Transition from Jiao to Toki: Difference between revisions
m (→Three emperors) |
m (→Overview) |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
{{nowrap|[[Togoti Khaganate]]}} | {{nowrap|[[Togoti Khaganate]]}} | ||
| commander1 = [[Toki Sinzou]]<br> | | commander1 = [[Toki Sinzou]]<br> | ||
Nagao Yosioki<br> | [[Toki Banrei]]<br> | ||
Chen Haiping<br> | [[Nagao Yosioki]]<br> | ||
Zhang Yuandao | [[Toki Yosinari]]<br> | ||
[[Toki Hisakane]]<br> | |||
Nagao Sigesane<br> | |||
[[Yamana Sigekatu]]<br> | |||
[[Ogawa Yorihiko]]<br> | |||
[[Ogawa Arikazu]]<br> | |||
[[Amago Naokuni]]<br> | |||
[[Saitou Tikanori]]<br> | |||
[[Mizuno Youhiko]]<br> | |||
[[Munakata Sadaharu]]<br> | |||
Itibasi Tadakatu<br> | |||
[[Asukai Yukitoki]]<br> | |||
[[Chen Haiping]]<br> | |||
[[Zhang Yuandao ]]<br> | |||
[[Dong Liqin]]<br> | |||
Lei Boqin<br> | |||
[[Lei Weizhe]]<br> | |||
Zheng Bolin<br> | |||
Xue Deming<br> | |||
Lai Zixin<br> | |||
Huang Xia | |||
| commander2 = [[Taichu Emperor]]<br> | | commander2 = [[Taichu Emperor]]<br> | ||
[[Taian Emperor]] (Liu Yuanjun)<br> | [[Taian Emperor]] (Liu Yuanjun)<br> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 78: | ||
[[Wei Nianzu]]<br> | [[Wei Nianzu]]<br> | ||
[[Yuan Yingjie]]<br> | [[Yuan Yingjie]]<br> | ||
[[Tao Jinjing]]<br> | |||
[[Dong Fenfang]]<br> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Intharatcha]]<br> | [[Intharatcha]]<br> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 87: | ||
[[Chuthamani]]<br> | [[Chuthamani]]<br> | ||
[[Vĩnh Nhật Tấn]]<br> | [[Vĩnh Nhật Tấn]]<br> | ||
[[Tanaka Tunemasa]]<br> | |||
[[Taizong Emperor]]<br> | [[Taizong Emperor]]<br> | ||
[[Liu Meilin, Prince of Chen]]<br> | [[Liu Meilin, Prince of Chen]]<br> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 141: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''transition from Jiao to Toki''', '''Jiao–Toki transition''', or the '''Toki unification of Xiaodong''' saw the transition between two major [[Xiaodongese dynasties]] from 1659 to 1694. After the [[Red Orchid Rebellion]] toppled the [[Jiao dynasty]], a power vacuum emerged in [[Xiaodong]]. The west saw the [[Red Orchid Rebellion|Red Orchid rebels]] divided between the [[Zhao dynasty|Zhao]] and [[Wei dynasty|Wei]] dynasties, and other minor factions, while the [[Togoti Khaganate]] invaded from the northern borders. In the east the [[Eastern Jiao|Jiao]] regrouped in [[Rongzhou]], but were surprised by an invasion by the [[Khaunban Empire]] and became divided between multiple emperors and factions. [[Toki Sinzou]], originally a Jiao retainer, organised an ambitious campaign led by other Senrian mercenaries, and declared the [[Toki dynasty]] in 1664. This period ended with the rise of the Toki, the fall of the Jiao, collapse of the Khaunban and Togoti empires, and suppression of other minor factions in the Toki's unification of Xiaodong. | The '''transition from Jiao to Toki''', '''Jiao–Toki transition''', or the '''Toki unification of Xiaodong''' saw the transition between two major [[Xiaodongese dynasties]] from 1659 to 1694. After the [[Red Orchid Rebellion]] toppled the [[Jiao dynasty]], a power vacuum emerged in [[Xiaodong]]. The west saw the [[Red Orchid Rebellion|Red Orchid rebels]] divided between the [[Zhao dynasty|Zhao]] and [[Wei dynasty|Wei]] dynasties, and other minor factions, while the [[Togoti Khaganate]] invaded from the northern borders. In the east the [[Eastern Jiao|Jiao]] regrouped in [[Rongzhou]], but were surprised by an invasion by the [[Khaunban Empire]] and became divided between multiple emperors and factions. [[Toki Sinzou]], originally a Jiao retainer, organised an ambitious campaign led by other [[Senria|Senrian]] mercenaries, and declared the [[Toki dynasty]] in 1664. This period ended with the rise of the Toki, the fall of the Jiao, collapse of the Khaunban and Togoti empires, and suppression of other minor factions in the Toki's unification of Xiaodong. | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The transition from the Jiao dynasty to the Toki dynasty saw a decades-long conflict involving: | |||
# the [[Toki dynasty]], established by the [[Senria|Senrian]] [[Tankenhei|tankenhei]] [[Toki Sinzou]] | |||
# the [[Jiao dynasty]], the incumbent dynasty ruled by the Liu clan. | |||
# the [[Khaunban Empire]], an expansionist empire in [[Southeast Coius]] led by [[Intharatcha]] | |||
# the [[Togoti Khaganate]], a {{wp|Nomadic empire|steppe empire}} also invading the [[Ansan Empire]] | |||
# various other polities, notably the short-lived dynasties of the Red Orchid rebels, the [[Wei dynasty]] led by [[Duan Siliang]], and the [[Zhao dynasty]], led by [[Yang Baochi]], as well as the {{wp|Hmong people|Bai}} [[Kayin Confederacy]], and the {{wp|Burmese people|Chanwan}} [[Kingdom of Myiang]] | |||
The Jiao dynasty had entered a decline by the 17th century, with inattentive emperors ceding authority to palace eunuchs, while military authority was largely usurped by ambitious princes of the imperial clan. Famines, floods, and banditry plagued the countryside while corruption, lavish spending, and widespread tax and census evasion crippled the finances of the imperial court. The [[Changzhi Emperor]] was an ambitious and attentive emperor in his youth, though by his later reign had come under the influence of a powerful faction led by the eunuch [[Wen Meifen]]. Wen encouraged the emperor to divert attention from these troubles by achieving a victory against the Senrian empire by re-conquering [[Tousuu]]. Thus in 1651 the [[Soukou War]] began after the local daimyous refused to submit. While Jiao forces achieved some successes, with the aid of defectors such as Toki Sinzou, they were ultimately forced to abandon the war in 1655 due to the emergence of the Red Orchid rebellion. | |||
-Red Orchid stuff here-. In 1659 the rebels, led by Duan Siliang, conquered Baiqiao. The Changzhi Emperor had refused to flee, and so he along with many other members of the Liu clan were captured, and subsequently put to death. Duan Siliang declared the Wei dynasty as the Mingqi Emperor, while his rival Yang Baochi declared his own Zhao dynasty as the Ruizong Emperor. | |||
While western Xiaodong, with the exception of [[Gaoming]], was under the control of rebels, the east largely remained under Jiao control. The Liu princes regrouped in Rongzhuo, and chose Liu Junjie, the fourth son of the Changzhi Emperor, to become the [[Taizong Emperor]]. A sudden invasion by the Khaunban king Intharatcha saw Rongzhuo fall, with the Liu princes becoming divided between allegiance to the Khaunban controlled [[Northern Jiao|Taizong Emperor]], and Liu Zihao, the Prince of Liang, who declared himself the [[Taichu Emperor]]. Toki Sinzou, in exile after the Soukou war, had been hired by the Jiao, along with other Senrian exiles and ''[[Tankenhei|tankenhei]]'' such as Nagao Yosioki, to hold frontier regions, such as [[Shenkong]] which he made his base. | |||
While the Jiao warred amongst themselves, Sinzou and Yosioki undertook ambitious campaigns against the Zhao and Wei dynasties respectively. The Zhao and Wei had become exhausted due to incessant warfare between themselves and the invading [[Togoti Khagante]]. By 1664 Chaozhou and Baiqiao, capitals of the Zhao and Wei, had been recaptured. The [[Shanju Meeting]] saw the ''tankenhei'' back Toki Sinzou as he declared himself emperor of a new Toki dynasty. Sinzou first consolidated his position by continuing his advances against the Zhao and Wei, while increasing his forces via Jiao and Red orchid defectors. In 1667 he moved against the Northern Jiao while Intharatcha was sorting out revolts in the east, and [[Transition from Jiao to Toki#Capture of Rongzhuo (1667)|captured Rongzhuo]], forcing the Taizong Emperor to abdicate in his favour. The [[Transition from Jiao to Toki#Battle of Yuan'an (1668)|Battle of Yuan'an]] in 1668 crippled the Khaunban army and secured the Toki's conquest of the Northern Jiao. The Eastern Jiao would hold out until 1675, when Liu Yuanjun, the Prince of Wu and self-proclaimed Taian Emperor, was captured after the siege of Yinbao and executed. | |||
The Toki dynasty had control over most of present-day Xiaodong by 1680, having defeated the Zhao and Wei remnants, and destroyed the last Eastern Jiao armies. They would be plagued by rebellions, particularly in the west, until the start of the 18th century. A punitive expedition against the Khaunban empire in 1682 was successful, killing king [[Borommarachathirat]] and burning the capital of Khaunban to the ground. The Toki's conquest of Xiaodong was completed in 1694, under Sinzou's successor [[Toki Banrei]], when the last [[Western Jiao|Jiao remnant]] in Gaoming was captured, and Liu Wenyan, Prince of Cao, and self-proclaimed [[Taiwu Emperor]], fled to Senria, where he would die in 1701. | |||
==Situation of the late Jiao dynasty== | |||
==Red Orchid Rebellion== | ==Red Orchid Rebellion== | ||
== | ==Eastern Jiao== | ||
===Khaunban invasion=== | ===Khaunban invasion=== | ||
[[File:Naresuan_life_-_Wat_Suwan_Dararam_-_Section_13_(2142_BE).jpg|thumb|left|200px|A contemporary Khaunban mural painting of [[Intharatcha]] entering [[Rongzhou]]]] | |||
The Jiao fixture on their troubles in the west meant that their eastern border with the belligirent Khaunban Empire had become effectively defenceless. Garrisons and commanders still loyal had been pilfered to prepare for expeditions to retake Baiqiao. A letter from Intharatcha to the Taizong Emperor also further lowered defences, as he professed his loyalty as a {{wp|Tributary system of China|subject}} and offered his aid, which was declined. Reports of attacks on Zhaili were dismissed as being the work of bandits, and the surrender of [[Juancheng]] by its commander Zou Qiuyue went unnoticed in the Imperial Court, which had greatly suffered from many officials being left behind in the flight from Baiqiao. | |||
Intharatcha had designs on expanding into Xiaodong as early as 1655, when he wrote to the [[Senria|Senrian]] [[Monarchy of Senria|Emperor]] [[Ninpei of Senria|Ninpei]] to encourage a joint invasion as a retaliation for the [[Soukou War]]. While Ninpei dismissed the notion, as he was organizing an effort to restore imperial power within Senria, Intharatcha was assured that the Senrians would take no action to hinder his plans. The implosion of the Jiao dynasty after the Red Orchids took Baiqiao in 1659 provided him the perfect opportunity to launch and invasion disguised as rendering aid to an ailing dynasty. | |||
By the time the Imperial Court was aware of Intharatcha's intentions, the Grand Army was only several days away from Rongzhou. The Taizong Emperor refused to abandon the city, believing that it would doom the Jiao's efforts to reconquer the west, and that Intharatcha was an ally. Several princes, led by [[Taichu Emperor|Liu Zihao, Prince of Liang]] disagreed with this policy, and fled the city. In the confusion many soldiers began looting and burning parts of the city, and several notable commanders such as [[Tao Jinjing]] and [[Dong Fenfang]] were killed attempting to end the riots. The Imperial Court and the emperor fled the city, and were found on a nearby hill by Intharatcha's advance guard, who took them to him. | |||
Intharatcha and his army entered the largely abandoned city with no resistance. Intharatcha declared his intention to restore the Jiao, and was invested by the Taizong Emperor as the 'Great King of the East' (偉大东王 ''Wěidà dōng wáng''). [[Liu Meilin, Prince of Chen]] was the only prince to accept Intharatcha's coup, with the Prince of Liang declaring himself the [[Taichu Emperor]], with his base in [[Zhoujia]]. The [[Jiao dynasty|Eastern Jiao]] became firmly split, although the lines between the Taizong and Taichu factions would become blurred, particularly after 1667. | |||
===Four emperors=== | ===Four emperors=== | ||
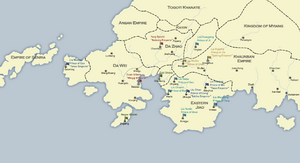
[[File:JiaotoToki.png|thumb|right|The situation in 1661]] | |||
==Jiao-Toki alliance== | ==Jiao-Toki alliance== | ||
| Line 145: | Line 198: | ||
==Khaunban expansion== | ==Khaunban expansion== | ||
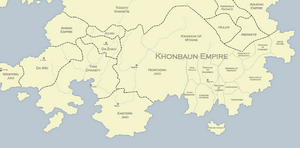
[[File:KhonbaunEmpire.png|thumb|left|The Khaunban Empire at its height, in 1665]] | |||
===Intharatcha's Grand Army=== | ===Intharatcha's Grand Army=== | ||
[[File:YamadaNagamasa.jpg|thumb|150px|right|The [[Senria|Senrian]] | [[File:YamadaNagamasa.jpg|thumb|150px|right|The [[Senria|Senrian]] ''[[Tankenhei|tankenhei]]'' [[Tanaka Tunemasa]] became a trusted general and advisor of [[Intharatcha]]]] | ||
The creation of the Khaunban Empire had primarily been through military means, and lacking longevity or legitimacy outside of its constituent rulers' personal ties to Intharatcha, required a strong military to remain consolidated. At the start of Intharatcha's reign his army was largely composed of Kasi peasant levies, supported by cavalry, largely from the nobility, and a small elephant corps. It was with this army that Intharatcha was able to overthrow [[Sippom|Sippommese]] rule of Khaunban and establish Khaunban as the new power in the [[Lueng|Lueng river valley]]. This small nucleus would form the basis of the later ' Grand Army' (''kongthap thiyingyai'') | The creation of the Khaunban Empire had primarily been through military means, and lacking longevity or legitimacy outside of its constituent rulers' personal ties to Intharatcha, required a strong military to remain consolidated. At the start of Intharatcha's reign his army was largely composed of Kasi peasant levies, supported by cavalry, largely from the nobility, and a small elephant corps. It was with this army that Intharatcha was able to overthrow [[Sippom|Sippommese]] rule of Khaunban and establish Khaunban as the new power in the [[Lueng|Lueng river valley]]. This small nucleus would form the basis of the later ' Grand Army' (''kongthap thiyingyai'') | ||
| Line 153: | Line 207: | ||
As the empire expanded so did the diversity within the army. The majority of the levies remained ethnically {{wp|Thai people|Kasi}}, but they were joined by {{wp|Vietnamese people|Namkwonese}}, {{wp|Khmer people|Svai}}, {{wp|Karen people|Kyin}}, and {{wp|Mon people|Niah}} conscripts, largely from {{wp|vassal kingdom|subject kingdoms}}. In 1557 Intharatcha divided the levies between the ''thammada'' (basic, or general) troops, who were raised for a specific campaign for short-term cyclical periods, and the ''phiset'' (extraordinary, special) soldiers, who constituted one of the first standing professional armies in Kuthine history. The phiset soldiers were entitled to a monthly salary, were given a uniform, underwent three years of training, and were expected to serve a minimum of 15 years. Villages which provided a certain ammount of phiset soldiers were excluded from the thammada registry. | As the empire expanded so did the diversity within the army. The majority of the levies remained ethnically {{wp|Thai people|Kasi}}, but they were joined by {{wp|Vietnamese people|Namkwonese}}, {{wp|Khmer people|Svai}}, {{wp|Karen people|Kyin}}, and {{wp|Mon people|Niah}} conscripts, largely from {{wp|vassal kingdom|subject kingdoms}}. In 1557 Intharatcha divided the levies between the ''thammada'' (basic, or general) troops, who were raised for a specific campaign for short-term cyclical periods, and the ''phiset'' (extraordinary, special) soldiers, who constituted one of the first standing professional armies in Kuthine history. The phiset soldiers were entitled to a monthly salary, were given a uniform, underwent three years of training, and were expected to serve a minimum of 15 years. Villages which provided a certain ammount of phiset soldiers were excluded from the thammada registry. | ||
While the infantry levies formed the core of the army, the various special branches proved key for Intharatcha's continuing successes. These were the the elephantry, cavalry, artillery, and navy. The elephantry grew substantially with the army, becoming a major part of Intharatcha's war strategy despite never being more than one percent of his total force. The cavalry diversified into several branches, from light [[Kingdom of Myiang|Myiang]] skirmishers to heavy {{wp|Mongol people|Merket}} lancers. For artillery and muskets the Grand Army was largely reliant upon [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] and [[Estmere|Estmerish]] merchants and mercenaries for cannon and officers respectively. Other notable mercenary regiments included Senrian veterans from the Soukou War, led by [[Tanaka | While the infantry levies formed the core of the army, the various special branches proved key for Intharatcha's continuing successes. These were the the elephantry, cavalry, artillery, and navy. The elephantry grew substantially with the army, becoming a major part of Intharatcha's war strategy despite never being more than one percent of his total force. The cavalry diversified into several branches, from light [[Kingdom of Myiang|Myiang]] skirmishers to heavy {{wp|Mongol people|Merket}} lancers. For artillery and muskets the Grand Army was largely reliant upon [[Gaullica|Gaullican]] and [[Estmere|Estmerish]] merchants and mercenaries for cannon and officers respectively. Other notable mercenary regiments included Senrian veterans from the Soukou War, led by [[Tanaka Tunemasa]], and cannonneers from the [[Aguda Empire]]. | ||
In order to keep together a vast and ethnically diverse army, Intharatcha had to rely upon a competent officer corps. In his initial reign he was forced to rely upon the aristocracy and gentry for leadership, but as the empire grew he established a permanent ''Kalahom'' Department to oversee the training of officers and creation of strategy. Three of his five 'Gods of War', his most famed generals, [[Kriang Krai]], [[Natthapong]], and [[Chuthamani]], came from peasant backgrounds and were able to rise on merit. The officer corp was equally as diverse as the army, with generals such as [[Vĩnh Nhật Tấn]], [[Tanaka | In order to keep together a vast and ethnically diverse army, Intharatcha had to rely upon a competent officer corps. In his initial reign he was forced to rely upon the aristocracy and gentry for leadership, but as the empire grew he established a permanent ''Kalahom'' Department to oversee the training of officers and creation of strategy. Three of his five 'Gods of War', his most famed generals, [[Kriang Krai]], [[Natthapong]], and [[Chuthamani]], came from peasant backgrounds and were able to rise on merit. The officer corp was equally as diverse as the army, with generals such as [[Vĩnh Nhật Tấn]], [[Tanaka Tunemasa]], [[Binnyadala]], and [[Tian Thassapak]] achieving high rank and status. | ||
During Intharatcha's campaigns in Xiaodong, his army expanded considerably both from the recruitment of local {{wp|Han people|Xiaodongese}}, and the addition of irregular conscripted bandit and rebel militias, as well as allied [[Jiao dynasty|Jiao]] armies. In contrast to his earlier policies, these units were rarely mixed with the rest of the Grand Army and were often under the command of local leaders or allied Jiao generals. This was likely due to Intharatcha's lack of trust in the loyalty of these troops, many of whom had served under various dynasties and rebel leaders in quick succession. | During Intharatcha's campaigns in Xiaodong, his army expanded considerably both from the recruitment of local {{wp|Han people|Xiaodongese}}, and the addition of irregular conscripted bandit and rebel militias, as well as allied [[Jiao dynasty|Jiao]] armies. In contrast to his earlier policies, these units were rarely mixed with the rest of the Grand Army and were often under the command of local leaders or allied Jiao generals. This was likely due to Intharatcha's lack of trust in the loyalty of these troops, many of whom had served under various dynasties and rebel leaders in quick succession. | ||
| Line 165: | Line 219: | ||
Image:Tượng_binh.jpg|An elephant and accompanying crew from {{wp|Vietnam|Namkwon}} | Image:Tượng_binh.jpg|An elephant and accompanying crew from {{wp|Vietnam|Namkwon}} | ||
Image:Wat_Suwan_Dararam_wihan_-_inside_-_2017-02-13_(030).jpg|Mural paintings of Kasi infantry during Intharactha's reign | Image:Wat_Suwan_Dararam_wihan_-_inside_-_2017-02-13_(030).jpg|Mural paintings of Kasi infantry during Intharactha's reign | ||
Image:SenrianMercenaries.png|Contemporary painting of the mercenary army of [[Senria|Senrian]] | Image:SenrianMercenaries.png|Contemporary painting of the mercenary army of [[Senria|Senrian]] ''[[Tankenhei|tankenhei]]'' Tanaka Tunemasa | ||
Image:1024px-Madrid_canons_indiens.png|[[Aguda Empire|Agudan]] double barrelled {{wp|cetbang}} on a carriage | Image:1024px-Madrid_canons_indiens.png|[[Aguda Empire|Agudan]] double barrelled {{wp|cetbang}} on a carriage | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 176: | Line 230: | ||
===Capture of Rongzhuo (1667)=== | ===Capture of Rongzhuo (1667)=== | ||
{{main|Siege of Rongzhuo}} | |||
[[File:Burning_Osaka_Castle.jpg|thumb|right|200px|The Toki army sacks the city of Rongzhou.]] | |||
Intharatcha's return eastwards to deal with domestic rebellions did not go unnoticed by Toki Sinzou or the Jiao princes. The Prince of Wu launched several attacks, aiming to take Wudan, but was ultimately unsuccessful due to the intervention by the Prince of Chen and Kriang Krai. This, and raids by the Prince of Ji, left the Prince of Chen and Kriang Krai preoccupied, and Hongyan open. Sinzou despatched a force under Ogawa Yorihiko to Wudan in a feint attack, while he took the bulk of his army to Hongyan. Hongyan's governor, Cui Changpu, held a grudge against the Prince of Chen, and defected, surrendering the city. | |||
The path to Rongzhuo became open, and Sinzou decided upon taking it before Wudan. Capturing the Taizong Emperor would give him greater legitimacy, and possessing Rongzhou and Baiqiao would mean possession of nearly all the Jiao institutions and officials. An army under Mizuno Youhiko was sent to tie down Kriang Krai, but the {{wp|Thai people|Kasi}} general was able to return to Rongzhou. The Prince of Chen remained near Wudan with orders to march to Rongzhou in the event of a siege, which due to threats from the Prince of Wu he was unable to comply with. | |||
Fearing an elongated siege would cause the Jiao garrison to turn on him, Kriang Krai elected to meet Sinzou in battle, where at the [[Battle of Rongzhuo]] he was beaten and forced to fall back. Sinzou put the city to siege for three months, after which, as Kriang had predicted, the Jiao garrison mutinied and defected. Kriang narrowly evaded capture by jumping into the Liaojing river, while the Taizong Emperor was captured by defecting troops and delivered to Toki Sinzou. | |||
The defection did not go smoothly, with Kriang's soldiers and elements of the garrison refusing to mutiny. This resulted in a day of sacking and looting, contrary to Sinzou's wishes, and the [[Rongzhuo massacre]], in which over 10,000 of Kriang's soldiers, as well as thousands of Xiaodongese 'collaborators' were executed, despite Sinzou's general pardon and desire to take hostages. The reason for the massacre is contentious, with Xiaodongese historians claiming it had been orchestrated by Sinzou and undertaken by Senrian mercenaries, while Kuthine and [[Euclea|Northern]] historians argue that it was largely undertaken by the defecting Jiao troops against official policy. | |||
Sinzou established Rongzhuo as his new headquarters, moving into its Forbidden City. He began the process of evicting the previous inhabitants of the inner city, replacing them with Senrians and loyal Xiaodongese, as well as some officials transferred from Baiqiao. The Taizong Emperor was forced to abdicate in favour of Sinzou, and was subsequently enfeoffed as the 'Duke of Feichang'. | |||
===Conquest of the Eastern Jiao=== | ===Conquest of the Eastern Jiao=== | ||
===Battle of Yuan'an=== | ===Battle of Yuan'an (1668)=== | ||
{{main|Battle of Yuan'an}} | {{main|Battle of Yuan'an}}[[File:Battle_of_Oroi-Jalatu.jpg|thumb|right|300px|The Battle of Yuan'an in 1669, [[Chen Haiping]] breaking into Intharatcha's supply camp.]] | ||
The Battle of Yuan'an was one of the most decisive and bloodiest battles of the Toki conquest of Xiaodong. After Toki Sinzou had taken advantage of Intharatcha's absence to capture Rongzhou, the Khaunban king intended to regain the initiative by defeating Sinzou in a pitched battle, and thus gain control over the beleagured Jiao forces. Intharatcha had at his disposal 150,000 of his Grand Army, with Natthapong, Tharathorn, and Vĩnh Nhật Tấn commanding, along with 30,000 Jiao soldiers under the [[Liu Meilin, Prince of Chen|Prince of Chen]]. An additional 80,000 under the [[Liu Weisheng, Prince of Teng|Prince of Teng]] had been promised to support him. He faced a force of 60,000 led by Chen Haiping, with [[Zhong Jianjun]] leading a relief army of 35,000, and Toki Sinzou besieging nearby Zhoujia with over 100,000 soldiers. | |||
Intharatcha had despatched Tharathorn with 60,000 men to take Batang fortress, to place pressure on Toki Sinzou and force him to relieve the siege of Zhoujia. He approached Chen's army on the 5th May, but neither side engaged the other until the 12th, with both waiting in vain for reinforcements. Unbeknownst to Intharatcha, Zhong Jianjun's army had ambushed Tharathorn's army at Batang and defeated it, killing Tharatorn in the process, while the Prince of Teng had elected to march instead to Zhoujia, before retreating to his stronghold in Yinbao. | |||
Although Intharatcha had the advantage in both quantity and quality of troops, he was indecisive over whether to give battle and was taken by surprise by Chen's attack. Initially he had the upper hand, inflicting heavy losses on Chen's forces. His decision to place the Prince of Chen on his right flank, protecting the road to his camp, proved a fatal mistake, as Chen Haiping was able to break the dispirited Jiao forces with a cavalry charge and outflank Intharatcha while pushing into his baggage train. Intharatcha's attempts to start an orderly retreat quickly turned into a rout. In the chaos Natthapong was killed, and Intharatcha narrowly escaped capture. Vĩnh Nhật Tấn was able to lead 30,000 survivors southwards, while Intharatcha led the remaining forces back to the safety of Juancheng. | |||
The battle was a turning point for the burgeoning Toki dynasty. The invincibility of Intharatcha and his Grand Army, already shaken by the capture of Rongzhou in 1667, had been shattered. His Grand Army lost two experienced commanders, most of its elephant corps and cannon, and a great deal of veterans, losses which Intharatcha was unable to replace. It also sowed further seeds of distrust between Intharatcha and the Jiao princes, as the former blamed the princes of Chen and Teng for the defeat. Most significantly, the battle secured Toki Sinzou's siege of Zhoujia, which would fall several months later. | |||
==Baiqiao and the west== | ==Baiqiao and the west== | ||
| Line 195: | Line 269: | ||
===Conquest of Gaoming=== | ===Conquest of Gaoming=== | ||
===Invasion of Khaunban=== | |||
[[File:KhaunbanBurning.png|thumb|left|250px|The city of [[Khaunban]] was completely destroyed and {{wp|Looting|looted}} by Toki forces]] | |||
==Rongzhou government== | ==Rongzhou government== | ||
===Bakuhu system and domains=== | ===Bakuhu system and domains=== | ||
[[File:Chosen_daihyoutei.jpg|thumb|right|300px|A contemporary {{wp|Japanese art|Senrian-style}} painting of the [[Rongzhuo Conference]]]] | |||
===Relations with the Senrian Emperor=== | ===Relations with the Senrian Emperor=== | ||
Relations between the Rongzhuo government and the [[Empire of Senria]] were initially deeply strained due to the fact that Sinzou had betrayed the Senrians during the [[Soukou War]] by defecting to the Jiao at the 1652 [[Battle of Tousokabe]]; following the betrayal Sinzou had been declared a traitor, and remained as such in the eyes of the imperial court in Keisi... [at some point though things are presumably gonna get more pragmatic and the relationship changes somehow] | |||
===Separate institutions=== | ===Separate institutions=== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:14, 18 December 2020
The transition from Jiao to Toki, Jiao–Toki transition, or the Toki unification of Xiaodong saw the transition between two major Xiaodongese dynasties from 1659 to 1694. After the Red Orchid Rebellion toppled the Jiao dynasty, a power vacuum emerged in Xiaodong. The west saw the Red Orchid rebels divided between the Zhao and Wei dynasties, and other minor factions, while the Togoti Khaganate invaded from the northern borders. In the east the Jiao regrouped in Rongzhou, but were surprised by an invasion by the Khaunban Empire and became divided between multiple emperors and factions. Toki Sinzou, originally a Jiao retainer, organised an ambitious campaign led by other Senrian mercenaries, and declared the Toki dynasty in 1664. This period ended with the rise of the Toki, the fall of the Jiao, collapse of the Khaunban and Togoti empires, and suppression of other minor factions in the Toki's unification of Xiaodong.
Overview
The transition from the Jiao dynasty to the Toki dynasty saw a decades-long conflict involving:
- the Toki dynasty, established by the Senrian tankenhei Toki Sinzou
- the Jiao dynasty, the incumbent dynasty ruled by the Liu clan.
- the Khaunban Empire, an expansionist empire in Southeast Coius led by Intharatcha
- the Togoti Khaganate, a steppe empire also invading the Ansan Empire
- various other polities, notably the short-lived dynasties of the Red Orchid rebels, the Wei dynasty led by Duan Siliang, and the Zhao dynasty, led by Yang Baochi, as well as the Bai Kayin Confederacy, and the Chanwan Kingdom of Myiang
The Jiao dynasty had entered a decline by the 17th century, with inattentive emperors ceding authority to palace eunuchs, while military authority was largely usurped by ambitious princes of the imperial clan. Famines, floods, and banditry plagued the countryside while corruption, lavish spending, and widespread tax and census evasion crippled the finances of the imperial court. The Changzhi Emperor was an ambitious and attentive emperor in his youth, though by his later reign had come under the influence of a powerful faction led by the eunuch Wen Meifen. Wen encouraged the emperor to divert attention from these troubles by achieving a victory against the Senrian empire by re-conquering Tousuu. Thus in 1651 the Soukou War began after the local daimyous refused to submit. While Jiao forces achieved some successes, with the aid of defectors such as Toki Sinzou, they were ultimately forced to abandon the war in 1655 due to the emergence of the Red Orchid rebellion.
-Red Orchid stuff here-. In 1659 the rebels, led by Duan Siliang, conquered Baiqiao. The Changzhi Emperor had refused to flee, and so he along with many other members of the Liu clan were captured, and subsequently put to death. Duan Siliang declared the Wei dynasty as the Mingqi Emperor, while his rival Yang Baochi declared his own Zhao dynasty as the Ruizong Emperor.
While western Xiaodong, with the exception of Gaoming, was under the control of rebels, the east largely remained under Jiao control. The Liu princes regrouped in Rongzhuo, and chose Liu Junjie, the fourth son of the Changzhi Emperor, to become the Taizong Emperor. A sudden invasion by the Khaunban king Intharatcha saw Rongzhuo fall, with the Liu princes becoming divided between allegiance to the Khaunban controlled Taizong Emperor, and Liu Zihao, the Prince of Liang, who declared himself the Taichu Emperor. Toki Sinzou, in exile after the Soukou war, had been hired by the Jiao, along with other Senrian exiles and tankenhei such as Nagao Yosioki, to hold frontier regions, such as Shenkong which he made his base.
While the Jiao warred amongst themselves, Sinzou and Yosioki undertook ambitious campaigns against the Zhao and Wei dynasties respectively. The Zhao and Wei had become exhausted due to incessant warfare between themselves and the invading Togoti Khagante. By 1664 Chaozhou and Baiqiao, capitals of the Zhao and Wei, had been recaptured. The Shanju Meeting saw the tankenhei back Toki Sinzou as he declared himself emperor of a new Toki dynasty. Sinzou first consolidated his position by continuing his advances against the Zhao and Wei, while increasing his forces via Jiao and Red orchid defectors. In 1667 he moved against the Northern Jiao while Intharatcha was sorting out revolts in the east, and captured Rongzhuo, forcing the Taizong Emperor to abdicate in his favour. The Battle of Yuan'an in 1668 crippled the Khaunban army and secured the Toki's conquest of the Northern Jiao. The Eastern Jiao would hold out until 1675, when Liu Yuanjun, the Prince of Wu and self-proclaimed Taian Emperor, was captured after the siege of Yinbao and executed.
The Toki dynasty had control over most of present-day Xiaodong by 1680, having defeated the Zhao and Wei remnants, and destroyed the last Eastern Jiao armies. They would be plagued by rebellions, particularly in the west, until the start of the 18th century. A punitive expedition against the Khaunban empire in 1682 was successful, killing king Borommarachathirat and burning the capital of Khaunban to the ground. The Toki's conquest of Xiaodong was completed in 1694, under Sinzou's successor Toki Banrei, when the last Jiao remnant in Gaoming was captured, and Liu Wenyan, Prince of Cao, and self-proclaimed Taiwu Emperor, fled to Senria, where he would die in 1701.
Situation of the late Jiao dynasty
Red Orchid Rebellion
Eastern Jiao
Khaunban invasion
The Jiao fixture on their troubles in the west meant that their eastern border with the belligirent Khaunban Empire had become effectively defenceless. Garrisons and commanders still loyal had been pilfered to prepare for expeditions to retake Baiqiao. A letter from Intharatcha to the Taizong Emperor also further lowered defences, as he professed his loyalty as a subject and offered his aid, which was declined. Reports of attacks on Zhaili were dismissed as being the work of bandits, and the surrender of Juancheng by its commander Zou Qiuyue went unnoticed in the Imperial Court, which had greatly suffered from many officials being left behind in the flight from Baiqiao.
Intharatcha had designs on expanding into Xiaodong as early as 1655, when he wrote to the Senrian Emperor Ninpei to encourage a joint invasion as a retaliation for the Soukou War. While Ninpei dismissed the notion, as he was organizing an effort to restore imperial power within Senria, Intharatcha was assured that the Senrians would take no action to hinder his plans. The implosion of the Jiao dynasty after the Red Orchids took Baiqiao in 1659 provided him the perfect opportunity to launch and invasion disguised as rendering aid to an ailing dynasty.
By the time the Imperial Court was aware of Intharatcha's intentions, the Grand Army was only several days away from Rongzhou. The Taizong Emperor refused to abandon the city, believing that it would doom the Jiao's efforts to reconquer the west, and that Intharatcha was an ally. Several princes, led by Liu Zihao, Prince of Liang disagreed with this policy, and fled the city. In the confusion many soldiers began looting and burning parts of the city, and several notable commanders such as Tao Jinjing and Dong Fenfang were killed attempting to end the riots. The Imperial Court and the emperor fled the city, and were found on a nearby hill by Intharatcha's advance guard, who took them to him.
Intharatcha and his army entered the largely abandoned city with no resistance. Intharatcha declared his intention to restore the Jiao, and was invested by the Taizong Emperor as the 'Great King of the East' (偉大东王 Wěidà dōng wáng). Liu Meilin, Prince of Chen was the only prince to accept Intharatcha's coup, with the Prince of Liang declaring himself the Taichu Emperor, with his base in Zhoujia. The Eastern Jiao became firmly split, although the lines between the Taizong and Taichu factions would become blurred, particularly after 1667.
Four emperors
Jiao-Toki alliance
Shenkong
Toki conquest of the Zhao dynasty
Yosioki's Wei campaign
Toki Sinzou and formation of the Toki dynasty
Five righteous clans
Jiao defectors and Red Orchid rebels
Khaunban expansion
Intharatcha's Grand Army
The creation of the Khaunban Empire had primarily been through military means, and lacking longevity or legitimacy outside of its constituent rulers' personal ties to Intharatcha, required a strong military to remain consolidated. At the start of Intharatcha's reign his army was largely composed of Kasi peasant levies, supported by cavalry, largely from the nobility, and a small elephant corps. It was with this army that Intharatcha was able to overthrow Sippommese rule of Khaunban and establish Khaunban as the new power in the Lueng river valley. This small nucleus would form the basis of the later ' Grand Army' (kongthap thiyingyai)
As the empire expanded so did the diversity within the army. The majority of the levies remained ethnically Kasi, but they were joined by Namkwonese, Svai, Kyin, and Niah conscripts, largely from subject kingdoms. In 1557 Intharatcha divided the levies between the thammada (basic, or general) troops, who were raised for a specific campaign for short-term cyclical periods, and the phiset (extraordinary, special) soldiers, who constituted one of the first standing professional armies in Kuthine history. The phiset soldiers were entitled to a monthly salary, were given a uniform, underwent three years of training, and were expected to serve a minimum of 15 years. Villages which provided a certain ammount of phiset soldiers were excluded from the thammada registry.
While the infantry levies formed the core of the army, the various special branches proved key for Intharatcha's continuing successes. These were the the elephantry, cavalry, artillery, and navy. The elephantry grew substantially with the army, becoming a major part of Intharatcha's war strategy despite never being more than one percent of his total force. The cavalry diversified into several branches, from light Myiang skirmishers to heavy Merket lancers. For artillery and muskets the Grand Army was largely reliant upon Gaullican and Estmerish merchants and mercenaries for cannon and officers respectively. Other notable mercenary regiments included Senrian veterans from the Soukou War, led by Tanaka Tunemasa, and cannonneers from the Aguda Empire.
In order to keep together a vast and ethnically diverse army, Intharatcha had to rely upon a competent officer corps. In his initial reign he was forced to rely upon the aristocracy and gentry for leadership, but as the empire grew he established a permanent Kalahom Department to oversee the training of officers and creation of strategy. Three of his five 'Gods of War', his most famed generals, Kriang Krai, Natthapong, and Chuthamani, came from peasant backgrounds and were able to rise on merit. The officer corp was equally as diverse as the army, with generals such as Vĩnh Nhật Tấn, Tanaka Tunemasa, Binnyadala, and Tian Thassapak achieving high rank and status.
During Intharatcha's campaigns in Xiaodong, his army expanded considerably both from the recruitment of local Xiaodongese, and the addition of irregular conscripted bandit and rebel militias, as well as allied Jiao armies. In contrast to his earlier policies, these units were rarely mixed with the rest of the Grand Army and were often under the command of local leaders or allied Jiao generals. This was likely due to Intharatcha's lack of trust in the loyalty of these troops, many of whom had served under various dynasties and rebel leaders in quick succession.
The Gaullican Gervasius Jacquet, in his letter to Francois II, wrote that the army of "Indharache" numbered "in the millions" with "hordes of beasts and no less than 100 cannon". Though an exaggeration, at its peak the Grand Army may well have had a strength of over one million, although more conservative estimates vary its wartime strength between 300,000 and 650,000.
A Chanwan horseman from the Kingdom of Myiang
An elephant and accompanying crew from Namkwon
Conquest of Yingtan
Southern push
Toki Eastern campaign
Capture of Rongzhuo (1667)
Intharatcha's return eastwards to deal with domestic rebellions did not go unnoticed by Toki Sinzou or the Jiao princes. The Prince of Wu launched several attacks, aiming to take Wudan, but was ultimately unsuccessful due to the intervention by the Prince of Chen and Kriang Krai. This, and raids by the Prince of Ji, left the Prince of Chen and Kriang Krai preoccupied, and Hongyan open. Sinzou despatched a force under Ogawa Yorihiko to Wudan in a feint attack, while he took the bulk of his army to Hongyan. Hongyan's governor, Cui Changpu, held a grudge against the Prince of Chen, and defected, surrendering the city.
The path to Rongzhuo became open, and Sinzou decided upon taking it before Wudan. Capturing the Taizong Emperor would give him greater legitimacy, and possessing Rongzhou and Baiqiao would mean possession of nearly all the Jiao institutions and officials. An army under Mizuno Youhiko was sent to tie down Kriang Krai, but the Kasi general was able to return to Rongzhou. The Prince of Chen remained near Wudan with orders to march to Rongzhou in the event of a siege, which due to threats from the Prince of Wu he was unable to comply with.
Fearing an elongated siege would cause the Jiao garrison to turn on him, Kriang Krai elected to meet Sinzou in battle, where at the Battle of Rongzhuo he was beaten and forced to fall back. Sinzou put the city to siege for three months, after which, as Kriang had predicted, the Jiao garrison mutinied and defected. Kriang narrowly evaded capture by jumping into the Liaojing river, while the Taizong Emperor was captured by defecting troops and delivered to Toki Sinzou.
The defection did not go smoothly, with Kriang's soldiers and elements of the garrison refusing to mutiny. This resulted in a day of sacking and looting, contrary to Sinzou's wishes, and the Rongzhuo massacre, in which over 10,000 of Kriang's soldiers, as well as thousands of Xiaodongese 'collaborators' were executed, despite Sinzou's general pardon and desire to take hostages. The reason for the massacre is contentious, with Xiaodongese historians claiming it had been orchestrated by Sinzou and undertaken by Senrian mercenaries, while Kuthine and Northern historians argue that it was largely undertaken by the defecting Jiao troops against official policy.
Sinzou established Rongzhuo as his new headquarters, moving into its Forbidden City. He began the process of evicting the previous inhabitants of the inner city, replacing them with Senrians and loyal Xiaodongese, as well as some officials transferred from Baiqiao. The Taizong Emperor was forced to abdicate in favour of Sinzou, and was subsequently enfeoffed as the 'Duke of Feichang'.
Conquest of the Eastern Jiao
Battle of Yuan'an (1668)

The Battle of Yuan'an was one of the most decisive and bloodiest battles of the Toki conquest of Xiaodong. After Toki Sinzou had taken advantage of Intharatcha's absence to capture Rongzhou, the Khaunban king intended to regain the initiative by defeating Sinzou in a pitched battle, and thus gain control over the beleagured Jiao forces. Intharatcha had at his disposal 150,000 of his Grand Army, with Natthapong, Tharathorn, and Vĩnh Nhật Tấn commanding, along with 30,000 Jiao soldiers under the Prince of Chen. An additional 80,000 under the Prince of Teng had been promised to support him. He faced a force of 60,000 led by Chen Haiping, with Zhong Jianjun leading a relief army of 35,000, and Toki Sinzou besieging nearby Zhoujia with over 100,000 soldiers.
Intharatcha had despatched Tharathorn with 60,000 men to take Batang fortress, to place pressure on Toki Sinzou and force him to relieve the siege of Zhoujia. He approached Chen's army on the 5th May, but neither side engaged the other until the 12th, with both waiting in vain for reinforcements. Unbeknownst to Intharatcha, Zhong Jianjun's army had ambushed Tharathorn's army at Batang and defeated it, killing Tharatorn in the process, while the Prince of Teng had elected to march instead to Zhoujia, before retreating to his stronghold in Yinbao.
Although Intharatcha had the advantage in both quantity and quality of troops, he was indecisive over whether to give battle and was taken by surprise by Chen's attack. Initially he had the upper hand, inflicting heavy losses on Chen's forces. His decision to place the Prince of Chen on his right flank, protecting the road to his camp, proved a fatal mistake, as Chen Haiping was able to break the dispirited Jiao forces with a cavalry charge and outflank Intharatcha while pushing into his baggage train. Intharatcha's attempts to start an orderly retreat quickly turned into a rout. In the chaos Natthapong was killed, and Intharatcha narrowly escaped capture. Vĩnh Nhật Tấn was able to lead 30,000 survivors southwards, while Intharatcha led the remaining forces back to the safety of Juancheng.
The battle was a turning point for the burgeoning Toki dynasty. The invincibility of Intharatcha and his Grand Army, already shaken by the capture of Rongzhou in 1667, had been shattered. His Grand Army lost two experienced commanders, most of its elephant corps and cannon, and a great deal of veterans, losses which Intharatcha was unable to replace. It also sowed further seeds of distrust between Intharatcha and the Jiao princes, as the former blamed the princes of Chen and Teng for the defeat. Most significantly, the battle secured Toki Sinzou's siege of Zhoujia, which would fall several months later.
Baiqiao and the west
Xiaodongese government and culture
Wei remnant
Toki consolidation
The north
Continuing rebellions
Conquest of Gaoming
Invasion of Khaunban
Rongzhou government
Bakuhu system and domains
Relations with the Senrian Emperor
Relations between the Rongzhuo government and the Empire of Senria were initially deeply strained due to the fact that Sinzou had betrayed the Senrians during the Soukou War by defecting to the Jiao at the 1652 Battle of Tousokabe; following the betrayal Sinzou had been declared a traitor, and remained as such in the eyes of the imperial court in Keisi... [at some point though things are presumably gonna get more pragmatic and the relationship changes somehow]
Separate institutions
-Xiaodongese in Baiqiao, Senrian and loyal Xiaodongese daimyos in Rongzhou
Literature and thought
-rule by barbarian crisis
Ending the century
-Toki consolidate rule