Oedipina nigrescens: Difference between revisions
ContraViper (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Taxobox | name = Ochacan Long-tailed Salamander | status = vu | status_system = IUCN3.1 | extinct = | image = inyur_longtailedsal_01.jpg | image_width = 300px | image_capti...") |
ContraViper (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Eggs are laid in the soil, and it is believed that juveniles spend their time under soil only to emerge as adults. However, a wild juvenile has never been found to date. | Eggs are laid in the soil, and it is believed that juveniles spend their time under soil only to emerge as adults. However, a wild juvenile has never been found to date. | ||
==Drug Trade== | ==Drug Trade== | ||
The [[Inyurstan Drug War|drug trade]] has been implicated in potential declines of this species. Production of coca releases chemical fertilizer into the soil, as well as altering the organic-clay balance of nearby terrestrial systems. This in turn affects the ability of ''O. nigrescens'' to reproduce, and further leakage of chemicals used in the process of refining coca leaves into cocaine also pollute the soil and cause downstream mortality of buried individuals. Coca production sites have been implicated in the extirpation of this species from at least two localities. | |||
Increased foot and vehicle traffic - both from growers & traffickers as well as Inyurstan law enforcement forces battling them - may also cause mortality during the two narrow windows of surface migration at the start and end of the rainy season. | |||
==National Icon== | ==National Icon== | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 10 February 2022
| Ochacan Long-tailed Salamander | |
|---|---|

| |
| Oedipina nigrescens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia
|
| Phylum: | Chordata
|
| Class: | Amphibia
|
| Order: | Caudata
|
| Family: | Plethodontidae
|
| Genus: | Oedipina
|
| Species: | O. nigrescens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Oedipina nigrescens Martel et al., 1982
| |
| |
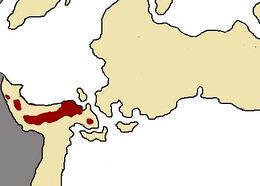
| Range of O. nigrescens in Inyursta | |
Oedipina nigrescens, the Ochacan Long-tailed salamander, is a species of salamander in the genus Oedipina. It is also known as the "Black Long-tailed salamander" or "Yana-qwarya" by the local indigenous Rim'talan Peoples, in reference to its colors.
It is remarkable due to its behavioral ecology, wherein it is both hyper-fossorial and hyper-arboreal, spending much of the year buried deep beneath the soil and the remainder of the year high up in the crevices and epiphyte microhabitats of trees.
Discovery
The Ochacan Long-tailed salamander was known to the Rim'talan people for centuries. During the Inyurstan Civil War, counter-revolutionary forces fighting in the area told of a long, rubbery snake-like creature with four legs and a prehensile tail.
In 1976, Dr. Ferdinand Martel led a small expedition into the reported locality, gleaned from then-commissioned Inyurstan soldiers. While his expedition was able to uncover a number of Inyurstan fauna previously unknown to science (such as the Sabo's Burrowing treefrog, they were unable to uncover the black climbing enigma. Due to violence in the region, all scientific expeditions were halting. Dr. Martel and his team got a second chance in 1982, with a small escort from the Inyurstan Army and new grant money from the (UNIVERSITY HERE). During this time, they were able to catch the seasonal transition between the dry season and rainy season. On the first monsoon, they observed multiple individuals emerging from the soaked soil and begin to climb trees. The emergence & migration event lasted about a week, but Martel had his first specimen of O. nigrescens.
Habitat & Conservation
Arboreal Cloud Forests
As a species with an extremely specialized behavioral ecology, the Ochacan Long-tailed salamander requires a very specific habitat. The ideal habitat is the ecotone between true lowland rainforest or swampland with upland or montane cloud forest. Such ecotones have deep, moist organic soils associated with lowland habitats, but tall trees which stretch into areas of higher elevation (along with a moisture & temperature gradient). For example, an area where the roots of a given tree might be in a consistently warm, humid jungle but the tall canopy & emergent layer stretches into cooler montane forest with a more persistent cloud layer.
Eggs are laid in the soil, and it is believed that juveniles spend their time under soil only to emerge as adults. However, a wild juvenile has never been found to date.
Drug Trade
The drug trade has been implicated in potential declines of this species. Production of coca releases chemical fertilizer into the soil, as well as altering the organic-clay balance of nearby terrestrial systems. This in turn affects the ability of O. nigrescens to reproduce, and further leakage of chemicals used in the process of refining coca leaves into cocaine also pollute the soil and cause downstream mortality of buried individuals. Coca production sites have been implicated in the extirpation of this species from at least two localities.
Increased foot and vehicle traffic - both from growers & traffickers as well as Inyurstan law enforcement forces battling them - may also cause mortality during the two narrow windows of surface migration at the start and end of the rainy season.