1979 Piraean national plebiscite: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
It is believed that international pressure from other [[Euclea]]n nations and Piraean big business were crucial in the decision of the junta of respecting the results, as Piraea was one of the few remaining dictatorships of East Euclea. | It is believed that international pressure from other [[Euclea]]n nations and Piraean big business were crucial in the decision of the junta of respecting the results, as Piraea was one of the few remaining dictatorships of East Euclea. | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
During the mid-1960s and 1970s, Piraea experienced an {{wp|economic miracle}} often credited to the program of economic liberalisation carried out by the military government following [[Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs]] and [[International Council for Democracy ]] advice and funding. Although the reforms proved efficient in Piraea's exit from recession, dissident voices became more prominent criticising persistent {{wp|political censorship}} and {{wp|repression}} as well as a growing {{wp|income inequalities}}. Towards the end of the decade, political demonstration from {{wp|leftist}} groups (often in clandestine) became more usual, and the Piraean exile reconducted international observation to their cause. | |||
In 1978, [[Konstantinos Athanopoulos]], who ruled the [[Second Piraean Republic]] as a military dictator of [[National Functionalism|Functionalist]] background, died in his palace of [[Alikianos]]. Athanopoulos had previously ordered that the {{wp|Commander-in-Chief}} of the Air Force, [[Ioannis Christodoulopoulos]], would succeed him in the position of Premier in the Junta. The military executive invested Christodoulopoulos as Premier, but sought to acquire the legitimacy of the people's vote in order to confirm the continuity of the military rule. | |||
===Electorate=== | ===Electorate=== | ||
{{multiple image|perrow=2|total_width=350 | |||
| image1 = Nai 1979.png | |||
| image2 = Oxi 1979.png | |||
| footer = Logos used by the two options during the campaign. | |||
}} | |||
The electorate for the plebiscite has been severely studied by Piraean sociologists and political analysts. The plebiscite is believed to have inaugurated an important mark in the country's politics and electoral history, with similar results by region and municipality across the elections. The electoral process was the first to be conducted after 30 years of severe political and social repression: it was also one of the first elections in which the vote of the women was specially sought after and counted with an important influence in the final results. | |||
Options that aligned under the campaign of the ''"Yes"'' (''Ναι'') were often connected to the {{wp|upper}} and {{wp|upper-middle}} classes, generally linked with the military government or the business world (the campaign used the economic stability and secureness as one of its slogans) and students' and youth groups of {{wp|far-right}} background. Although the [[Episemilist Church]] did not expressed opinion, it is widely known that priests and patriarchs of the [[Metropolitanate of Alikianos]] showed a preferable option for the continuity of the military junta. In the vote of the ''"No"'' (''Όχι''), groups. | |||
==Plebiscite== | ==Plebiscite== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="line-height:1.35em; font-size:95%; text-align:left;" | {| class="wikitable" style="line-height:1.35em; font-size:95%; text-align:left;" | ||
Revision as of 01:56, 17 January 2023
| 1979 Piraean national plebiscite | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuation of Ioannis Christodoulopoulos and the rest of the Junta | |||||||||||||||||||
| Date | 5 July 1979 | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
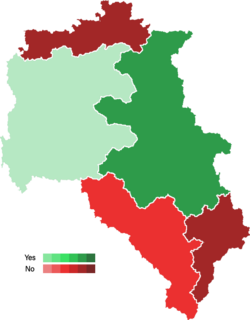
The 1979 Piraean national plebiscite (Piraean: 1979 Εθνικό δημοψήφισμα της Πειραεάς) was a referendum conducted in Piraea during July 1979, in which the electorate was asked about the continuation of Ioannis Christodoulopoulos and the military junta as Head of State and Government.
The referendum was conducted a year after the death of Konstantinos Athanopoulos, who ruled the Second Piraean Republic as a military dictatorship. That same year, the members of the military junta voted Ioannis Christodoulopoulos, who occupied the role of Commander-in-Chief of the Air Force, to be the Premier and sought to renew their term in power through the plebiscite. If the population approved the candidate of the junta and voted "Yes", the military institution would continue exercising as the executive, but if the result proved negative, a newly elected office and legislature would have been needed to be voted. Finally, the "No" to the candidate of the junta won by a 56% of the vote, igniting a process known as "Metapolitefsi" (Piraean: Μεταπολίτευση) or "regime change", which concluded with the general elections of 1980.
It is believed that international pressure from other Euclean nations and Piraean big business were crucial in the decision of the junta of respecting the results, as Piraea was one of the few remaining dictatorships of East Euclea.
Background
During the mid-1960s and 1970s, Piraea experienced an economic miracle often credited to the program of economic liberalisation carried out by the military government following Global Institute for Fiscal Affairs and International Council for Democracy advice and funding. Although the reforms proved efficient in Piraea's exit from recession, dissident voices became more prominent criticising persistent political censorship and repression as well as a growing income inequalities. Towards the end of the decade, political demonstration from leftist groups (often in clandestine) became more usual, and the Piraean exile reconducted international observation to their cause.
In 1978, Konstantinos Athanopoulos, who ruled the Second Piraean Republic as a military dictator of Functionalist background, died in his palace of Alikianos. Athanopoulos had previously ordered that the Commander-in-Chief of the Air Force, Ioannis Christodoulopoulos, would succeed him in the position of Premier in the Junta. The military executive invested Christodoulopoulos as Premier, but sought to acquire the legitimacy of the people's vote in order to confirm the continuity of the military rule.
Electorate
The electorate for the plebiscite has been severely studied by Piraean sociologists and political analysts. The plebiscite is believed to have inaugurated an important mark in the country's politics and electoral history, with similar results by region and municipality across the elections. The electoral process was the first to be conducted after 30 years of severe political and social repression: it was also one of the first elections in which the vote of the women was specially sought after and counted with an important influence in the final results.
Options that aligned under the campaign of the "Yes" (Ναι) were often connected to the upper and upper-middle classes, generally linked with the military government or the business world (the campaign used the economic stability and secureness as one of its slogans) and students' and youth groups of far-right background. Although the Episemilist Church did not expressed opinion, it is widely known that priests and patriarchs of the Metropolitanate of Alikianos showed a preferable option for the continuity of the military junta. In the vote of the "No" (Όχι), groups.
Plebiscite
| Option | Parties and alliances |
Candidate or leading face |
Gov. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ioannis Christodoulopoulos | |||||

|
Andrianos Rodiales [a] | ||||
Results
Aftermath
Notes
- ↑ The "No" option was not allowed a candidate in the plebiscite, and thus Andrianos Rodiales is generally considered the face that led most of the public appearences during the campaign and also the two debates/interviews.