Kontech999/sandbox
Nutarra, officially the People's Republic of Nutarra is a country in Eastern Cesylle. The country is bordered by (placeholder) to the west and (placeholder) to the south. It has a population of 160 million, making it the most populated on Cesylle. Its capital is Rotbaum, and its most populous city is Buchtberg. Nutarra is a Federal Council wikipedia:Republic composed of 21 states. It is the only country on Cesylle to have Naocadon as an official language. Nutarra is in the Alliance for Socialist Liberation and its economy is a computerized socialist planned system.
Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of 7,491 kilometers (4,655 mi).[1] It borders all other countries and territories in South America except Ecuador and Chile and covers roughly half of the continent's land area.[2] Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, home to diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, and extensive natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats.[1] This unique environmental heritage positions Brazil at number one of 17 megadiverse countries, and is the subject of significant global interest, as environmental degradation through processes like deforestation has direct impacts on global issues like climate change and biodiversity loss.
The territory which would become known as Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the discovered land for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808 when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. Slavery was abolished in 1888. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d'état. An authoritarian military dictatorship emerged in 1964 and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current constitution, formulated in 1988, defines it as a democratic federal republic.[3] Due to its rich culture and history, the country ranks thirteenth in the world by number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[4]
Brazil is a regional and middle power[5][6][7] and is also classified as an emerging power and a major non-NATO ally.[8][9][10][11][12] Categorised as a developing country with a high Human Development Index,[13] Brazil is considered an advanced emerging economy,[14] having the ninth largest GDP in the world by nominal, and eighth by PPP measures, the largest in Latin America.[15][16] As an upper-middle income economy by the World Bank[17] and a newly industrialized country,[18] Brazil has the largest share of global wealth in South America and it is one of the world's major breadbaskets, being the largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years.[19] However, the country retains noticeable corruption, crime and social inequality. Brazil is a founding member of the United Nations, the G20, BRICS, G4, Mercosul, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the Community of Portuguese Language Countries. Brazil is also an Observer State of the Arab League.[20]
People's Republic of Nutarra Nutarranische Volksrepublik (Valkian) República Popular Nutarresa (Naocadon) | |
|---|---|
Coat of Arms
| |
| Anthem: Internationale | |
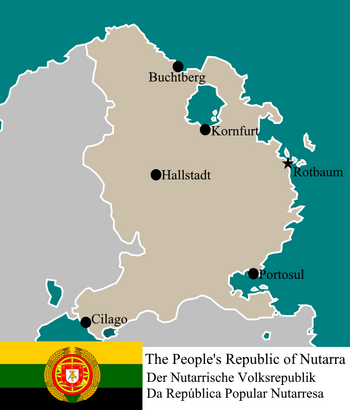 | |
| Capital | Rotbaum |
| Largest city | Buchtberg |
| Official languages | |
| Demonym(s) | Nutarran |
| Government | Federal presidential council republic |
| Hons Lula | |
| Felix Imhoff | |
| Arthur Lira | |
| Rodrigo Pacheco | |
| Legislature | National People's Assembly |
| Supreme Labor Council | |
| National People's Representative Chamber | |
| Independence | |
• Declared | 7 September 1822 |
| 1 June 1831 | |
• Republic | 15 November 1875 |
| 5 October 1941 | |
| 1 March 1971 | |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 160,062,512 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high (41th) |
| Currency | Schild (S$) (NTS) |
| Time zone | UTC−2 to −5 (NST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +55 |
| Internet TLD | .nt |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Template:Cite CIA World Factbook
- ↑ "Brazil – Land". Permanent Missions. United Nations. Geography. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014.
- ↑ "Brazilian Federal Constitution" (in português). Presidency of the Republic. 1988. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 3 June 2008. "Brazilian Federal Constitution". v-brazil.com. 2007. Archived from the original on 28 September 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2008.
Unofficial translate
- ↑ "UNESCO World Heritage Centre — World Heritage List". UNESCO. Retrieved 25 May 2012.
- ↑ M. Schaefer; J. Poffenbarger (2014). The Formation of the BRICS and its Implication for the United States: Emerging Together. Springer. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-137-38794-3.
- ↑ Sean W. Burges (2016). Latin America and the Shifting Sands of Globalization. Routledge. pp. 114–15. ISBN 978-1-317-69658-2.
- ↑ Gardini, Gian Luca (2016). "Brazil: What Rise of What Power?". Bulletin of Latin American Research. 35: 5–19. doi:10.1111/blar.12417.
- ↑ Gratius, Susanne (April 2008). "The international arena and emerging powers: stabilising or destabilising forces?" (PDF). FRIDE. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2016.
- ↑ Peter Collecott (29 October 2011). "Brazil's Quest for Superpower Status". The Diplomatic Courier. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ↑ Clendenning, Alan (17 April 2008). "Booming Brazil could be world power soon". USA Today. The Associated Press. p. 2. Retrieved 12 December 2008.
- ↑ Jorge Dominguez; Byung Kook Kim (2013). Between Compliance and Conflict: East Asia Latin America and the New Pax Americana. Center for International Affairs, Harvard University. pp. 98–99. ISBN 978-1-136-76983-2.
- ↑ Vandiver, John (May 9, 2019). "Trump bumps up Brazil to 'major non-NATO' ally". Stars and Stripes. Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ↑ "Human Development Insights". United Nations Development Programme.
- ↑ "FTSE Country Classification" (PDF). FTSE Group. September 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-11-21. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIMFWEO.BR - ↑ "CIA – The World Factbook – Country Comparisons – GDP (purchasing power parity)". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2011.
- ↑ "Country and Lending Groups". World Bank. Archived from the original on 18 March 2011. Retrieved 5 March 2011.
Uppermiddle Income defined as a per capita income between $3,976 – $12,275
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedNeilson102 - ↑ "Brazil must be a 'facilitator' in the Middle East, says VP". 14 August 2019.
