Parliament of Gristol-Serkonos
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Parlamentum Stortinget Kanonhséshne | |
|---|---|
| 50th Parliament | |
 | |
 Logo | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Council of the State Council of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | July 1, 1867 |
| Preceded by | Diet of Gristol Longhouse of Serkonos |
| Leadership | |
Monarch of Gristol | Anna |
Monarch of Serkonos | Tehwehron |
Lord Speaker of the Council of the State | TBD, (Conservative) since 2019 |
Lord Speaker of the Council of Representatives | TBD, (Conservative) since 2019 |
Kaniehtí:io Fox, (Conservative) since 2019 | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 1010 200 Hereditary and Elected Senators 810 Members of Parliament |
 | |
Council of the State political groups | Hereditary Senators
Gristol Senators: 20
Serkonan Senators: 20
Elected Senators Government Coalition PC: 63
PPF: 8
NC: 7
DU: 9
Opposition SDP: 54
ML: 18
DS: 7
GN: 8
Absentionist IG: 9
|
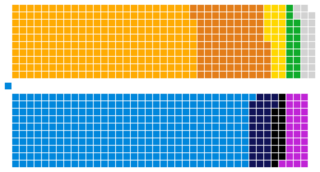 | |
Council of Representatives political groups | Government Coalition PC: 322
PPF: 31
DU: 31
NC: 17 Official Opposition SDP: 248 Other Opposition ML: 97
DS: 25
GN: 18 Absentionist IG: 21
|
| Elections | |
Council of the State voting system |
|
Council of Representatives voting system | Parallel Voting:
|
Council of Representatives last election | 2023 |
Council of Representatives next election | 2027 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Palace of the People, Federal Government District, Pontiac-Bernadotte | |
The Parliament of Gristol-Serkonos (Latin: Parlamentum, Nordic: Stortinget, Kanienʼkéha: Kanonhséshne) is the bicameral federal legislature of the United Kingdom of Gristol-Serkonos. The body consists of the Gristol and Serkonan monarchs, who make up the Federal Crowns, an upper house, the Council of the State; and a lower house, the Council of Representatives. Under the doctrine of parliamentary supremacy, the Parliament holds the ultimate power over all other political bodies in Gristol-Serkonos. The two chambers meet at the Palace of the People in Pontiac-Bernadotte, the national capital.
Each element has its own officers and organization. By convention, the Council of Representatives hold parliamentary dominance, with the Council of the State rarely opposing its will. The Council of the State reviews legislation from a less partisan standpoint and the monarch or viceroy provides royal assent to make bills into law.
The Council of the State includes two types of senators. There are 40 Hereditary Senators are appointed by the Federal Crowns which represents the hereditary Tribal Chiefs in Serkonos and the lesser Lords of the Manor Lands in Gristol. Second, is the 160 Elected Senators who are appointed by the party leaders from the Council of Representatives based on their seats. The Council of Representatives is an elected chamber with elections to 810 single member constituencies held at least every four years under the first-past-the-post system for 626 local area representatives while the remaining 184 members are elected through proportional representation based on their national vote. General elections must be called by the monarchs either by the advice of the Chancellor or if the government loses a confidence vote in the House. All government ministers, including the prime minister, are members of the Council of Representatives, less commonly, the Senators from the Council of the State and are thereby accountable to the respective branches of the legislature. Most cabinet ministers are from the Council of Representatives, whilst junior ministers can be from either house.
In theory, the supreme legislative power in Gristol-Serkonos is officially vested in the Crown-in-Parliament. However, the Federal Crowns normally acts on the advice of the Chancellor, and the powers of the Council of the State are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is de facto vested in the Council of Representatives. The most recent Parliament, summoned by Queen Anna of Gristol and Grand Duke Tehwehron of Serkonos in 2023, is the 50th since Union.
Composition
The body consists of the Gristo-Serkonan Federal Monarchs; an upper house, the Council of the State; and a lower house, the Council of Representatives. Each elements has its own officers and organization. Each has their own distinct role, but works in conjuction within the legislative process. Only those who sit in the Council of Representatives are granted the title of Member of Parliament. Though legislatively less powerful, Senators are ranked higher in the national order of precedence. No individual may serve in more than one chamber at the time.
Monarchs
Council of the State
Council of Representatives
See also: List of political parties in Gristol-Serkonos
Jurisdiction
Powers of the Parliament of Gristol-Serkonos are limited by the Federal Constitution. The legislative powers are divided between the Federal Government and the Constituent Countries. In general, legislatures of the Constituent Countries are granted powers to pass legislation relating to topics explicitly reserves for them in the constitution such as education, provincial officers, municipal government, charitable institutions, and "matters of a merely local or private nature".
Matters not under the exclusive authority of the Constituent Countries are within the scope of the federal Parliament's power. The Federal Parliament alone can pass laws relating to, among other things, the postal service, census, military, navigation and shipping, fishing, currency, banking, weights and measures, bankruptcy, copyrights, patents, and naturalization.
Jurisdictions of the federal and legislatures of the Constituent Countries in certain areas may be vague. For instance, the federal parliament regulates marriage and divorce in general, but the solemnization of marriage is regulated only by the legislatures of the Constituent Countries. Other examples include the powers of both the federal and the legislatures of the Constituent Countries to impose taxes, borrow money, punish crimes, and regulate agriculture.
Officers
Standing Committees
The Gristo-Serkonan Parliament has 43 standing committees, with 23 committees in the Council of Representatives, 16 in the Council of the State, and three joint committees. These committees are established by Standing Orders of the Council of Representatives or the Council of the State. These committees have many particular responsibilities to examine the administration, policy development, and budgetary estimates of certain government departments and agencies.
| Council of Representatives Standing Committee | Committee Chair | Council of the State Standing Committee | Committee Chair | Joint Standing Committee | Joint Committee Chairs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access to Information, Privacy and Ethics | Éloïse Duval, MP (SDA) | Agriculture and Forestry | Sen. Hélier Dufour (PC) | National Security and Intelligence Oversight | Sen. Kahenrahtiio Hemlock (SDA) Konrad Storstrand, MP (PC) | ||||
| Agriculture and Agri-Food | Ruth Rasmussen, MP (PC) | Banking, Trade, and Commerce | Sen. Hristofor Nogueira (SDA) | Library of Parliament | Sen. Hrœrekr Devlin (SDA) Atená:ti Luke, MP (PC) | ||||
| Heritage and Culture | Yoshi Okamoto, MP (PC) | Ethics and Conflict of Interest for Senators | Sen. Iostha Pratt (SDA) | Scrutiny Regulations | Sen. Kawennitake Deere (SDA) Alix Samuel, MP (PC) | ||||
| Citizenship and Immigration | Léonide Adam, MP (PC) | Energy, the Environment and Natural Resources | Sen. Harper Spalding (PC) | ||||||
| Environment and Sustainable Development | Raleigh Belcher, MP (PC) | Fisheries and Oceans | Sen. Loreto Matos (PC) | ||||||
| Finance | Aemilius Claudius, MP (PC) | Foreign Affairs and International Trade | Sen. Natalia Papadimitriou (PC) | ||||||
| Fisheries and Oceans | Andreas Kontos, MP (PC) | Human Rights | Sen. Estève Fabre (PC) | ||||||
| Foreign Affairs and International Development | Loís Soler, MP (PC) | Internal Economy, Budgets, and Administration | Sen. Johan Akselsen (SDA) | ||||||
| Government Operations and Estimates | Frans Antonsen, MP (SDA) | Legal and Constitutional Affairs | Sen. Shawátis Jacobs (SDA) | ||||||
| Human Resources, Skills and Social Development and the Status of Persons with Disabilities |
Tá:wit Horn, MP (PC) | National Finance | Sen. Terés Raven (PC) | ||||||
| Industry, Science and Technology | Tier Davidson, MP (PC) | National Security and Defence | Sen. Teioshontathe McGregor (SDA) | ||||||
| International Trade | Ojistah Doreen, MP (PC) | Official Languages | Sen. Iain Phillips (PC) | ||||||
| Constituent Countries and Devolved Administrations | Irénée Villeneuve, MP | Rules, Procedure and the Rights of Parliament | Sen. Linus Naess (PC) | ||||||
| Justice and Human Rights | Alex Aartsen, MP (PC) | Selection Committee | Sen. Mick Van Antwerpen (SDA) | ||||||
| National Defence | Lambert Cousineau, MP (SDA) | Social Affairs, Science and Technology | Sen. Athanase Traverse (PC) | ||||||
| Natural Resources | Vilhelm Martinsen, MP (PC) | Transport and Communications | Sen. Severin Baardsen (PC) | ||||||
| Official Languages | Tor Lind, MP (PC) | ||||||||
| Procedure and Chamber Affairs | Harald Lunde, MP (PC) | ||||||||
| Public Accounts | Edmundo Belmonte, MP (SDA) | ||||||||
| Public Safety and National Security | Bjørnar Hanssen, MP (PC) | ||||||||
| Status of Women | Finn Albertsen, MP (SDA) | ||||||||
| Transport, Infrastructure and Communities | Yngve Holt, MP (PC) | ||||||||
| Veterans Affairs | Céleste Carpentier, MP (PC) | ||||||||
Term
Procedure and Legislative Functions
Historical Composition
| ||||||||||||||||
| Election | Total seats |
Composition | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1867 (1st) |
490 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 1872 (2nd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1873 (3rd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1878 (4th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1882 (5th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1887 (6th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1891 (Interim) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1892 (Interim) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1894 (Interim) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1896 (Interim) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1896 (7th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1900 (8th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1904 (9th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1908 (10th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1911 (11th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1915 (12th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1919 (13th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1920 (Interim) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1921 (14th) |
626 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 1925 (15th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1926 (16th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1930 (17th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1934 (18th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1938 (19th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1942 (20th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1946 (21st) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1950 (22nd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1953 (23rd) |
720 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 1956 (24th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1960 (25th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1964 (26th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1968 (27th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1972 (28th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1976 (29th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1978 (30th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1984 (31st) |
790 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 1986 (32nd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1990 (33rd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1994 (34th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 1996 (35th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2000 (36th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2004 (37th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2006 (38th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2008 (39th) |
810 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 2011 (40th) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2015 (41st) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2019 (42nd) |
| |||||||||||||||
| 2023 (43rd) |
| |||||||||||||||