United Congress
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
United Congress (UC)
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
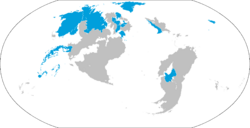 Map showing the members states of the United Congress | |||||||||||
| Headquarters | Zollhafen, Gonece, Dahemia (international territory) | ||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||
| Type | Intergovernmental organization | ||||||||||
| Membership | 10 member states | ||||||||||
| Leaders | |||||||||||
| X (X) | |||||||||||
| X (X) | |||||||||||
| Isabella Salváez (Nadauro) | |||||||||||
| X (X) | |||||||||||
| Establishment | |||||||||||
• X signed | X | ||||||||||
• UC Charter ratified | 1 December 1940 | ||||||||||
• First UC Congress meeting | 1 January 1941 | ||||||||||
Website www.uc.org www.uc.int | |||||||||||
The United Congress (UC, or sometimes UNCO or UCO) is an intergovernmental organization established to provide and maintain international peace and security, developing close relations among member states, achieving widespread international co-operation, and being a forum for the diplomatic interaction between nations as defined by its Charter instrument. Its headquarters, with all UC territories as subjects to a status of extraterritoriality, is located in Gonece, Dahemia, and it has other main offices in X.
It was founded after the Great War during the X in 1940, with its aim of preventing any future wars on the scale of the Great War; it rapidly evolved into an organization dealing with maintaining international peace and security at large, protecting human rights as defined in the Charter of the Rights of Man, providing humanitarian aid, promoting sustainable development, and upholding international law.
The organization is divided into six principal organs: the UC Security Council (UCSC) as the executive organ tasked with enforcing UC Resolutions and intiating peacekeeping missions, the UC Congress (UCC) of the organization's member states as its deliberative assembly organ, the UC Mandateship Council (UCMC) for administrating UC Mandates, the UC Secretariat (USCE) with the head administrative office of the UC Secretary-General, the judicial International Courts of Justice, and the UC General Socio-Economic Council (UCGSEC) for interregional economic and socio-demographic affairs.
The UC is the largest, most familiar, most internationally represented and most powerful intergovernmental organization in the world. Its specialised agencies include the World Monetary Fund, ICHEF, the International Bank, the International Health Committee, and the International Food Programme and are active in all of the UC's participating countries. At its founding in 1940, the UC had 7 member states. As of 2022, there are now 10, all mutually recognized sovereign countries.
History
Aftermath of the Great War
Atomic Order
Contemporary period
Structure
UC Security Council
The Security Council of the United Congress is primarly tasked with upholding, preserving and enforcing international peace and security by the means of issuing binding resolutions for all member states. Actions taken by the Security Council can include opening investigations and electing reccomendations to international disputes relevant to the broader global community, enacting economic and diplomatic sanctions and sending peacekeeping troops in the form of UC Missions as outright military action.
The permanent members of the United Congress Security Council are the six states which are given a permanent seat in the Security Council by the X of X and further additional permissions by the UC Congress throughout its history. These states are: the Fourth Republic of Yingok, the Union of Elian Free States, the Waldish Confederation, and the Worker's Republic of Hyacinthe. Waldrich, Hyacinthe and the Free States were the principal allies of the Transmedan Powers in the Great War, as well as its victors; Yingok was granted a permanent seat as part of the X. All of the members are considered to be the world's great powers; the W3 Initiative between Razan, Nadauro and Falland support each other's claim of having permanent access to the Security Council as a broader organizational reform proposal.
Decisions are made upon the plurality vote of the five members, in which for a binding decision two-thirds must approve; a power of veto does not exist. The Security Council is added by seven non-permanent member states rotating every two years from all member states of the UC Congress. While they have no initiative in proposing or recommending specific UCSC action, they have the possibility to vote in UCSC decisions with a vote half as significant as those of the permanent members. The uneven number of the UCSC members theoretically allows for every decision to pass without a draw.
| Country | Current state representation | Former state representation | Current executive leaders | Current representative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | President of the Supreme Executive Council: Eugenio Vial | X | ||
| — | First Representative: Alban Vaillancourt | X | ||
| — | Forsitter: Solveig I Lawspeaker: Anders Kjeldsen |
X | ||
| President: Yeung Kapkaa Chancellor: Nam Gat |
X |
UC Congress
UC Mandateship Council
The Mandateship Council of the United Congress was tasked to administrate and govern designated UC Mandates in accordance to the maintenance or fostering of the inhabitants' living conditions on their behalf or in interest of international security and peace, ultimately intended to prepare the mandated territories for attained self-rule by the merger with another neighbouring sovereign state, or independence. Historically most UC Mandates have been former colonies and dependent territories of the defeated Sydenham Powers after the Great War which were transferred to a Mandatory power, undertaking obligations to the protection and development of the attained territories which were then regarded as too underdeveloped or politically instable to receive sovereignty; a notable exception to this was the Dahemian Protectorate after the 1946 Dahemian Crisis. All UC Mandates have either received independence or were annexed by sovereign states, and with the establishment of X as a member state of the UC in 19XX the Mandateship Council has largely remained inactive since.
UC Secretariat
International Courts of Justice
Specialized agencies
| No. | Agency | Acronym | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | World Labor Organization | WLO | |
| 2 | World Maritime Organization | WMO | |
| 3 | World Civil Aviation Organization | WCAO | |
| 4 | International Agricultural Bureau | IAB | |
| 5 | International Food and Agricultural Fund | IFAF | |
| 6 | World Telecommunications Bureau | WTB | |
| 7 | International Tourism Bureau | ITB | |
| 8 | World Economic Development Organization | WEDO | |
| 9 | World Postal Bureau | WPO | |
| 10 | Universal Cultural and Educational Organization | UCEO | |
| 11 | World Monetary Fund | WMF | |
| 11 | Global Bank Organization | GBO | |
| 12 | International Health Organization | IHO | |
| 13 | World Meteorological Bureau | WMB | |
| 14 | International Intellectural Property Bureau | IIPB |
UC peacekeeping missions
Membership
Member states
| Flag | Country | Date of admission | Further role in the UC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yingok | 1 December 1940 | ||
| Vistulzka | 1 December 1940 | ||
| Nadauro | 27 March 1955 | ||
| Dahemia | 16 June 1957 |





