Gmunenhochwald: Difference between revisions
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
===Government=== | ===Government=== | ||
====Executive=== | |||
Gmunenhochwald has a monarch as head of state and an elected parliament that enacts the law. The monarch, the Raugrave (Alemannisch: ''Raugraf'', feminine: ''Raugräfin'') retains substantial political authority. The Constitution of Gmunenhochwald was adopted in 1997 and significantly reduced the powers of the Raugrave and established the office of ''Staatskanzler'' (Anglic: "State Chancellor") as Prime Minister, abolishing the old office of ''Erzkanzler'' (Anglic: Archchancellor). This change meant that the Chancellor was no longer appointed by the Raugrave at their whim but chosen by the party that held the majority in the parliament, although they still had to gain the consent of the Raugrave. The parliamentary system had been established by the old constitution, adopted in 1961. | Gmunenhochwald has a monarch as head of state and an elected parliament that enacts the law. The monarch, the Raugrave (Alemannisch: ''Raugraf'', feminine: ''Raugräfin'') retains substantial political authority. The Constitution of Gmunenhochwald was adopted in 1997 and significantly reduced the powers of the Raugrave and established the office of ''Staatskanzler'' (Anglic: "State Chancellor") as Prime Minister, abolishing the old office of ''Erzkanzler'' (Anglic: Archchancellor). This change meant that the Chancellor was no longer appointed by the Raugrave at their whim but chosen by the party that held the majority in the parliament, although they still had to gain the consent of the Raugrave. The parliamentary system had been established by the old constitution, adopted in 1961. | ||
| Line 153: | Line 154: | ||
The executive authority of the government is vested in a collegiate government formed of the head of government, the State Chancellor, and ten ministers. The State Chancellor is chosen by the party that holds the majority, whilst the other ten are chosen by the parliament as a whole and appointed by the Raugrave. The ministers reflect the balance of parties in the parliament. The government is collectively responsible to the parliament, as well as individually. The parliament can approach the Raugrave to remove them individually or the government as a whole. | The executive authority of the government is vested in a collegiate government formed of the head of government, the State Chancellor, and ten ministers. The State Chancellor is chosen by the party that holds the majority, whilst the other ten are chosen by the parliament as a whole and appointed by the Raugrave. The ministers reflect the balance of parties in the parliament. The government is collectively responsible to the parliament, as well as individually. The parliament can approach the Raugrave to remove them individually or the government as a whole. | ||
====Legislature==== | |||
The bicameral ''Raugraflichetag'' (Anglic: "Raugrave's Assembly") holds legislative authority in the Raugraviate. It is split up into two houses, the upper Hirtenrat and the lower Schäferrat. The ''Hirtenrat'' (Anglic: "Herders' Council") consists of 20 members of the state's nobility, who hold their positions due to feudal rights. The ''Schäferrat'' (Anglic: "Shepherds' Council") consist of 120 members, and are elected by the wider population of the state itself, using a first-past-the-post system. Elections are held every five years and two members are elected from each of the electoral districts of the state. Candidates for elections must be put before the Raugrave and the Hirtenrat, who then approve or reject them. The Schäferrat, whether a single party if it holds a majority or a coalition of parties if one does not, proposes a government to the Raugrave, who then approves it. Legislation is proposed in a similar manner - the government proposes legislation to the Schäferrat, where it must be voted on and then it is put before the Raugrave, who can then accept or reject it. The Hirtenrat acts in an oversight manner, as they are able to review any potential legislation before it is put before the Raugrave, either passing it through or requiring changes made. Once changes have been made, it goes back to the Schäferrat to be voted on again. | The bicameral ''Raugraflichetag'' (Anglic: "Raugrave's Assembly") holds legislative authority in the Raugraviate. It is split up into two houses, the upper Hirtenrat and the lower Schäferrat. The ''Hirtenrat'' (Anglic: "Herders' Council") consists of 20 members of the state's nobility, who hold their positions due to feudal rights. The ''Schäferrat'' (Anglic: "Shepherds' Council") consist of 120 members, and are elected by the wider population of the state itself, using a first-past-the-post system. Elections are held every five years and two members are elected from each of the electoral districts of the state. Candidates for elections must be put before the Raugrave and the Hirtenrat, who then approve or reject them. The Schäferrat, whether a single party if it holds a majority or a coalition of parties if one does not, proposes a government to the Raugrave, who then approves it. Legislation is proposed in a similar manner - the government proposes legislation to the Schäferrat, where it must be voted on and then it is put before the Raugrave, who can then accept or reject it. The Hirtenrat acts in an oversight manner, as they are able to review any potential legislation before it is put before the Raugrave, either passing it through or requiring changes made. Once changes have been made, it goes back to the Schäferrat to be voted on again. | ||
The 1997 Constitution abolished all property requirements to be eligible to vote, lowered the voting age to 18, gave women the right to vote. To be eligible to vote, a person needs to be a registered resident of the Raugraviate, as well as not having any criminal convictions from anywhere in Dolchland. In order to be able to stand for election, a person needs to own a house of least two bedrooms and a hearth. Previously, a herd of at least ten cows and a bull or fifty sheep was also necessary. | The 1997 Constitution abolished all property requirements to be eligible to vote, lowered the voting age to 18, gave women the right to vote. To be eligible to vote, a person needs to be a registered resident of the Raugraviate, as well as not having any criminal convictions from anywhere in Dolchland. In order to be able to stand for election, a person needs to own a house of least two bedrooms and a hearth. Previously, a herd of at least ten cows and a bull or fifty sheep was also necessary. | ||
====Judiciary==== | |||
Within the state, the ''Raugraflichegericht'' (Anglic: "Raugrave's Court") is the highest judicial authority. It plays both a constitutional role, as it rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution of the state, as well as acting as the highest court of criminal and civil appeal with the Raugraviate. Its members are chosen by the Raugrave from candidates selected by the ''Raugraflichetag'' and are usually the most experienced lawyers and judges in the state. Below the Raugrave's Court is the ''Staatgericht'', the State Court and below them the Regional Courts. These act in both criminal and civil cases, in line with the constitutional and laws of the state. | |||
===Districts=== | ===Districts=== | ||
Revision as of 20:50, 19 November 2021
Raugraviate of Gmunenhochwald Raugrafschaft auf Gmunenhochwald (Alemannisch) | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
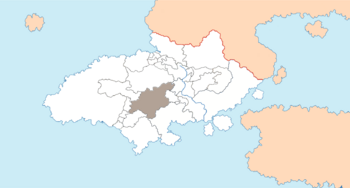 Gmunenhochwald within Dolchland. | |
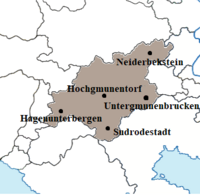 Map of Gmunenhochwalden | |
| Capital | Untergmunenbrucken |
| Official languages | Alemannisch |
| Demonym(s) | Gmunenhochwalder |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy |
• Raugrave | Ernst Klemens VI |
• Staatanzler | Johann-Heinrich von Altenheim |
| Legislature | Raugrafstag |
| Hirtenrat | |
| Schäferrat | |
| Constituent State of Dolchland Semi-independent State | |
Gmunenhochwald, officially the Raugraviate of Gmunenhochwald (Alemannisch: Raugrafschaft auf Gmunenhochwald), is a semi-independent constituent state of Dolchland, in south-eastern Argis. It is located at almost the geographic centre of the country, between the two mountain ranges of $$$ and $$$. It borders the states of Greater Vethringen to the north, the Duchy of Gloschlick (an exclave of Panedonia), Randstadt and Witternen to east, the southern part of Panedonia to the south-east, Macklenover and Märzwald to the south and $$$ and $$$ to the west. Gmunenhochwald is a landlocked nation and it has no direct route to the coast. The Raugraviate has a population of $$$, which is mainly rural and is concentrated along the length of the river Gmune, although much of the population still lives amongst the valleys, upland fields and forests of the mountains themselves. The Gmune, which is fed by tributaries from the mountains, runs through the central valley and down through the country, forming a broad fertile floodplain in the east of the nation where it exits into Witternen. There are very few urban areas of any real size and most of these are clustered along the Gmune. The total area of the Raugraviate is $$$. The official language is Alemannisch, athough there are numerous different dialects spoken, some of them with very small geographic spreads, sometimes of only an isolated valley.
The Raugraviate is a unitary parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy, with the power of the Raugrave defined by the constitution, the $$$. The Raugrave does retain significant powers, however, with the ability to dismiss the government at will, as well as to define laws as they see fit. In practice, however, this is limited by the often personal relationship between the monarch and their government, as well as years of tradition and protocol. The current Raugrave is Ernst Klemens VI of the House of Hochgmunentorf, who has ruled the state since 1957. The capital and most populous city, Untergmunenbrucken, is in the south-east of the country, towards the Witternen border. It is the political, economic and cultural centre of the state and it has a population of $$$. The next most populous city is Niederbekstein in the north east, with a population of $$$. The other large cities are Sudrodestadt in the south, Hagenunterbergen in the west and Hochgmunentorf, which is also the seat of the House of Hochgmunentorf, in roughly the geographic centre of the state.
Gmunenhochwald has seen many thousands of years of human habitation. The earliest human remains and artefacts date from the end of the last Ice Age, forming groups of hunter-gathers with worked flint tools. The Dolchic peoples arrived in the Gmune Valley by 2000BCE and either pushed out or subsumed the native inhabitants. The small valleys, isolated plateaus and uplands formed tribal territories, which slowly coalesced into petty kingdoms. The south of Gmunenhochwald was a key battleground during the War of the Habstrian Succession, as the valley of the Gmune formed a major trade and transportation route across southern Dolchland. A force holding any one of the fortified cities of Untergmunenbrucken, Hochgmunentorf and Hagenunterbergen could close the valley to the opposing side, or at least force them into a costly siege. Since then, the Raugraviate has attempted to stay apart from imperial politics of Dolchland, especially since it borders two of the five kingdoms of Dolchland. During the Schlammburg Crisis, the young Raugraf Ernst Klemens attempted to distance himself from either side but, due to being bordered to the south and east by Panedonia, Gmunenhochwald was more drawn to the Panedonian side. Since then, Ernst Klemens has striven to maintain a steady course within Imperial politics.
The Raugraviate is a developing economy, with a GDP of $$$ and a per capita GDP of $$$, lagging behind the other, similarly sized Dolchland states. The state has a mixed economy and is predominantly based in the natural sector, with livestock and arable farming making up the largest parts of the economy. There is also a small heavy industrial sector, with some mining of iron and coal taking place within the $$$ mountains. Logging and other timber related activities also add to the economy. In the internal politics of Dolchland, Gmunenhochland is more aligned to Panedonia than Habstria when political differences between those two powerful states arise, but the state's government tries to keep itself aloof to them and act in the best interests of the empire as a whole. The state has few international contacts, primarily due to it being landlocked and no direct route beyond Dolchland's borders.
Etymology
Gmunenhochwald takes its name from the river Gmune, which runs roughly in a west to east direction through the country, before flowing out of the Raugraviate where the borders of Witternen and Panedonia meet. The river's name is thought to derive from a possessive variation of Gmu, a proto-Dolchic river god and personification of the river itself. The latter parts of the name refers to the high forests that dominate the flanks of the mountains that rise above the river's northern and southern banks.
The river's name is also seen in the names of many of the important and lesser settlements within the state, such as Untergmunenbrucken ("Bridge over the lower reaches of the Gmune") and Hochgmunentorf ("Village high above the Gmune"), the latter of which is also from where the ruling house takes its name.
The title of the ruler of Gmunenhochwald is also unique amongst the states of Dolchland. The title derives its name from the properties of the land itself, coming from the its "raw" (Alemannisch: Rau) nature of the terrain, the rough and rugged mountains, isolated valleys, deep forests and windswept moors. This was then appended to the common title of Graf.
Geography
History
Politics
Government
=Executive
Gmunenhochwald has a monarch as head of state and an elected parliament that enacts the law. The monarch, the Raugrave (Alemannisch: Raugraf, feminine: Raugräfin) retains substantial political authority. The Constitution of Gmunenhochwald was adopted in 1997 and significantly reduced the powers of the Raugrave and established the office of Staatskanzler (Anglic: "State Chancellor") as Prime Minister, abolishing the old office of Erzkanzler (Anglic: Archchancellor). This change meant that the Chancellor was no longer appointed by the Raugrave at their whim but chosen by the party that held the majority in the parliament, although they still had to gain the consent of the Raugrave. The parliamentary system had been established by the old constitution, adopted in 1961.
The reigning Raugrave is the Head of State and represents the state in the [Dolchland Imperial Diet], as well as every other interstate forum where Gmunenhochwald's interests need to be represented. The Raugrave may veto any laws adopted by the parliament, as well as call referendums, propose new legislation and dissolve parliament as they see fit.
The executive authority of the government is vested in a collegiate government formed of the head of government, the State Chancellor, and ten ministers. The State Chancellor is chosen by the party that holds the majority, whilst the other ten are chosen by the parliament as a whole and appointed by the Raugrave. The ministers reflect the balance of parties in the parliament. The government is collectively responsible to the parliament, as well as individually. The parliament can approach the Raugrave to remove them individually or the government as a whole.
Legislature
The bicameral Raugraflichetag (Anglic: "Raugrave's Assembly") holds legislative authority in the Raugraviate. It is split up into two houses, the upper Hirtenrat and the lower Schäferrat. The Hirtenrat (Anglic: "Herders' Council") consists of 20 members of the state's nobility, who hold their positions due to feudal rights. The Schäferrat (Anglic: "Shepherds' Council") consist of 120 members, and are elected by the wider population of the state itself, using a first-past-the-post system. Elections are held every five years and two members are elected from each of the electoral districts of the state. Candidates for elections must be put before the Raugrave and the Hirtenrat, who then approve or reject them. The Schäferrat, whether a single party if it holds a majority or a coalition of parties if one does not, proposes a government to the Raugrave, who then approves it. Legislation is proposed in a similar manner - the government proposes legislation to the Schäferrat, where it must be voted on and then it is put before the Raugrave, who can then accept or reject it. The Hirtenrat acts in an oversight manner, as they are able to review any potential legislation before it is put before the Raugrave, either passing it through or requiring changes made. Once changes have been made, it goes back to the Schäferrat to be voted on again.
The 1997 Constitution abolished all property requirements to be eligible to vote, lowered the voting age to 18, gave women the right to vote. To be eligible to vote, a person needs to be a registered resident of the Raugraviate, as well as not having any criminal convictions from anywhere in Dolchland. In order to be able to stand for election, a person needs to own a house of least two bedrooms and a hearth. Previously, a herd of at least ten cows and a bull or fifty sheep was also necessary.
Judiciary
Within the state, the Raugraflichegericht (Anglic: "Raugrave's Court") is the highest judicial authority. It plays both a constitutional role, as it rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution of the state, as well as acting as the highest court of criminal and civil appeal with the Raugraviate. Its members are chosen by the Raugrave from candidates selected by the Raugraflichetag and are usually the most experienced lawyers and judges in the state. Below the Raugrave's Court is the Staatgericht, the State Court and below them the Regional Courts. These act in both criminal and civil cases, in line with the constitutional and laws of the state.
