Gruening F5M Lynx: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(→Design) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
The Lynx's weapons system was based around the utilization of the TAI-81 X band pulse-doppler radar, the first in use capable of launching using {{wpl|track while scan}}; and the {{wpl|AIM-54 Phoenix|MUA-55 Phoenix}} missile, a very long range air to air missile intended for intercepting targets at ranges in excess of 100 nautical miles. Utilizing the Phoenix for long-range intercepts and the {{wpl|AIM-7 Sparrow|MUA-7 Falcon}} for escort and air intercept missions. From the outset it was armed with the {{wpl|M61 Vulcan|Mark 40 20mm cannon}} in a nose mount with 600 rounds of ammunition. The Lynx carries a radar warning receiver, chaff, flare, and models from the F5M4 and later are integrated with electronics countermeasures systems to defend against incoming missiles. | The Lynx's weapons system was based around the utilization of the TAI-81 X band pulse-doppler radar, the first in use capable of launching using {{wpl|track while scan}}; and the {{wpl|AIM-54 Phoenix|MUA-55 Phoenix}} missile, a very long range air to air missile intended for intercepting targets at ranges in excess of 100 nautical miles. Utilizing the Phoenix for long-range intercepts and the {{wpl|AIM-7 Sparrow|MUA-7 Falcon}} for escort and air intercept missions. From the outset it was armed with the {{wpl|M61 Vulcan|Mark 40 20mm cannon}} in a nose mount with 600 rounds of ammunition. The Lynx carries a radar warning receiver, chaff, flare, and models from the F5M4 and later are integrated with electronics countermeasures systems to defend against incoming missiles. | ||
The Lynx | The Lynx featured pioneering developments in pilot interface in Meridonian fighter craft, including the first multi-function HUD, hands-on throttle and stick (HOTAS), and early multifunction displays, features which would prove instrumental in the design of later combat aircraft. | ||
Lynx models from the F5M6 and later improve | Lynx models from the F5M6 and later improve vastly upon the original design of the base model F5Ms (F5M through F5M5). The F5M6 introduced leading-edge extensions (LEX) to the wing root, enhanced visibility cockpit glass, full multifunction glass flight displays, integrated NAV/attack FLIR pods, and HMD integration, as well as allowing for the carrying of standoff weaponry including cruise, anti-satellite, and anti-ship missiles. The so-called "Super Lynx" upgrade vastly improved performance in nearly all aspects over the airframe. F5M7 upgrades, first fielded by the Air Force, feature a full glass display replacing all 'steam gauge' instruments | ||
[[File:F5m_cockpit.png|thumb|right|550px|Pilot cockpit layouts of the F5M2 (left), F5M5 (center) and F5M6 (right).]] | |||
The AFASF-12 has an all-metal semi-monocoque fuselage possessing broad aerodynamic similarities to the earlier [[NSF-12 Albatro Strike Fighter|NSF-12 ''Albatro'']]. It has mid-mounted swept wings with blended leading-edge root extensions swept at approximately 40°. A pair of tailplanes and vertical fins are mounted on booms outboard of the engines. Automatic, five-segmented slates are mounted on the leading of the wings with maneuvering flaps and wingtip ailerons mounted on the trailing edges. The boron-composite skin used in the construction of the Drago gives the aircraft very high heat resistance as well as exceptionally thin wing edges. | |||
The cockpit of the Drago is high-mounted and equipped with a bubble canopy that gives it increased visibility in comparison to previous Cacertian-designed fighters. The avionics systems includes a heads-up display, advanced radar, inertial guidance system, flight instruments, ultra high frequency communications, an advanced air navigation system, and instrument landing receivers. | The cockpit of the Drago is high-mounted and equipped with a bubble canopy that gives it increased visibility in comparison to previous Cacertian-designed fighters. The avionics systems includes a heads-up display, advanced radar, inertial guidance system, flight instruments, ultra high frequency communications, an advanced air navigation system, and instrument landing receivers. | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 18 January 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Gruening F5M Lynx | |
|---|---|

| |
| A pair of Meridonian Navy F5M7s of the High Spades conducting an overhead break at MNAS Marin Bay. | |
| Role | Air superiority fighter Multirole fighter |
| National origin | |
| Manufacturer | Gruening Defense Aerospace |
| First flight | 14 August 1970 |
| Introduction | 2 February 1974 |
| Status | In active service |
| Primary user | |
| Produced | 1969-present |
| Number built | 924 |
| Unit cost |
86.2 million MD (F5M7)
|
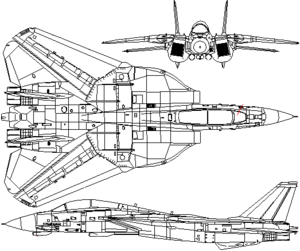
The Gruening F5M Lynx is a Meridonian carrier-capable, supersonic, twin engine, two seat, twin tail, variable sweep jet fighter. Originally designed for the Meridonian Navy to supplement and eventually replace the F4M Spectre in an air superiority fighter and interceptor role, it has been significantly developed and upgraded since its initial introduction to compose a major part of the tactical aircraft of both the Navy and the Template:Meridonian Air Forces, where it has been made capable of multirole missions.
Originally designed and optimized for long-range air to air interception of cruise missiles, bombers, and fighter aircraft, a need for long-range strike capabilities on naval aircraft became apparent, which saw later variants upgraded to become capable of precision bombing and reconnaissance via the Tactical Aircraft Navigation and Designation Module (TANDEM) pod. Following the collapse of the Air Force's Air Supremacy Initiative in the 1980s, the F5M was introduced as an interim solution to fill a gap in the air superiority field. Collaboration with the Navy and Air Forces in the 90s saw the introduction of the "Super Lynx", an enhanced design featuring leading edge extensions, integrated targeting and navigation systems, enhanced avionics and airframe construction, and a substantial enhancement in its mission profile with the ability to launch standoff air-to-ground munitions.
Currently, it serves as one of the mainline fighter aircraft of both services alongside the F6M2 Wasp, where it remains ideally suited for air combat missions. Built around the MUA-55 Phoenix long-range air-to-air missile as its primary armament, it remains one of the most potent long-range interceptors in service, though it has been upgraded to be able to field the MUA-120 CAIMS alongside the Wasp.
Development
Design
The F5M was designed based both on experience flying the F4M Spectre as a naval fighter, and on perceived needs of the carrier air wing in conducting force projection and self-defense operations. Seeing the threat of missile-armed bomber flights as an emerging threat towards the carrier group, the F5M was designed with long range and an air-to-air focus in mind while ground attack missions would be relegated to the F4, a role in which it had proved itself more than capable of performing. Like the F4M, the F5M was designed around a two-crew design with a pilot and radar intercept officer deemed better able to manage air intercepts.
A number of emerging technologies were included in its design, chief among those its variable geometry wings, which move forward for slower flight and move rearward for faster supersonic flight. It included a number of innovative control surfaces to improve its low-speed handling, which was necessary for carrier operations. Originally it was powered by a pair Altern MG-410 afterburning turbofan engines, which proved to be prone to compressor stall incidents at high angles of attack, and was later replaced by Hollon FT80 engines, which provided a substantial increase in both reliability and performance. Both engines are supplied with rectangular intakes equipped with movable ramps, bleed doors and other such functions. Landing gear is provided in a tricycle arrangement, and is reinforced for carrier landings.
The Lynx's weapons system was based around the utilization of the TAI-81 X band pulse-doppler radar, the first in use capable of launching using track while scan; and the MUA-55 Phoenix missile, a very long range air to air missile intended for intercepting targets at ranges in excess of 100 nautical miles. Utilizing the Phoenix for long-range intercepts and the MUA-7 Falcon for escort and air intercept missions. From the outset it was armed with the Mark 40 20mm cannon in a nose mount with 600 rounds of ammunition. The Lynx carries a radar warning receiver, chaff, flare, and models from the F5M4 and later are integrated with electronics countermeasures systems to defend against incoming missiles.
The Lynx featured pioneering developments in pilot interface in Meridonian fighter craft, including the first multi-function HUD, hands-on throttle and stick (HOTAS), and early multifunction displays, features which would prove instrumental in the design of later combat aircraft.
Lynx models from the F5M6 and later improve vastly upon the original design of the base model F5Ms (F5M through F5M5). The F5M6 introduced leading-edge extensions (LEX) to the wing root, enhanced visibility cockpit glass, full multifunction glass flight displays, integrated NAV/attack FLIR pods, and HMD integration, as well as allowing for the carrying of standoff weaponry including cruise, anti-satellite, and anti-ship missiles. The so-called "Super Lynx" upgrade vastly improved performance in nearly all aspects over the airframe. F5M7 upgrades, first fielded by the Air Force, feature a full glass display replacing all 'steam gauge' instruments
The AFASF-12 has an all-metal semi-monocoque fuselage possessing broad aerodynamic similarities to the earlier NSF-12 Albatro. It has mid-mounted swept wings with blended leading-edge root extensions swept at approximately 40°. A pair of tailplanes and vertical fins are mounted on booms outboard of the engines. Automatic, five-segmented slates are mounted on the leading of the wings with maneuvering flaps and wingtip ailerons mounted on the trailing edges. The boron-composite skin used in the construction of the Drago gives the aircraft very high heat resistance as well as exceptionally thin wing edges. The cockpit of the Drago is high-mounted and equipped with a bubble canopy that gives it increased visibility in comparison to previous Cacertian-designed fighters. The avionics systems includes a heads-up display, advanced radar, inertial guidance system, flight instruments, ultra high frequency communications, an advanced air navigation system, and instrument landing receivers.
An integrated helmet mounted display projects all essential fight information gathered by the integrated avionics and is visible to the pilot in any light condition. This allows operators to track and destroy enemy aircraft without the necessity of looking down at cockpit instruments.

The Drago is equipped with an advanced pulse-doppler radar that allows the aircraft to look up at high-flying targets as well as look-down at low-flying targets without confusing ground clutter. Despite the fact the Drago was more purposefully designed as a low-to-mid altitude dogfighter, it is equipped with radars capable of tracking targets beyond visual range.
The armament for a Drago often varies depending on its mission profile. As a dedicated air superiority fighter, this primarily focused on medium range air-to-air missiles, but as newer variants of the Drago were developed, this would later expand to also include multi-mission munitions. The Drago is equipped with eight external pylons, four under each wing. A single 30mm cannon with a 150-round magazine is located in the port wing root.
Since their introduction in 1983, the Drago has undergone a number of upgrades to improve performance and expand its capabilities. As of 2008, the majority of Dragos in service with the Cacertian Royal Air Fleet have been overhauled with newer hardware and sensors, which greatly increased a pilot’s situational awareness, as well as a new radar capable of provided instantaneous updates and enhanced multitarget tracking.
Dragos in Ruvelkan service saw extensive modifications and upgrades during their action in the Zemplen War. Designated AFASF-12Ks, the domestically developed Ruvelkan Dragos possess precision-guided targeting and an enhanced optical locator system that allows Ruvelkan Dragos to operate independently of ground-control interception. Among other upgrades, several Ruvelkan Dragos were later equipped with low-drag conformal fuel tanks which greatly increased their operational range for increased aerodynamic drag.
Operational History
Variants
- F5M
- The initial production version that entered service with the Royal Air Fleet in 1983. Following an upgrade and refit program (which resulted in the AFASF-12A) in the mid-1990s, only a handful of examples of the original version of the Drago currently exist, most of which are listed in the Air Fleet’s reserve or are preserved in museums.
- F5M2
- The AFASF-12E (Esportazione) is the export variant of the original Drago. Many of the features remain the same between the original and the export, the only differences being a commercial variant, and not the Air Fleet standard, radar and electronic suite.
- F5M3
- In 1993, Ersilia began a program designed to upgrade the systems of the Drago to modern standards and equipment; the final product was designated as the AFASF-12A (Aggiornamento). A number of flight control improvements provided better stability and controllability as well as an improved mechanical-hydraulic flight control system. The package also included a new radar and ECM system as well as the ability for the Drago to carry underwing and centerline drop tanks for increased range. The AFASF-12A was the first of the Drago family capable of engaging ground targets, although its overall focus was still air-to-air dominance.
- F5M4
- Ersilia offered a limited upgrade program to its export customers in 1998 following the success and release of the AFASF-12A designated as the AFASF-12EA (Esportazione Aggiornata). Many of the improvements that were installed on the As were included in the package, however the radar and electronic suits were once again commercial and not the Air Fleet’s standard.
- F5M5
- The lack of air-to-air engagements in the modern era resulted in the creation of the newer AFASF-12NG (Nuova Generazione). Originally, the NGs (later nicknamed Drago IIs) were simply further upgraded AFASF-12As with expanded ground attack capabilities. As of 2008, however, the AFASF-12NG entered its own serialized production and NGs that are now entering service are considered brand new aircraft.
- F5M6
- The AFASF-12K (Korszerűsített) is a Ruvelkan-developed variant improving on the original AFASF-12EAs purchased from Cacerta. The aircrafts' performance during the Zemplen War affected further development of Ruvelka's air-superiority program and the native Ruvelkan design began deployment in late 2008. New precision-guided targeting capabilities and a uniquely designed optical locator system relieves the Ruvelkan AFASF-12EAs from their reliance on ground-control interception systems. These systems allow the AFASF-12K to conduct its missions independently.
- F5M7
Operators
Current Operators
 Meridon- 662 in service of F5M6 and F5M7 variants across both Air Forces and Navy.
Meridon- 662 in service of F5M6 and F5M7 variants across both Air Forces and Navy.
Former Operators
Specifications (F5M7)
General Characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 62 ft 9 in (19.13m)
- Wingspan: 64 ft 1.5 in (19.545 m)
- Swept wingspan: 38 ft 2.5 in (11.646 m) swept
- Height: 16 ft (4.9 m)
- Wing Area: 565 sq ft (52.5 m2) wings only
- Empty Weight: 45,624 lb (20,694 kg)
- Max Takeoff Weight: 76,820 lb (34,844 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Hollon FT80E afterburning turbofans
- Fuel Capacity: 17,000lb internal, 2x optional 267gal (1,756lb/797kg) external tanks
Performance
- Maximum Speed: Mach 2.41 (2,975 km/h, 1,849 mph) at altitude
- Service Ceiling: 55,000 ft (16,764 m) +
- Rate of Climb: 45,000 ft/min plus (230 m/s)
- Wing Loading: 96 lb/sq ft (470 kg/m2)
- Thrust/Weight: 1.14, clean configuration, 50*
Armament
- Guns: 1 × Mark 40 20mm cannon with 600 rounds
- Payload: 10 hardpoints total: 4 between engine fairing, 2 under engine nacelle, 2 per wing glove (1 wing glove per wing) with capacity of 15,000lbs (6,803 kg) of munition to carry the following: