South Misai: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |ethnic_groups_year = | ||
|demonym = {{hlist|South Misainese|Misainese}} | |demonym = {{hlist|South Misainese|Misainese}} | ||
|government_type = {{wp|Unitarism|Unitary}} {{wp|constitutionalism|Constitutional}} {{wp| | |government_type = {{wp|Unitarism|Unitary}} {{wp|constitutionalism|Constitutional}} {{wp|Republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = [[President of the Republic of Misai|President]] | |leader_title1 = [[President of the Republic of Misai|President]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Ai Obama]] | |leader_name1 = [[Ai Obama]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|established_event5 = [[Ebiwan Revolution]] | |established_event5 = [[Ebiwan Revolution]] | ||
|established_date5 = 1919 | |established_date5 = 1919 | ||
|established_event6 = [[Misai Council]] | |established_event6 = [[Misai South Islands High Government]] | ||
| | |established_date6 = 1920 | ||
|established_event7 = [[Misai Council]] | |||
|established_date7 = 1944 | |||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
| Line 70: | Line 73: | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = 24 748 331 | ||
|population_census_year = 2016 | |population_census_year = 2016 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = | ||
| Line 80: | Line 83: | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = $ | |GDP_nominal = 737$ billion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2018 | |GDP_nominal_year = 2018 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $ | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $29 791 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = 30.2 | |Gini = 30.2 | ||
| Line 90: | Line 93: | ||
|Gini_change = decrease | |Gini_change = decrease | ||
|Gini_category = Medium | |Gini_category = Medium | ||
|HDI = 0. | |HDI = 0.891 | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
|HDI_year = 2018 | |HDI_year = 2018 | ||
| Line 101: | Line 104: | ||
|time_zone_DST = | |time_zone_DST = | ||
|antipodes = | |antipodes = | ||
|date_format = | |date_format = cc-{{sfrac|d|m}}-yy | ||
|DST_note = | |DST_note = | ||
|utc_offset_DST = | |utc_offset_DST = | ||
| Line 118: | Line 121: | ||
Discontent towards daimyo rule and an increased public will for a democratic system led to the [[Ebiwan Revolution]] where the Republic of Misai was proclaimed which plunged Misai into a civil war. Fighting in the war quickly drew into a stalemate on the main island while the Republican Armed Forces consolidated its control over the southern islands. Due to the stalemate of the war, an armstice was called in 1924. Tensions between the north and south slowly declined as public sentiment in both countries turned against the hostile relations between north and south. This culminated in the creation of the [[Misai Council]] in 1944 where both sides began the process of deep integration. Today North and South Misai are two of the most well-inegrated countries in the world to the point that many view reunification as redundant. | Discontent towards daimyo rule and an increased public will for a democratic system led to the [[Ebiwan Revolution]] where the Republic of Misai was proclaimed which plunged Misai into a civil war. Fighting in the war quickly drew into a stalemate on the main island while the Republican Armed Forces consolidated its control over the southern islands. Due to the stalemate of the war, an armstice was called in 1924. Tensions between the north and south slowly declined as public sentiment in both countries turned against the hostile relations between north and south. This culminated in the creation of the [[Misai Council]] in 1944 where both sides began the process of deep integration. Today North and South Misai are two of the most well-inegrated countries in the world to the point that many view reunification as redundant. | ||
Today South Misai is a part of various international organizations such as the [[Misai Council]]. South Misai is ranked very high in the {{wp|Human Development Index}} and has one of the world's highest life expectancies at 83.6 years. South Misai is a {{wp|developped country}} with a high-income economy. It is also a high preformer in a myriad of international listings of {{wp|democracy}}, {{wp|civil liberties}} and {{wp|press freedoms}}. South Misainese citizens also receive {{wp|free education}}, {{wp|universal healthcare}} and some of the longest paid {{wp|maternity leave}} in the world. Despite all this, South Misai is one of the most regionally unequal nations as the main island accounts for over 80% of South Misai's economy even though it is home to only around 67% of the population. | |||
==Etymology== | |||
The {{wp|Japanese language|Hananese}} name for Misai is 美西. The characters for ''beaty'' (美, ''bi'') and ''west'' (西, ''nishi'') are used for their compound reading of Misai. The meaning behind the characters used for Misai is therefore beautiful west referring to its location west of the island of [[Ōshima]]. The actual meaning behind Misai is unkown but some linguistists hypothise that it is a Hananised version of the {{wp|Samoan language|Soifun}} name for the lower islands of the archipelago Isai'i. | |||
==History== | |||
===Precolonial History=== | |||
Little remains of the aboriginal people groups in the northern portion of the [[Misai archipelago]]. Human habitation has been estimated to have been present on the archipelago since the {{wp|Stone Age}}. Human remains that were thought to have originated from the {{wp|Paleolithic Era}} were found in [[Inishiro]] in the late 1800s but were lost during shipment before this could be proven. | |||
Due to the isolated geography of the southern islands, some native groups, the largest of which are the {{wp|Samoan people|Soifun peoples}}, have survived in relatively isolated communities. The various aboriginal groups of southern Misai have been linked through linguistic and biological evidence to the larger immigration of seafaring peoples from [[Yidao|Southeast Catai]] to [[Savai]]. According to {{wp|Samoan people|Soifun}} oral tradition and history, fishermen and traders sailed up to the main island of Misai as well as [[Oshima]] on a regular basis. | |||
===Hananese Colonisation=== | |||
The Misai archipelago was known by {{wp|Japanese people|Hananese}} traders and fishermen for about two hundred years prior to any actual settlement. The first {{wp|Japanese people|Hananese}} settlers arrived on the main island in 1122. The period between 1122 and the early 1200s is refered to as the first phase of colonisation. According to early literary sources, initial contact between the natives and the {{wp|Japanese people|Hananese}} was peaceful, yet with an increase in the number of arriving settlers, ties between the two groups quickly soured. Aboriginal groups faced sharp decline due to disease and conflict with the ever-increasing number of settlers. These initial settlers were primarily fishermen and traders looking for economic opportunity on the islands. Due to the hostile ties bewteen the settlers and natives, the population of colonists had to arm itself alongside forming small groups of volunteer mercenaries. | |||
[[File:Arion Matoi.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Painting depicting a fictional early settler of Misai]] | |||
The second phase of colonisation is considered to have taken place bewteen the early 1200s and 1390s. It is characterised by an increase in inland settlement and a considerably rapid establishment of farming communities on Misai. Accompanying this increase in the population of settlers on the island was the complete importation of the {{wp|Japanese people|Hananese}} social order to the islands. Several minor nobles were granted the high status of daimyo in exchange for moving to these new territories and governing them on behalf of the emperor back on the mainland. The presence of these newly-appointed daimyo and the rule of law they brought with them displeased many early traders and fishermen who were no longer able to conduct business freely. The daimyo also brought with them significant numbers of {{wp|Affinity_(medieval)|retainers}} that eventually replaced the makeshift mercenary groups formed by early settlers. During this second phase of colonisation, mentions of native peoples on the main island cease which is credited to the creation of more professional warrior class. | |||
The third and final phase of colonisation is considered to have taken place from the 1390s to the late 1500s. It is characterised by the settlement of the southern islands by Misainese settlers from the main island itself unlike the two prior phases where settlers largely came from the mainland. Also unlike the two prior phases, the third phase was largely started by the Daimyo on the main island wishing to increase their holdings size considerably in part to be able to afford yearly tributes to the mainland. Due to the more isolated geography of the southern islands, native groups were able to presist in the southern islands islands to the modern-day. Despite this, diseases brought by interactions with the main island greatly decreased their population. Due to limitations to the what jobs they could work and which areas they could live in, most natives in Misainese society had to work as low-skilled contractual labour most often on farms or as house laborers. Natives were treated as the lowest class in society. Eventually settlers and natives began to intermarry largely due to the fact that settlers to the southern islands were overwhelmingly male. This racially mixed class called the Jokujin was considered racially inferior to {{wp|Japanese people|Hananese people}} but became a significant portion of the population in the southern islands. | |||
===Early Kingdom Period=== | |||
[[File:King Sho Gen.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The first Great Daimyo of the Kingdom of Misai ]] | |||
Because of the distance between Misai and the mainland, the daimyo of Misai were able to rule relatively autonomously with actual mainland rule | |||
In 1437 the Daimyo X, the most influential daimyo of Misai, declared himself the Great Daimyo of the | |||
===Southern Daimyo Period=== | |||
===Rokuda Unification=== | |||
===Ebiwan Revolution=== | |||
===Misainese Rapprochement=== | |||
===Territorial Timeline=== | |||
==Geography== | |||
===Climate=== | |||
[[File:Köppen Climte Classification of South Misai.png|300px|thumb|right|Köppen climate classification of South Misai]] | |||
The South Misainese climate is largely divided into two: a tropical maritime climate which is the dominant climate type in South Misai and a temperate climate on the northern portion of the main island. Typhoons are common in South Misai reaching their peak in July, August and September. The northern temperate region experiences wider temperature changes in its climate than their southern tropical counterparts where such changes in temperature are noticeably lesser. | |||
===Regions=== | |||
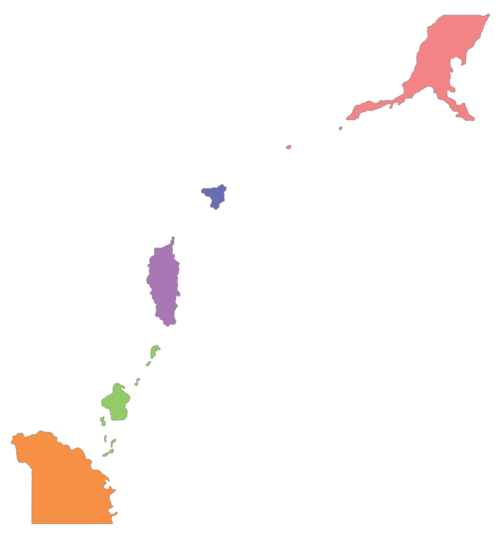
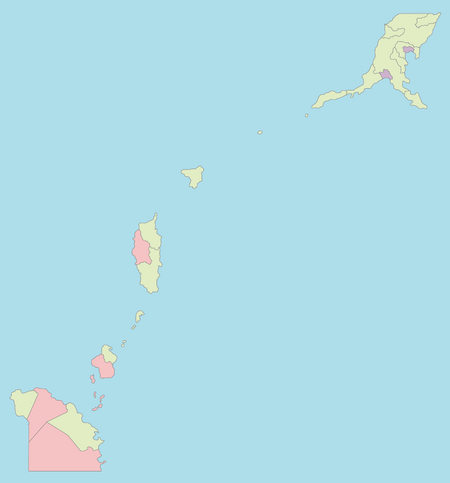
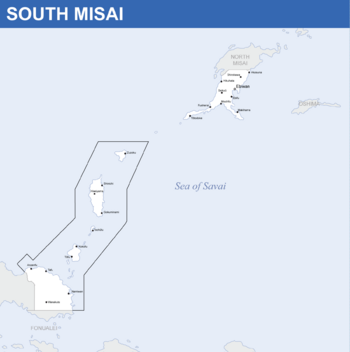
Misai is divided into five regions: [[Southern Misai]], [[Yoshikageshima]], [[Chūkanshima]], [[Īsai]] and [[Equatorial Savai]]. Regions represent gradual cultural, dialectical and economic differences better than prefectures. They serve a supporting role facilitating cooperation between prefectures and the federal government. Each region has a separate regional assembly where prefectural governments send representatives with the exeption of [[Yoshikageshima]] the prefectural assembly of which fills the role of regional assembly as well because of its small size. Due to the high degree of autonomy prefectures and municipalities enjoy in South Misai, regional governments are mostly in charge of coordinating healthcare services as well as monitoring agricultural and environmental policies and laws. | |||
Regional differences in South Misai are extremely stark. Two-thirds of the nation's population and 80% of its economy are represented by only one of there regions: Southern Misai. Historically the treatment of the soutern islands has been mired in colonialism where their econmies were heavily based on the extraction of labour and resources to the main island. The southern islands are also more ethnically diverse than their northern counterpart with both native and immigrant communities making up a substantial portion of the populations. In recent years, the central government of South Misai has attempted several economic stimulus plans to revitalize the southern economy. These policies have worked in most regions except for [[Equatorial Savai]] where economic problems continue. | |||
{{South Misai RegionsBox}} | |||
===Administrative Divisions=== | |||
South Misai is composed from 20 free commanderies ({{wp|Japanese Language|Hananese}}:無料郡, ''Muryō-gun''). The term free commandery refers to a prefecture that is under the administration of the Republic of Misai. South Misainese prefectures are further divided into 16 prefectures and four special prefectures. Prefectures are further divided into counties and two cities. | |||
{{South Misai Province Box|map=show}} | |||
==Government and Politics== | |||
===Government=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; float:right; margin-right:9px; margin-left:2px;" | |||
|- | |||
| style="text-align:left;"| [[File:Ai-Obama.png|220px]] || style="text-align:left;" | [[File:Emperor Akihito cropped 1 Barack Obama Emperor Akihito and Empress Michiko 20140424 1.jpg|205px]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="text-align:center;"|[[Ai Obama]]<br /><small>[[President of the Republic of Misai|President]] since 2016</small> | |||
| style="text-align:center;"|[[Kenobe Takamaki]]<br /><small>[[Premier of the Republic of Misai|Premier]] since 2007</small> | |||
|} | |||
The Republic of Misai is a {{wp|unitarism|unitary}} {{wp|constitutionalism|constitutional}} {{wp|republic}} with the president as the head of state and the premier as head of government. Highest political power in South Misai resides in the democratically-elected {{wp|unicameral}} {{wp|legislature}}, the [[Grand Diet of the Republic of Misai|Grand Diet]] ({{wp|japanese language|Hanasenese}}: 大議会, ''Dai Gikai''). | |||
The President of the Republic of Misai ({{wp|Japanese language|Hanasenese}}: 美西共和国大統領, ''Misai Kyōwakoku Daitōryō'') is largely a symbolic role but it still retains some appointive powers as well as power over foreign policy however, even this is shared with the [[Misai Council]]. The presidency is officially defined as the head of state of the Republic of Misai as well as the head of the Republican Armed Forces in the constitution. Over most of its history, South Misai had a {{wp|semi-presidential system}} but in recent decades the powers of the president have been diminished significantly. The current sitting president of South Misai, [[Ai Obama]] is the first democratically-elected disabled head of state as she has cerebral palsy and is paralysed from her neck down but retains the use of her right hand. | |||
Executive power in South Misai primarily resides in the [[Premier of the Republic of Misai|Premier]] ({{wp|Japanese language|Hanasenese}}: 美西共和国の首相, ''Misai Kyōwakoku no Shushō'') who wields it with the consent of the [[Grand Diet of the Republic of Misai|Grand Diet]]. The premier is appointed by the [[Grand Diet of the Republic of Misai|Grand Diet]] to a term of 5 years that is indefinetly renewable. The premier is usually the individual who is most trusted by the majority of the representatives of the [[Grand Diet of the Republic of Misai|Grand Diet]]. This means that the premier is most often the head of the largest political party or multi-party coalition. It is up to the Premier to assemble a cabinet whose members are appointed by the president with the premier's recomendation. | |||
Judicial power in South Misai resides in the Misai Supreme Court ({{wp|Japanese language|Hanasenese}}: 美西最高裁判所, ''Misai Saikōsaibansho''), a supranational organ that fills the role of highest judicial authority in borth [[North Misai|North]] and South Misai. Unlike in some other countries, the Misai Supreme Court is an apolitical institution. A member of the Supreme Administrative Court can serve their an indefinite term, yet most members choose to retire after a ''de facto'' term of 20 years. Its membership is formed from a total of 12 judges refered to as High Justices that are equally appointed by each of the two countries. | |||
Legislative power is vested within the [[Grand Diet of the Republic of Misai|Grand Diet]] ({{wp|Japanese language|Hanasenese}}: 大議会, ''Dai Gikai'') that is defined in the constitution as being the wielder of supreme legislative authority within the Republic of Misai. Representatives to the 200-seat Grand Diet are elected every 8 years according to the {{wp|D'Hondt method}}. The Grand Diet can draft laws, alter existing laws and the constitution, dismiss the premier or their cabinet as well as override presidential vetoes. The Grand Diet is not subject to judicial review instead, a committee within the Grand Diet evaluates the constitutionality of a given proposal. The Grand Diet can be dismissed by the president with the recommendation of the premier, however, this has never been used since 1988. Before 1988 the Grand Diet was dismissed numerous times when the act was the sole prerogative of the president. | |||
===Foreign Relations=== | |||
Latest revision as of 06:58, 23 April 2020
Republic of Misai 美西共和国 Misai Kyōwakoku (Hananese) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "人類の仕事に貢献する" Jinrui no Shigoto ni Kōken Suru "Contribute to the Work of Mankind" | |
| Anthem: "Without the Revolution, There Would Be No New Misai" "革命がなければ、新しい美西はないでしょう" Kakumei ga Nakereba, Atarashī Misai Hana Ideshou | |
 | |
| Capital | |
| Official languages | Hananese |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary Constitutional Republic |
| Ai Obama | |
• Premier | Kenobe Takamaki |
| Legislature | Grand Diet |
| Establishment | |
• Hananese Colonisation | 1122 |
| 1437 | |
• Southern Court Period | 1682 |
| 1792 | |
| 1919 | |
| 1920 | |
| 1944 | |
| Population | |
• 2016 census | 24 748 331 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | 737$ billion |
• Per capita | $29 791 |
| Gini (2018) | medium |
| HDI (2018) | very high |
| Currency | 美西銅, Misai Dō (MSĐ (MSD)) |
| Date format | cc-d/m-yy |
| Driving side | left |
| ISO 3166 code | SM |
| Internet TLD | .sm |
South Misai (Hananese: 南美西, Minamimisai) officially the Republic of Misai (Hananese: 美西共和国, Misai Kyōwakoku) is a nation in the Sea of Savai occupying the southern portion of the Misai Archipelago. It borders North Misai to the north and Savai to the south. Misai also shares a maritime border with Oshima. South Misai is a democratic constitutional republic. The capital city and the largest city of South Misai is Ebiwan. Despite only controling the southern portion of the Misai Archipelago, the Republic of Misai claims to be the legitimate and rightful government of the entirety of the archipelago.
The Misai archipelago was inhabited by various people groups prior to the arrival of the Hananese settlers in 1122. Hananese colonisation led to the creation of highly autonomous fiefdoms led by local daimyos. Eventually Misai would declare itself the indipendent Kingdom of Misai in 1437; however, disagreements between the northern and southern daimyos on the main island would lead to the division of the kingdom into north and south. It is largely during this period that Southern Misai came under Midrasian influence. The kingdom would be reunified in 1792 in the Rokuda Unification but would continue to be subjected to Asuran influence in the region.
Discontent towards daimyo rule and an increased public will for a democratic system led to the Ebiwan Revolution where the Republic of Misai was proclaimed which plunged Misai into a civil war. Fighting in the war quickly drew into a stalemate on the main island while the Republican Armed Forces consolidated its control over the southern islands. Due to the stalemate of the war, an armstice was called in 1924. Tensions between the north and south slowly declined as public sentiment in both countries turned against the hostile relations between north and south. This culminated in the creation of the Misai Council in 1944 where both sides began the process of deep integration. Today North and South Misai are two of the most well-inegrated countries in the world to the point that many view reunification as redundant.
Today South Misai is a part of various international organizations such as the Misai Council. South Misai is ranked very high in the Human Development Index and has one of the world's highest life expectancies at 83.6 years. South Misai is a developped country with a high-income economy. It is also a high preformer in a myriad of international listings of democracy, civil liberties and press freedoms. South Misainese citizens also receive free education, universal healthcare and some of the longest paid maternity leave in the world. Despite all this, South Misai is one of the most regionally unequal nations as the main island accounts for over 80% of South Misai's economy even though it is home to only around 67% of the population.
Etymology
The Hananese name for Misai is 美西. The characters for beaty (美, bi) and west (西, nishi) are used for their compound reading of Misai. The meaning behind the characters used for Misai is therefore beautiful west referring to its location west of the island of Ōshima. The actual meaning behind Misai is unkown but some linguistists hypothise that it is a Hananised version of the Soifun name for the lower islands of the archipelago Isai'i.
History
Precolonial History
Little remains of the aboriginal people groups in the northern portion of the Misai archipelago. Human habitation has been estimated to have been present on the archipelago since the Stone Age. Human remains that were thought to have originated from the Paleolithic Era were found in Inishiro in the late 1800s but were lost during shipment before this could be proven.
Due to the isolated geography of the southern islands, some native groups, the largest of which are the Soifun peoples, have survived in relatively isolated communities. The various aboriginal groups of southern Misai have been linked through linguistic and biological evidence to the larger immigration of seafaring peoples from Southeast Catai to Savai. According to Soifun oral tradition and history, fishermen and traders sailed up to the main island of Misai as well as Oshima on a regular basis.
Hananese Colonisation
The Misai archipelago was known by Hananese traders and fishermen for about two hundred years prior to any actual settlement. The first Hananese settlers arrived on the main island in 1122. The period between 1122 and the early 1200s is refered to as the first phase of colonisation. According to early literary sources, initial contact between the natives and the Hananese was peaceful, yet with an increase in the number of arriving settlers, ties between the two groups quickly soured. Aboriginal groups faced sharp decline due to disease and conflict with the ever-increasing number of settlers. These initial settlers were primarily fishermen and traders looking for economic opportunity on the islands. Due to the hostile ties bewteen the settlers and natives, the population of colonists had to arm itself alongside forming small groups of volunteer mercenaries.
The second phase of colonisation is considered to have taken place bewteen the early 1200s and 1390s. It is characterised by an increase in inland settlement and a considerably rapid establishment of farming communities on Misai. Accompanying this increase in the population of settlers on the island was the complete importation of the Hananese social order to the islands. Several minor nobles were granted the high status of daimyo in exchange for moving to these new territories and governing them on behalf of the emperor back on the mainland. The presence of these newly-appointed daimyo and the rule of law they brought with them displeased many early traders and fishermen who were no longer able to conduct business freely. The daimyo also brought with them significant numbers of retainers that eventually replaced the makeshift mercenary groups formed by early settlers. During this second phase of colonisation, mentions of native peoples on the main island cease which is credited to the creation of more professional warrior class.
The third and final phase of colonisation is considered to have taken place from the 1390s to the late 1500s. It is characterised by the settlement of the southern islands by Misainese settlers from the main island itself unlike the two prior phases where settlers largely came from the mainland. Also unlike the two prior phases, the third phase was largely started by the Daimyo on the main island wishing to increase their holdings size considerably in part to be able to afford yearly tributes to the mainland. Due to the more isolated geography of the southern islands, native groups were able to presist in the southern islands islands to the modern-day. Despite this, diseases brought by interactions with the main island greatly decreased their population. Due to limitations to the what jobs they could work and which areas they could live in, most natives in Misainese society had to work as low-skilled contractual labour most often on farms or as house laborers. Natives were treated as the lowest class in society. Eventually settlers and natives began to intermarry largely due to the fact that settlers to the southern islands were overwhelmingly male. This racially mixed class called the Jokujin was considered racially inferior to Hananese people but became a significant portion of the population in the southern islands.
Early Kingdom Period
Because of the distance between Misai and the mainland, the daimyo of Misai were able to rule relatively autonomously with actual mainland rule In 1437 the Daimyo X, the most influential daimyo of Misai, declared himself the Great Daimyo of the
Southern Daimyo Period
Rokuda Unification
Ebiwan Revolution
Misainese Rapprochement
Territorial Timeline
Geography
Climate
The South Misainese climate is largely divided into two: a tropical maritime climate which is the dominant climate type in South Misai and a temperate climate on the northern portion of the main island. Typhoons are common in South Misai reaching their peak in July, August and September. The northern temperate region experiences wider temperature changes in its climate than their southern tropical counterparts where such changes in temperature are noticeably lesser.
Regions
Misai is divided into five regions: Southern Misai, Yoshikageshima, Chūkanshima, Īsai and Equatorial Savai. Regions represent gradual cultural, dialectical and economic differences better than prefectures. They serve a supporting role facilitating cooperation between prefectures and the federal government. Each region has a separate regional assembly where prefectural governments send representatives with the exeption of Yoshikageshima the prefectural assembly of which fills the role of regional assembly as well because of its small size. Due to the high degree of autonomy prefectures and municipalities enjoy in South Misai, regional governments are mostly in charge of coordinating healthcare services as well as monitoring agricultural and environmental policies and laws.
Regional differences in South Misai are extremely stark. Two-thirds of the nation's population and 80% of its economy are represented by only one of there regions: Southern Misai. Historically the treatment of the soutern islands has been mired in colonialism where their econmies were heavily based on the extraction of labour and resources to the main island. The southern islands are also more ethnically diverse than their northern counterpart with both native and immigrant communities making up a substantial portion of the populations. In recent years, the central government of South Misai has attempted several economic stimulus plans to revitalize the southern economy. These policies have worked in most regions except for Equatorial Savai where economic problems continue.
| Region | Hananese Name | Population | GDP per capita | GDP (Nominal) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern Misai | 南美西 (Minami Misai) |
16 547 665 | $40 027 | $662 billion | |
| Yoshikageshima | 吉影島 | 656 053 | $22 355 | $14 billion | |
| Chūkanshima | 中間島 | 3 624 213 | $10 021 | $36 billion | |
| Īsai | イーサイ | 1 140 199 | $12 543 | $14 billion | |
| Equatorial Savai | 赤道サヴアイ (Sekidō Savai) |
2 780 201 | $3 957 | $11 billion |
Administrative Divisions
South Misai is composed from 20 free commanderies (Hananese:無料郡, Muryō-gun). The term free commandery refers to a prefecture that is under the administration of the Republic of Misai. South Misainese prefectures are further divided into 16 prefectures and four special prefectures. Prefectures are further divided into counties and two cities.
| Republic of Misai | |||||
| Free Commandery (無料郡, Muryō-gun) | North Misai | ||||
| Special Prefecture (特別府, Tokubetsu-fu) |
Prefectures (府, fu) | Not administered | |||
| Counties | Cities | ||||
| Indigenous District | District | Townships | Urban District | ||
| Villages | |||||
| Neighborhoods | |||||
Government and Politics
Government
 |

|
| Ai Obama President since 2016 |
Kenobe Takamaki Premier since 2007 |
The Republic of Misai is a unitary constitutional republic with the president as the head of state and the premier as head of government. Highest political power in South Misai resides in the democratically-elected unicameral legislature, the Grand Diet (Hanasenese: 大議会, Dai Gikai).
The President of the Republic of Misai (Hanasenese: 美西共和国大統領, Misai Kyōwakoku Daitōryō) is largely a symbolic role but it still retains some appointive powers as well as power over foreign policy however, even this is shared with the Misai Council. The presidency is officially defined as the head of state of the Republic of Misai as well as the head of the Republican Armed Forces in the constitution. Over most of its history, South Misai had a semi-presidential system but in recent decades the powers of the president have been diminished significantly. The current sitting president of South Misai, Ai Obama is the first democratically-elected disabled head of state as she has cerebral palsy and is paralysed from her neck down but retains the use of her right hand.
Executive power in South Misai primarily resides in the Premier (Hanasenese: 美西共和国の首相, Misai Kyōwakoku no Shushō) who wields it with the consent of the Grand Diet. The premier is appointed by the Grand Diet to a term of 5 years that is indefinetly renewable. The premier is usually the individual who is most trusted by the majority of the representatives of the Grand Diet. This means that the premier is most often the head of the largest political party or multi-party coalition. It is up to the Premier to assemble a cabinet whose members are appointed by the president with the premier's recomendation.
Judicial power in South Misai resides in the Misai Supreme Court (Hanasenese: 美西最高裁判所, Misai Saikōsaibansho), a supranational organ that fills the role of highest judicial authority in borth North and South Misai. Unlike in some other countries, the Misai Supreme Court is an apolitical institution. A member of the Supreme Administrative Court can serve their an indefinite term, yet most members choose to retire after a de facto term of 20 years. Its membership is formed from a total of 12 judges refered to as High Justices that are equally appointed by each of the two countries.
Legislative power is vested within the Grand Diet (Hanasenese: 大議会, Dai Gikai) that is defined in the constitution as being the wielder of supreme legislative authority within the Republic of Misai. Representatives to the 200-seat Grand Diet are elected every 8 years according to the D'Hondt method. The Grand Diet can draft laws, alter existing laws and the constitution, dismiss the premier or their cabinet as well as override presidential vetoes. The Grand Diet is not subject to judicial review instead, a committee within the Grand Diet evaluates the constitutionality of a given proposal. The Grand Diet can be dismissed by the president with the recommendation of the premier, however, this has never been used since 1988. Before 1988 the Grand Diet was dismissed numerous times when the act was the sole prerogative of the president.