JCh-8.
In spite of high hopes for the vehicle's design, combat experience in Ummayah revealed that modern armor-piercing ammunition could still penetrate the JCh-6 with relative ease across the 60-degree frontal arc. This led to new overhauls of the tank's protection in each subsequent variant.
Main Armament
The "A" variant's main armament consists of a 125mm L/48 smoothbore gun mounted in the turret. The weapon is designated JChP-125/48, with JChP indicating Jŏncha-Po, or "tank gun." It has a barrel life of 300-600 rounds, depending on the combination of ammunition types used, with high-velocity APFSDS rounds inflicting more wear. It can be replaced without dismantling the inside of the turret.
As on previous Menghean main battle tanks, the gun's elevation range is limited by the cramped size of the turret, though it is somewhat better off than its predecessors. The gun can depress to an angle of -8 degrees from the horizontal, and elevate to +14 degrees. This somewhat constrains its usefulness in mountainous terrain, and limits its ability to fight from a hull-down position. The turret's low profile partially compensates for this disadvantage.
The main armament's effective range is mainly governed by the optics and fire-control system, as well as the available line-of-sight available in the surrounding terrain. On the "A" variant, the optics were relatively primitive, and the maximum range was variously cited as 2000, 2500, and 3000 meters. On the "Ch," "D," and "E" variants, the laser rangefinder is instrumented out to a range of 5,000 meters, but effective firing range is still probably closer to 3,000 meters at most.
Autoloader
The JCh-6 uses a conventional cycling belt autoloader in the turret bustle, as opposed to the carousel autoloader in the JCh-5. In order to load a new round, the belt cycles to the selected ammunition type, then rams it forward into the open breech of the gun, which is turned to an elevation of zero degrees horizontal in order to align with the incoming round. After each round is fired, a lever extracts the non-combustible stub at the end of the cartridge and ejects it from a hatch in the top of the turret, with air overpressure inside the tank preventing external contaminants from entering.
Under ideal circumstances, the firing cycle is as short as five seconds, but it can increase to six seconds or more if the gun is significantly out of alignment from zero degrees or if the next required round type is further down the cycling chain. Official Army sources list the maximum rate of fire as 10-12 rounds per minute. If the autoloader's cycling system is disabled, the turret crew can manually cycle the chain and ram rounds by means of hand cranks extending through the protective bulkhead. The firing cycle under these circumstances varies with the skill of the crew and the extent of the damage, but has been described as anywhere from fifteen to thirty seconds.
Ammunition
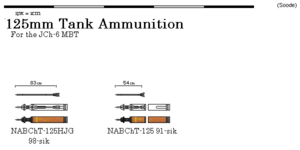
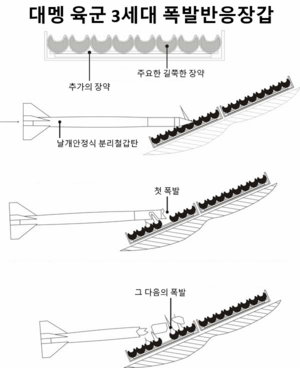
The crowning achievement of the JCh-6 main battle tank is the NABChT-125HJG, (abbr. 날개안정식 분리철갑탄, Nalgaeanjŏngsik Bunrichŏlgabtan, Fin-stabilized discarding-sabot armor-piercing round), an APFSDS-T anti-tank munition designed to take advantage of the full length of the cartridge rather than being limited to the first half like previous Menghean tank ammunition. The penetrator is 83 centimeters long, excluding the tracer, and 28 millimeters in diameter, and has a muzzle velocity of 1650 meters per second. At a range of 2,000 meters, it is reportedly able to penetrate 850 millimeters RHA equivalent, though performance varies depending on the composite armor scheme it is facing.
Apart from this, the JCh-6 is capable of handling the same two-piece HE and HEAT ammunition used by the JCh-5, a feature intended to streamline logistics on the battlefield. The chain assembly holding the rounds, the semi-rigid ramming chain, and the folding tray behind the breach prevent the two halves from separating.
For engagements at longer ranges, the JCh-6G through 6D can fire the YDCh-19 beam-riding ATGM through the gun barrel. Unlike the YDCh-16 before it, this projectile can be loaded directly from the autoloader, without requiring a human loader to insert a third compressed-air stage. Because they are stored in assembled form, rather than in separated units, YDCh-19 rounds fired from the JCh-6's autoloader reportedly have a lower failure rate. Increasing accuracy of fire-control systems on the JCh-6D onward, however, rendered the guided missile redundant, and the "R" and "M" variants are not configured to fire it.
Apart from poor side protection, another disadvantage of the angled turret bustle is that it limits the amount of space available for ammunition. Only 18 main gun rounds can be carried in the tank's autoloader, compared to 22 on other tanks of similar size and configuration. This compares poorly with the 26 ready rounds in the JCh-5. To increase the overall ammunition load, twenty additional rounds are stored under the turret floor, beneath armored hatches that can be pulled away by the crew. Two-piece ammunition can be manually passed into the autoloader without unbuttoning the tank, but the larger one-piece APFSDS rounds must be lifted through one of the hatches and inserted through the autoloader's roof. In both cases, the floor storage is notoriously hard to access, requiring that the turret be rotated to different angles in order to access each compartment. Reloading of this kind would only be performed while the tank is out of battle.
Other armament
The commander of the JCh-6 is provided with a 12.7mm GCh-75Ch heavy machine gun. This weapon is mounted to a rotating ring around the cupola, and can be rotated through 360 degrees with relative ease. As on the JCh-4 and JCh-5, it can be either manually operated from an open hatch or remotely operated from inside the tank, though in the latter case its optics are greatly improved over earlier Menghean tanks, improving the weapon's accuracy and range in the buttoned-up mode. A total of 400 rounds for the GCh-75Ch are carried in four 100-round boxes, one on the gun mount and three more in an external storage bin.
The JCh-6's other secondary armament is a single GCh-77Ch medium machine gun mounted co-axially with the main gun, on the commander's side. This weapon fires through a slot cut in the armor, with a canvas covering to maintain a protective air seal. The weapon fires 7.62x51mm ammunition, fed from a bin at the commander's feet. The ready bin carries 500 rounds of 7.62x51mm ammunition, with an additional 4,000 rounds stored around the tank, some inside the fighting compartment and others in external stowage bins.
Mobility
The JCh-6G is driven by a single 10-cylinder, 1,150-horsepower D130 diesel engine manufactured by Taekchŏn Heavy Industries. This gives it a power-to-weight ratio of 22.9 horsepower per tonne. The engine and transmission can be removed as a single unit to facilitate maintenance and replacement. Top speed on roads is cited as 65 kilometers per hour, while top speed offroad is dictated by the terrain. The tank has an operational range of 800 kilometers when relying on internal fuel only, and was not initially designed to accept fuel drums, though these became optional on the "D" variant onward.
To reduce production costs, the JCh-6 uses torsion bar suspension, at a time when hydropneumatic suspension was already becoming common on contemporary main battle tanks. The six roadwheels on each side are offset slightly to allow each one's torsion bar to pass all the way through to the other side.
Like previous Menghean MBTs, the JCh-6 carries a snorkel on the turret rear. The crew can mount this on a matching port over the gunner's hatch and extend it to its full length, allowing the tank to ford water obstacles up to five meters deep while maintaining constant airflow to the crew compartment and engine. In this configuration, the tank is blind until it surfaces at the far side of the water obstacle.
Early variants
JCh-6N
The JCh-6N was an interim response to the 6G's poor performance in the Ummayan Civil War. It added ERA plates to the turret face and glacis plate, with the goal of increasing protection against HEAT and APFSDS ammunition. The plates used are described in Menghean sources as "second-generation ERA," and feature multiple steel layers that expand apart on impact, inducing shear forces in APFSDS ammunition. These are believed to be the same armor plates used on the JCh-5R main battle tank.
JCh-6G tanks upgraded to "N" standard are formally designated JCh-6N1, but in practice JCh-6N applies to both, as the two are functionally identical.
JCh-6D
Introduced in 2008, the JCh-6D was a more substantial upgrade, and it is believed that work on the necessary changes was already underway when the -6N entered production. Its most visible feature was a different array of reactive armor plates, this time consisting of "third-generation ERA." This type uses linear shaped charges which detonate on impact and then spread up and down the plate, cutting apart projectiles and HEAT jets before they can strike the main armor. A secondary layer of conventional ERA underneath provides additional protection. This system is considered to be more effective against APFSDS ammunition than the ERA plates used on the JCh-5R, and is claimed to be effective against soft-tip and expanding-rod penetrators.
The JCh-6D also incorporates new fire-control systems, which were imported from Dayashina. The most visible of these is a much larger gunner's sight incorporating side-by-side visual-band and infrared-band cameras, as well as a more precise laser rangefinder. Combined with a new temperature and crosswind measurement mast, and a new firing computer, this upgrade greatly increases the gunner's likelihood of landing a first-round hit on a moving enemy vehicle at long ranges. Reportedly, the firing computer on the JCh-6D is capable of maintaining a "lock" on an enemy target, continuously updating the necessary lead as both tanks' velocity change. The "D" variant also brought the main armament stabilization system up to international standards, and added a laser reference module on top of the gun for easier calibration.
Additional protection on the JCh-6D comes in the form of an automated softkill active protection system. This consists of infrared sensors which are capable of detecting missile launches, and jamming devices designed to spoof, blind, or disrupt hostile missile guidance and laser rangefinder systems. The system is integrated with the tank's existing multi-spectral smoke grenade launchers, which are relocated to improve ERA protection, allowing the tank to automatically deploy defensive smokescreens at short notice. It also automatically reports the direction of the missile launch to the commander, who can then slew the turret to face the threat. Because wire-guided missiles can take seven seconds or more to travel 2,000 meters, this gives the gunner ample time to fire a main-gun round at the launch platform, breaking the lock for SACLOS, SALH, and beam-riding missiles.
Less visible was the addition of a new type of two-piece 125mm gun round. Designated "dual-purpose," this round's projectile incorporates a tandem HEAT warhead with a prefragmented outer casing around the main charge. It also has an airbursting fuse, which detonates the round near the target based on the distance calculated by the laser rangefinder and the time-of-flight predicted by the firing computer. This increases effectiveness against infantry in trenches or other open-topped covered positions, and allows the tank to more easily engage loitering or slow-moving helicopters. By combining high-explosive and light anti-armor capabilities, this also allows the tank to split its ready ammunition load between only two types of ammunition, APFSDS for heavy armor and dual-purpose for all other targets.
Another interesting feature of the JCh-6D was the reworking of the tank's communications suite. It was the first operational Menghean tank to carry the MChGJ-0800 C-band radio communications system. Limited to line-of-sight signals, but by the same virtue difficult to intercept and jam, the C-band antenna allows tanks within the same platoon or company to continue communicating even when lower frequencies are being targeted and jammed. For longer-ranged communications, the tank also carries UHF and VHF antennas. Apparently deemed a success in operational testing, the MChGJ-0800 was later carried over onto the JCh-6R and 6M, and to the JCh-5/6 and JCh-8.
A limited number of "G" and "N" variant tanks were upgraded to partial D standard, through the addition of third-generation ERA and the installation of updated optics. On close inspection, these can be distinguished from standard D-variant tanks by the welds and cuts around the gunner's optic and the mounting of the commander's optic on a more elevated mount. They also lack some components of the full fire-control system, including the automatic firing-solution update capability. These tanks are formally designated JCh-6D1.
JCh-6R
When unnamed photographs of the JCh-6R on trials were released to the public on May 4th, 2014, several foreign intelligence agencies provisionally designated it JCh-8, mistaking it for the new tank prototype rumored to be in development. In fact, it was a variant of the JCh-6 with a number of major modifications, including a new turret and applique frontal armor.
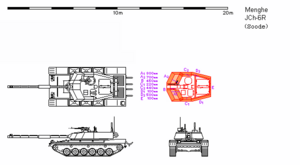
The JCh-6R pioneered several technologies that would later appear on the JCh-8 main battle tank, and in some respects served as a design testbed as well as a service vehicle. Indeed, it was a sufficiently revolutionary advance during its development that the Menghean Army nearly suspended work on the new tank project altogether. Its most recognizable improvement is a new turret, which maintains the same internal layout as the JCh-6G but uses a new external shape with thicker armor on all surfaces except directly to the rear.
Armament
Some early reports suggested that the JCh-6R was also designed to accept a 140mm gun, but this appears to have been false. It did, however, carry a revised variant of its predecessors' armament: the Jŏncha-Po 125/58, a 58-caliber artillery gun which was 1.25 meters longer than previous variants' JChP 125/48. It is also reportedly capable of handling new 125mm APFSDS ammunition, with stronger propellant optimized for the gun's longer length. Together, these modifications impart a considerably higher muzzle velocity to APFSDS projectiles, increasing penetration power.
Protection
The JCh-6R features a heavily revised turret face incorporating a new type of composite armor, which state sources claim is easier to manufacture but also more effective against APFSDS and HEAT ammunition. In contrast to previous variants, the turret's composite armor modules are mounted on top of an internal steel shell roughly 50 millimeters thick, and damaged modules can be replaced at a forward operating base with the assistance of a small crane. New "applique composite panels," possibly similar in structure to spaced armor, are also mounted on top of the hull glacis, to induce additional deflection in APFSDS rounds.
With the addition of these modules, the JCh-6R's conventional armor protection increased considerably by comparison with the JCh-6G, especially at the edges of the 60-degree frontal arc. According to the line-of-sight estimates in the image at right, the "R" turret's armor is 800 millimeters thick when viewed head-on, and the turret cheeks are nowhere thinner than 440 millimeters when viewed at a 60-degree angle. Because the armor uses composite plating, effective thickness may be even higher, depending on the threat; the "R" turret reportedly incorporates strike plates made of depleted uranium.
Mobility
As a result of these changes to its armor and armament, the JCh-6R also took on a great deal of additional weight, rising to over 57 metric tonnes. This required the addition of a new powerplant in order to maintain acceptable mobility. The designers responded by incorporating a 1500-horsepower diesel engine, bringing the power-to-weight ratio to 25.8 horsepower per tonne. This made the JCh-6R one of the more agile tanks in Menghe's arsenal at the time, with a top speed of 70 kilometers per hour on hard, level ground and good performance on slopes and obstacles.
The new engine required an expansion of the hull rear, which angles up to incorporate the larger powerplant and transmission. Exhaust is ducted through the left rear track cover and then vented upward, modestly reducing the tank's infrared signature in comparison with the side exhaust port on previous variants. To counteract the decreased fuel efficiency of the more powerful engine, the designers also restored the external fuel tank mounts.
To cope with the higher weight, the designers also added new, slightly stronger torsion bars. A mixed hydrobar suspension was considered, but eventually rejected as too radical for a variant in the same family.
JCh-6M
The JCh-6M, introduced in 2018, is a modest upgrade to the JCh-6R incorporating additional protective measures. The most notable change is the addition of "third-generation ERA" of the same type used on the JCh-6D on the turret face, and a Jŏgran-un active protection system. Third-generation ERA was also added to the hull glacis plate. These measures further improved the JCh-6R's survivability against long-rod 120mm and 125mm APFSDS, though they also increased weight and unit cost.
JCh-6R1
First seen in early 2019, the JCh-6R1 is a JCh-6R hull with third-generation ERA plates attached to the turret face and hull glacis plate. It lacks the JCh-6M's hardkill and softkill APS suite. It is apparently being prepared for export, as the Jŏgran-un suite is not authorized for shipment beyond Menghe, but could also be a low-cost interim upgrade for existing JCh-6R hulls. As of March 2019, no export deals involving the JCh-6R1 have been announced.
Service
See also