1935 Weranian federal election: Difference between revisions
Britbong64 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Britbong64 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
The '''22<sup>nd</sup> federal election''' was held in the [[Werania|Weranian Confederation]] for the [[House of Deputies (Werania)|House of Deputies]] (the lower house of the [[Bundestag of Werania|Bundestag]]) on the 17<sup>th</sup> April 1935. All 584 members of the House of Deputies were elected under a system of {{wp|proportional representation}} with each ''{{wp|regierungsbezirke}}'' treated as an electoral districts. The elections were the first held in almost a decade as elections had been suspended during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. | The '''22<sup>nd</sup> federal election''' was held in the [[Werania|Weranian Confederation]] for the [[House of Deputies (Werania)|House of Deputies]] (the lower house of the [[Bundestag of Werania|Bundestag]]) on the 17<sup>th</sup> April 1935. All 584 members of the House of Deputies were elected under a system of {{wp|proportional representation}} with each ''{{wp|regierungsbezirke}}'' treated as an electoral districts. The elections were the first held in almost a decade as elections had been suspended during the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. | ||
The first election held under {{wp|universal suffrage}} (with women being granted the vote five months prior to the election) the 1935 election saw the wartime coalition of the [[Catholic Social Party (Werania)|Catholic]], [[National Liberal Party (Werania)|National Liberals]], [[Social Democratic Party of Werania|Social Democrats]], [[Radical Party (Werania)|Radicals]] and the [[Centre Party (Werania)|Agrarians]] (the | The first election held under {{wp|universal suffrage}} (with women being granted the vote five months prior to the election) the 1935 election saw the wartime coalition of the [[Catholic Social Party (Werania)|Catholic]], [[National Liberal Party (Werania)|National Liberals]], [[Social Democratic Party of Werania|Social Democrats]], [[Radical Party (Werania)|Radicals]] and the [[Centre Party (Werania)|Agrarians]] (the [[Constitutionalist Bloc]]) under [[Premier of Werania|premier]] [[Otto Röttgen]] splinter on the issue of post-war reconstruction. In particular there was within the coalition opposition to the [[Leopoldism|Leopoldist]] programme of premier Röttgen with some accusing Röttgen and [[Leopold IV of Werania|Leopold IV]] of attempting to create a {{wp|dictatorship}}. Nevertheless Röttgen was popular due to his wartime leadership and aimed to secure a firm mandate to implement post-war reforms. | ||
The wartime abolition of Ruttish parties meant that this was the first Weranian election in decades contested purely by federal parties. The abolition of Ruttish parties and the increased influence of the leftists in [[Euclea]] benefitted the [[Weranic Section of the Workers' International]]. The OSAI supported the notion of entering the government for the first time since its split in 1920 but refused to cooperate with Röttgen. | The wartime abolition of Ruttish parties meant that this was the first Weranian election in decades contested purely by federal parties. The abolition of Ruttish parties and the increased influence of the leftists in [[Euclea]] benefitted the [[Weranic Section of the Workers' International]]. The OSAI supported the notion of entering the government for the first time since its split in 1920 but refused to cooperate with Röttgen. | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
The government introduced several changes prior to the election however. The seats in the chamber were reduced from 621 to 584, making a majority in the chamber 293 deputies. The government also passed {{wp|women's suffrage}} granting women the right to vote for the first time in Weranian history. The measure was the result of rare cooperation between the Catholics and socialists who were seen as the most likely beneficiaries. In addition the voting age was lowered from 25 to 20. | The government introduced several changes prior to the election however. The seats in the chamber were reduced from 621 to 584, making a majority in the chamber 293 deputies. The government also passed {{wp|women's suffrage}} granting women the right to vote for the first time in Weranian history. The measure was the result of rare cooperation between the Catholics and socialists who were seen as the most likely beneficiaries. In addition the voting age was lowered from 25 to 20. | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
The election occurred in the aftermath of the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]] which changed the political landscape of Werania. Prior to the war Werania had undergone a period of political instability with anti-parliamentarian parties such as the {{wp|national syndicalism|national syndicalist}} [[Weranic Syndicalist Union]] undermining Weranian democracy. The presence of these parties alongside the {{wp|Cordon sanitaire (politics)|cordon sanitaire}} around the [[Weranic Section of the Workers' International]] meant that governments often became unwieldy coalitions of the so-called "constitutionalist parties" (the [[Catholic Social Party (Werania)|Catholics]], [[National Liberal Party (Werania)|National Liberals]], [[Social Democratic Party of Werania|Social Democrats]], [[Radical Party (Werania)|Radicals]] and the [[Centre Party (Werania)|Agrarians]]). At the outbreak of war however the government banned the anti-parliamentarian parties whilst forming a {{wp|national unity government}} in support of the war effort | The election occurred in the aftermath of the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]] which changed the political landscape of Werania. Prior to the war Werania had undergone a period of political instability with anti-parliamentarian parties such as the {{wp|national syndicalism|national syndicalist}} [[Weranic Syndicalist Union]] undermining Weranian democracy. The presence of these parties alongside the {{wp|Cordon sanitaire (politics)|cordon sanitaire}} around the [[Weranic Section of the Workers' International]] meant that governments often became unwieldy coalitions of the so-called "constitutionalist parties" (the [[Catholic Social Party (Werania)|Catholics]], [[National Liberal Party (Werania)|National Liberals]], [[Social Democratic Party of Werania|Social Democrats]], [[Radical Party (Werania)|Radicals]] and the [[Centre Party (Werania)|Agrarians]]). At the outbreak of war however the government banned the anti-parliamentarian parties whilst forming a {{wp|national unity government}} in support of the war effort. The OSAI was split on the war question although its most prominent personality, Aurimas Kreickamas, supported the war on anti-functionalist grounds. | ||
As the war neared its end the matter of the post-war settlement begun to enter the Weranian political discourse. The socialists had been gaining in popularity both due to increased [[Valduvia]]n influence and a shift by the socialists towards assimilating patriotism and reverence for the army into their political discourse, notions they had previously belittled. To counter this the monarch [[Leopold IV of Werania|Leopold IV]] and the [[Premier of Werania|premier]] [[Otto Röttgen]] formulated a political programme, [[Leopoldism]], that sought to introduce moderate social reform whilst centralising governmental control and limiting parliamentary democracy. | As the war neared its end the matter of the post-war settlement begun to enter the Weranian political discourse. The socialists had been gaining in popularity both due to increased [[Valduvia]]n influence and a shift by the socialists towards assimilating patriotism and reverence for the army into their political discourse, notions they had previously belittled. To counter this the monarch [[Leopold IV of Werania|Leopold IV]] and the [[Premier of Werania|premier]] [[Otto Röttgen]] formulated a political programme, [[Leopoldism]], that sought to introduce moderate social reform whilst centralising governmental control and limiting parliamentary democracy. | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
The 1925-1929 legislative term had technically elapsed in 1929 but was extended for another four years twice, in 1929 and 1933. Röttgen and Leopold IV both supported holding an election when the legislative extension expired in 1937 due to the belief that an earlier election would benefit the socialists due to the poor social conditions. The governments post-war reconstruction scheme, the Bader-Fritz Plan, had only begun to take effect and wartime devastation still afflicted the country. Röttgen privately aimed to dissolve the Bundestag following the conclusion of peace treaties with [[Gaullica]] and [[Shangea]] in order to take advantage of post-war triumphalism. | The 1925-1929 legislative term had technically elapsed in 1929 but was extended for another four years twice, in 1929 and 1933. Röttgen and Leopold IV both supported holding an election when the legislative extension expired in 1937 due to the belief that an earlier election would benefit the socialists due to the poor social conditions. The governments post-war reconstruction scheme, the Bader-Fritz Plan, had only begun to take effect and wartime devastation still afflicted the country. Röttgen privately aimed to dissolve the Bundestag following the conclusion of peace treaties with [[Gaullica]] and [[Shangea]] in order to take advantage of post-war triumphalism. | ||
However the continual postponement of elections sat uneasily with Röttgen's coalition partners, particularly the | However the continual postponement of elections sat uneasily with Röttgen's coalition partners, particularly the largest of the bourgeois parties the Catholics. The Catholics distrusted Röttgen seeing him as a potentially authoritarian figure to close to both the monarchy and pushed for an early election in order to reassert the power of the legislature. After Shangea officially surrendered to the [[Grand Alliance]] forces in December 1934 the KSP parliamentary delegation requested to Röttgen to call an early election but the premier demurred. By February 1935 relations between the KSP and Radicals had collapsed leading to the KSP to threaten to withdraw from the government and call for early elections. | ||
The withdrawal of the | The threatened withdrawal of the KSP from the coalition caused a crisis for Röttgen. Röttgen had hoped to continue the wartime unity government in order to have societal consensus for post-war reforms and to isolate the socialists from executive power. In response to the KSP's decision the OSAI stated it would be willing to support a centre-left government provided Röttgen had no role in it, threatening the premiers position among the left-wing of the Radicals. Röttgen additionally was not the leader of his party, the Radicals, and so with his coalition diminished faced greater uncertainty on his ability to run the country. | ||
As a result shortly | As a result shortly after receiving the KSP's ultimatum withdrawal Röttgen announced that he had obtained consent from the monarch to dissolve the Bundestag in the hope that voters would re-elect the wartime coalition. Röttgen had not consulted the cabinet regarding an election and so his announcement was greeted with surprise. Notably the socialists were caught off guard by the holding of an electing predicting that Röttgen would attempt to cling onto office and so entered the campaign unprepared. | ||
==Parties== | ==Parties== | ||
{| class=wikitable style=text-align:left | {| class=wikitable style=text-align:left | ||
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
==Campaign== | ==Campaign== | ||
[[File:Holdovaci průvod na Hrad roku 1930.JPG|thumb|The Radical's women branch campaigning in [[Ruttland]].|250px]] | [[File:Holdovaci průvod na Hrad roku 1930.JPG|thumb|The Radical's women branch campaigning in [[Ruttland]].|250px]] | ||
The campaign saw the pro-government parties - the Radicals, KSP, Landbund and NLP - rally around premier Röttgen with the far-right being marginalised as a political force as they were discredited due to their association with wartime collaboration. Röttgen and his allies campaigned on a vague platform of social reform and virulent anti-socialism, warning voters of the danger of electing a left-leaning government. Röttgen denounced the OSAI as a sect that represented "narrow class interests" and appealed to the spirit of wartime unity. The right-wing parties largely were unable to tap into the spirit of post-war reformism leading to the Radicals to soon become the choice for many centrist voters as Röttgen moved to the right. | The campaign saw the pro-government parties - the Radicals, KSP, Landbund, SPO and NLP - rally around premier Röttgen with the far-right being marginalised as a political force as they were discredited due to their association with wartime collaboration. Röttgen and his allies campaigned on a vague platform of social reform and virulent anti-socialism, warning voters of the danger of electing a left-leaning government. Röttgen denounced the OSAI as a sect that represented "narrow class interests" and appealed to the spirit of wartime unity. The right-wing parties largely were unable to tap into the spirit of post-war reformism leading to the Radicals to soon become the choice for many centrist voters as Röttgen moved to the right. | ||
The OSAI were split on the prospect of either leading or merely supporting a left-wing government, although its senior leadership supported a coalition with the SPO and the left-wing the radicals. The SPO did not support a coalition with the OSAI but were uncomfortable with working with Röttgen who they increasingly perceived to be moving in a right-wing direction. SPO chairman August Olbrich called for a renewal of the wartime unity government in order to herald in social reforms but without the figure of Röttgen, instead proposing that the Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt lead an all-party government. | The OSAI were split on the prospect of either leading or merely supporting a left-wing government, although its senior leadership supported a coalition with the SPO and the left-wing the radicals. The SPO did not support a coalition with the OSAI but were uncomfortable with working with Röttgen who they increasingly perceived to be moving in a right-wing direction. SPO chairman August Olbrich called for a renewal of the wartime unity government in order to herald in social reforms but without the figure of Röttgen, instead proposing that the Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt lead an all-party government. | ||
| Line 264: | Line 264: | ||
Turnout was very high at 83.61% despite fears that demobilised servicemen and women would not vote. Female suffrage had less of an effect then many predicted with women voters showing little divergence from men outside a slight preference for the three largest parties. | Turnout was very high at 83.61% despite fears that demobilised servicemen and women would not vote. Female suffrage had less of an effect then many predicted with women voters showing little divergence from men outside a slight preference for the three largest parties. | ||
===Government formation=== | ===Government formation=== | ||
Following the election talks began for the creation of a centrist government based around the Radicals. Although Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt was proposed as a compromise candidate to replace Röttgen as premier | Following the election talks began for the creation of a centrist government based around the Radicals. Although Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt was proposed as a compromise candidate to replace Röttgen as premier the monarch Leopold IV refused to appoint a cabinet that excluded Röttgen. The KSP agreed to continue the coalition after being promised the post of finance minister, thereby re-creating the five-party alliance that had governed Werania since 1922. Röttgen eventually created a cabinet with the Radicals, NLP, SPO, KSP and Landbund heading the majority of cabinet posts. The cabinet was sworn in on the 2 May 1935. | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; font-size:98%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; font-size:98%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 6 March 2023
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 584 seats to the House of Deputies 292 seats are needed for a majority in the Volkstag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 16,470,368 (83.71%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 22nd federal election was held in the Weranian Confederation for the House of Deputies (the lower house of the Bundestag) on the 17th April 1935. All 584 members of the House of Deputies were elected under a system of proportional representation with each regierungsbezirke treated as an electoral districts. The elections were the first held in almost a decade as elections had been suspended during the Great War.
The first election held under universal suffrage (with women being granted the vote five months prior to the election) the 1935 election saw the wartime coalition of the Catholic, National Liberals, Social Democrats, Radicals and the Agrarians (the Constitutionalist Bloc) under premier Otto Röttgen splinter on the issue of post-war reconstruction. In particular there was within the coalition opposition to the Leopoldist programme of premier Röttgen with some accusing Röttgen and Leopold IV of attempting to create a dictatorship. Nevertheless Röttgen was popular due to his wartime leadership and aimed to secure a firm mandate to implement post-war reforms.
The wartime abolition of Ruttish parties meant that this was the first Weranian election in decades contested purely by federal parties. The abolition of Ruttish parties and the increased influence of the leftists in Euclea benefitted the Weranic Section of the Workers' International. The OSAI supported the notion of entering the government for the first time since its split in 1920 but refused to cooperate with Röttgen.
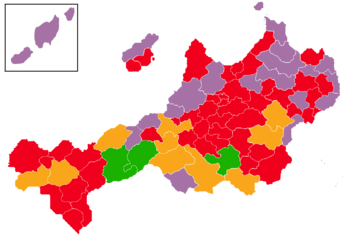
The election saw a swing to the left with the OSAI retaining its status as the largest party in the House of Deputies increasing its seat and vote share signalling clear desire from the electorate for social reform to be adopted. The right-wing parties suffered major losses with the KSP losing half of its parliamentary delegation and the Radicals becoming the largest non-socialist party. As such Röttgen reformed the five-party alliance made of Radical, NLP, KSP, SPO and Landbund parliamentarians. The five-party coalition would continue to hold office during the legislative term under Röttgen's successor Gustav Blumentritt.
Electoral process
The election was held using a system of proportional repsentation that had been introduced in 1905. The country had 76 electoral districts based on the regierungsbezirke with no electoral threshold. There were calls to amend the electoral system prior to the election as it had consistently delivered heavily divided legislatures in the period leading up to the Great War that struggled to produce majority governments - however a proposal to introduce a two-round system was rejected by the cabinet.
The government introduced several changes prior to the election however. The seats in the chamber were reduced from 621 to 584, making a majority in the chamber 293 deputies. The government also passed women's suffrage granting women the right to vote for the first time in Weranian history. The measure was the result of rare cooperation between the Catholics and socialists who were seen as the most likely beneficiaries. In addition the voting age was lowered from 25 to 20.
Background
The election occurred in the aftermath of the Great War which changed the political landscape of Werania. Prior to the war Werania had undergone a period of political instability with anti-parliamentarian parties such as the national syndicalist Weranic Syndicalist Union undermining Weranian democracy. The presence of these parties alongside the cordon sanitaire around the Weranic Section of the Workers' International meant that governments often became unwieldy coalitions of the so-called "constitutionalist parties" (the Catholics, National Liberals, Social Democrats, Radicals and the Agrarians). At the outbreak of war however the government banned the anti-parliamentarian parties whilst forming a national unity government in support of the war effort. The OSAI was split on the war question although its most prominent personality, Aurimas Kreickamas, supported the war on anti-functionalist grounds.
As the war neared its end the matter of the post-war settlement begun to enter the Weranian political discourse. The socialists had been gaining in popularity both due to increased Valduvian influence and a shift by the socialists towards assimilating patriotism and reverence for the army into their political discourse, notions they had previously belittled. To counter this the monarch Leopold IV and the premier Otto Röttgen formulated a political programme, Leopoldism, that sought to introduce moderate social reform whilst centralising governmental control and limiting parliamentary democracy.
The 1925-1929 legislative term had technically elapsed in 1929 but was extended for another four years twice, in 1929 and 1933. Röttgen and Leopold IV both supported holding an election when the legislative extension expired in 1937 due to the belief that an earlier election would benefit the socialists due to the poor social conditions. The governments post-war reconstruction scheme, the Bader-Fritz Plan, had only begun to take effect and wartime devastation still afflicted the country. Röttgen privately aimed to dissolve the Bundestag following the conclusion of peace treaties with Gaullica and Shangea in order to take advantage of post-war triumphalism.
However the continual postponement of elections sat uneasily with Röttgen's coalition partners, particularly the largest of the bourgeois parties the Catholics. The Catholics distrusted Röttgen seeing him as a potentially authoritarian figure to close to both the monarchy and pushed for an early election in order to reassert the power of the legislature. After Shangea officially surrendered to the Grand Alliance forces in December 1934 the KSP parliamentary delegation requested to Röttgen to call an early election but the premier demurred. By February 1935 relations between the KSP and Radicals had collapsed leading to the KSP to threaten to withdraw from the government and call for early elections.
The threatened withdrawal of the KSP from the coalition caused a crisis for Röttgen. Röttgen had hoped to continue the wartime unity government in order to have societal consensus for post-war reforms and to isolate the socialists from executive power. In response to the KSP's decision the OSAI stated it would be willing to support a centre-left government provided Röttgen had no role in it, threatening the premiers position among the left-wing of the Radicals. Röttgen additionally was not the leader of his party, the Radicals, and so with his coalition diminished faced greater uncertainty on his ability to run the country.
As a result shortly after receiving the KSP's ultimatum withdrawal Röttgen announced that he had obtained consent from the monarch to dissolve the Bundestag in the hope that voters would re-elect the wartime coalition. Röttgen had not consulted the cabinet regarding an election and so his announcement was greeted with surprise. Notably the socialists were caught off guard by the holding of an electing predicting that Röttgen would attempt to cling onto office and so entered the campaign unprepared.
Parties
| Affiliation | Party | Ideology | Political position | Spitzenkandidat | 1925 result | In government | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | 
|
Weranic Section of the Workers' International | Socialism, Revolutionary socialism | Left-wing | Aurimas Kreickamas | 164 / 621
|
||
| Centre-left | 
|
Social Democratic Party of Werania | Social democracy, Reformism | Centre-left | August Olbrich | 58 / 621
|
||

|
Radical Party | Radicalism, Anti-clericalism | Centre | Otto Röttgen | 54 / 621
|
|||
| Centre-right | Landbund | Agrarianism, Liberalism | Centre-right | Gustav Blumentritt | 72 / 621
|
|||
| National Liberal Party | National Liberalism, Classical liberalism | Centre-right | Elmar Künneth | 66 / 621
|
||||

|
Catholic Social Party | Political Catholicism, Sotirian Democracy | Centre-right | Thomas Bechtold | 142 / 621
|
|||
| Right | 
|
Weranian Fatherland Party | National conservatism, Monarchism | Right-wing | Karl Theophil von Pölten | 42 / 621
|
||
Campaign

The campaign saw the pro-government parties - the Radicals, KSP, Landbund, SPO and NLP - rally around premier Röttgen with the far-right being marginalised as a political force as they were discredited due to their association with wartime collaboration. Röttgen and his allies campaigned on a vague platform of social reform and virulent anti-socialism, warning voters of the danger of electing a left-leaning government. Röttgen denounced the OSAI as a sect that represented "narrow class interests" and appealed to the spirit of wartime unity. The right-wing parties largely were unable to tap into the spirit of post-war reformism leading to the Radicals to soon become the choice for many centrist voters as Röttgen moved to the right.
The OSAI were split on the prospect of either leading or merely supporting a left-wing government, although its senior leadership supported a coalition with the SPO and the left-wing the radicals. The SPO did not support a coalition with the OSAI but were uncomfortable with working with Röttgen who they increasingly perceived to be moving in a right-wing direction. SPO chairman August Olbrich called for a renewal of the wartime unity government in order to herald in social reforms but without the figure of Röttgen, instead proposing that the Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt lead an all-party government.
The campaign was noted for its hyper-partisan nature which made many disillusioned with politics. In particular the banning of many Ruttish parties caused resentment in the province allowing the OSAI to tap into autonomist sentiment to gain traction.
Results
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weranic Section of the Workers' International | 6,148,372 | 37.37 | 224 | +60 | |
| Radical Party | 2,206,843 | 13.41 | 80 | +26 | |
| Catholic Social Party | 2,206,843 | 13.29 | 79 | -63 | |
| Social Democratic Party of Werania | 1,559,570 | 9.48 | 56 | -2 | |
| Rural Federation | 1,478,944 | 8.99 | 54 | -18 | |
| National Liberal Party | 1,475,936 | 8.97 | 53 | −13 | |
| Weranian Fatherland Party | 1,058,302 | 6.43 | 38 | −4 | |
| Others | 115,832 | 0.70 | 0 | - | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 220,485 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 16,451,312 | 100 | 584 | ±0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 19,675,832 | 83.61 | – | – | |
Aftermath
Outcome
The election saw only two parties - OSAI and the Radicals - gain seats with every other contesting party seeing losses. The KSP in particular saw a catastrophic result losing almost half their deputies and emerging behind the Radicals for the first time since 1918. The success of the OSAI was attributed to the popularity of radical socialism after the end of the war and the widespread desire for social reform, particularly in Ruttland where the OSAI won a convincing majority of seats beginning a foothold in the region that would continue for several decades.
The success of the Radicals was attributed both to Röttgens firm anti-socialist rhetoric and his support for social reform (albeit in line with the Leopoldist programme) thereby enabling him to present his party as being representative of national unity. This would be somewhat of a last hurrah for the Radicals who would after the retirement of Röttgen in 1937 decline as many right-wing voters moved back to the more traditional bourgeois parties.
Turnout was very high at 83.61% despite fears that demobilised servicemen and women would not vote. Female suffrage had less of an effect then many predicted with women voters showing little divergence from men outside a slight preference for the three largest parties.
Government formation
Following the election talks began for the creation of a centrist government based around the Radicals. Although Landbund leader Gustav Blumentritt was proposed as a compromise candidate to replace Röttgen as premier the monarch Leopold IV refused to appoint a cabinet that excluded Röttgen. The KSP agreed to continue the coalition after being promised the post of finance minister, thereby re-creating the five-party alliance that had governed Werania since 1922. Röttgen eventually created a cabinet with the Radicals, NLP, SPO, KSP and Landbund heading the majority of cabinet posts. The cabinet was sworn in on the 2 May 1935.
| Investiture Otto Röttgen (Radical) | ||
| Ballot → | 2 May 1935 | |
|---|---|---|
| Required majority → | 292 out of 584 | |
318 / 584
| ||
262 / 584
| ||
Abstentions
|
4 / 584
| |
| Absentees | 0 / 584
| |






