GBM-23/5 Bulkkot
| GBM-23/5 Bulkkot | |
|---|---|
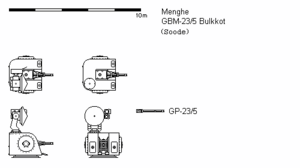 3-view diagram of the GBM-23/5, without pedestal | |
| Type | Close-in weapon system |
| Place of origin | Menghe |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2001–present |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1996-2001 |
| Produced | 2001-present |
| Specifications | |
| Height | 3.86 m (above turret ring) |
| Crew | 1 (can be automated) |
| Shell | 23×133mm |
| Caliber | 23mm |
| Barrels | 5 |
| Elevation | -20 to +85 degrees at 80 degrees/sec |
| Traverse | unlimited |
| Rate of fire | 4,600 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,109 m/s |
| Effective firing range | 4000 m (aircraft) 3000 m (missiles) |
| Feed system | linkless feed (2,200 rounds) |
Main armament | 1 x GP-23/5 rotary cannon |
The GBM-23/5 (Formal designation: 근접 방어 무기 23/5, Gujŏb Bang-ŏ Mugi isam-o, "Close-Range Defensive Weapon 23/5;" Short designation 불꽃, Bulkkot, "Blaze") is a naval close-in weapon system designed for the Menghean Navy in the late 1990s. It consists of an enclosed turret with a 23mm rotary cannon, multi-mode fire-control system, and 2,200 rounds of ammunition. It replaced the AK-630, which Menghe license-produced as the GBM-30/6, and achieves comparable performance with a more compact mount and improved accuracy.
Development
Menghean engineers had already begun work on an improved CIWS mount in the early 1980s, with the goal of correcting shortcomings in the Letnian-designed AK-630. These included the mount's large below-deck supporting space for ammunition and equipment and its need for a separate fire-control radar. Scale models were produced in 1984, but it appears that no working prototype was ever manufactured. Development of the new CIWS mount was suspended in 1985 to focus on mass-production of existing ship designs.
In 1995, Menghe placed an order for 40 GIA Iolar 4th-generation fighters. As part of the contract, Menghe also imported several spare 23mm rotary autocannons for testing and training, with an option for license production in future contracts. One of these was passed on to the Navy's design and engineering department for evaluation in the close air defense role. It met expectations in the preliminary evaluation stage, and work on a CIWS mount incorporating it began the following year. The design of the new mount incorporated some features from the early-80s project, most notably the arrangement of the ammunition drums and guidance radar, but the result was an entirely different system.
Description
Sensors
The GBM-23/5 has a multi-mode fire-control system, consisting of a radar antenna, a visual-spectrum camera, an infrared-spectrum camera, and a broad-beam ranging laser. Some sources also claim that later variants have a passive radar mode, which can detect the radar emissions from an active anti-ship missile. This multi-mode system makes the mount highly resistant to jamming, countermeasures, adverse weather conditions, and restricted radar-emission doctrine.
All fire control sensors are grouped on a single mount located on the back right corner of the turret. The sensor array can traverse and elevate independently of the gun, allowing the system to lead the target with the gun while tracking it directly with the camera. On most variants of the GBM-23/5 system, the turret has no air search radar of its own, and relies on other shipboard systems to track and allocate targets. A few variants include a built-in search radar on the same sensor mast, though its range is limited. Placement of the fire-control system and its computers within the mount itself not only reduces the necessary deck space for a functioning system, but also speeds up the reaction time of the system.
Fire control
The exact designation of the fire-control radar is unknown, but it is known to be a domestic Menghean design, and was purpose-built for the GBM-23/5. Menghean sources claim that it has a detection range of 8 kilometers against a missile-sized target and 12 kilometers against a fighter-sized target. Gun engagement range is limited to 4 kilometers, but the longer radar range allows additional time to acquire, track, and calculate a firing solution before engaging.
The multi-mode electro-optical system provides a video feed to the operator's screen, with color and high-contrast IR modes. This allows visual identification of aircraft and helicopters of unknown type. It also allows the system to engage surface targets such as small boats and floating mines, either through automatic electro-optical tracking or manual pointing by the operator.
In manual mode, used during low-intensity operations, a crew member operates a control panel in the combat information center corresponding to the mount in question. This allows manual confirmation of each target engagement. In a high-intensity environment, the gun operator can also activate the system's automatic mode. Under this mode, the GBM-23/5 automatically selects incoming targets, ranks them by priority, tracks them as they approach, and engages as they enter range, without user input.
Gun
The armament of the GBM-23/5 is a single five-barreled 23mm autocannon of Glasic design. Its Menghean designation is GP-23/5. The gun has a maximum rate of fire of 4,800 rounds per minute on the naval mount, and unlike the mount on the SR-8, it is not limited to 3,600 rpm. It cannot fire for more than one minute continuously without damaging the barrels. The gun also has a "reduced" fire rate of 300 rounds per minute, which is achieved by adjusting the speed of the electrical motor driving the gun's rotation. Menghean Navy doctrine instructs personnel to activate this mode when engaging surface targets, in order to reduce ammunition expenditure. When a mount is assigned to engage an airborne target, it automatically reverts to the maximum rate of fire setting, whether in manual or automatic engagement mode.
The GBM-23/5 carries 2,200 rounds of 23mm ammunition, which are split across two 1,100 round drums, one on either side of the gun. This layout means that the GBM-23/5 does not require any ammunition or equipment space below the deck on which it is mounted, unlike the AK-630, which stores its ammunition and turret drive in a one-level compartment below the turret.
On naval mounts, both ammunition drums are loaded with APDS ammunition, consisting of a solid steel subcaliber projectile seated in a nylon sabot. This allows for a higher muzzle velocity and reduced drag in flight. Combat experience during the Innominadan Crisis revealed that this ammunition was inadequate for engaging small boats, requiring more hits to sink a target than an AK-630 firing high-explosive 30mm rounds. This was a factor in the development of a new naval gun turret system.
Menghean sources claim that the GBM-23/5 has an effective range of 4,000 meters against aircraft and 3,000 meters against missiles. It reportedly achieved a 95% kill rate in trials.
Variants
GBM-23/5R Bulkkot-R
This variant adds a new sensor mast to the back-left corner of the turret. This mast carries a 3D air search radar, allowing the mount to independently detect and track targets without input from a separate shipboard radar system. Menghean sources claim that this radar has a range of 15 kilometers against aircraft and 10 kilometers against missiles.
GBM-23/5Y Dungji
The GBM-23/5Y, marketed as Dungji ("nest"), consists of an enlarged and reinforced GBM-23/5 turret with sixteen YDG-61 surface-to-air missiles. These are loaded into four quad-missile boxes, two on each side. The resulting mount has the same gun-based capabilities as the baseline "Bulkkot" model, and the same surface-to-air missile capacity as the HYB-61/16 ship-based missile launcher, while also benefiting from the use of onboard radar to acquire targets at longer range. To compensate for the increased mass, the larger turret carries more powerful traverse motors.
Dungji-R refers to a modification of the Dungji system with a short-range 3D search radar, identical to the one on the Bulkkot-R. Its formal designation is GBM-23/5YR.
GBM-23/5Y2 Gungsu
Like the "Dungji", this system uses the enlarged and reinforced version of the GBM-23/5 turret, but instead of YDG-61 SAMs it carries two launch boxes for a total of eight YDG-64 surface-to-air missiles. These launch boxes are derived from self-defense-length Mark 41 VLS canisters, and are not reloadable on ship; they must be replaced in port with the help of a crane. While it has only half as many missiles as the GBM-23/5Y Dungji, these missiles have a higher hit probability and a greater range.
JGBM-23/5
The JGBM-23/5 is a land-based variant, with "J" indicating jaju, or "self-propelled." It is mounted on a Taekchŏn T512 8x8 utility truck, along with a command module containing a gunner, a commander, a radar operator, and some of the turret drive systems which would normally be located in the mount's pedestal. The command module also carries a 3D air-search radar to independently acquire targets. Because of the placement of the command module, the gun mount can only cover a 270-degree arc to the rear of the truck, so multiple vehicles are required to achieve full coverage.
The JGBM-23/5 cannot fire from the move like a self-propelled anti-air gun. Instead, it is intended to be parked near stationary high-value targets, such as large unit headquarters, airfields, and long-range surface-to-air missile launchers. As a C-RAM system, it is able to intercept rockets, artillery shells, and mortar bombs, as well as anti-radiation missiles and cruise missiles.
Users
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
By ship class
GBM-23/5 Bulkkot
- Chanjok Jachido-class cruiser (as GBM-23/5, after refits)
- Mirun-class corvette
- Sŏwicho-class corvette
- Yajjdan-class frigate
- Yechŏn-class frigate
GBM-23/5Y Dungji
GBM-23/5Y2 Gungsu