Eastarland: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (289 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|conventional_long_name = | |conventional_long_name = Eastarland Empire | ||
|native_name = '' | |native_name ={{collapsible list | ||
|titlestyle = background:transparent;text-align:center;line-height:normal;font-size:84%; | |||
|title = 3 other official names | |||
| {{Infobox|subbox=yes|bodystyle=font-size:77%;font-weight:normal; | |||
| rowclass1 = mergedrow | label1 = {{wp|Latvian language|Letian}}: | |||
| data1 = ''Austrumzemes Impērija'' | |||
| rowclass4 = mergedrow | label4 = {{wp|Lithuanian language|Levurian}}: | |||
| data4 = ''Rytųžemės Imperija'' | |||
| rowclass5 = mergedrow | label5 = {{wp|Estonian language|Trondic}}: | |||
| data5 = ''Idamaade Impeerium'' | |||
}}}} | |||
|common_name = Eastarland | |common_name = Eastarland | ||
|image_flag = | |image_flag = | ||
[[File: | [[File:Empire 's banner.jpg|190 px|frameless]] | ||
|image_coat = | |image_coat = | ||
[[File: | [[File:Coa of Empire.jpg|130 px|frameless]] | ||
|symbol_type = Coat of Arms | |symbol_type = Coat of Arms | ||
|national_motto = "Loyalty to the Crown and Fatherland" | |national_motto = "Fidelitas ad supernae patriae desiderium et coronam" | ||
<br><small>"Loyalty to the Crown and Fatherland"</small><br> | |||
|national_anthem = " | |national_anthem = "Gloria aeterna!" | ||
<br><small>"Eternal Glory!"</small><br>[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_bk5iZViZgc|upright=0.65|center|]] | |||
|image_map = | |image_map = [[File:Blank Map.jpg|frameless|center]] | ||
[[File: | |capital = [[Hansakalns]] | ||
| | |largest_city = [[Labunavos]] | ||
| | |national_languages = {{wp|Latvian language|Letian}}, {{wp|Lithuanian language|Levurian}}, {{wp|Estonian language|Trondic}} | ||
| | |official_languages = {{wp|Latvian language|Letian}} | ||
| | |regional_languages = {{wp|Russian language|Lusivetian}} | ||
| | |ethnic_groups = Letians (51%) <br>Levurians(27.3%) <br>Trondians (16.2%) <br>Lusivetians (4.7%) <br>Others (0.8%) | ||
| | |||
|ethnic_groups = | |||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | |ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | ||
|demonym = | |religion = {{wp|Catholicism}} (44.1%), {{wp|Protestantism}} (8.2%) | ||
|government_type = | |demonym = Livurs | ||
|leader_title1 = | |government_type = {{wp|Parliamentary}} {{wp|Constitutional}} {{wp|Federal Monarchy}} | ||
|leader_name1 = [[ | |leader_title1 = Monarch of the Eastarland | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Armīns VI]] | |||
|leader_title2 = Prime Minister | |leader_title2 = Prime Minister | ||
|leader_name2 = [[ | |leader_name2 = [[Ieva Ulmaņa]] | ||
|leader_title3 = | |leader_title3 = President of the Senate | ||
|leader_name3 = [[ | |leader_name3 = [[Allar Eskola]] | ||
|leader_title4 = Сhairman of the | |leader_title4 = Сhairman of the Seima | ||
|leader_name4 = [[ | |leader_name4 = [[Marija Česnauskaite]] | ||
|leader_title5 = Chief of Justice | |leader_title5 = Chief of Justice | ||
|leader_name5 = [[ | |leader_name5 = [[Gothards Gulbis]] | ||
|legislature = States General | |legislature = [[States General]] | ||
|upper_house = Senate | |upper_house = [[Senate]] | ||
|lower_house = | |lower_house = [[Seima]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = Foundation | |sovereignty_type = Foundation | ||
|sovereignty_note = | |sovereignty_note = | ||
|established_event1 = | |established_event1 = Livurian Coalition | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = 1779 | ||
|established_event2 = Unification of the | |established_event2 = Unification of the Eastarland Empire | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 1804 | ||
|established_event3 = | |established_event3 = [[Constitution]] | ||
|established_date3 | |established_date3 = May 17, 1855 | ||
|established_event4 = | |||
|established_date4 = | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|area_km2 = 612,097 | |area_km2 = 612,097 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |area_sq_mi = | ||
|percent_water = | |percent_water = 3.1% | ||
|population_estimate = 97,428,353 | |population_estimate = 97,428,353 | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = 2020 | |population_estimate_year = 2020 | ||
|population_census = 95,117,901 | |population_census = 95,117,901 | ||
| Line 69: | Line 76: | ||
|HDI = 0.934 | |HDI = 0.934 | ||
|HDI_year = 2020 | |HDI_year = 2020 | ||
|currency = | |currency = [[Auksinas]] (₳) | ||
|currency_code = | |currency_code = EAK | ||
|time_zone = East Time | |time_zone = East Time | ||
|utc_offset = +2 | |utc_offset = +2 | ||
|date_format = yyyy | |date_format = yyyy.dd.mm | ||
|drives_on = right | |drives_on = right | ||
|cctld = .etl | |cctld = .etl | ||
|iso3166code = ETL | |iso3166code = ETL | ||
|calling_code = | |calling_code = +371 | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Eastarland''' | '''Eastarland''', officially the '''Eastarland Empire''' officially is a country on the Meredonne continent of [[Anteria]]. The area of the territory is 612,097 km2. The population as of December 31, 2020 is 97,428,353. | ||
Located in the center of the | Located in the center of the [[Meredonne]] continent, it is washed by the waters of the [[Kaldaz Ocean]] in the west, the [[Castarilian Sea]] in the east and has an inland [[Gulthav Sea]]. It shares borders with [[Gavrilia]] in the northwest, [[Ykanjo]] in the south. | ||
According to the state structure, it is a | According to the state structure, it is a federal monarchy, it consists of 20 States (Hansakalns (capital region), Selia, Lusivets, Kurona, Baltesia, Laciden, Abrene, Kulaiga, Jurbarkas, Taavetti, Koppola, Vanhamoisio, Brandow, Suodenniemi, Rautensey, Zhuklia, Gubray, Zhaluky, Kierinki, Jurkrasts). The form of government is a constitutional parliamentary monarchy. The Emperor of Eastarland since 3 August 2006 is [[Armīns VI]] from the [[Farenburg]] dynasty, since 2 July 2019 [[Ieva Ulmania]] has been the Prime Minister and Head of Government. | ||
The capital is | The capital is [[Hansakalns]]. The largest city is [[Labunavos]]. The state language is {{wp|Latvian language|Letian}}. | ||
Eastarland is a country with a dynamically developing economy. GDP for 2020 was 4.971 trillion ducats (about 51.022 ducats per capita). The monetary unit is the | Eastarland is a country with a dynamically developing economy. GDP for 2020 was 4.971 trillion ducats (about 51.022 ducats per capita). The monetary unit is the [[Auksinas]]. | ||
=Etymology= | =Etymology= | ||
=History= | =History= | ||
===13th - 14th centuries=== | |||
[[File:1590254844199243930.png|200px|thumb|left|Livurian pioneer travelers. "On the shores of a new land"]] | |||
Until the end of the 12th century, the territory of modern Eastarland was uninhabited land with vast impenetrable dense forests. It was inhabited by a large number of animal species that have survived from prehistoric times. | |||
<br>The Slavic tribes of the [[Samts]] lived around this wooded mountainous area, mainly on the northwest coast. Their main occupation was hunting, fishing and gathering. | |||
[[File:East1300s (2).jpg|thumb|200px|right|'''Red''' - Labunavos; '''Blue''' - Sauslaukė <br>'''Green''' - Kalnciems <br>'''Purple''' - Pacēlums <br>'''Pink''' - Vikonys; '''Yellow''' - Padegliai]] | |||
The first Livurian colonists from the southeastern [[Thrismari]] continent of Anteria arrived on the southwestern coast of present-day Eastarland between 1199 and 1218. | |||
<br>The first city, Labunavos, was founded in 1213. Three years later - the city of Sauslaukė. Over time, more and more settlers arrived, driven by the desire to build a new life, to enrich themselves on new, untouched by man, rich lands. | |||
By the 80s of the 13th century, five kingdoms had already been founded - Horten, Sauslaukė, Labunavos, Vikonys and Padegliai; and one city-state Kalnciems. | |||
<br>In 1237, the King of Sauslaukė landed on the left bank of the Strait of Malsund and founds the Duchy of Varšpils, with its capital in the fortress of the same name. | |||
At the beginning of the 14th century, the "Colonization Race" began - a race between five kingdoms for control of the richest regions with gold, diamonds, coal and sources of drinking water. | |||
By the 1350s, the richest explored lands belonged to the kingdoms of Labunavos and Horten. However, the richest and largest trading port was the Commercial Republic of Kalnciems. | |||
<br>Due to the low duties on export and import goods in the city, free traders preferred to conduct their trade there. Having become, in fact, a trade monopoly, the city quickly grew rich, merchants from all kingdoms and from overseas countries came there. Schools and universities were built, Kalnciems had a law on religious tolerance for all religions, which many other states of that time did not have. | |||
===15th - 16th centuries=== | |||
===17th - 18th centuries=== | |||
===19th century=== | |||
===20th century=== | |||
===21th century=== | |||
=Geografy= | =Geografy= | ||
==Relief== | ==Relief== | ||
[[File:Easterlandphysicalmap2.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Physical map of Eastarland]] | |||
Eastarland is located in the central part of the western coast of the [[Meredonne]] continent of Anteria, bordered by [[Ykanjo]] in the south, [[Gavrilia]] in the northwest and the [[Pomekli desert]] in the northeast. In addition, it has an internal [[Alkai Sea]], which connects with the [[Kaldaz Ocean]] in the west through the [[Gullö Strait]], and with the [[Castarilian Sea]] in the east through the [[Šedava Strait]]. The territorial extent of Eastarland covers an area of 612,097 km2, 3.1% or 18,975 km2 of which are water areas. | |||
Its most notable feature is the abundance of diverse topographic and geological features accumulated over the course of its turbulent geographic history. The Baltkalns Mountains in the center of the country are the highest elevations, with Zaļalance summit (3243 meters), and numerous deserts and small ridges dot the northeastern region. The coastal areas are dominated by two low-lying agricultural and lightly forested plains. | |||
These regions are crossed by some of the longest and largest rivers, including Paranda, Nivala, Čiūrai, and are distinguished by an abundance of waterways and lakes, the most notable of which is Lake Tālava. Due to its geological activity and varied landscape, Eastarland is a treasure trove of numerous natural resources and biodiverse habitats. | |||
{{Gallery | |||
|title=Images of the geography of Eastarland | |||
|width=200 |height=120 | |||
|align=center | |||
|footer= | |||
|Weissfjell Mountains.jpg | |||
|alt1= | |||
|Baltkalns Mountains | |||
|File:Hōldhopiggen.jpg | |||
|alt2= | |||
|Zaļalance, Baltkalns Mountains, Rautensey | |||
|File:Ostelv river.jpg | |||
|alt3= | |||
|National Park "Rumokų", Jurbarkas | |||
|File:Ostelvriver.jpg | |||
|alt4= | |||
|Čiūrai river | |||
}} | |||
==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
[[File:Easterlandclimat.jpg|thumb|left|Eastarland temperature zones; from cooler blue to hotter brown]] | |||
Eastarland is entirely located in the temperate zone in the eastern zone of the planet and in the transition zone between the subtropical climate in the south and the desert climate in the north. The climate is also influenced by the Kalf Stream, which is responsible for unusually high average annual temperatures at this local latitude, providing Eastarland with mostly humid and soft oceanic air. The influence of the World Ocean is significantly reduced when moving from west to east. A maritime climate with small temperature fluctuations between winter and summer is observed along the coastlines (Jurbarkas, Zhuklia, Zhaluky), adjacent hinterlands and regions, while seasonal temperature fluctuations increase when traveling south, to Kierinki and Jurkrasts. However, significant climatic differences also arise from the difficult and rugged terrain, which makes it difficult for warm and cold air to pass, especially in the central regions of Eastarland. | |||
The average annual temperature, based on national measurements from 1950-2000, is approximately 8.6 ° C, and the amount of precipitation for the country is estimated at 596.8 mm. While Eastarland enjoys most of the calibration and control of the meteorological effects of large bodies of water, it has witnessed many extreme weather events. The highest temperature ever recorded and confirmed by the meteorological service was 39.0 ° on July 25, 1993 at Ternopol in Lusivets, while the lowest temperature was -27.5 ° on January 4, 1969, recorded at Lepšiškė, Rautensey. Natural meteorological hazards in Eastarland include wildfires, hurricanes, as well as thunderstorms, floods, storm surges and landslides. | |||
{{Weather box|location = [[Eastarland]] | |||
| collapsed = yes | |||
| metric first = y | |||
| single line = y | |||
| Jan record high C = 9.7 | |||
| Feb record high C = 12.0 | |||
| Mar record high C = 20.3 | |||
| Apr record high C = 26.4 | |||
| May record high C = 29.1 | |||
| Jun record high C = 34.8 | |||
| Jul record high C = 39.0 | |||
| Aug record high C = 33.8 | |||
| Sep record high C = 26.8 | |||
| Oct record high C = 21.2 | |||
| Nov record high C = 15.1 | |||
| Dec record high C = 11.4 | |||
| Jan high C = 4.9 | |||
| Feb high C = 8.7 | |||
| Mar high C = 10.0 | |||
| Apr high C = 12.2 | |||
| May high C = 17.6 | |||
| Jun high C = 19.1 | |||
| Jul high C = 24.8 | |||
| Aug high C = 26.4 | |||
| Sep high C = 21.7 | |||
| Oct high C = 19.5 | |||
| Nov high C = 12.5 | |||
| Dec high C = 4.7 | |||
| year high C = 15.4 | |||
| Jan mean C = 1.8 | |||
| Feb mean C = 2.3 | |||
| Mar mean C = 5.3 | |||
| Apr mean C = 11.0 | |||
| May mean C = 14.1 | |||
| Jun mean C = 16.9 | |||
| Jul mean C = 18.4 | |||
| Aug mean C = 20.2 | |||
| Sep mean C = 16.6 | |||
| Oct mean C = 7.4 | |||
| Nov mean C = 5.6 | |||
| Dec mean C = 2.7 | |||
| year mean C = 9.5 | |||
| Jan low C = −2.7 | |||
| Feb low C = −1.2 | |||
| Mar low C = 1.1 | |||
| Apr low C = 4.6 | |||
| May low C = 7.2 | |||
| Jun low C = 10.4 | |||
| Jul low C = 13.8 | |||
| Aug low C = 15.0 | |||
| Sep low C = 12.3 | |||
| Oct low C = 8.8 | |||
| Nov low C = 3.4 | |||
| Dec low C = 1.2 | |||
| year low C = 6.4 | |||
| Jan record low C = −27.5 | |||
| Feb record low C = −19.8 | |||
| Mar record low C = −9.9 | |||
| Apr record low C = −5.3 | |||
| May record low C = −4.0 | |||
| Jun record low C = 1.7 | |||
| Jul record low C = 3.3 | |||
| Aug record low C = 6.5 | |||
| Sep record low C = 2.9 | |||
| Oct record low C = −1.6 | |||
| Nov record low C = −13.7 | |||
| Dec record low C = −20.2 | |||
| precipitation colour = green | |||
| Jan precipitation mm = 47.3 | |||
| Feb precipitation mm = 40.5 | |||
| Mar precipitation mm = 39.7 | |||
| Apr precipitation mm = 36.0 | |||
| May precipitation mm = 58.8 | |||
| Jun precipitation mm = 70.1 | |||
| Jul precipitation mm = 62.1 | |||
| Aug precipitation mm = 59.2 | |||
| Sep precipitation mm = 86.9 | |||
| Oct precipitation mm = 31.3 | |||
| Nov precipitation mm = 26.9 | |||
| Dec precipitation mm = 38.0 | |||
| year precipitation mm = 596.8 | |||
| unit precipitation days = 1.0 mm | |||
| Jan precipitation days = | |||
| Feb precipitation days = | |||
| Mar precipitation days = | |||
| Apr precipitation days = | |||
| May precipitation days = | |||
| Jun precipitation days = | |||
| Jul precipitation days = | |||
| Aug precipitation days = | |||
| Sep precipitation days = | |||
| Oct precipitation days = | |||
| Nov precipitation days = | |||
| Dec precipitation days = | |||
| year precipitation days = | |||
|Jan snow days = 22 | |||
|Feb snow days = 16 | |||
|Mar snow days = 12 | |||
|Apr snow days = 5 | |||
|May snow days = 0 | |||
|Jun snow days = 0 | |||
|Jul snow days = 0 | |||
|Aug snow days = 0 | |||
|Sep snow days = 1 | |||
|Oct snow days = 4 | |||
|Nov snow days = 12 | |||
|Dec snow days = 18 | |||
|year snow days = 90 | |||
|Jan humidity = | |||
|Feb humidity = | |||
|Mar humidity = | |||
|Apr humidity = | |||
|May humidity = | |||
|Jun humidity = | |||
|Jul humidity = | |||
|Aug humidity = | |||
|Sep humidity = | |||
|Oct humidity = | |||
|Nov humidity = | |||
|Dec humidity = | |||
|year humidity = | |||
| Jan sun = 61.7 | |||
| Feb sun = 77.6 | |||
| Mar sun = 119.4 | |||
| Apr sun = 165.6 | |||
| May sun = 228.1 | |||
| Jun sun = 236.9 | |||
| Jul sun = 240.3 | |||
| Aug sun = 216.2 | |||
| Sep sun = 160.8 | |||
| Oct sun = 119.4 | |||
| Nov sun = 63.5 | |||
| Dec sun = 57.3 | |||
| year sun = 1746.8 | |||
| Jan uv = 1 | |||
| Feb uv = 1 | |||
| Mar uv = 3 | |||
| Apr uv = 4 | |||
| May uv = 6 | |||
| Jun uv = 6 | |||
| Jul uv = 6 | |||
| Aug uv = 6 | |||
| Sep uv = 4 | |||
| Oct uv = 2 | |||
| Nov uv = 1 | |||
| Dec uv = 1 | |||
| source = Royal Committee of Statistics | |||
}} | |||
=Demographics= | =Demographics= | ||
==Religion== | ==Religion== | ||
{{ | {{Bar box | ||
| | |title=Religions in Eastarland(''2019 census'') | ||
| | |float=left | ||
| | |bars= | ||
| | {{Bar percent|{{wp|Catholicism}}|#F7CD45|44.1}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|{{wp|Protestantism}}|#5B6CB7|8.2}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|{{wp|Orthodox Church}}|#6DADDB|4.7}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Not Religious|#CECECE|41.0}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|{{wp|Islamism}}|#267F00|1.8}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|{{wp|Buddism}}|#267F00|0.2}} | ||
| | }} | ||
| | [[File:Moscow, Catholic Church in Presnya.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Catholic Church St. Jones and crowning place of monarchs since 1804, Hansakalns]] | ||
| | According to the 2011 census, 34.5% of citizens do not identify themselves as belonging to any religion or church. In a 2019 survey, only 59% of respondents said they believe in God, 13% said they believe in some kind of natural or spiritual power, and 28% that they don't believe in any of this. The largest number of believers are Catholics (but only 44.1% of the total population as of 2019), the next largest group is Protestants (8.2%). | ||
}}[[File:Moscow, Catholic Church in Presnya.jpg|200px|thumb|Catholic Church | [[File:Normally-picture-from.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Protestant Cathedral of St. Jacob, Labunavos]] | ||
According to the 2011 census, 34.5% of citizens do not identify themselves as belonging to any religion or church. In a 2019 survey, only | According to the amendment to the Constitution of the Empire of Eastarland, the Empire of Eastarland is a secular state with secular values and views. The church is separated from the state, and the schools from the church. There is also a ban on secondary education in parish schools. | ||
[[File:Normally-picture-from.jpg|250px|thumb|Protestant | |||
According to the amendment to the Constitution of the | In the Governor-Generalship of Lusivets, the Orthodox Church is extremely widespread among a deeply religious fanatical population. It is the official religion of the region, but is semi-official in the Empire, meaning it does not receive any government funding. This led to the fact that over the past 130 years the number of Orthodox churches and cathedrals has decreased from 318 at the time of the annexation of the region, to 72 at the moment. | ||
According to universal law, any kind of discrimination based on affiliation with any religion, incitement to wrongdoing, incitement to hatred, causing physical, psychological or financial harm is prohibited to freedom of religion, and is punishable. | According to universal law, any kind of discrimination based on affiliation with any religion, incitement to wrongdoing, incitement to hatred, causing physical, psychological or financial harm is prohibited to freedom of religion, and is punishable. | ||
==Ethnicity== | ==Ethnicity== | ||
{{ | {{Bar box | ||
| | |title=Ethnicity in Eastarland(''2020 census'') | ||
| | |float=left | ||
| | |bars= | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Letians|#8B0000|51}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Levurians|#228B22|27.3}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Trondians|#5B6CB7|16.2}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Lusivetians|#FF8C00|4.7}} | ||
| | {{Bar percent|Others|#808080|0.8}} | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
The population for 2020 is 97,428,353 people. The largest cities are | {{Historical populations | ||
|percentages = | |||
|footnote = '''Source''':Federal Royal Committee of Statistics (FRCS) | |||
|shading = off | |||
|1805|64840113 | |||
|1845|66573910 | |||
|1865|70673729 | |||
|1885|78114712 | |||
|1900|85568708 | |||
|1910|86506031 | |||
|1920|85264184 | |||
|1930|85553270 | |||
|1940|86289706 | |||
|1950|84883977 | |||
|1960|87589384 | |||
|1970|87107066 | |||
|1980|90648009 | |||
|1990|91702835 | |||
|2000|94150821 | |||
|2010|96844067 | |||
|2020|97428353 | |||
}} | |||
The population for 2020 is 97,428,353 people. The largest cities are Labunavos (3,336,187 people), Hansakalns (3,170,613 people), Kristianpils (3,149,700 people), Honkala (2,925,059 people). The average life expectancy is 78 years for men, 86 for women. Age composition: from 1 to 17 years old - 21.1%, from 18 to 66 - 65.2%, over 67 - 13.7%. 20 million students. More than 40 million families. 55 out of 100 families own their own houses. | |||
Letian is spoken throughout the country, although a small proportion of the population living in Lusivets also speaks Lusivetian. Many Letians are also fluent in English, especially in large cities and young people who are learning English in schools. | |||
With an area of 612,097 km², according to data for 2020, Eastarland has a population density of 159.2 people per square kilometer. The most densely populated are 3 | With an area of 612,097 km², according to data for 2020, Eastarland has a population density of 159.2 people per square kilometer. The most densely populated are 3 States: Selia, Jurbarkas and Taavetti (the average population density is 440 people / km2 and more; the maximum indicators are observed in urbanized areas - over 600 people / km2). Largely due to this, Eastarland is one of the countries with the most developed transport and information infrastructure. 90.5 million people, or 93% of the country's population, use the Internet. Eastarland had over 10 million fixed telephones and 12.5 million mobile telephones in 2002-2003. More than 320 radio stations and 37 television stations (as well as 31 repeaters) operate in the country. | ||
Ethnically, the population of Eastarland is very mono-ethnic. The largest ethnic minority in Eastarland are the Lusivetians, but of the total population of the country, their number is 4.7%, which is just over 4.5 million people. This nationality is located entirely in the northern state of Lusivets. The annexation of this region was preceded by a war between the Kingdom of Ōsallandet and the Principality of Lusivets. | |||
However, in the Empire they not only do not have a special status, but are also non-citizens (they have a passport of a non-citizen of Eastarland, which deprives them of the right to all political activities, such as creating or joining political parties, voting in elections at any level, participating in referendums. It also deprives them of the right to serve in the army). | |||
==Language== | ==Language== | ||
== | In the Eastarland Empire, three languages of the Livurian group are officially recognized as equal state languages (Letian, Levurian, Trondic). Also in the northeastern lands of Lusivets, the Lusivetian language is widely spoken and has the status of a recognized regional language of the national minority. | ||
===Letian language=== | |||
Eastarland state language is {{wp|Latvian language|Letian language}} (self-name - ''Letiešu valoda''), along with Levurian and Trondic, it is one of the official languages of the Eastarland Empire and is the language of government, legislation and judicial proceedings, about 51 million people speak Letian (most of them live in Eastarland), and is the most common. | |||
It is estimated that 57% of the population speak Letian as their first language, while close to 87% are estimated to have a high level of proficiency in the language. | |||
<br>The first written monuments appeared in the 11th century. The modern Letian Latin-based alphabet contains 33 letters. | |||
The stress is fixed on the first syllable. By morphological structure, is an inflectional and synthetic language. The syntax is characterized by a relatively free word order, the basic one being the SVO order. The vocabulary is mostly primordial, Germanisms prevail among the borrowings. | |||
===Levurian and Trondic languages=== | |||
{{wp|Lithuanian language|Levurian}} (self-name - ''Lievurių kalba'') and {{wp|Estonian language|Trondic}} (self-name - ''Trōnski keel'') are widely-spoken languages of the Livurian group, both of these languages are enshrined in the Eastarland constitution as co-official national languages. Speakers of the two languages have the right to be use their native tongue in government and business across the country, and the languages are used on signage alongside Letian. Levurian is estimated to be the first language of 12% of the population, while the figure is estimated to be 17% for Trondic. | |||
<br>Both languages have been known since the middle of the 11th century, and are based on the Latin alphabet, containing 32 letters each. | |||
In Eastarland schools, it compulsorary for students to learn Letian and their national tongue of either Levurian and Trondic, in addition to one foreign language up to the age of 14. | |||
===Lusivetian=== | |||
There are other minority languages spoken alongside Levurian and Trondic. {{wp|Russian language|Lusivetian}} (self-name - ''Лузиветский язык''), spoken in the northeast, is recognised as a regional minority language, and a number of languages have been brought to the country by immigrant communities. According to the 2017 census, 4.7% of the population speaks a Lusivetian language. | |||
==Education== | ==Education== | ||
[[File:Usuniversitetas (18).jpg|300px|thumb|right|Hansakalna Valsts Universitāte (HVU), Eastarland's oldest university in Hansakalns]] | |||
Education in Eastarland is compulsory from 3 to 16 years old. From 2020, studies between the ages of 16 and 18 will be compulsory (this can be education, employment or civil service). The basic principles of Eastarlandian education are: freedom of teaching (public and private institutions), free education, neutrality of education, secularism, non-religious education. | |||
<br> Eastarland legislation guarantees its citizens a universal secondary education (school attendance is not a prerequisite, and about 1200 children are homeschooled).<br> | |||
The school year lasts 188 days and the municipalities distribute them independently between the autumn and spring semesters; most often, the first half of the year lasts 89 training days, and the spring - 98. Classes begin in August and end at the end of May. Schools pay attention to ensuring the safety of children and the educational process. | |||
The child goes to the school closest to home, but there is a tendency among parents to send their children to educational institutions that are more prestigious from their point of view. If the school is more than two and a half kilometers away, then according to the law, the student (up to the 6th grade) must be brought back and forth by taxi at the expense of the municipality. The school gives out textbooks and all stationery free of charge and teaches the Letian language, mathematics, natural science, and home economics. Education in the basics of religion (Protestantism or Catholicism) occurs only with parental consent and in accordance with the religion. Atheists have the right to allow secular ethics to be taught to a child, and if objected, children are exempt from any of the courses. The library shelves are in the hallway and are freely accessible. | |||
[[File:1231435.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Labunavos State University]] | |||
There are no grades in the lower grades; verbal gradation is used: excellent, good, changeable and “training required”. Starting from the 4th grade, grades are put in the range from 4 to 10 points. There are also grades for behavior - the ability to work in a group and alone, good breeding, and the desire to influence others for the better. | |||
<br>From grade 3, the first foreign language is added to the subjects - English. A foreign-speaking child (for example, from an immigrant family) is entitled to learn his native language from the first grade.<br> | |||
<br>In the lower grades, subjects are combined (chemistry with physics and biology, language with literature) and home economics is taught to everyone, regardless of gender. They write a lot in the school: all kinds of essays are designed to teach the child to have his own opinion on each issue and to express it in literary language.<br> | |||
[[File:18797582 401.jpg|300px|frameless|right]] | |||
After graduating from school, a young person can continue his studies at a gymnasium, where his studies end with an examination for a matriculation certificate, or enter a secondary vocational educational institution. | |||
<br>As of 2013, 358 higher educational institutions operated in Eastarland: 174 universities, 180 specialized institutes (they study technology, business and economics, art), and 4 military academies.<br> | |||
<br>Higher education, like primary education, is completely free for citizens of the country, as well as exchange students. For other groups of students, paid tuition has been introduced since 2016, the cost of which will be ~ 4 thousand ducats per year.<br> | |||
==Largest Cities== | ==Largest Cities== | ||
{{Largest cities | |||
| name = Largest cities of the Eastarland | |||
| country = Eastarland | |||
| stat_ref = Federal Royal Committee of Statistics (FRCS) | |||
| list_by_pop = | |||
| class = info | |||
| div_name = State | |||
| div_link = | |||
| city_1 = Labunavos | |||
| div_1 = Jurbarkas | |||
| pop_1 = 3,336,187 | |||
|img_1 = 1q.jpg | |||
| city_2 = Hansakanls | |||
| div_2 = Capital City | |||
| pop_2 = 3,170,613 | |||
|img_2 = 12-K.jpg | |||
| city_3 = Kristianpils | |||
| div_3 = Selia | |||
| pop_3 = 3,149,700 | |||
|img_3 = 1280.jpg | |||
| city_4 = Honkala | |||
| div_4 = Taavetti | |||
| pop_4 = 2,925,059 | |||
|img_4 = 2q.jpg | |||
| city_5 = Čedasai | |||
| div_5 = Jurbarkas | |||
| pop_5 = 2,643,167 | |||
| city_6 = Liepāpils | |||
| div_6 = Kulaiga | |||
| pop_6 = 2,189,359 | |||
| city_7 = Preiļīņās | |||
| div_7 = Selia | |||
| pop_7 = 2,064,065 | |||
| city_8 = Torņukalns | |||
| div_8 = Baltesia | |||
| pop_8 = 2,028,763 | |||
| city_9 = Villikkala | |||
| div_9 = Suodenniemi | |||
| pop_9 = 1,886,851 | |||
| city_10 = Lepšiškė | |||
| div_10 = Rautensey | |||
| pop_10 = 1,879,265 | |||
| city_11 = Janušava | |||
| div_11 = Rautensey | |||
| pop_11 = 1,632,331 | |||
| city_12 = Užukalniai | |||
| div_12 = Zhuklia | |||
| pop_12 = 1,520,596 | |||
| city_13 = Ābrene | |||
| div_13 = Abrene | |||
| pop_13 = 1,037,828 | |||
| city_14 = Ternopol | |||
| div_14 = Lusivets | |||
| pop_14 = 1,019,594 | |||
| city_15 = Giloyne | |||
| div_15 = Gubray | |||
| pop_15 = 976,493 | |||
| city_16 = Brandö | |||
| div_16 = Brandow | |||
| pop_16 = 719,219 | |||
| city_17 = Visulahti | |||
| div_17 = Kieriniki | |||
| pop_17 = 654,111 | |||
| city_18 = Laha | |||
| div_18 = Koppola | |||
| pop_18 = 629,892 | |||
| city_19 = Reisu | |||
| div_19 = Vanhamoisio | |||
| pop_19 = 383,502 | |||
| city_20 = Jūrāva | |||
| div_20 = Jurkrasts | |||
| pop_20 = 307,875 | |||
}} | |||
=State structure= | =State structure= | ||
==Administrative division== | ==Administrative division== | ||
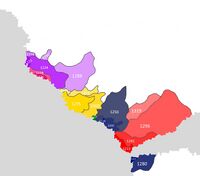
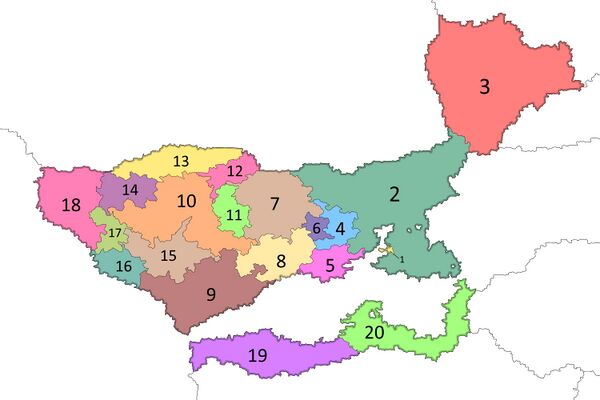
Eastarland is a federal Empire made up of 20 States (Stater): 18 Monarchies, the Governor-Generalship of Lusivets and the Hansakalns Capital Region. There are 3 Kingdoms, 2 Principalities, 5 Grand Duchies, 8 Duchies in Eastarland. States can be divided into districts (Novads), districts into cities and communities (Kopienas), some communities into urban areas (Pilsētas). Communities are the main units of local administration. The city of Hansakalns is also considered a region, but its institutions are different from those of the States: the city council acts as the regional legislature, and the mayor acts as the elected representative. Each of the States has its own budget and independence in its allocation. | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto;" | |||
|- | |||
| valign="top" | | |||
{| style="margin:auto;" cellpadding="10" | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Eastarlandkindgoms.jpg|600px|right]] | |||
|style="font-size: 85%; font-weight:bold;"| | |||
# [[File:11cc.jpg|30px]] [[Hansakalns]] | |||
# [[File:Coa angevin empire.png|30px]] [[Selia]] | |||
# [[File:D3a959dbeff5a918cb03ef8c1604e6f7.jpg|30px]] [[Lusivets]] | |||
# [[File:Royal Arms of Greece.svg.png|30px]] [[Kurona]] | |||
# [[File:Denmark_CoA_(The_Kalmar_Union).png|30px]] [[Baltesia]] | |||
# [[File:Coa of Dōnolagb9.jpg|30px]] [[Laciden]] | |||
# [[File:Paringien.jpg|30px]] [[Abrene]] | |||
# [[File:Ee73a85cb96c6fdfa834bdb99e79e974.jpg|30px]] [[Kulaiga]] | |||
# [[File:C143e63a82d65e5f5ce06e5aae46ea01.jpg|30px]] [[Jurbarkas]] | |||
# [[File:947e149f99f0d1a35b3dfd3ba69ddf41.jpg|30px]] [[Taavetti]] | |||
|style="font-size: 85%; font-weight:bold;"| <ol start=11> | |||
<li>[[File:84a52e9d68c6557d54baca2cd1276614.jpg|30px]] [[Koppola]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:0a91383d8e032b64a91a580fd7e3dcec.jpg|30px]] [[Vanhamoisio]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:90fca01687d81f71ea90bd45d1338980.jpg|30px]] [[Brandow]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:168165a391d008d8b9367b77f7594bf3.jpg|30px]] [[Suodenniemi]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:F7baa706f28b0b357e458144e8c38269.jpg|30px]] [[Rautensey]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:Ed9d5004e519cd8cf46a849de8310cbb.jpg|30px]] [[Zhuklia]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:Aa98627698321c4bacbc41866edff22a.jpg|30px]] [[Gubray]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:86330ca7a431dc3ce205468.jpg|30px]] [[Zhaluky]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:Dbymdnn.png|30px]] [[Kierinki]]</li> | |||
<li>[[File:Large Coat of Arms of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.svg.png|30px]] [[Jurkrasts]]</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:85%" | |||
|- | |||
! State !! Capital city !!Largest city!! Population<br><small>(2020)</small> !! GDP<br><small>(Billions)</small> !! GDP<br><small>(Per capita)</small> !! Leader !! Native name!! Area <br><small>km2</small></br> !! Density !! Language | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="11" |Republics | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Qazw.jpg}} Federal city [[Hansakanls]] || Capital city || Capital city || 3,170,613 || 172.1 || 54,280 || Mayor [[Ilze Laiviņa]] || Hansakanls || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Flag_of_the_Grand_Duchy_of_Baden_(1871–1891).svg}} [[Governor-Generalship of Lusivets]] || [[Ternopol]] || [[Ternopol]] || 3,880,667 || 92.2 || 23,759 || Governor-General [[Deinis Melderis]] || Лузивец || x || x || Lusivetian | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="11" |Kingdoms | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|111111.jpg}} [[Kingdom of Jurbarkas]] || [[Labunavos]] || [[Labunavos]] || 12,866,655 || 684.1 || 53,168 || [[Queen Daina I]] || Jurbarkas || x || x || Levurian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Normandy.jpg}} [[Kingdom of Selia]] || [[Kristianpils]] || [[Kristianpils]] || 14,277,700 || 786.3 || 55,071 || [[King Armīns VI]] || Selija || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|7ff4f08d2effc36c6b5b3e0644e3a3df.jpg}} [[Kingdom of Taavetti]] || [[Honkala]] || [[Honkala]] || 9,260,741 || 436.8 || 52,566 || [[King Mattias II]] || Taavettimaa || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="11" |Principalities | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|E3.jpg}} [[Principality of Baltesia]] || [[Torņukalns]] || [[Torņukalns]] || 3,042,138 || 204.7 || 67,288 || [[Prince Ainārs II]] || Baltēzija || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Zudderland.png}} [[Principality of Kieriniki]] || [[Visulahti]] || [[Visulahti]] || 4,114,655 || 203.0 || 49,336 || [[Prince Mattias XII]] || Kierinikimaa || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="11" |Grand Duchies | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|B4f6feb432c7fc3552d25049f716d281.jpg}} [[Grand Duchy of Abrene]] || [[Ābrene]] || [[Ābrene]] || 4,251,768 || 270.4 || 63,597 || [[Grand Duke Kristians V]] || Ābrene || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|3er.jpg}} [[Grand Duchy of Jurkrasts]] || [[Jūrāva]] || [[Jūrāva]] || 3,149,307 || 130.1 || 41,311 || [[Grand Duke Maris I]] || Jūrkrasts || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|44578.jpg}} [[Grand Duchy of Kulaiga]] || [[Kulaiga]] || [[Kulaiga]] || 4,987,343 || 213.0 || 42,708 || [[Grand Duke Ēriks III]] || Kulaiga || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Ee33333.jpg}} [[Grand Duchy of Rautensey]] || [[Lepšiškė]] || [[Lepšiškė]] || 5,759,470 || 269.8 || 46,845 || [[Grand Duchess Paulina I]] || Rautensee || x || x || Levurian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|20c25a067c42d06feec43489b6477403.jpg}} [[Grand Duchy of Zhaluky]] || [[Rubikiai]] || [[Rubikiai]] || 5,604,678 || 264.6 || 47,210 || [[Grand Duke Algimantas VI]] || Žaliūkė || x || x || Levurian | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="11" |Duchies | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|2241.jpg}} [[Duchy of Brandow]] || [[Brandö]] || [[Brandö]] || 3,342,112 || 129.5 || 38,748 || [[Duke Peeter IV]] || Brandömaa || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
|{{flagicon image|3589.png}} [[Duchy of Gubray]] || [[Baltriškių]] || [[Giloyne]] || 3,113,008 || 211.0 || 51,718 || [[Duchess Gražina III]] || Gubriai || x || x || Levurian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|2562.jpg}} [[Duchy of Koppola]] || [[Laha]] || [[Laha]] || 2,093,579 || 113.1 || 54,022 || [[Duke Taavi I]] || Koppolamaa || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|6464.jpg}} [[Duchy of Kurona]] || [[Salmi]] || [[Salmi]] || 2,250,811 || 126.4 || 56,158 || [[Duke Aivars IV]] || Kūršija || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Ee333333.jpg}} [[Duchy of Laciden]] || [[Līnezers]] || [[Līnezers]] || 1,966,218 || 95.7 || 48,672 || [[Duchess Alexandra V]] || Lacidens || x || x || Letian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|01.jpg}} [[Duchy of Suodenniemi]] || [[Villikkala]] || [[Villikkala]] || 3,884,460 || 249.0 || 64,102 || [[Duke Jaakob VII]] || Suodenniemi || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
| {{flagicon image|Ee3333.jpg}} [[Duchy of Vanhamoisio]] || [[Reisu]] || [[Reisu]] || 1,952,109 || 83.7 || 42,877 || [[Duke Raimond VI]] || Vanhamoisio || x || x || Trondian | |||
|- | |||
|{{flagicon image|Ee333.jpg}} [[Duchy of Zhuklia]] || [[Užukalniai]] || [[Užukalniai]] || 4,460,321 || 285.7 || 64,053 || [[Duke Petras III]] || Žuklija || x || x || Levurian | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Government== | ==Government== | ||
Eastarland is a federal constitutional monarchy. The main law of the state is the constitution (Satversme), adopted on May 17, 1855. It regulates the functioning of the Empire's authorities: it establishes a monarchical constitutional-parliamentary form of government. | |||
The political structure of Eastarland consists of the Monarch of the Eastarland, who is the head of state, the Prime Minister of Eastarland, the government, the head of which is the Prime Minister, the parliament, which consists of two chambers: the Seima and the Senate, and the Constitutional Council. | |||
At the local level, power is represented by the leadership of the Kingdoms, Principalities, Grand Duchies and Duchies, counties, and communes. | |||
===Constitution=== | |||
The '''Constitution''' (Satversme) of Eastarland regulates the relationship between the legislative and executive branches, and also enshrines the fundamental rights and freedoms of citizens. The constitution consists of four basic laws: | |||
The '''Form of Government Act''' guarantees citizens the right to hold demonstrations, form political parties and practice their religion. | |||
The '''Act of Succession''' defines the rights of members of the Farenburg dynasty to the Eastarland throne. | |||
The '''Freedom of the Press Act''' establishes the principles of an open society and guarantees general access to official information. According to it, anyone has the right to access the documents of the Kejsarstag, the government and other state bodies, including any financial statements. Another important principle of the Freedom of the Press Act is freedom of information transfer, which means that Eastarland citizens have the right to provide any information to the media. At the same time, a journalist or publisher has no right to disclose his source if the person who provided it wishes to remain anonymous. | |||
The '''Freedom of Expression Act''', which came into force in 1992, largely reflects the principles already enshrined in the Freedom of the Press Act, such as the unconditional prohibition on censorship, freedom of transfer of information and the right to anonymity. | |||
The provisions of the Constitution take precedence over all other legislative acts, and no law can contradict it. In order to amend the Constitution (Satversme), the Seima must adopt it in two readings - before and after the next parliamentary elections. | |||
===Executive power=== | ===Executive power=== | ||
The head of state and the head of the executive branch of government is the Monarch of the Eastarland, currently Armīns VI. In Eastarland, the Prime Minister is responsible for current domestic and economic policy and has the authority to issue general decrees. He is considered to be responsible for government policy. The Prime Minister directs government activities and enforces laws. | |||
[[File:7086937.jpg|thumb|right|Ieva Ulmania , Prime Minister of Eastarland]] | |||
The Prime Minister is appointed by the monarch. The confirmation of his candidacy by the States General is not required, since the Seima has the right to declare a vote of no confidence in the government at any time. Usually the Prime Minister represents the party with the majority of seats in the Seima. The Prime Minister draws up a list of ministers in his cabinet and submits it to the Monarch for approval. | |||
The Prime Minister initiates the adoption of laws in the Seima and ensures their implementation, he is also responsible for national defense. The Prime Minister replaces the Monarch as Chairman of Councils and Committees. | |||
Since July 2, 2019, the government is headed by Ieva Ulmania. | |||
===Legislature=== | ===Legislature=== | ||
[[File:Un.jpg|thumb|left|Allar Eskola , President of the Senate]] | |||
Legislative power in Eastarland belongs to the States General, which includes two chambers - the Senate and the Seima. | |||
The [[Senate]], whose members are elected by indirect universal suffrage, consists of 350 senators. Senators are elected for four-year terms by the members of the States councils (Valsts Seima) every four years following elections to the States councils. The last Senate elections were held on September 6, 2019. The President of the Senate is Allar Eskola. | |||
[[File:124795 1.jpg|thumb|right|200 px|Marija Česnauskaite , Chairman of the Seima]] | |||
The [[Seima]] consists of 500 deputies, whose deputies are elected on the basis of direct universal suffrage for a period of 4 years, therefore, in case of leaving the party, a deputy can remain independent or join another. The last elections for the Seima deputies took place on June 12, 2019. The Chairman of the Seima is Marija Česnauskaite. | |||
In addition to their function of overseeing government activities, both chambers develop and pass laws. In case of disagreement, the final decision rests with Seima. | |||
===Judicial branch=== | ===Judicial branch=== | ||
The highest court in criminal and civil justice is the '''Supreme Court''' in Selia. One step below are the Highest Land Courts (hereinafter land courts and the lowest level of the judicial system - district courts). | |||
The highest court of administrative justice is the '''Administrative Court''' in Labunavos, the courts of appeal of administrative justice are the '''Supreme Administrative Courts''' in Baltesia, Gubray and Kierinki are the administrative courts of justice, the courts of first instance of administrative justice are the administrative courts. | |||
The highest court of labor justice is the '''Labor Court''', the courts of appeal of labor justice are land labor courts, and the courts of first instance of labor justice are labor courts. | |||
The highest court of social justice is the '''Social Court''', the courts of appeal of social justice are the land social courts (one for each land), the courts of first instance of social justice are the social courts. | |||
The highest court of financial justice is the '''Financial Court''' in Lepšiškė, the state financial courts are the financial courts. | |||
There is also a copyright court - a '''Patent Court''', an official discipline court. | |||
Prosecutorial oversight bodies are the Prosecutor General under the Supreme Court, Prosecutors General of Lands, prosecutors of district courts. | |||
==Migration policy== | ==Migration policy== | ||
After a series of terrorist acts in the world, the government has consistently tightened immigration laws. | After a series of terrorist acts in the world, the government has consistently tightened immigration laws. | ||
| Line 171: | Line 675: | ||
==Agriculture== | ==Agriculture== | ||
Eastarland has a highly productive agriculture. It occupies a leading position in the world in terms of agricultural production, grain production, livestock products and milk. Eastarland is a land of predominantly small family farms. Agricultural production efficiency is very high. At the same time Eastarland lags behind in the average yield of corn and sugar beet. In the agro-industrial complex, agriculture plays a subordinate role. | Eastarland has a highly productive agriculture. It occupies a leading position in the world in terms of agricultural production, grain production, livestock products and milk. Eastarland is a land of predominantly small family farms. Agricultural production efficiency is very high. At the same time Eastarland lags behind in the average yield of corn and sugar beet. In the agro-industrial complex, agriculture plays a subordinate role. | ||
[[File:Germany selskoe hozyistvo 1.jpg| | [[File:Germany selskoe hozyistvo 1.jpg|frameless|right]] | ||
Livestock breeding provides about 70% of marketable agricultural products. Cattle breeding is the main branch of animal husbandry, it provides more than 2/5 of all marketable agricultural products, with the main part being milk (about ¼). Pig breeding is in second place. The country's self-sufficiency in milk and beef systematically exceeds 100%, but in pork it is less than 4/5. | Livestock breeding provides about 70% of marketable agricultural products. Cattle breeding is the main branch of animal husbandry, it provides more than 2/5 of all marketable agricultural products, with the main part being milk (about ¼). Pig breeding is in second place. The country's self-sufficiency in milk and beef systematically exceeds 100%, but in pork it is less than 4/5. | ||
| Line 177: | Line 681: | ||
There are much more fodder crops than food crops, since a large amount of fodder grains, especially corn, are imported. However, the country ranked (2014) seventh in the world in terms of wheat exports (8.2 million tons). | There are much more fodder crops than food crops, since a large amount of fodder grains, especially corn, are imported. However, the country ranked (2014) seventh in the world in terms of wheat exports (8.2 million tons). | ||
Of great importance is the cultivation of fodder root crops (fodder beets, etc.), corn for green fodder and silage, alfalfa, clover and other fodder grasses. Of the oilseeds, the most important is rapeseed, the crops of which are more than 10 times higher than those of sunflower. | Of great importance is the cultivation of fodder root crops (fodder beets, etc.), corn for green fodder and silage, alfalfa, clover and other fodder grasses. Of the oilseeds, the most important is rapeseed, the crops of which are more than 10 times higher than those of sunflower. | ||
[[File:Unnamed (2).jpg| | [[File:Unnamed (2).jpg|frameless|right]] | ||
In areas with high natural soil fertility, the main crops are wheat, barley, maize and sugar beets. The poorer soils of the Northern Lowland and the middle-altitude mountains are traditionally used for sowing rye, oats, potatoes and natural forage crops. The traditional nature of | In areas with high natural soil fertility, the main crops are wheat, barley, maize and sugar beets. The poorer soils of the Northern Lowland and the middle-altitude mountains are traditionally used for sowing rye, oats, potatoes and natural forage crops. The traditional nature of Eastarland agriculture has significantly changed technological progress. Today, the so-called light soils are valued more, due to their suitability for machine cultivation, using artificial fertilizers; for example, corn is now widely cultivated in the Northern Lowlands, where it replaces potatoes. | ||
Viticulture surpasses, in marketable products, fruit growing and vegetable growing combined. Vineyards are located mainly in the valleys of | Viticulture surpasses, in marketable products, fruit growing and vegetable growing combined. Vineyards are located mainly in the valleys of Gaudava, Tekkava and other rivers. | ||
==Tourism== | ==Tourism== | ||
Tourism as a sector of the economy has made a significant contribution to the national economy, generating revenue of 452.361 billion ducats, or 9.1% of Eastarland's GDP in 2020. It is also an important source of employment in urban areas and, to a lesser extent, in rural areas. Of the 19,562 villages and towns in Eastarland, approximately 500 are registered with some form of travel agency, and 41 of these are recognized resorts and seaside resorts. 10,281 museums, 537 theaters, 11 amusement parks, over 700,000 kilometers of hiking trails and 571,000 kilometers of bike paths, as well as numerous special thematic trails (Tematiskās takas) are all accessible and accessible for tourism activities. | |||
The country is home to a number of well-known cultural, iconic and ecological tourism destinations. Hansakalns and Labunavos are the top tourist destinations in Eastarland, attracting up to 10.6 million tourists in 2010; The most popular attractions are the States General Building, the Hansakalns Zoo (Zooloģiskais dārzs), the Ziemaspils Old Royal Winter Palace in Čedasai, the Cathedral of St. Laura and St. Jakobs in Labunavos, the National Opera of Jozefs Krūmiņ in Hansakalns and the Brūnapils Palace in Čedasai. Other major tourist destinations in Eastarland include Palace of Karlis Rozītis in Zhuklia, Nožogojpilis Palace in Čedasai, Princis Ārens Parks in Abrene and National Park in Taavetti, the Paipis beach in Kierinki, as well as old towns, city centers: Labunavos, Hansakalns, Čedasai, Abrene, Kurona, Rautensey, Vanhamoisio and Koppola. | |||
===Attractions=== | |||
{{Gallery | |||
|title=Images of the Attractions of Eastarland | |||
|width=200 |height=120 | |||
|align=center | |||
|footer= | |||
|File:Vinterpalasset .jpg | |||
|alt1= | |||
|Ziemaspils Old Royal Winter Palace in Čedasai | |||
|File:Cathedral of St. Laura and St. Jakob.jpg | |||
|alt2= | |||
|Cathedral of St. Laura and St. Jakobs | |||
|File:National Opera of Ludwig Johannessen.jpg | |||
|alt3= | |||
|National Opera of Jozefs Krūmiņš | |||
|File:Muzeum of Eastarlandian History.jpg | |||
|alt4= | |||
|Museum of Eastarland History | |||
|File:Prins Gustav Park in Brynefjord.jpg | |||
|alt5= | |||
|Princis Ārens Parks in Abrene | |||
|File:Karl Georg Palace in Safeks.jpg | |||
|alt6= | |||
|Palace of Karlis Rozītis in Zhuklia | |||
|File:Efoypalasset Palace in Kongshelm.jpg | |||
|Brūnapils Palace in Čedasai | |||
|File:Hokklan beach in Ōienvikket.jpg | |||
|alt8= | |||
|Paipis beach in Kierinki | |||
}} | |||
==Extractive industry== | ==Extractive industry== | ||
Forests make up more than 20% of the territory. There are 79 tree species in the Eastarland. | Forests make up more than 20% of the territory. There are 79 tree species in the Eastarland. | ||
Eastarland has significant reserves of iron ore, uranium ores, bauxite, potash and rock salts, coal, zinc, copper, lead, nickel, oil, timber. | Eastarland has significant reserves of iron ore, uranium ores, bauxite, potash and rock salts, coal, zinc, copper, lead, nickel, oil, timber. | ||
The main coal mining regions are | The main coal mining regions are Gubray and the Kulaiga coal basins. Eastarland proven brown coal reserves were 40.5 billion tonnes. Since 1994, imports of coal have exceeded production. | ||
Gas production does not exceed 3 billion m³. One of the largest Eastarland gas fields is | Gas production does not exceed 3 billion m³. One of the largest Eastarland gas fields is ''Ropa'' in Suodenniemi. "East Oil&Gas" is one of the largest gas and oil companies in Eastarland. The main activities of the company are exploration, production, marketing and distribution of natural gas and oil. | ||
==Transport and Energy== | ==Transport and Energy== | ||
===Transport=== | ===Transport=== | ||
[[File:4940002010.jpg| | [[File:4940002010.jpg|frameless|left]] | ||
'''Railway transport''' | '''Railway transport''' | ||
Eastarland rail transport is highly developed. Local and overnight trains, including high-speed trains, connect the capital with all major cities in the country, as well as with neighboring countries. The speed of these trains is 320 km / h. The railway network is | Eastarland rail transport is highly developed. Local and overnight trains, including high-speed trains, connect the capital with all major cities in the country, as well as with neighboring countries. The speed of these trains is 320 km / h. The railway network is 51,850 km long and is one of the longest railway networks. Rail links exist with all neighboring countries. | ||
Metro is available in | Metro is available in Hansakanls, Labunavos, Honkala, Kristianpils, Čedasai. In Lāčupils partly underground light rail. | ||
'''Automobile transport''' | '''Automobile transport''' | ||
After winning the 2016 elections in | After winning the 2016 elections in Seima, and forming a majority coalition with the Peasant Union, the Green Party banned all non-electric cars. Also, the cost of roads was reduced, but more attention was paid to public transport, railways, etc. | ||
The road network does not cover the entire territory of the country. The total length of highways is | The road network does not cover the entire territory of the country. The total length of highways is 610,500 km. | ||
The main roads are divided into the following groups: | The main roads are divided into the following groups: | ||
[[File:48215960 303.jpg| | [[File:48215960 303.jpg|frameless|right]] | ||
'''Motorways''' - The name of the road is made up of the letter A followed by the road number. Permissible speed - 130 km / h, obligatory filling stations every 50 km, concrete dividing strip, absence of traffic lights, pedestrian crossings. | '''Motorways''' - The name of the road is made up of the letter A followed by the road number. Permissible speed - 130 km / h, obligatory filling stations every 50 km, concrete dividing strip, absence of traffic lights, pedestrian crossings. | ||
'''National roads''' - prefix N. Permissible speed - 90 km / h (if there is a concrete dividing strip - 110 km / h). | <br>'''National roads''' - prefix N. Permissible speed - 90 km / h (if there is a concrete dividing strip - 110 km / h). | ||
'''Department roads''' - prefix D. Permissible speed - 90 km / h. | <br>'''Department roads''' - prefix D. Permissible speed - 90 km / h. | ||
In cities, the permissible speed is 50 km / h. The use of seat belts is mandatory. Children under 10 years old must be transported in special seats. | In cities, the permissible speed is 50 km / h. The use of seat belts is mandatory. Children under 10 years old must be transported in special seats. | ||
'''Air transport''' | '''Air transport''' | ||
Eastarland has about 475 airports. 325 of them have asphalt or concrete runways, and the remaining 150 are unpaved (data for 2017). The largest airport is the | Eastarland has about 475 airports. 325 of them have asphalt or concrete runways, and the remaining 150 are unpaved (data for 2017). The largest airport is the «Princis Raimonds» located in the suburbs of Hansakanls. The national Eastarlandian airline «EastarAir» operates flights to almost every country in the world. | ||
===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
| Line 220: | Line 759: | ||
==Gastronomy== | ==Gastronomy== | ||
==Holidays== | ==Holidays== | ||
==Architecture== | ==Architecture== | ||
=Military establishment= | =Military establishment= | ||
=National symbols= | |||
{{main|National symbols of Eastarland}} | |||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 10 May 2021
Eastarland Empire | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Fidelitas ad supernae patriae desiderium et coronam"
"Loyalty to the Crown and Fatherland" | |
| Anthem: "Gloria aeterna!"
"Eternal Glory!" | |
| Capital | Hansakalns |
| Largest city | Labunavos |
| Official languages | Letian |
| Recognised national languages | Letian, Levurian, Trondic |
| Recognised regional languages | Lusivetian |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | Letians (51%) Levurians(27.3%) Trondians (16.2%) Lusivetians (4.7%) Others (0.8%) |
| Religion | Catholicism (44.1%), Protestantism (8.2%) |
| Demonym(s) | Livurs |
| Government | Parliamentary Constitutional Federal Monarchy |
• Monarch of the Eastarland | Armīns VI |
• Prime Minister | Ieva Ulmaņa |
• President of the Senate | Allar Eskola |
• Сhairman of the Seima | Marija Česnauskaite |
• Chief of Justice | Gothards Gulbis |
| Legislature | States General |
| Senate | |
| Seima | |
| Foundation | |
• Livurian Coalition | 1779 |
• Unification of the Eastarland Empire | 1804 |
| May 17, 1855 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 612,097 km2 (236,332 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 3.1% |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 97,428,353 |
• 2015 census | 95,117,901 |
• Density | 159.2/km2 (412.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 4.971 trillion |
• Per capita | 51,022 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 3.783 trillion |
• Per capita | 38,829 |
| Gini (2020) | 29.6 low |
| HDI (2020) | 0.934 very high |
| Currency | Auksinas (₳) (EAK) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (East Time) |
| Date format | yyyy.dd.mm |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +371 |
| ISO 3166 code | ETL |
| Internet TLD | .etl |
Eastarland, officially the Eastarland Empire officially is a country on the Meredonne continent of Anteria. The area of the territory is 612,097 km2. The population as of December 31, 2020 is 97,428,353.
Located in the center of the Meredonne continent, it is washed by the waters of the Kaldaz Ocean in the west, the Castarilian Sea in the east and has an inland Gulthav Sea. It shares borders with Gavrilia in the northwest, Ykanjo in the south.
According to the state structure, it is a federal monarchy, it consists of 20 States (Hansakalns (capital region), Selia, Lusivets, Kurona, Baltesia, Laciden, Abrene, Kulaiga, Jurbarkas, Taavetti, Koppola, Vanhamoisio, Brandow, Suodenniemi, Rautensey, Zhuklia, Gubray, Zhaluky, Kierinki, Jurkrasts). The form of government is a constitutional parliamentary monarchy. The Emperor of Eastarland since 3 August 2006 is Armīns VI from the Farenburg dynasty, since 2 July 2019 Ieva Ulmania has been the Prime Minister and Head of Government.
The capital is Hansakalns. The largest city is Labunavos. The state language is Letian.
Eastarland is a country with a dynamically developing economy. GDP for 2020 was 4.971 trillion ducats (about 51.022 ducats per capita). The monetary unit is the Auksinas.
Etymology
History
13th - 14th centuries
Until the end of the 12th century, the territory of modern Eastarland was uninhabited land with vast impenetrable dense forests. It was inhabited by a large number of animal species that have survived from prehistoric times.
The Slavic tribes of the Samts lived around this wooded mountainous area, mainly on the northwest coast. Their main occupation was hunting, fishing and gathering.
The first Livurian colonists from the southeastern Thrismari continent of Anteria arrived on the southwestern coast of present-day Eastarland between 1199 and 1218.
The first city, Labunavos, was founded in 1213. Three years later - the city of Sauslaukė. Over time, more and more settlers arrived, driven by the desire to build a new life, to enrich themselves on new, untouched by man, rich lands.
By the 80s of the 13th century, five kingdoms had already been founded - Horten, Sauslaukė, Labunavos, Vikonys and Padegliai; and one city-state Kalnciems.
In 1237, the King of Sauslaukė landed on the left bank of the Strait of Malsund and founds the Duchy of Varšpils, with its capital in the fortress of the same name.
At the beginning of the 14th century, the "Colonization Race" began - a race between five kingdoms for control of the richest regions with gold, diamonds, coal and sources of drinking water.
By the 1350s, the richest explored lands belonged to the kingdoms of Labunavos and Horten. However, the richest and largest trading port was the Commercial Republic of Kalnciems.
Due to the low duties on export and import goods in the city, free traders preferred to conduct their trade there. Having become, in fact, a trade monopoly, the city quickly grew rich, merchants from all kingdoms and from overseas countries came there. Schools and universities were built, Kalnciems had a law on religious tolerance for all religions, which many other states of that time did not have.
15th - 16th centuries
17th - 18th centuries
19th century
20th century
21th century
Geografy
Relief
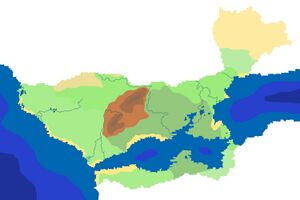
Eastarland is located in the central part of the western coast of the Meredonne continent of Anteria, bordered by Ykanjo in the south, Gavrilia in the northwest and the Pomekli desert in the northeast. In addition, it has an internal Alkai Sea, which connects with the Kaldaz Ocean in the west through the Gullö Strait, and with the Castarilian Sea in the east through the Šedava Strait. The territorial extent of Eastarland covers an area of 612,097 km2, 3.1% or 18,975 km2 of which are water areas.
Its most notable feature is the abundance of diverse topographic and geological features accumulated over the course of its turbulent geographic history. The Baltkalns Mountains in the center of the country are the highest elevations, with Zaļalance summit (3243 meters), and numerous deserts and small ridges dot the northeastern region. The coastal areas are dominated by two low-lying agricultural and lightly forested plains.
These regions are crossed by some of the longest and largest rivers, including Paranda, Nivala, Čiūrai, and are distinguished by an abundance of waterways and lakes, the most notable of which is Lake Tālava. Due to its geological activity and varied landscape, Eastarland is a treasure trove of numerous natural resources and biodiverse habitats.
Climate
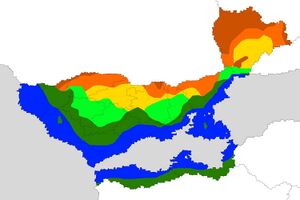
Eastarland is entirely located in the temperate zone in the eastern zone of the planet and in the transition zone between the subtropical climate in the south and the desert climate in the north. The climate is also influenced by the Kalf Stream, which is responsible for unusually high average annual temperatures at this local latitude, providing Eastarland with mostly humid and soft oceanic air. The influence of the World Ocean is significantly reduced when moving from west to east. A maritime climate with small temperature fluctuations between winter and summer is observed along the coastlines (Jurbarkas, Zhuklia, Zhaluky), adjacent hinterlands and regions, while seasonal temperature fluctuations increase when traveling south, to Kierinki and Jurkrasts. However, significant climatic differences also arise from the difficult and rugged terrain, which makes it difficult for warm and cold air to pass, especially in the central regions of Eastarland.
The average annual temperature, based on national measurements from 1950-2000, is approximately 8.6 ° C, and the amount of precipitation for the country is estimated at 596.8 mm. While Eastarland enjoys most of the calibration and control of the meteorological effects of large bodies of water, it has witnessed many extreme weather events. The highest temperature ever recorded and confirmed by the meteorological service was 39.0 ° on July 25, 1993 at Ternopol in Lusivets, while the lowest temperature was -27.5 ° on January 4, 1969, recorded at Lepšiškė, Rautensey. Natural meteorological hazards in Eastarland include wildfires, hurricanes, as well as thunderstorms, floods, storm surges and landslides.
| Climate data for Eastarland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
12.0 (53.6) |
20.3 (68.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
29.1 (84.4) |
34.8 (94.6) |
39.0 (102.2) |
33.8 (92.8) |
26.8 (80.2) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.1 (59.2) |
11.4 (52.5) |
39.0 (102.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
4.7 (40.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
2.3 (36.1) |
5.3 (41.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
14.1 (57.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
16.6 (61.9) |
7.4 (45.3) |
5.6 (42.1) |
2.7 (36.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.7 (27.1) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
1.1 (34.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.4 (50.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
1.2 (34.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.5 (−17.5) |
−19.8 (−3.6) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−4 (25) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.3 (37.9) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.9 (37.2) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−20.2 (−4.4) |
−27.5 (−17.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 47.3 (1.86) |
40.5 (1.59) |
39.7 (1.56) |
36.0 (1.42) |
58.8 (2.31) |
70.1 (2.76) |
62.1 (2.44) |
59.2 (2.33) |
86.9 (3.42) |
31.3 (1.23) |
26.9 (1.06) |
38.0 (1.50) |
596.8 (23.50) |
| Average snowy days | 22 | 16 | 12 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 12 | 18 | 90 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 61.7 | 77.6 | 119.4 | 165.6 | 228.1 | 236.9 | 240.3 | 216.2 | 160.8 | 119.4 | 63.5 | 57.3 | 1,746.8 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Source: Royal Committee of Statistics | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Religion
According to the 2011 census, 34.5% of citizens do not identify themselves as belonging to any religion or church. In a 2019 survey, only 59% of respondents said they believe in God, 13% said they believe in some kind of natural or spiritual power, and 28% that they don't believe in any of this. The largest number of believers are Catholics (but only 44.1% of the total population as of 2019), the next largest group is Protestants (8.2%).
According to the amendment to the Constitution of the Empire of Eastarland, the Empire of Eastarland is a secular state with secular values and views. The church is separated from the state, and the schools from the church. There is also a ban on secondary education in parish schools.
In the Governor-Generalship of Lusivets, the Orthodox Church is extremely widespread among a deeply religious fanatical population. It is the official religion of the region, but is semi-official in the Empire, meaning it does not receive any government funding. This led to the fact that over the past 130 years the number of Orthodox churches and cathedrals has decreased from 318 at the time of the annexation of the region, to 72 at the moment.
According to universal law, any kind of discrimination based on affiliation with any religion, incitement to wrongdoing, incitement to hatred, causing physical, psychological or financial harm is prohibited to freedom of religion, and is punishable.
Ethnicity
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1805 | 64,840,113 | — |
| 1845 | 66,573,910 | +2.7% |
| 1865 | 70,673,729 | +6.2% |
| 1885 | 78,114,712 | +10.5% |
| 1900 | 85,568,708 | +9.5% |
| 1910 | 86,506,031 | +1.1% |
| 1920 | 85,264,184 | −1.4% |
| 1930 | 85,553,270 | +0.3% |
| 1940 | 86,289,706 | +0.9% |
| 1950 | 84,883,977 | −1.6% |
| 1960 | 87,589,384 | +3.2% |
| 1970 | 87,107,066 | −0.6% |
| 1980 | 90,648,009 | +4.1% |
| 1990 | 91,702,835 | +1.2% |
| 2000 | 94,150,821 | +2.7% |
| 2010 | 96,844,067 | +2.9% |
| 2020 | 97,428,353 | +0.6% |
| Source:Federal Royal Committee of Statistics (FRCS) | ||
The population for 2020 is 97,428,353 people. The largest cities are Labunavos (3,336,187 people), Hansakalns (3,170,613 people), Kristianpils (3,149,700 people), Honkala (2,925,059 people). The average life expectancy is 78 years for men, 86 for women. Age composition: from 1 to 17 years old - 21.1%, from 18 to 66 - 65.2%, over 67 - 13.7%. 20 million students. More than 40 million families. 55 out of 100 families own their own houses. Letian is spoken throughout the country, although a small proportion of the population living in Lusivets also speaks Lusivetian. Many Letians are also fluent in English, especially in large cities and young people who are learning English in schools.
With an area of 612,097 km², according to data for 2020, Eastarland has a population density of 159.2 people per square kilometer. The most densely populated are 3 States: Selia, Jurbarkas and Taavetti (the average population density is 440 people / km2 and more; the maximum indicators are observed in urbanized areas - over 600 people / km2). Largely due to this, Eastarland is one of the countries with the most developed transport and information infrastructure. 90.5 million people, or 93% of the country's population, use the Internet. Eastarland had over 10 million fixed telephones and 12.5 million mobile telephones in 2002-2003. More than 320 radio stations and 37 television stations (as well as 31 repeaters) operate in the country.
Ethnically, the population of Eastarland is very mono-ethnic. The largest ethnic minority in Eastarland are the Lusivetians, but of the total population of the country, their number is 4.7%, which is just over 4.5 million people. This nationality is located entirely in the northern state of Lusivets. The annexation of this region was preceded by a war between the Kingdom of Ōsallandet and the Principality of Lusivets. However, in the Empire they not only do not have a special status, but are also non-citizens (they have a passport of a non-citizen of Eastarland, which deprives them of the right to all political activities, such as creating or joining political parties, voting in elections at any level, participating in referendums. It also deprives them of the right to serve in the army).
Language
In the Eastarland Empire, three languages of the Livurian group are officially recognized as equal state languages (Letian, Levurian, Trondic). Also in the northeastern lands of Lusivets, the Lusivetian language is widely spoken and has the status of a recognized regional language of the national minority.
Letian language
Eastarland state language is Letian language (self-name - Letiešu valoda), along with Levurian and Trondic, it is one of the official languages of the Eastarland Empire and is the language of government, legislation and judicial proceedings, about 51 million people speak Letian (most of them live in Eastarland), and is the most common.
It is estimated that 57% of the population speak Letian as their first language, while close to 87% are estimated to have a high level of proficiency in the language.
The first written monuments appeared in the 11th century. The modern Letian Latin-based alphabet contains 33 letters.
The stress is fixed on the first syllable. By morphological structure, is an inflectional and synthetic language. The syntax is characterized by a relatively free word order, the basic one being the SVO order. The vocabulary is mostly primordial, Germanisms prevail among the borrowings.
Levurian and Trondic languages
Levurian (self-name - Lievurių kalba) and Trondic (self-name - Trōnski keel) are widely-spoken languages of the Livurian group, both of these languages are enshrined in the Eastarland constitution as co-official national languages. Speakers of the two languages have the right to be use their native tongue in government and business across the country, and the languages are used on signage alongside Letian. Levurian is estimated to be the first language of 12% of the population, while the figure is estimated to be 17% for Trondic.
Both languages have been known since the middle of the 11th century, and are based on the Latin alphabet, containing 32 letters each.
In Eastarland schools, it compulsorary for students to learn Letian and their national tongue of either Levurian and Trondic, in addition to one foreign language up to the age of 14.
Lusivetian
There are other minority languages spoken alongside Levurian and Trondic. Lusivetian (self-name - Лузиветский язык), spoken in the northeast, is recognised as a regional minority language, and a number of languages have been brought to the country by immigrant communities. According to the 2017 census, 4.7% of the population speaks a Lusivetian language.
Education
Education in Eastarland is compulsory from 3 to 16 years old. From 2020, studies between the ages of 16 and 18 will be compulsory (this can be education, employment or civil service). The basic principles of Eastarlandian education are: freedom of teaching (public and private institutions), free education, neutrality of education, secularism, non-religious education.
Eastarland legislation guarantees its citizens a universal secondary education (school attendance is not a prerequisite, and about 1200 children are homeschooled).
The school year lasts 188 days and the municipalities distribute them independently between the autumn and spring semesters; most often, the first half of the year lasts 89 training days, and the spring - 98. Classes begin in August and end at the end of May. Schools pay attention to ensuring the safety of children and the educational process.
The child goes to the school closest to home, but there is a tendency among parents to send their children to educational institutions that are more prestigious from their point of view. If the school is more than two and a half kilometers away, then according to the law, the student (up to the 6th grade) must be brought back and forth by taxi at the expense of the municipality. The school gives out textbooks and all stationery free of charge and teaches the Letian language, mathematics, natural science, and home economics. Education in the basics of religion (Protestantism or Catholicism) occurs only with parental consent and in accordance with the religion. Atheists have the right to allow secular ethics to be taught to a child, and if objected, children are exempt from any of the courses. The library shelves are in the hallway and are freely accessible.
There are no grades in the lower grades; verbal gradation is used: excellent, good, changeable and “training required”. Starting from the 4th grade, grades are put in the range from 4 to 10 points. There are also grades for behavior - the ability to work in a group and alone, good breeding, and the desire to influence others for the better.
From grade 3, the first foreign language is added to the subjects - English. A foreign-speaking child (for example, from an immigrant family) is entitled to learn his native language from the first grade.
In the lower grades, subjects are combined (chemistry with physics and biology, language with literature) and home economics is taught to everyone, regardless of gender. They write a lot in the school: all kinds of essays are designed to teach the child to have his own opinion on each issue and to express it in literary language.
After graduating from school, a young person can continue his studies at a gymnasium, where his studies end with an examination for a matriculation certificate, or enter a secondary vocational educational institution.
As of 2013, 358 higher educational institutions operated in Eastarland: 174 universities, 180 specialized institutes (they study technology, business and economics, art), and 4 military academies.
Higher education, like primary education, is completely free for citizens of the country, as well as exchange students. For other groups of students, paid tuition has been introduced since 2016, the cost of which will be ~ 4 thousand ducats per year.
Largest Cities
Largest cities or towns in Eastarland
Federal Royal Committee of Statistics (FRCS) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | State | Pop. | Rank | State | Pop. | ||||
 Labunavos  Hansakanls |
1 | Labunavos | Jurbarkas | 3,336,187 | 11 | Janušava | Rautensey | 1,632,331 |  Kristianpils  Honkala |
| 2 | Hansakanls | Capital City | 3,170,613 | 12 | Užukalniai | Zhuklia | 1,520,596 | ||
| 3 | Kristianpils | Selia | 3,149,700 | 13 | Ābrene | Abrene | 1,037,828 | ||
| 4 | Honkala | Taavetti | 2,925,059 | 14 | Ternopol | Lusivets | 1,019,594 | ||
| 5 | Čedasai | Jurbarkas | 2,643,167 | 15 | Giloyne | Gubray | 976,493 | ||
| 6 | Liepāpils | Kulaiga | 2,189,359 | 16 | Brandö | Brandow | 719,219 | ||
| 7 | Preiļīņās | Selia | 2,064,065 | 17 | Visulahti | Kieriniki | 654,111 | ||
| 8 | Torņukalns | Baltesia | 2,028,763 | 18 | Laha | Koppola | 629,892 | ||
| 9 | Villikkala | Suodenniemi | 1,886,851 | 19 | Reisu | Vanhamoisio | 383,502 | ||
| 10 | Lepšiškė | Rautensey | 1,879,265 | 20 | Jūrāva | Jurkrasts | 307,875 | ||
State structure
Administrative division
Eastarland is a federal Empire made up of 20 States (Stater): 18 Monarchies, the Governor-Generalship of Lusivets and the Hansakalns Capital Region. There are 3 Kingdoms, 2 Principalities, 5 Grand Duchies, 8 Duchies in Eastarland. States can be divided into districts (Novads), districts into cities and communities (Kopienas), some communities into urban areas (Pilsētas). Communities are the main units of local administration. The city of Hansakalns is also considered a region, but its institutions are different from those of the States: the city council acts as the regional legislature, and the mayor acts as the elected representative. Each of the States has its own budget and independence in its allocation.
|
|
| State | Capital city | Largest city | Population (2020) |
GDP (Billions) |
GDP (Per capita) |
Leader | Native name | Area km2 |
Density | Language |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republics | ||||||||||
| Capital city | Capital city | 3,170,613 | 172.1 | 54,280 | Mayor Ilze Laiviņa | Hansakanls | x | x | Letian | |
| Ternopol | Ternopol | 3,880,667 | 92.2 | 23,759 | Governor-General Deinis Melderis | Лузивец | x | x | Lusivetian | |
| Kingdoms | ||||||||||
| Labunavos | Labunavos | 12,866,655 | 684.1 | 53,168 | Queen Daina I | Jurbarkas | x | x | Levurian | |
| Kristianpils | Kristianpils | 14,277,700 | 786.3 | 55,071 | King Armīns VI | Selija | x | x | Letian | |
| Honkala | Honkala | 9,260,741 | 436.8 | 52,566 | King Mattias II | Taavettimaa | x | x | Trondian | |
| Principalities | ||||||||||
| Torņukalns | Torņukalns | 3,042,138 | 204.7 | 67,288 | Prince Ainārs II | Baltēzija | x | x | Letian | |
| Visulahti | Visulahti | 4,114,655 | 203.0 | 49,336 | Prince Mattias XII | Kierinikimaa | x | x | Trondian | |
| Grand Duchies | ||||||||||
| Ābrene | Ābrene | 4,251,768 | 270.4 | 63,597 | Grand Duke Kristians V | Ābrene | x | x | Letian | |
| Jūrāva | Jūrāva | 3,149,307 | 130.1 | 41,311 | Grand Duke Maris I | Jūrkrasts | x | x | Letian | |
| Kulaiga | Kulaiga | 4,987,343 | 213.0 | 42,708 | Grand Duke Ēriks III | Kulaiga | x | x | Letian | |
| Lepšiškė | Lepšiškė | 5,759,470 | 269.8 | 46,845 | Grand Duchess Paulina I | Rautensee | x | x | Levurian | |
| Rubikiai | Rubikiai | 5,604,678 | 264.6 | 47,210 | Grand Duke Algimantas VI | Žaliūkė | x | x | Levurian | |
| Duchies | ||||||||||
| Brandö | Brandö | 3,342,112 | 129.5 | 38,748 | Duke Peeter IV | Brandömaa | x | x | Trondian | |
| Baltriškių | Giloyne | 3,113,008 | 211.0 | 51,718 | Duchess Gražina III | Gubriai | x | x | Levurian | |
| Laha | Laha | 2,093,579 | 113.1 | 54,022 | Duke Taavi I | Koppolamaa | x | x | Trondian | |
| Salmi | Salmi | 2,250,811 | 126.4 | 56,158 | Duke Aivars IV | Kūršija | x | x | Letian | |
| Līnezers | Līnezers | 1,966,218 | 95.7 | 48,672 | Duchess Alexandra V | Lacidens | x | x | Letian | |
| Villikkala | Villikkala | 3,884,460 | 249.0 | 64,102 | Duke Jaakob VII | Suodenniemi | x | x | Trondian | |
| Reisu | Reisu | 1,952,109 | 83.7 | 42,877 | Duke Raimond VI | Vanhamoisio | x | x | Trondian | |
| Užukalniai | Užukalniai | 4,460,321 | 285.7 | 64,053 | Duke Petras III | Žuklija | x | x | Levurian | |
Government
Eastarland is a federal constitutional monarchy. The main law of the state is the constitution (Satversme), adopted on May 17, 1855. It regulates the functioning of the Empire's authorities: it establishes a monarchical constitutional-parliamentary form of government.
The political structure of Eastarland consists of the Monarch of the Eastarland, who is the head of state, the Prime Minister of Eastarland, the government, the head of which is the Prime Minister, the parliament, which consists of two chambers: the Seima and the Senate, and the Constitutional Council.
At the local level, power is represented by the leadership of the Kingdoms, Principalities, Grand Duchies and Duchies, counties, and communes.
Constitution
The Constitution (Satversme) of Eastarland regulates the relationship between the legislative and executive branches, and also enshrines the fundamental rights and freedoms of citizens. The constitution consists of four basic laws:
The Form of Government Act guarantees citizens the right to hold demonstrations, form political parties and practice their religion.
The Act of Succession defines the rights of members of the Farenburg dynasty to the Eastarland throne.
The Freedom of the Press Act establishes the principles of an open society and guarantees general access to official information. According to it, anyone has the right to access the documents of the Kejsarstag, the government and other state bodies, including any financial statements. Another important principle of the Freedom of the Press Act is freedom of information transfer, which means that Eastarland citizens have the right to provide any information to the media. At the same time, a journalist or publisher has no right to disclose his source if the person who provided it wishes to remain anonymous.
The Freedom of Expression Act, which came into force in 1992, largely reflects the principles already enshrined in the Freedom of the Press Act, such as the unconditional prohibition on censorship, freedom of transfer of information and the right to anonymity.
The provisions of the Constitution take precedence over all other legislative acts, and no law can contradict it. In order to amend the Constitution (Satversme), the Seima must adopt it in two readings - before and after the next parliamentary elections.
Executive power
The head of state and the head of the executive branch of government is the Monarch of the Eastarland, currently Armīns VI. In Eastarland, the Prime Minister is responsible for current domestic and economic policy and has the authority to issue general decrees. He is considered to be responsible for government policy. The Prime Minister directs government activities and enforces laws.
The Prime Minister is appointed by the monarch. The confirmation of his candidacy by the States General is not required, since the Seima has the right to declare a vote of no confidence in the government at any time. Usually the Prime Minister represents the party with the majority of seats in the Seima. The Prime Minister draws up a list of ministers in his cabinet and submits it to the Monarch for approval.
The Prime Minister initiates the adoption of laws in the Seima and ensures their implementation, he is also responsible for national defense. The Prime Minister replaces the Monarch as Chairman of Councils and Committees.
Since July 2, 2019, the government is headed by Ieva Ulmania.
Legislature
Legislative power in Eastarland belongs to the States General, which includes two chambers - the Senate and the Seima.
The Senate, whose members are elected by indirect universal suffrage, consists of 350 senators. Senators are elected for four-year terms by the members of the States councils (Valsts Seima) every four years following elections to the States councils. The last Senate elections were held on September 6, 2019. The President of the Senate is Allar Eskola.
The Seima consists of 500 deputies, whose deputies are elected on the basis of direct universal suffrage for a period of 4 years, therefore, in case of leaving the party, a deputy can remain independent or join another. The last elections for the Seima deputies took place on June 12, 2019. The Chairman of the Seima is Marija Česnauskaite.
In addition to their function of overseeing government activities, both chambers develop and pass laws. In case of disagreement, the final decision rests with Seima.
Judicial branch
The highest court in criminal and civil justice is the Supreme Court in Selia. One step below are the Highest Land Courts (hereinafter land courts and the lowest level of the judicial system - district courts).
The highest court of administrative justice is the Administrative Court in Labunavos, the courts of appeal of administrative justice are the Supreme Administrative Courts in Baltesia, Gubray and Kierinki are the administrative courts of justice, the courts of first instance of administrative justice are the administrative courts.
The highest court of labor justice is the Labor Court, the courts of appeal of labor justice are land labor courts, and the courts of first instance of labor justice are labor courts.
The highest court of social justice is the Social Court, the courts of appeal of social justice are the land social courts (one for each land), the courts of first instance of social justice are the social courts.
The highest court of financial justice is the Financial Court in Lepšiškė, the state financial courts are the financial courts.
There is also a copyright court - a Patent Court, an official discipline court.
Prosecutorial oversight bodies are the Prosecutor General under the Supreme Court, Prosecutors General of Lands, prosecutors of district courts.
Migration policy
After a series of terrorist acts in the world, the government has consistently tightened immigration laws. Anti-immigration measures have significantly reduced the inflow of certain categories of migrants to Eastarland. In particular, in 2018, 4198 entry permits for family reunification were issued, which is 70% less than in 2013, and 1038 people were granted political asylum (82.5% less). At the same time, over the period 2013-2018, the number of those who received a study visa increased from 10 to 28.4 thousand people (an increase of 2.8 times), and those who entered on a work visa - from 5.9 to 12.8 thousand people (an increase 100%). In 2019, the measures were further tightened - in particular, a point system was introduced for spouses of immigrants wishing to enter the country.
Economy
Industry
Extraction of iron and uranium ores, bauxite is carried out. Leading manufacturing industries are mechanical engineering, including automotive, electrical and electronic (TVs, washing machines, etc.), aviation, shipbuilding (tankers, sea ferries) and machine tools. Eastarland is one of the world's largest manufacturers of chemical and petrochemical products (including synthetic rubber, plastics, mineral fertilizers, pharmaceuticals and others), ferrous and non-ferrous (aluminum, lead and zinc) metals. Eastarlandian clothing and footwear, jewelry, cheeses are well known in the world market (about 700 varieties are produced).
Agriculture
Eastarland has a highly productive agriculture. It occupies a leading position in the world in terms of agricultural production, grain production, livestock products and milk. Eastarland is a land of predominantly small family farms. Agricultural production efficiency is very high. At the same time Eastarland lags behind in the average yield of corn and sugar beet. In the agro-industrial complex, agriculture plays a subordinate role.
Livestock breeding provides about 70% of marketable agricultural products. Cattle breeding is the main branch of animal husbandry, it provides more than 2/5 of all marketable agricultural products, with the main part being milk (about ¼). Pig breeding is in second place. The country's self-sufficiency in milk and beef systematically exceeds 100%, but in pork it is less than 4/5.
Dairy and beef cattle breeding is most typical for well-moistened coastal areas, rich in meadows and pastures, as well as for the periphery of urban agglomerations. Due to the rather cold winter, stall keeping is common. Pig breeding is developed everywhere, but especially in areas close to the ports of import of imported feed, areas of sugar beet, potato and fodder root crops cultivation. Broiler production, production of eggs, veal, and pig breeding are concentrated in large livestock farms, the location of which depends little on natural factors. There are much more fodder crops than food crops, since a large amount of fodder grains, especially corn, are imported. However, the country ranked (2014) seventh in the world in terms of wheat exports (8.2 million tons). Of great importance is the cultivation of fodder root crops (fodder beets, etc.), corn for green fodder and silage, alfalfa, clover and other fodder grasses. Of the oilseeds, the most important is rapeseed, the crops of which are more than 10 times higher than those of sunflower.
In areas with high natural soil fertility, the main crops are wheat, barley, maize and sugar beets. The poorer soils of the Northern Lowland and the middle-altitude mountains are traditionally used for sowing rye, oats, potatoes and natural forage crops. The traditional nature of Eastarland agriculture has significantly changed technological progress. Today, the so-called light soils are valued more, due to their suitability for machine cultivation, using artificial fertilizers; for example, corn is now widely cultivated in the Northern Lowlands, where it replaces potatoes.
Viticulture surpasses, in marketable products, fruit growing and vegetable growing combined. Vineyards are located mainly in the valleys of Gaudava, Tekkava and other rivers.
Tourism
Tourism as a sector of the economy has made a significant contribution to the national economy, generating revenue of 452.361 billion ducats, or 9.1% of Eastarland's GDP in 2020. It is also an important source of employment in urban areas and, to a lesser extent, in rural areas. Of the 19,562 villages and towns in Eastarland, approximately 500 are registered with some form of travel agency, and 41 of these are recognized resorts and seaside resorts. 10,281 museums, 537 theaters, 11 amusement parks, over 700,000 kilometers of hiking trails and 571,000 kilometers of bike paths, as well as numerous special thematic trails (Tematiskās takas) are all accessible and accessible for tourism activities.
The country is home to a number of well-known cultural, iconic and ecological tourism destinations. Hansakalns and Labunavos are the top tourist destinations in Eastarland, attracting up to 10.6 million tourists in 2010; The most popular attractions are the States General Building, the Hansakalns Zoo (Zooloģiskais dārzs), the Ziemaspils Old Royal Winter Palace in Čedasai, the Cathedral of St. Laura and St. Jakobs in Labunavos, the National Opera of Jozefs Krūmiņ in Hansakalns and the Brūnapils Palace in Čedasai. Other major tourist destinations in Eastarland include Palace of Karlis Rozītis in Zhuklia, Nožogojpilis Palace in Čedasai, Princis Ārens Parks in Abrene and National Park in Taavetti, the Paipis beach in Kierinki, as well as old towns, city centers: Labunavos, Hansakalns, Čedasai, Abrene, Kurona, Rautensey, Vanhamoisio and Koppola.
Attractions
Extractive industry
Forests make up more than 20% of the territory. There are 79 tree species in the Eastarland.
Eastarland has significant reserves of iron ore, uranium ores, bauxite, potash and rock salts, coal, zinc, copper, lead, nickel, oil, timber. The main coal mining regions are Gubray and the Kulaiga coal basins. Eastarland proven brown coal reserves were 40.5 billion tonnes. Since 1994, imports of coal have exceeded production. Gas production does not exceed 3 billion m³. One of the largest Eastarland gas fields is Ropa in Suodenniemi. "East Oil&Gas" is one of the largest gas and oil companies in Eastarland. The main activities of the company are exploration, production, marketing and distribution of natural gas and oil.
Transport and Energy
Transport
Railway transport Eastarland rail transport is highly developed. Local and overnight trains, including high-speed trains, connect the capital with all major cities in the country, as well as with neighboring countries. The speed of these trains is 320 km / h. The railway network is 51,850 km long and is one of the longest railway networks. Rail links exist with all neighboring countries. Metro is available in Hansakanls, Labunavos, Honkala, Kristianpils, Čedasai. In Lāčupils partly underground light rail.
Automobile transport
After winning the 2016 elections in Seima, and forming a majority coalition with the Peasant Union, the Green Party banned all non-electric cars. Also, the cost of roads was reduced, but more attention was paid to public transport, railways, etc. The road network does not cover the entire territory of the country. The total length of highways is 610,500 km.
The main roads are divided into the following groups:
Motorways - The name of the road is made up of the letter A followed by the road number. Permissible speed - 130 km / h, obligatory filling stations every 50 km, concrete dividing strip, absence of traffic lights, pedestrian crossings.
National roads - prefix N. Permissible speed - 90 km / h (if there is a concrete dividing strip - 110 km / h).
Department roads - prefix D. Permissible speed - 90 km / h.
In cities, the permissible speed is 50 km / h. The use of seat belts is mandatory. Children under 10 years old must be transported in special seats.
Air transport Eastarland has about 475 airports. 325 of them have asphalt or concrete runways, and the remaining 150 are unpaved (data for 2017). The largest airport is the «Princis Raimonds» located in the suburbs of Hansakanls. The national Eastarlandian airline «EastarAir» operates flights to almost every country in the world.
Energy
About 99% of the country's population is supplied with electricity. National electricity needs are met almost entirely at the expense of our own capacities; a small part of the electricity produced is exported.
Most of the electricity - 67.79% - is generated at thermal power plants, including 44.9% using coal, 26.5% - oil and 15.8% - natural gas. Hydroelectric power plants account for 20.35% of production, while nuclear power plants account for 11.80%. Solar energy accounts for about 0.03%. Less than 0.01% comes from wind farms.