Jindao: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
}} | }} | ||
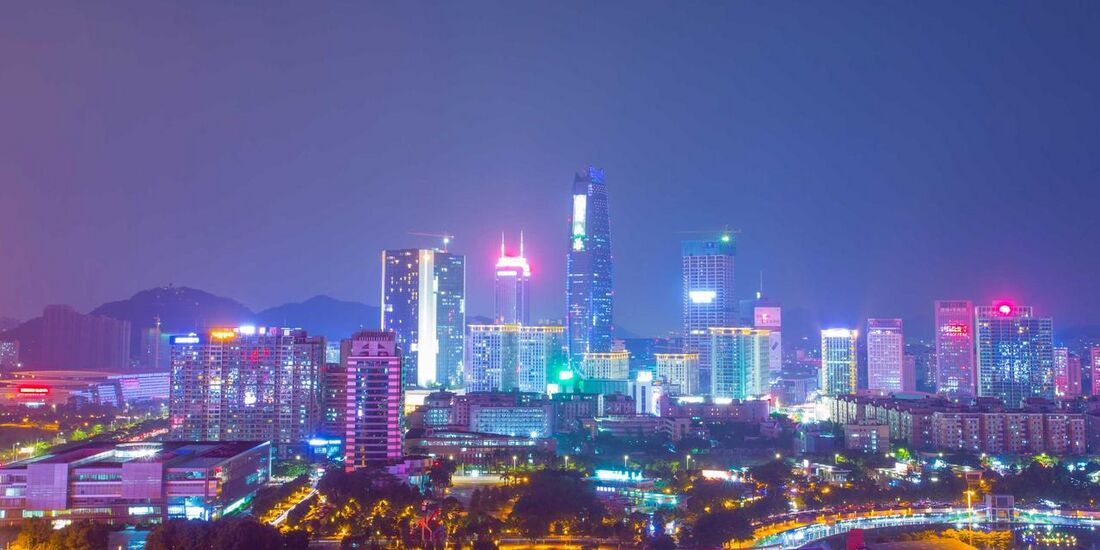
'''Jindao''', officially the '''Jindao Autonomous Administrative Territory of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong''' is a special administrative region in the centre of the X in central [[Xiaodong]]. With 6,541,201 people and an area of 1,125.6 km², around 60% of which is water, it is one of the most densely populated regions in the world. | '''Jindao''', officially the '''Jindao Autonomous Administrative Territory of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong''' is a special administrative region in the centre of the X in central [[Xiaodong]]. With 6,541,201 people and an area of 1,125.6 km², around 60% of which is water, it is one of the most densely populated regions in the world. The city of [[Shilou]], within the Jindao metropolitan area, is the most densely populated city in the world, with a population of 2,541,205 and an area of 63.83km² (including the Tanpe, Tangqiu, Mathratown and Weikan districts), the city has a population density of 39,812 people per square kilometre. | ||
The city-state of Jindao was an independent kingdom for much of its history, with little instability ever rocking the nation and the port of Jindao being a hub for trade in the southern Coius region. Coming under Xiaodongese subjugation at the start of the 13th century, the city continued to flourish under Xiaodongese control as more resources and revenue from mainland Xiaodong were directed in the way of the island due to the decreased trade regulations between the two states. Also formerly a colony of [[Gaullica]] after it was relinquished by Xiaodong as a {{wp|treaty port}} in 1884, Jindao acted as a naval base for Gaullica (and Xiaodong) throughout the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. After Gaullica's loss in the war, the city's sovereignty was transferred to [[Estmere]], under whom more rights were guaranteed and more democratic reforms were instated, including the reformation of the [[Biao]] as a devolved government under Estmere in 1951. The country flourished as women's suffrage was introduced in 1953, and the legal recognition of homosexual marriage being introduced in 1966. In 1990, Estmere and Xiaodong signed the [[Xiao-Estmerish Jindao Treaty]], an agreement which promised the sovereignity of Jindao to be returned to Xiaodong in exchange for the customs of rights of the city to remain unchanged and guaranteed. Estmere officially relinquished sovereignity of the island in 1996, returning it to Xiaodong after 112 years of Euclean rule. Jindao acts as an Autonomous Administrative Territory (AAT) of Xiaodong, whose legislature and government is separate from that of the mainland. | The city-state of Jindao was an independent kingdom for much of its history, with little instability ever rocking the nation and the port of Jindao being a hub for trade in the southern Coius region. Coming under Xiaodongese subjugation at the start of the 13th century, the city continued to flourish under Xiaodongese control as more resources and revenue from mainland Xiaodong were directed in the way of the island due to the decreased trade regulations between the two states. Also formerly a colony of [[Gaullica]] after it was relinquished by Xiaodong as a {{wp|treaty port}} in 1884, Jindao acted as a naval base for Gaullica (and Xiaodong) throughout the [[Great War (Kylaris)|Great War]]. After Gaullica's loss in the war, the city's sovereignty was transferred to [[Estmere]], under whom more rights were guaranteed and more democratic reforms were instated, including the reformation of the [[Biao]] as a devolved government under Estmere in 1951. The country flourished as women's suffrage was introduced in 1953, and the legal recognition of homosexual marriage being introduced in 1966. In 1990, Estmere and Xiaodong signed the [[Xiao-Estmerish Jindao Treaty]], an agreement which promised the sovereignity of Jindao to be returned to Xiaodong in exchange for the customs of rights of the city to remain unchanged and guaranteed. Estmere officially relinquished sovereignity of the island in 1996, returning it to Xiaodong after 112 years of Euclean rule. Jindao acts as an Autonomous Administrative Territory (AAT) of Xiaodong, whose legislature and government is separate from that of the mainland. | ||
Revision as of 13:51, 8 July 2019
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Jindao Autonomous Administrative Territory of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong 小东吉祥共和国金岛自治区 Xiǎodōng jíxiáng gònghéguó Jīndǎo zìzhìqū (Xiaodongese) Territoire administratif autonome de Jindao de la République de bon augure de Xiaodong (Gaullican) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "要为金岛而荣耀" "To glory for Jindao!" | |
| Anthem: "英勇的戰士" ("Heroic Warriors") | |
 Location of Jindao | |
| Official languages | Jindanese Xiaodongese Gaullican Estmerish |
| Ethnic groups (2019) | 70.8% Jindanese 14.2% Xiaodongese 9.6% Mathra 2.1% Estmerish 1.7% Gaullican 0.5% Other |
| Religion (2019) | 44.1% Solarian Catholic 38.2% Taojiao 15.6% Irreligious 2.1% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Jindanese |
| Government | Devolved executive-led government within a unitary authoritarian republic |
• Chief Executive | Guo Zhenya |
• Chief Secretary | Liao Cai |
| Legislature | Biao |
| Autonomous Region of Xiaodong | |
• Xiaodongese subjucation | 1202 |
• Gaullican colony | 1884 |
• Estmerish colony | 1935 |
• Xiao-Estmerish Jindao Treaty | 1990 |
• Transfer of sovereignty from Estmere | 1995 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,125.6 km2 (434.6 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 61.4 |
| Population | |
• 2019 census | 6,541,201 |
• Density | 15,055/km2 (38,992.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | $541.7 billion |
• Per capita | $82,819 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $506 billion |
• Per capita | $77,361 |
| Gini | high |
| HDI | very high |
| Currency | Jindanese Nacar (NAC) Xiaodongese Renjin (RJN) |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +891 |
| Internet TLD | .jn |
Jindao, officially the Jindao Autonomous Administrative Territory of the Auspicious Republic of Xiaodong is a special administrative region in the centre of the X in central Xiaodong. With 6,541,201 people and an area of 1,125.6 km², around 60% of which is water, it is one of the most densely populated regions in the world. The city of Shilou, within the Jindao metropolitan area, is the most densely populated city in the world, with a population of 2,541,205 and an area of 63.83km² (including the Tanpe, Tangqiu, Mathratown and Weikan districts), the city has a population density of 39,812 people per square kilometre.
The city-state of Jindao was an independent kingdom for much of its history, with little instability ever rocking the nation and the port of Jindao being a hub for trade in the southern Coius region. Coming under Xiaodongese subjugation at the start of the 13th century, the city continued to flourish under Xiaodongese control as more resources and revenue from mainland Xiaodong were directed in the way of the island due to the decreased trade regulations between the two states. Also formerly a colony of Gaullica after it was relinquished by Xiaodong as a treaty port in 1884, Jindao acted as a naval base for Gaullica (and Xiaodong) throughout the Great War. After Gaullica's loss in the war, the city's sovereignty was transferred to Estmere, under whom more rights were guaranteed and more democratic reforms were instated, including the reformation of the Biao as a devolved government under Estmere in 1951. The country flourished as women's suffrage was introduced in 1953, and the legal recognition of homosexual marriage being introduced in 1966. In 1990, Estmere and Xiaodong signed the Xiao-Estmerish Jindao Treaty, an agreement which promised the sovereignity of Jindao to be returned to Xiaodong in exchange for the customs of rights of the city to remain unchanged and guaranteed. Estmere officially relinquished sovereignity of the island in 1996, returning it to Xiaodong after 112 years of Euclean rule. Jindao acts as an Autonomous Administrative Territory (AAT) of Xiaodong, whose legislature and government is separate from that of the mainland.
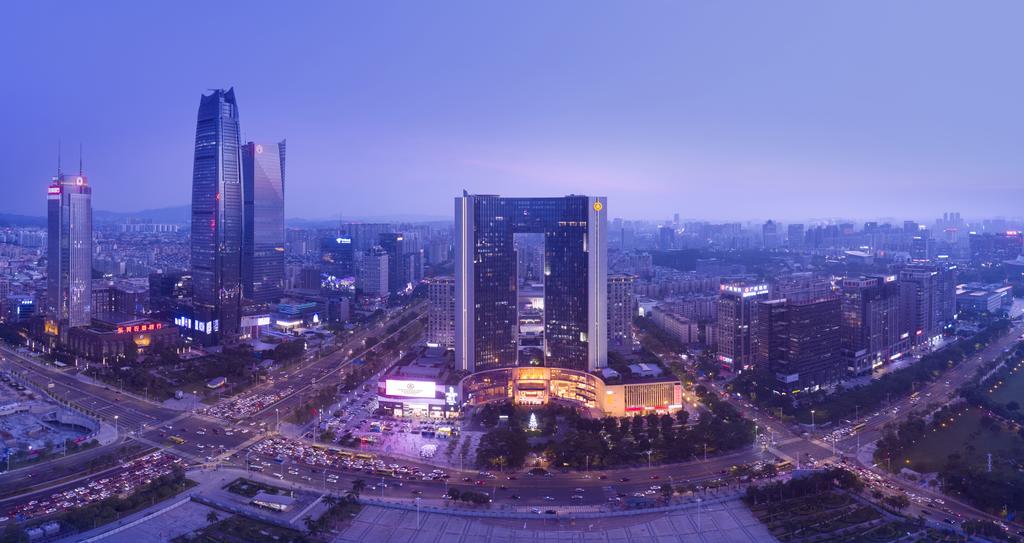
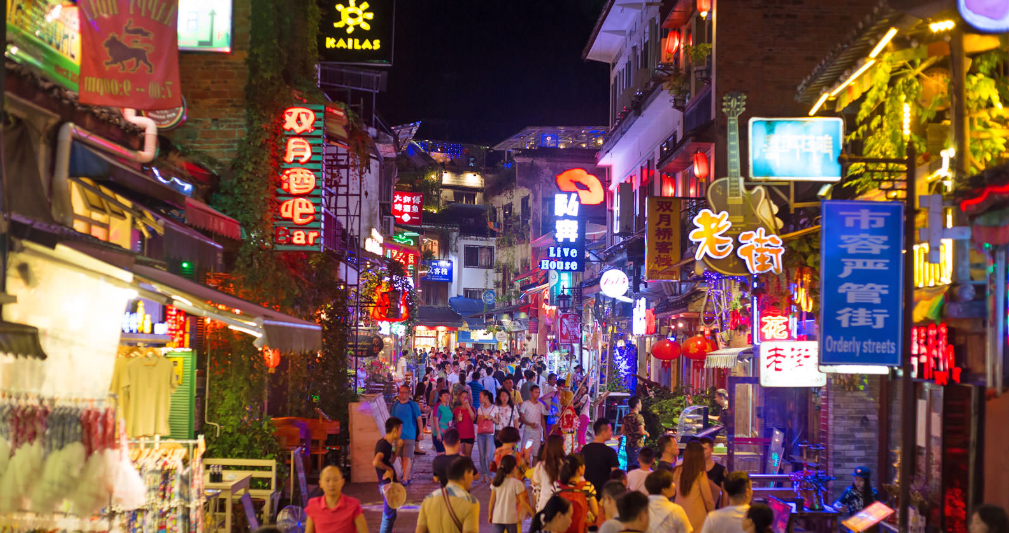
A bustling city off the coast of Xiaodong, Jindao is a major resort city with the highest tourists-per-capita of any city in Coius. The Jade Square in central Jindao is renowned for its wide assortment of cultures, cuisines and activities, with entertainment such as theatres, casinos and restaurants adorning much of the square. It is one of the highest recipients of tourism revenue and tourism accounts for most of country's economy.
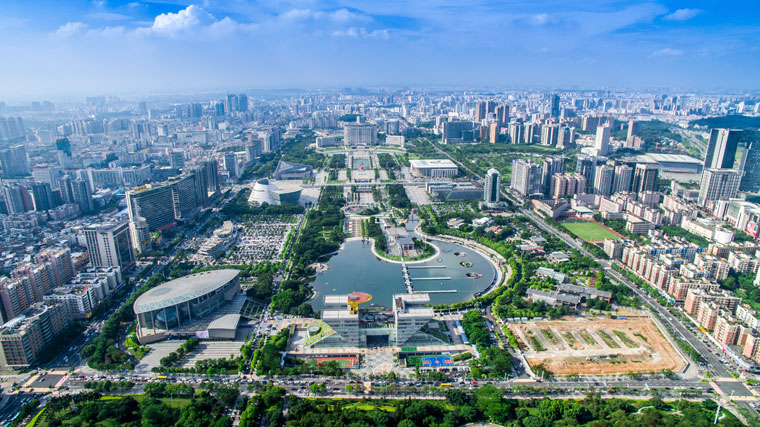
Jindao has high rates of urbanisation centred around the main Jindao island, with one of the highest Human Development Indexes in Kylaris, standing at 0.914. The Jindanese government is working on increasing residential capacity on the outlying islands as well as reclaiming land from the sea to use as residential suburbs and estates.
Etymology
The first instance of the island being called "Jindao" is from the early 2nd century, when Xiao settlers began to inhabit the island and naming it after its fabled beaches, likely where the Jindao Harbour is today, albeit the name was used to refer to the island itself rather than the name of the country owning it. Jindao has also been known under several different similar names, with "Jindau" sometimes being used to refer to the island and "Chintow" being the official name of the island whilst it was under Gaullican rule and also partially under Estmerish rule until the postal romanisation stopped being used in X, where it was renamed to its traditional name.
History
Jindao was first settled in the 2nd century AD, when Xiaodongese settlers migrated in from what is now the city of Lunkeng, around 12 kilometres north of the island. The Xiaodongese settlers brought their customs and traditions of classical antiquity Xiaodong to the island and it effectively functioned as an offshoot of Xiaodong despite the island being an independent entity. The knowledge of rice cultivation was brought from the mainland and the island flourished as an ideal place for rice growth and farming. Due to its unique climate, Jindao was initially a slow-developing city, with most of the island being used exclusively for rice farming. In 281 AD, Yao Jin consolidated the city of Jindao and proclaimed the Yao Dynasty as a separate kingdom to the mainland and claimed the entire island for the empire. His armies quickly seized the island (at this point mainly unsettled forest) to prevent the intervention of the Xiang dynasty of Xiaodong.

The Yao dynasty of Jindao did not last long, and Yao Jin would be its first and last independent emperor. News of the formation and breakaway of the Yao dynasty from the now-centralised Xiang dynasty angered the Emperor, who ordered that Jindao be vassalised and later fully integrated into the Xiang realm. In 286 AD, the Xiang Emperor launched a full invasion of Jindao utilising much of the standing Xiao forces. With the combined forces of the Xiang navy and army ready to launch a full naval invasion of Jindao, Emperor Yao Jin presented a peace offering to the Xiang Emperor, in which Jindao would surrender the island provided it is given some autonomy and the Yao dynasty retaining the right to rule the island as a subordinate leader under the Xiang. Fearing a possibly costly battle for the small and largely uninhabited island, the Xiang Emperor conceded and allowed Jindao to keep its autonomy provided it surrendered the island. The Xiang forces were allowed through the Jindao Harbour and docked in Jindao, where Xiang general Ma Xue, commander of the forces invading Jindao, was invited into the Yuhan Palace to sign the agreement. Xue and Emperor Yao Jin are told to have walked out of the palace together, treaty in hand, and announcing to the gathered crowd of Jindanese farmers, civilians and Xiao soldiers of the peace between the nations. The treaty was known as the Yuhan Palace Treaty and was the first step in Jindao's long endowment of autonomous status.
Government and politics
Administrative divisions
Sociopolitical issues
Geography
Climate
Architecture
Demographics
Economy
Infrastructure
Transport
Utilities
Culture
Cuisine
Cinema
Music
Sport and recreation
Education
Media
Cityscapes
Twin towns and sister cities
Jindao has two sister cities, listed alphabetically by country:






