User:BrackishWater/Sandbox1: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{WIP}} {{Region icon Astraleaux}} {{Short description|Legislative association of Aosta}} {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2021}} {{Infobox legislature | name = Fre...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WIP}} | {{WIP}} | ||
{{Region icon Astraleaux}} | {{Region icon Astraleaux}} | ||
{{ | {{Infobox country | ||
|native_name = ''Repubblica Socialista di Aosta'' | |||
|conventional_long_name = Socialist Republic of Aosta | |||
|common_name = Aosta | |||
|image_flag = [[File:Aosta flag.png|thumb]] | |||
|image_coat = | |||
|symbol_type = Emblem | |||
|national_motto = Nati Uguali o Resi Uguali<br><small>''Born Equal or Made Equal''</small> | |||
|national_anthem = <br>In Comradum Memoria <small>(official)<br>''In Comradum Memoria''</small><br> | |||
[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GKlAHqsiG1w|200px]] | |||
|royal_anthem = | |||
|other_symbol_type = | |||
|other_symbol = | |||
|image_map = File:Aosta map simple.png | |||
|alt_map = | |||
|map_caption = Map of Aosta | |||
|image_map2 = | |||
|alt_map2 = | |||
|map_caption2 = | |||
|capital = [[Rivoluzione]] | |||
|largest_city = [[Rivoluzione]] | |||
|official_languages = | |||
|national_languages = {{wp|Italian language|Lancian}} | |||
|regional_languages = | |||
|languages_type = | |||
|languages = | |||
|ethnic_groups = | |||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |||
|demonym = Aostan (ethnic)<br>Aostan (citizen) | |||
|legislature = [[Free People's Assembly|Libera Assemblea del Popolo]] | |||
|lower_house = | |||
|upper_house = | |||
|government_type = {{wp|Anarcho-syndicalism|Anarcho-councilist}} {{wp|Non-partisan_democracy|republic}} | |||
|leader_title1 = {{wp|President|Presidente}} | |||
|leader_name1 = [[Ko'êtî Argento]] | |||
| | |leader_title2 = {{wp|Ambassador|Primo Ambasciatore}} | ||
|leader_name2 = [[Gianotan Banche]] | |||
|sovereignty_type = | |||
|sovereignty_note = | |||
|established_event1 = First Contact | |||
|established_date1 = 500 BCE | |||
|established_event2 = Province of Aosta | |||
|established_date2 = 111 BCE | |||
|established_event3 = Aostan Colonial Authority | |||
|established_date3 = 1530 | |||
|established_event4 = Socialist Republic of Aosta | |||
|established_date4 = 1921 | |||
|established_event5 = | |||
|established_date5 = | |||
|established_event6 = | |||
|established_date6 = | |||
|area_rank = | |||
|area_magnitude = | |||
|area_km2 = | |||
|area_sq_mi = | |||
|area_footnote = | |||
|percent_water = | |||
|area_label = | |||
|area_dabodyalign = | |||
|population_estimate = 27,013,112 | |||
|population_estimate_rank = | |||
|population_estimate_year = 2020 | |||
|population_census = | |||
|population_census_year = | |||
|population_density_km2 = | |||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |||
|population_density_rank = | |||
|GDP_PPP = | |||
|GDP_PPP_rank = | |||
|GDP_PPP_year = | |||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |||
|GDP_nominal = | |||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |||
|GDP_nominal_year = | |||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = | |||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |||
|Gini = | |||
|Gini_rank = | |||
|Gini_change = | |||
|Gini_year = | |||
|Gini_category = | |||
|HDI = | |||
|HDI_rank = | |||
|HDI_year = | |||
|HDI_change = | |||
|HDI_category = | |||
|currency = | |||
|currency_code = | |||
|time_zone = | |||
|utc_offset = | |||
|time_zone_DST = | |||
|antipodes = | |||
|date_format = dd.mm.yyyy | |||
|DST_note = | |||
|utc_offset_DST = | |||
|drives_on = right | |||
|cctld = .ao | |||
|iso3166code = AO | |||
|calling_code = | |||
|image_map3 = | |||
|alt_map3 = | |||
|footnotes = | |||
|footnote1 = | |||
|footnote2 = | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Aosta''', officially the '''Socialist Republic of Aosta''' ({{wpl|Italian|Lancian}}: ''Repubblica Socialista di Aosta''), is a {{wp|Anarcho-syndicalism|Anarcho-councilist}} {{wp|Non-partisan_democracy|republic}} located in southeastern [[Cesylle]] in [[Portal:Astraleaux|Cel]]. It is bordered to the south by the [[Southern Ocean]], to the east by the [[Ultima Sea]], to the north by [BLANK], and to the west by the [[Cape of Aosta]]. It shares a land border with [BLANK]. Its capital of [[Rivoluzione]] stands in the [[list of Aostan regions|Speranza Region]] with a population of 8.1 million. Legislative, executive, and judicial powers encompassing Aosta's participating communes rests in the [[Free Assembly of the People]]. The President of the Assembly is [[Ko'êtî Argento]], while the Prime Ambassador is [[Gianotan Banche]]. Aosta is divided into 6 regions and 1 capital commune. | |||
==Etymology== | |||
==History== | |||
===Antiquity=== | |||
The origins of Aosta date back to 500 BCE when Lancian Emperor Caerndal declared the land beyond the Aostan (now Aeptan) Mountain chain to be named Aosta, erroneously believing the island to be leagues smaller than in actuality. Settlements on the eastern peninsula, such as Lux, would over time become culturally significant settlements and centers of Lancian imperialism throughout history. | |||
===Lancian Empire=== | |||
Aosta quickly became the gateway from the heart of the Lancian Empire to the continent of Cesylle. While more quicker routes were discovered later, being the first Lancian settlement on Cesylle meant that Aosta made for a far more developed colony and therefore a more economically sound source of continental resources. The Governatores of Aosta were not immune to the political machinations of mainland Lancia, however, and the countless plots through the centuries kept Aosta from gathering any functional support for independence until the Era of Shadows. | |||
===Era of Shadows=== | |||
With the decline of the Lancian Empire came the decline of the Aostan province. Ports once busy with commerce and soldiers struggled for decades as trade diminished and with it, the value of the Lancian lira. The Lancian settlements on the western portion of Aosta fell into siginificant disrepair and entire towns were abandoned as people moved to the eastern side of the island in search of better living standards and respite from native attackers. | |||
===Four Kingdoms Period=== | |||
In the absence of imperial dominion, the mantle of power was assumed by the four most populous settlements and the surrounding regions: [BLANK], [BLANK], [BLANK], and Carcosa. Given the distance between Aosta and Maris, few attempts were made to communicate between these kingdoms and Marisian societies, and so these kingdoms were largely left to their own devices. During their reign, the kingdoms managed to consolidate control over the remaining territory of the Aostan island and some of its daughter islands. However, much like the provinces in the fallen Lancian Empire, they were prone to competing power struggles, treacherous schemes, and at times, open warfare. | |||
===Lancian Riconquista=== | |||
The following centuries saw the nation state of Lancia rise again as a fervor for reclaiming the empire's former glory swept the region. However, its growth on Maris was stifled by the birth of other kingdoms and nation states that fiercely their own cultures and autonomy. So, Lancia turned outward and began to colonize Cel. One of its first priorities was to reclaim Aosta, which by now resembled a patchwork of kingdoms and polities. As the Aostan kingdoms were quite fierce in their attempts to remain independent (and the Lancian leadership were impatient to see their plans through), Lancia entered a state of open war against the many kingdoms of the island. Partway through this campaign, knowledge of firearms became known to Lancia, and so developed scenes of Lancian musketeers doing battle with Aostan knights and archers. In the end, it only took 77 years for Lancia to reclaim control over Aosta. | |||
===Aostan Colonial Authority=== | |||
The end of the Lancian Riconquista arrived near the beginning of Sante Serafino's reign as Lancia's Reggente. He appointed his childhood friend Valeriano D'Aiuto as Governatore of Aosta in a move to secure the loyalty of the colony's armed forces and formed the organization known as the Aostan Colonial Authority (Autorità Coloniale di Aosta). The ACA's regime was known for its jingoist attitude, brutal treatment of lower classed laborers, and rapid industrialization, often at the cost of the native peoples and environment. D'Aiuto followed Serafino's example in Lancia and formed a cult of personality centered around himself, and surrounded himself with people whose loyalty could be assured. The following decades saw a marked rise in population as technologies that improved longevity spread to the island, but also the formation of a large wealth gap between the Lancian elite and Aostan lower class. | |||
===Independence=== | |||
Aosta achieved its independence by declaring neutrality in the First Great War, ignoring Lancia's call to war. D'Aiuto was convinced by his generals that the Aostan military was ill-equipped for offensive actions against [BLANK] forces, and by complying to Lancia's request to join the war, they would be opening the nation to invasion by multiple nations who would capitalize on the current internal tensions to spark a national revolt. By all accounts this decision amounted to treason, but because the ACA's leadership was comprised of people loyal to D'Aiuto, none dared to raise a finger against him. Moreover, already mired in a global war involving the rest of its colonies, Lancia spared next to nothing attempting to attack Aosta for its betrayal. Lancia did carry out several attempts to influence and assassinate key officials who refused to join the war on Lancia's behalf, but these attempts were stifled by the surveilance culture built by D'Aiuto. | |||
===August Revolution=== | |||
Not long after the First Great War did the ACA's fears of a national revolt come true. Inspired by the revolutions occurring across the globe and supplied money and arms from Nutarra and [BLANK], Aostan revolutionaries took arms against the Authority. A portion of the Authority's officer class defected to the rebels, providing them with armored and aerial support in a small number of theatres, but not least as famously as the Raid on the Governatore's Palace. Displeased by the Authority's treasonous attitude during the war, the Lancian Provisional Government provided aid to the rebels as well, hoping to topple the dictatorship and reset the island nation's diplomacy. After [BLANK] hard years of fighting, the revolutionaries claimed victory on [BLANK] at the Treaty of Rivoluzione, formerly D'Aiuto. | |||
===Second Great War=== | |||
Seizing the opportunity against the exhausted Aostan military, [BLANK] declared invasion on Aosta during the onset of the Second Great War. Aosta managed to fend off the invaders long enough for their new allies, the ASL, to arrive. When the war ended, [BLANK] ceded their southern peninsula to Aosta as part of the peace treaty. | |||
===Cataclysm=== | |||
===Civil Crisis=== | |||
The following decade was rife with internal conflict as a number of factions within the revolutionary government vied for control. The most prominent split was between the [[Ordinati]], led by [BLANK], whom argued that Aosta must adopt the centralized framework left behind by the Authority in order to enact revolutionary change; the [[Anarchisti]], led by [BLANK], whom believed that Aostans should be largely left to their own devices after so many decades of surveilance and oppression; and finally the [[Liberati]], led by [BLANK], who wanted to form what more or less resembled a classically liberal republic. The Liberati were almost entirely pushed out of mainstream politics by the end of the Civil Crisis, being derided by the other factions as "foreign interlopers" and opportunists. After much turmoil and many lost lives from every faction, the Anarchisti won out and set about dividing Aosta into self-autonomous communes. | |||
===Quiet Duel Onwards=== | |||
==Politics== | |||
===Governance=== | |||
Aosta is constituted of many local and regional communes that are governed according to each commune’s preference, although most communes elect their leadership through direct democracy. Most of these communes participate in the Free Assembly of the People where issues can be brought to the attention of other communes and they can coordinate a response. Matters of international importance are also coordinated through the Assembly as it is the internationally recognized legal representation of Aostan society. | |||
===Administrative Divisions=== | |||
The lowest administrative division in Aosta is the commune, which is a municipal designation. Communes that share a heightened level of local cooperation, culture, or important geographical landmarks are organized into provinces. These provinces are then further grouped into regions, which serve as the highest administrative division. Provinces and regions often, but not always, maintain a council composed of representatives from their constituent communes who provide macroeconomic analysis to their constituent communes. | |||
====Largest Cities==== | |||
[[Rivoluzione]] | |||
[[Carcosa]] | |||
[[Ignis]] | |||
[[Lorica]] | |||
[[Brixias]] | |||
===Foreign Relations=== | |||
Aosta is an active member of the [[Alliance for Socialist Liberation]] and the [[International Assembly]]. It is well known for its medical and humanitarian internationalism. It has tenuous ties with [[Ilbon]] after the 1994 Koai Protests, during which the Ilbonese government harshly cracked down on student and anarchist protesters, and [BLANK], which ceded its southern peninsula to Aosta at the end of the Second Great War. | |||
===People's Militia=== | |||
==Geography== | |||
===Climate=== | |||
===Wildlife=== | |||
==Economy== | |||
===Agriculture=== | |||
===Mining=== | |||
===Industry=== | |||
===Commerce and Finance=== | |||
===Media=== | |||
===Infrastructure=== | |||
====Transportation==== | |||
====Telecommunications==== | |||
====Energy==== | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
===Public Policy=== | |||
==Demographics== | |||
===Ethnicity=== | |||
== | ===Religion=== | ||
===Education=== | |||
===Healthcare=== | |||
== | ==Culture== | ||
===Architecture=== | |||
===Cuisine=== | |||
== | ===Holidays=== | ||
===Literature=== | |||
== | ===Music=== | ||
===Theater=== | |||
== | ===Sports=== | ||
Revision as of 06:38, 22 October 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Socialist Republic of Aosta Repubblica Socialista di Aosta | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: Nati Uguali o Resi Uguali Born Equal or Made Equal | |
| Anthem: In Comradum Memoria (official) In Comradum Memoria | |
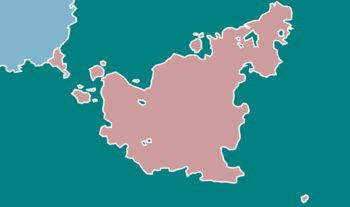 Map of Aosta | |
| Capital and largest city | Rivoluzione |
| Recognised national languages | Lancian |
| Demonym(s) | Aostan (ethnic) Aostan (citizen) |
| Government | Anarcho-councilist republic |
| Ko'êtî Argento | |
| Gianotan Banche | |
| Legislature | Libera Assemblea del Popolo |
| Establishment | |
• First Contact | 500 BCE |
• Province of Aosta | 111 BCE |
• Aostan Colonial Authority | 1530 |
• Socialist Republic of Aosta | 1921 |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 27,013,112 |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| ISO 3166 code | AO |
| Internet TLD | .ao |
Aosta, officially the Socialist Republic of Aosta (Lancian: Repubblica Socialista di Aosta), is a Anarcho-councilist republic located in southeastern Cesylle in Cel. It is bordered to the south by the Southern Ocean, to the east by the Ultima Sea, to the north by [BLANK], and to the west by the Cape of Aosta. It shares a land border with [BLANK]. Its capital of Rivoluzione stands in the Speranza Region with a population of 8.1 million. Legislative, executive, and judicial powers encompassing Aosta's participating communes rests in the Free Assembly of the People. The President of the Assembly is Ko'êtî Argento, while the Prime Ambassador is Gianotan Banche. Aosta is divided into 6 regions and 1 capital commune.
Etymology
History
Antiquity
The origins of Aosta date back to 500 BCE when Lancian Emperor Caerndal declared the land beyond the Aostan (now Aeptan) Mountain chain to be named Aosta, erroneously believing the island to be leagues smaller than in actuality. Settlements on the eastern peninsula, such as Lux, would over time become culturally significant settlements and centers of Lancian imperialism throughout history.
Lancian Empire
Aosta quickly became the gateway from the heart of the Lancian Empire to the continent of Cesylle. While more quicker routes were discovered later, being the first Lancian settlement on Cesylle meant that Aosta made for a far more developed colony and therefore a more economically sound source of continental resources. The Governatores of Aosta were not immune to the political machinations of mainland Lancia, however, and the countless plots through the centuries kept Aosta from gathering any functional support for independence until the Era of Shadows.
Era of Shadows
With the decline of the Lancian Empire came the decline of the Aostan province. Ports once busy with commerce and soldiers struggled for decades as trade diminished and with it, the value of the Lancian lira. The Lancian settlements on the western portion of Aosta fell into siginificant disrepair and entire towns were abandoned as people moved to the eastern side of the island in search of better living standards and respite from native attackers.
Four Kingdoms Period
In the absence of imperial dominion, the mantle of power was assumed by the four most populous settlements and the surrounding regions: [BLANK], [BLANK], [BLANK], and Carcosa. Given the distance between Aosta and Maris, few attempts were made to communicate between these kingdoms and Marisian societies, and so these kingdoms were largely left to their own devices. During their reign, the kingdoms managed to consolidate control over the remaining territory of the Aostan island and some of its daughter islands. However, much like the provinces in the fallen Lancian Empire, they were prone to competing power struggles, treacherous schemes, and at times, open warfare.
Lancian Riconquista
The following centuries saw the nation state of Lancia rise again as a fervor for reclaiming the empire's former glory swept the region. However, its growth on Maris was stifled by the birth of other kingdoms and nation states that fiercely their own cultures and autonomy. So, Lancia turned outward and began to colonize Cel. One of its first priorities was to reclaim Aosta, which by now resembled a patchwork of kingdoms and polities. As the Aostan kingdoms were quite fierce in their attempts to remain independent (and the Lancian leadership were impatient to see their plans through), Lancia entered a state of open war against the many kingdoms of the island. Partway through this campaign, knowledge of firearms became known to Lancia, and so developed scenes of Lancian musketeers doing battle with Aostan knights and archers. In the end, it only took 77 years for Lancia to reclaim control over Aosta.
Aostan Colonial Authority
The end of the Lancian Riconquista arrived near the beginning of Sante Serafino's reign as Lancia's Reggente. He appointed his childhood friend Valeriano D'Aiuto as Governatore of Aosta in a move to secure the loyalty of the colony's armed forces and formed the organization known as the Aostan Colonial Authority (Autorità Coloniale di Aosta). The ACA's regime was known for its jingoist attitude, brutal treatment of lower classed laborers, and rapid industrialization, often at the cost of the native peoples and environment. D'Aiuto followed Serafino's example in Lancia and formed a cult of personality centered around himself, and surrounded himself with people whose loyalty could be assured. The following decades saw a marked rise in population as technologies that improved longevity spread to the island, but also the formation of a large wealth gap between the Lancian elite and Aostan lower class.
Independence
Aosta achieved its independence by declaring neutrality in the First Great War, ignoring Lancia's call to war. D'Aiuto was convinced by his generals that the Aostan military was ill-equipped for offensive actions against [BLANK] forces, and by complying to Lancia's request to join the war, they would be opening the nation to invasion by multiple nations who would capitalize on the current internal tensions to spark a national revolt. By all accounts this decision amounted to treason, but because the ACA's leadership was comprised of people loyal to D'Aiuto, none dared to raise a finger against him. Moreover, already mired in a global war involving the rest of its colonies, Lancia spared next to nothing attempting to attack Aosta for its betrayal. Lancia did carry out several attempts to influence and assassinate key officials who refused to join the war on Lancia's behalf, but these attempts were stifled by the surveilance culture built by D'Aiuto.
August Revolution
Not long after the First Great War did the ACA's fears of a national revolt come true. Inspired by the revolutions occurring across the globe and supplied money and arms from Nutarra and [BLANK], Aostan revolutionaries took arms against the Authority. A portion of the Authority's officer class defected to the rebels, providing them with armored and aerial support in a small number of theatres, but not least as famously as the Raid on the Governatore's Palace. Displeased by the Authority's treasonous attitude during the war, the Lancian Provisional Government provided aid to the rebels as well, hoping to topple the dictatorship and reset the island nation's diplomacy. After [BLANK] hard years of fighting, the revolutionaries claimed victory on [BLANK] at the Treaty of Rivoluzione, formerly D'Aiuto.
Second Great War
Seizing the opportunity against the exhausted Aostan military, [BLANK] declared invasion on Aosta during the onset of the Second Great War. Aosta managed to fend off the invaders long enough for their new allies, the ASL, to arrive. When the war ended, [BLANK] ceded their southern peninsula to Aosta as part of the peace treaty.
Cataclysm
Civil Crisis
The following decade was rife with internal conflict as a number of factions within the revolutionary government vied for control. The most prominent split was between the Ordinati, led by [BLANK], whom argued that Aosta must adopt the centralized framework left behind by the Authority in order to enact revolutionary change; the Anarchisti, led by [BLANK], whom believed that Aostans should be largely left to their own devices after so many decades of surveilance and oppression; and finally the Liberati, led by [BLANK], who wanted to form what more or less resembled a classically liberal republic. The Liberati were almost entirely pushed out of mainstream politics by the end of the Civil Crisis, being derided by the other factions as "foreign interlopers" and opportunists. After much turmoil and many lost lives from every faction, the Anarchisti won out and set about dividing Aosta into self-autonomous communes.
Quiet Duel Onwards
Politics
Governance
Aosta is constituted of many local and regional communes that are governed according to each commune’s preference, although most communes elect their leadership through direct democracy. Most of these communes participate in the Free Assembly of the People where issues can be brought to the attention of other communes and they can coordinate a response. Matters of international importance are also coordinated through the Assembly as it is the internationally recognized legal representation of Aostan society.
Administrative Divisions
The lowest administrative division in Aosta is the commune, which is a municipal designation. Communes that share a heightened level of local cooperation, culture, or important geographical landmarks are organized into provinces. These provinces are then further grouped into regions, which serve as the highest administrative division. Provinces and regions often, but not always, maintain a council composed of representatives from their constituent communes who provide macroeconomic analysis to their constituent communes.
Largest Cities
Rivoluzione Carcosa Ignis Lorica Brixias
Foreign Relations
Aosta is an active member of the Alliance for Socialist Liberation and the International Assembly. It is well known for its medical and humanitarian internationalism. It has tenuous ties with Ilbon after the 1994 Koai Protests, during which the Ilbonese government harshly cracked down on student and anarchist protesters, and [BLANK], which ceded its southern peninsula to Aosta at the end of the Second Great War.
