Mulak Empire: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Mulak Empire''', also known as the '''Mulakan Empire''' or the '''Mulāk Empire''', and at the time known as the '''Empire of Two Abodes''', | The '''Mulak Empire''', also known as the '''Mulakan Empire''' or the '''Mulāk Empire''', and at the time known as the '''Empire of Two Abodes''', [[Rha]]:''Thaichhati''. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of [[Cúbūmā]], written also as ''Khubwihmah''. The [[History of Rhava|Mulak civilization]] arose from the Rhavanese central mountains sometime in 331 AD. The Mulak Empire collapsed in 558 AD. | ||
From 331-558, the Mulakans incorporated a large portion of Indonadisi, centered on the [[Camdong Plateau|Khamdong Plateau]]. At its largest, the kingdom contained parts of [[Rhava]], [[Kharai]], and [[Ngoc Luat]]. Its official language was [[Standard Rha|Rha]], while it also used an early form of [[Kham Rha]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.tourmasyidinh.org/blog/rha-language-mulakan|title=Language of Thaichhati|date=17 October 2002}}</ref> Notable features of the Mulak Empire included its monumental [[Rha architecture|architecture]], unique to the ethnic [[Rhavanese Ethnicities|Kham Rha]] people, to succeed in the central-rhavanese enviroment, Rhavanese [[Beang Khāmkhe]] bracelets, associated with Sichaeng Baci, and the elaborate caste system. | From 331-558, the Mulakans incorporated a large portion of Indonadisi, centered on the [[Camdong Plateau|Khamdong Plateau]]. At its largest, the kingdom contained parts of [[Rhava]], [[Kharai]], and [[Ngoc Luat]]. Its official language was [[Standard Rha|Rha]], while it also used an early form of [[Kham Rha]].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.tourmasyidinh.org/blog/rha-language-mulakan|title=Language of Thaichhati|date=17 October 2002}}</ref> Notable features of the Mulak Empire included its monumental [[Rha architecture|architecture]], unique to the ethnic [[Rhavanese Ethnicities|Kham Rha]] people, to succeed in the central-rhavanese enviroment, Rhavanese [[Beang Khāmkhe]] bracelets, associated with Sichaeng Baci, and the elaborate caste system. | ||
Revision as of 00:36, 4 June 2022
Empire of Two Abodes (Mulak Empire) Thaichhati (Rha)
| |
|---|---|
| 331 AD–$$$ | |
|
Flag | |
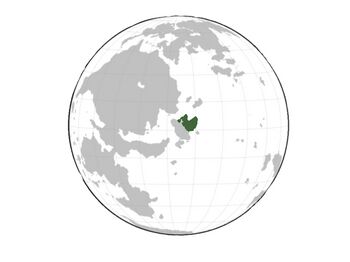 Mulak Empire at greatest extent | |
| Capital | Cúbūmā ($$$) |
| Official languages | Standard Rha |
| Common languages | Rawang, Nhai, Kham Rha family, Sokhaos, Linh, Sichaeng and scores of smaller languages. |
| Religion | Bikåmmā |
| Government | absolute monarchy |
| Mâhåt Rhā | |
• 331-$$$ | Pheihavànphê Sâthōu |
• $$$ | Thú Khōnkhumthat |
• $$$ | TBD |
• $$$-558 | Khedôki Vaisālib |
| Historical era | Pre-Colonial era |
• Pheihavànphê Sâthōu created the Thaichhati | 331 AD |
• TBD | $$$ |
• TBD | $$$ |
• TBD | $$$ |
| Area | |
| $$$$$$ | [convert: invalid number] |
The Mulak Empire, also known as the Mulakan Empire or the Mulāk Empire, and at the time known as the Empire of Two Abodes, Rha:Thaichhati. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of Cúbūmā, written also as Khubwihmah. The Mulak civilization arose from the Rhavanese central mountains sometime in 331 AD. The Mulak Empire collapsed in 558 AD.
From 331-558, the Mulakans incorporated a large portion of Indonadisi, centered on the Khamdong Plateau. At its largest, the kingdom contained parts of Rhava, Kharai, and Ngoc Luat. Its official language was Rha, while it also used an early form of Kham Rha.[1] Notable features of the Mulak Empire included its monumental architecture, unique to the ethnic Kham Rha people, to succeed in the central-rhavanese enviroment, Rhavanese Beang Khāmkhe bracelets, associated with Sichaeng Baci, and the elaborate caste system.
- ↑ "Language of Thaichhati". 17 October 2002.
