Zacapican: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
===Biodiversity=== | ===Biodiversity=== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 102: | ||
===Conservation=== | ===Conservation=== | ||
==Government and Politics== | ==Government and Politics== | ||
{The national government is operates under a {{wp|semi-presidential system|dual executive system}} headed by a {{wp|Direct election|directly elected}} Tepachoani and the Huetetlacualtiani who is elected by the legislature, while its constituent states are {{wp|Presidential system|single executive republics}} under Tlayacapixqui governors.} | {The national government is operates under a {{wp|semi-presidential system|dual executive system}} headed by a {{wp|Direct election|directly elected}} Tepachoani and the Huetetlacualtiani who is elected by the legislature, while its constituent states are {{wp|Presidential system|single executive republics}} under Tlayacapixqui governors.} | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 18 July 2022
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
United Zacapine Republics Cepan Tlacatlatocayome Zacapiyotl Iámendu Uniachá Zakapikoni | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital | Quitzapatzaro |
| Largest city | Angatahuaca |
| Official languages | Nahuatl Purépecha |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Demonym(s) | Zacapitec, Zacapine |
| Government | Federal semi-presidential republic |
• Tepachoani | Zianya Xcaret |
• Huetetlacualtiani | Tizaro Sesasi |
| Legislature | Necentlatiloyan |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,845,600 km2 (712,600 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2022 census | 70,103,619 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $2.105 trillion |
• Per capita | $30,031 |
| HDI (2019) | very high |
| Currency | Amatl |
| Driving side | right |
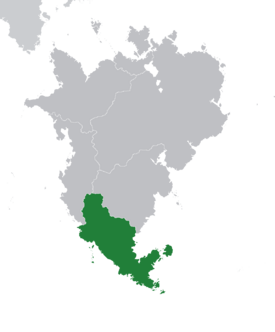
Zacapican, formally the United Zacapine Republics (Nahuatl: Cepan Tlacatlatocayome Zacapiyotl, CTZ), is is a country located in southern Oxidentale bordered to the north by Kayahallpa and Yadokawona, to the east by the Ooreqapi ocean, to the south by the Amictlan ocean, and to the west by the Makrian ocean. It is a federation of nine constituent republics and one federal district governing a population of 70 million inhabiting a territory of 1.8 million square kilometers across the southern reaches of the continent and several outlying islands and archipelagos. The largest city is Angatahuaca with a population of 10 million located in the Aztaco Republic while the national capital and third largest city is Quitzapatzaro with a population of 4 million located in the Autonomous Federal District. The Zacapine population is made of more than two dozen distinct native ethnicities and foreign nationalities, however the largest by far are the Nahuas followed by the Purépecha. Nahuatl is the lingua franca across all of the nations and tribes across the country while the predominant Nahua-Purépecha coalition forms the historical and cultural cement bindind the disparate groups of Zacapian together.
Since its inception, Zacapican has operated under a unique economic system called Calpollism, a system that has been categorized a hybrid of capitalism and communalism. Although it originated as an agrarian system, the modern Industrial Calpollism focuses predominantly on heavy industry and manufacturing and the development of an export oriented economy based in the secondary sector. Zacapican is the third of the Oxidentale economic giants and takes up a large global share of many industries, chiefly shipbuilding, aviation and the machine industry. Significant iron, coal and copper rescources in northern and central Zacapican have facilitated a strong steel and copper products industry which primarily supplies the many manufacturing centers across the country with their raw materials. A significant portion of the energy rescources and industrial materials consumed by the Zacapine economy are imported from its main trading partners in Malaio and the Ozeros nations, as well as the neighboring states of Oxidentale, while finished Zacapine exports have a more global reach. Zacapican possesses an advanced technology sector and is a world leader in aerospace and nuclear engineering.
History
{Aztapamatlan a medieval republic ruled by the two Cuauhtlatoani "Eagle Rulers" (Consuls), under the Cuauhtlatolo, the "Eagle Rule" or government by military elite.}
Geography
Biodiversity

The varied environments of Zacapican house an abundance of life including many unique species found nowhere else. Zacapican is a megadiverse country with an myriad of ecosystems and biomes ranging from sub-tropical forest, wetlands, temperate, dry and cold steppes, mountains, semi-arid and even polar climate regions. The Zacaco region boasts a tremendous degree of diversity in fauna including the Capybara, Zacaco deer, Maned wolf and Ñandu. Mixtepemec is home to the Spectacled bear, the Puma and the Guanaco while Xallipan is known for its many species of scorpions and the Vicuña which often used as a mascot by Zacapine children's media. Aztlacapallco is better known for the species of the surrounding waters, but is nevertheless recognized for such unique species as the Southern river otter and varied avian species such as the Aztlacapalltli woodpecker. Much of the Zacaco, Xallipan and Aztlacapallco regions posses little forest cover and are mostly grasslands, with very few tree species, such as the native Ombu or imported Norumbrian sycamore. The mountainsides and valleys of Mixtepemec are heavily forested by pines and other evergreens such as the native Araucaria tree, and are the main site of logging activities in Zacapican.
In addition to terrestrial life, Zacapican is known for its abundant maritime biology sustained by highly fertile polar waters. An abundance of plankton and krill in Zacapine waters and parts of the surrounding ocean sustains not only a tremendous number and variety of fish species, but also larger and iconic marine species including penguins, seals and whales. The Orca, a common sight on Zacapine shores, is particularly prevalent in local cultures and is regarded as a Zacapitec national symbol. The extremely rich marine ecosystem of Zacapican's waters has sustained an extensive fishing industry particularly within the world-renowned Zacapine Sea Fishery off the country's eastern shore. This fishery specifically has suffered from overfishing historically, but is considered to be in the process of recovering its normal fish stocks thanks to fishing restrictions put in place by the Zacapine government for the express purpose of regenerating the economically important Zacapine Sea Fishery. Historically, many Zacapitec mariners undertook whaling as a means to exploit the abundance of Minke, Humpback, Sei and Cachalot whales. In response to the depletion of these species and the decline in economic demands for baleen and whale oil, whaling of any type has been strictly prohibited by federal law since 1910.
Conservation
Government and Politics
{The national government is operates under a dual executive system headed by a directly elected Tepachoani and the Huetetlacualtiani who is elected by the legislature, while its constituent states are single executive republics under Tlayacapixqui governors.}
Economy
Agriculture
The economic and political significance of agriculture in Zacapican is of central importance despite the increasing role of modern industrial activities, thanks in no small part to the central role of agricultural communities in the political system since the Red Banner uprisings. An estimated 9 million Zacapitecs, roughly 15% of the population, are farmers or belong to a farming household according to the 2019 census. All land in Zacapican is publically owned and held by the state, which subsequently divides lands designated for farming into individual parcels which form agricultural calpolli. Under the Zacapitec Calpolli system, usufruct rights for portions of the publically held land are granted to individuals and households to use exclusively or in common. While most often these small family operated farms are held exclusively by that household, the land is owned by the federal state and administered by committee under the local calpolli. A plot of farmland which falls into disuse for a certain period or is voluntarily given up by the rights holder returns as state property to be reissued again to peasants applying for their own rights to use the land. Under the Red Banner constitution, it is illegal for any tax or free to be charged to registered land users for their farmland, however profits from agricultural activities may be taxed by the calpolli, the Atlepetl and the federal government. Because only monetary profits from sale may be taxed, portions of an agricultural calpolli's land may be used to produce food for the farmers' own subsistence for free not accounting for any labor costs. Land use rights once granted do not expire and cannot be revoked so long as the land remains in agricultural use except by criminal penalty for misuse of the land or a separate conviction rendering the rights holder unable or unfit to exercise their use rights. Land rights can be inherited, particularly within the same farming household typically living on the granted lands allowing for inherited multi-generational farms without the need for private land ownership. Direct contribution of agriculture to the GDP has fallen to less than 15% since the waves of industrialization in the 1960s and the rapid expansion of other areas of the national economy and today contributes roughly the equivalent of $247 billion. However, agricultural products both raw and processed make up a significant portion of national exports. These exports have arguably served as the catalyst for the growth and modernization of the Zacapitec economy. Agriculture which considered to include pastoral farming as well as fishing is overseen nationally by the Secretariat of Agriculture, which also oversees the National Agrarian Registry responsible for issuing usufruct rights to farmers.
Agriculture in Zacapican is primarily based on cereals but includes a variety of other crops to maximize yields across Zacapican's many climate regions and soil types. In particular, maize, wheat and barley form the common crops and are used to produce most of the staple foods of the Zacapitec diet. Sunflower seeds, soybeans, sugar cane and grapes are also cultivated both for food and as the base elements of processed goods such as sunflower and soybean oil, refined sugar and wine. Orchards of lemon, orange and apple trees are also common particularly in the Zacaco region. Zacapican is the world's largest producer of Ca'a tea, which is a culturally significant beverage in the country but has also become popular in foreign markets. A significant portion of the agricultural sector in Zacapican is devoted to livestock, especially in less fertile steppe ecosystems such as those found in the Aztlacapallco region which are poorly suited for crop cultivation. Cattle are the primary livestock in Zacapican and are raised primarily for beef, desired as a dietary staple across much of the country as well as an important export since the advent of refrigeration. Poultry such as chicken and turkey are also raised, typically alongside crop fields as part of the average farmstead, for both eggs and meat. Historically, the pastoral regions of Zacapican also hosted large herds of sheep which produced wool for export. This aspect of pastoral agriculture has largely faded, as sheep are now far less common in Zacapican and are raised primarily for mutton.
Manufacturing

Heavy industry and industrial manufacturing has been the cornerstone of the Zacapitec economy since a wave of modernization and industrialization swept the country in the 1960s. The manufacturing sector is the product of a massive and ongoing investment by the state and the national treasury, which has been focused not on any particular finished product or process, but rather on the general capability to establish industries in new and varied sectors as they emerge or become relevant. This has led to a focus on industrial production of machinery and other industrial equipment, defined by influential Zacapitec economist Calcui Xipil as "machines to build machines", alongside the industries for the processing and mass production of steel and other key materials required for many kinds of manufacturing and construction such as glass, plastic, concrete and cement. As a result of this industrial policy, Zacapican lacks many world renowned producers of finished goods but is well a well established exporter of components used in almost all industries, securing Zacapican a spot in the global supply chain. Aerospace, automotive, elecronics and paper industries are represented in the Zacapitec economy, but are either local subsidiaries of international companies or are domestic firms which largely confined to markets within Zacapican as they rely on protective tariffs to operate.
Under the Calpolli systems, factories, workhouses and other manufacturing facilities operate in a similar system to that of the agricultural calpolli, with some minor differences. All industrial facilities remain publically owned, but cannot be individually granted for use to each worker or worker's household due to economies of scale and their effect on the workplace, putting the facility under the control of the calpolli community the workers belong to which holds and exercises their use rights on their behalf. Because the industrial calpolli is no longer based on the management of individual use rights for fixed assets which can be revoked or granted to others freely, manufacturing assets as well as other enterprises of a non-agricultural nature are effectively the property of the local calpolli or in some cases the atlepetl above the calpolli which uses it. In this way, the Calpolli system when applied beyond the agricultural context creates communities specialized in a particular industry or more often a particular element of an industry, in which all or most of the working adults of that community participate in that specialized economic role by way of the publically owned factory or work facility which forms the economic centerpiece of the community. These calpolli units often serve as individual links in a supply chain, with multiple adjacent calpolli entities each operating facilities which compliment each other or add complexity and value to a product in a linear sequence from one calpolli to the next. The industrial aspects of these communities, such matters concerning the output, technical processes or quality of a manufactured product, or broader economic concerns affecting the factories held by industrial calpolli are governed by the Secretariat of Trade and Industry. Human aspects of the manufacturing process, such as workplace safety, working conditions and requirements or duties regarding the workers are governed by the Secretariat of Labor. These two government bodies, along with the Secretariat of Transportation, are known as the "Industrial Trifecta" and are responsible for administering the bulk of the Zacapitec economy.
Energy
The energy infrastructure of Zacapican has undergone several transformative processes since the electrification of the country at the turn of the 20th century. Initially, the nascent national power grid was supplied entirely by coal power plants, although in a short amount of time minor rivers were being dammed for hydroelectric power. This status quo remained in place until the massive industrialization of the country in the 1960s, shortly after which federal authorities began experimenting with alternative sources of power in response to the generally negative view of the public towards coal power which was somewhat exacerbated by the proliferation of factories and other heavy industrial centers. Hydroelectric power was expanded first, with new dams built and many old ones undergoing retrofits or in some cases being completely rebuilt. In the following decades of the late 20th century, domestically manufactured wind turbines were being installed in wind farms across the country. Early solar power initiatives consisted of thermal solar plants, which have been largely discontinued in favor of solar plants based on photovoltaic cells as the technology has become cheaper and contrasts favorably with the costlier and technically complex thermal solar plants. The most recent addition to the Zacapitec energy sector is nuclear power which has been introduced recently and is not yet widespread in the country. Only two nuclear power stations exist in Zacapican, the first being the large Ahuizotzi power plant completed in 2014 which serves the considerable energy demands of the Tecolotlan metropolitan area, while Yatlaxapan power plant intended to serve the Tequitinitlan area is still under construction. Electric power is considered a public service nationwide guaranteed by the government and provided by the Secretariat of Energy and its subsidiary organizations. Power plants and other electric infrastructure are operated by the federal government and provided directly to the individual users bypassing the atlepetl and calpolli tiers of government. A controversial electricity tax is levied at the federal level, and contributes directly to the national treasury. This tax charges a flat rate to each household connected to the national grid rather than charging per kilowatt hour, although tax exemptions have been implemented to provide relief under certain conditions to the moderately high tax rate charged for electricity. These exemptions were put in place in response to criticism of the tax which claimed that it would disproportionally affect poorer households which typically use less electricity in their daily lives, while officials have stated in defense of the tax that when adjusted for purchasing power and inflation, the monetary cost of the tax for a Zacapitec would still be less than the electricity bills paid to private companies for the same amount of power usage in foreign countries, arguing that even with the tax being levied power is still cheaper in Zacapican than in most other developed countries.
Infrastructure

In Zacapican, there are 179 airports with paved runways including 22 international airports, out of over 1000 airports and local airfields across the country. Air travel is the primary means to transportation to and from many Zacapitec territories such as the outlying islands of the Aztlacapallco region, the islands of the Michnamanalco archipelago and many particularly isolated locations in the inaccessible mountains and highlands across Aztlacapallco, Xallipan and the Mixtepemec. Itzcoatl International Airport serving the Tequitinitlan metropolitan area is the largest and busiest of Zacapican's airports since its opening in 1941. Tequitinitlan serves as the central hub for a network of roadways consisting of 71,361 km (44,342 miles) of paved roads out of roughly 255,000 km (158,450 miles) of total roadways. A large number of expressways were established in the mid 20th century connecting many of the major Atlepetl capital cities, the national capital and several sub Atlepetl grade urban centers especially across the Zacaco region and along the coastal strip of western Mixtepemec. The inadequacy of these expressways and modern road systems has been noted, specifically citing poorly maintained roads, which may have contributed to the increasing demand for rail transportation particularly between major urban centers.
The Zacapitec public transportation system is organized around the National Transportation Service (Nahuatl: Cecnitlacayoh Tlacazazacalo Atlepetequipanoliztli) known by the nahuatl acronym CTA which serves as the standardized national transportation system governing most forms of rail transit as well as some bus services particularly those in the major cities. CTA was formed in the year 1960 through the unification of over 200 individual light rail, commuter rail, heavy rail, inter-city rail, tram and bus networks which existed within and between numerous Atlepetl level transit authorities. While many mid-sized cities had in the previous decades developed extensive public transportation systems of their own to keep up with a growing population and more interconnected economy, the federal government found that such systems in very large cities such as Tecolotlan and Tequitinitlan were underdeveloped, and moreover that connectivity between city-state level territories was in a poor state. Under the CTA, all levels of a city's transportation scheme are integrated with one another and linked into regional and national transportation networks, allowing for seamless transition from local light rail and bus systems to city-wide and regional heavy rail as well as the national high-speed rail network. CTA fares vary depending on the number and type of connecting services involved in any one journey and are usually specific to the atlepetl, but are typically flat fares for subway, light rail and bus systems within a city or town, switching to a distance based fare for regional, inter-regional and national systems such as the high speed rail network. With maintenance and extensive network expansions as well as heavily subsidized fares, the NAT has operated at a net loss since its inception and requires a yearly subsidy from the national treasury to balance its internal budget. Public transportation and specifically the massive expansion and integration of transit systems under the CTA is correlated with the so called Second Wave of the 1970s, an period of explosive economic growth in the cities of Zacapican which occurred several years after the initial economic boom of the industrialization years of the 1960s had slowed down, particularly leading to great stimulation and growth of the economy in previously isolated suburban areas which became connected to metropolitan transit networks. The CTA operates as a subordinate organization to the Secretariat of Transportation and is considered a part of the federal government.
Communication law in Zacapican generally follows the trend of nationally operated and regulated public services. Internet services operates under a public option system, in which residents or visitors in Zacapican have the option of using the Zacapitec state ISP, the National Public Telecommunicatins Service also known as Cecnitlacayoh Nuhhuian Macho Huehcacaquiztli Atlepetequipanoliztli or CNMHA or their choice of alternatives including community owned local providers or even domestic subsidiaries of foreign providers. CNMHA operates as the state owned telecommunications company and is also the sole provider of fixedline and mobile telephone service in Zacapican, in addition to providing much of the communications infrastructure used in digital and analog TV broadcasting. As such, major Zacapitec TV networks such as the news network Tzatzihua broadcast using CNMHA's telecoms infrastructure. A majority, however not a totality, of Zacapican's communications infrastructure is owned and operated by CNMHA, which itself operates under the auspices of the Secretariat of Communication. CNMHA has been accused of carrying out censorship of the internet on behalf of the Zacapitec government, however accusations of censorship do not extend to CNMHA's other services which are considered to critics to be more openly run and lacking apparent censorship. Spokespeople of CNMHA and the government have independently asserted the state owned company's adherence to the principle of net neutrality, claiming that the ISP does not block or restrict access to content of any kind except in collaboration with the government when shutting down access to sites that are in clear violation of criminal law. Similar to its transportation counterpart in the CTA, CNMHA has rarely seen a year of net profit and generally looses money due to its low prices on the user end and high costs of relatively high end infrastructure. Both CTA and CNMHA as state owned companies are considered to be maintaining public infrastructure at a loss using tax revenue to make up the difference, with the understanding that the vital services these companies provide in the name of the state foster economic growth and prosperity that, if quantified, would be greater than the subsidy paid by the national treasury to each of these companies in a given year.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1919 | 33,124,894 | — |
| 1924 | 33,974,251 | +2.6% |
| 1929 | 35,025,002 | +3.1% |
| 1934 | 36,084,261 | +3.0% |
| 1939 | 36,820,675 | +2.0% |
| 1944 | 38,354,870 | +4.2% |
| 1949 | 39,541,104 | +3.1% |
| 1954 | 41,188,651 | +4.2% |
| 1959 | 43,817,714 | +6.4% |
| 1964 | 46,172,513 | +5.4% |
| 1969 | 48,348,182 | +4.7% |
| 1974 | 50,362,690 | +4.2% |
| 1979 | 51,760,216 | +2.8% |
| 1984 | 53,361,048 | +3.1% |
| 1989 | 54,729,281 | +2.6% |
| 1994 | 55,960,411 | +2.2% |
| 1999 | 56,986,162 | +1.8% |
| 2004 | 57,853,972 | +1.5% |
| 2009 | 58,438,356 | +1.0% |
| 2014 | 59,630,976 | +2.0% |
| 2019 | 60,785,909 | +1.9% |
Zacapican is considered a medium to large nation relative to the world standard, playing host to a variety of unique ethnic groups and populations. There are 60,785,909 people living in Zacapican according to the 2019 census carried out by the Statistics and Data Collection Agency within the Secretariat of Internal Affairs. 63.6% of the recorded population, roughly 38,659,838 people, is between the ages of 15 and 64 while 24.2% (aproximately 14,710,189 people) are under 14 while only 12.2% or 7,415,880 people were recorded as being over 64 years of age. In general, the population has a mostly balanced sex ration averaging 0.98 males to females across all ages, with a surplus of males under 15 at a ration of 1.05 males to females in that cohort, compared to a ratio of 0.72 males to females 65 and over. The average life expectancy is 77.14 years at birth. More than 80% of Zacapitecs identify as Nahua ethnically, while 88.9% speak Nahuatl as a first language compared to 97.9% of the population which are proficient in Nahuatl. 99.6% of those aged over 15 can read and write in at least one language. Over the past 40 years, Zacapican has maintained a relatively stable rate of population growth averaging at a 2.1% increase every 5 years. The nation experienced its most precipitous growth in the past hundred years between 1954 and 1964, a period of Zacapitec history marked by industrialization and urbanization, following which the growth rate stabilized towards its current norm.
Ethnicity and Language
Zacapican is not officially an ethnically oriented state despite its strong nahuatl affiliation and history, as the Red Banner constitution defines a “Zacapitec” person as "any person born within the territories and possesions of the Panchichiltic Tlatoloyan, or any person having naturalized into the Panchichiltic Tlatoloyan by legal and social processes". Consequently, the term Zacapitec does not officially carry any ethnic connotation as a person so described could be of any number of ethnic inclinations which may or may not be nahua in character. The stance of the Zacapitec government is that nationality and ethnicity should not be equated in the contect of Zacapican, and that therefore the many peoples native to Zacapican as well as those who have migrated into the country should be considered by others and should consider themselves as members of the Zacapitec nation without conflicting with any ethnic identity they may hold. However, Zacapican is a heavily Nahua-inclined nation with an almost unbroken history of rule by Nahua groups as well as the historical and allegedly ongoing Nahuanization (assimilation into the Nahua ethnicity) of non-Nahuas.
Cultural assimilation is a controversial topic in Zacapican, which is claimed to have been resolved in the 1980s with a number of protections particularly preserving regional languages and enabling their public use to prevent their disuse and extinction. Statistics of self-reported ethnic identity show the proportion of Nahua groups growing relative to the whole. Disputed claims suggest this trend could be the result of higher population growth rates in majority Nahua areas, or ongoing processes of assimilation on non-Nahuas into the Nahua identity despite national intervention to halt this. Roughly 20% of the Zacapitec population self reported affiliation with a non-Nahua ethnic identity in 2019, including at least two groups considered to be non-native immigrant communities. However the majority of the non-Nahua population of Zacapican represent native cultures which have existed in the region for centuries or millennia and have become entrenched within their local communities to resist assimilation.
Nahuatl is the official language of Zacapican and is taught across all communities uniformly, irrespective of any secondary recognized language. Many regional dialects and variations of nahuatl are present in politics, within the workplace and in everyday social life and are nominally mutually intelligible with one another and the national standard verion. The Nahuatl League is an independent academic body endorsed by the federal government which serves as the pre-eminent authority on the Nahuatl language in both spoken and written aspects. Nahuatl Zacapiyotl, also called Zacapiyotl or "standard nahautl", is the state sanctioned dialect of the nahuatl language which is used in all official government documentation, is taught as a standard part of the curriculum in schools, and is utilized by most national and local publications. The council of the Nahuatl League advises the government as well as dictionary publishers on changes and updates to the standard nahuatl lexicon to be accounted for and acknowledged as an accepted common use of the national language.
Under the No True Foreigner Act (Huecachane Iztlaca Itlatlalil Tl.Itl 339) put into place in 1984, regional languages and the languages of recognized immigrant enclaves are protected from state repression and discriminatory treatment. As a result of this law a variety of local and federal government offices are required to offer documents and forms in multiple languages and to provide interpreter services at courthouses, hospitals and certain schools. Officially, language recognition and protections are applied at the calpolli level, allowing small minority enclaves to enjoy language protections within their neighborhood. Informally, large regions where a minority language is prevalent may form atlepetl and inter-atlepetl level organizations to standardize the status and treatment of the local language. In these regions, the recognized local language may be taught in schools alongside nahuatl through the calpolli level control over schooling, as well as used in public signage and government announcements. Publications in any language are freely permitted anywhere in the country under the constitutional documents of Zacapican since the 1780s.
Urbanization
Zacapican is a urbanized nation with close to 50% of the nation's population living within the city limits of the country's twenty largest urban centers. However, it is not uniformly urbanized across all regions. Most Zacapitecs live on the Zacaco plains and on the coastal strip of the Mixtepemec. These areas boast the most concentrated and densely packed population centers, as the Mixtepemec coast plays host to almost no rural communities although such towns and villages may still be sound in some quantity across the Zacaco. Conversely, the Mixtepemec highlands as well as the Xallipan, Aztlacapallco and Michnamanalco regions play host to few significant urban centers and host a widely dispersed rural population. According to the 2019 census, 82% of the Zacapitec population live in urban zones, whether inside city limits or within urbanized satellite communities.
| Rank | Atlepetl | Pop. | Rank | Atlepetl | Pop. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tecolotlan  Tequitinitlan |
1 | Tecolotlan | Tecolotlan | 9,209,944 | 11 | Tequenitlan | Tequenitlan | 870,611 |  Acazacatlan  Tzopilopan |
| 2 | Tequitinitlan | Tequitinitlan | 4,310,645 | 12 | Zolatepec | Xochimixtlan | 813,852 | ||
| 3 | Acazacatlan | Acazacatlan | 2,943,123 | 13 | Huitzilopochco | Tecolotlan | 800,802 | ||
| 4 | Tzopilopan | Tzopilopan | 1,493,909 | 14 | Xochimixtlan | Xochimixtlan | 775,127 | ||
| 5 | Cuauhquecholan | Cuauhquecholan | 1,157,220 | 15 | Mazapan | Mazapan | 691,111 | ||
| 6 | Tzinacantlan | Tzinacantlan | 1,170,003 | 16 | Acalhuatlan | Acalhuatlan | 640,536 | ||
| 7 | Tlatlauhquitepec | Tlatlauhquitepec | 1,001,332 | 17 | Coyoacan | Tequitinitlan | 612,002 | ||
| 8 | Cuahuacan | Cuahuacan | 955,375 | 18 | Tlamatzinco | Tlamatzinco | 401,104 | ||
| 9 | Xocotlan | Xocotlan | 913,997 | 19 | Xochicalco | Xochicalco | 300,011 | ||
| 10 | Onatlan | Onatlan | 911,000 | 20 | Yopico | Xochicalco | 271,358 | ||