Vohland: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
}} | }} | ||
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi). Poland has a population of 37.7 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. | |||
Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast,[e] Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. | |||
The | The history of human activity on Polish soil dates to circa 10,000 BC. Culturally diverse throughout late antiquity, the region became inhabited by tribal Polans who gave Poland its name in the early medieval period. The establishment of statehood in 966 coincided with a pagan ruler of the Polans converting to Christianity under the auspices of the Roman Church. The Kingdom of Poland emerged in 1025 and in 1569 cemented its longstanding association with Lithuania, thus forming the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was one of the largest great powers of Europe at the time, with a uniquely liberal political system that adopted Europe's first modern constitution in 1791. | ||
With the passing of a prosperous Polish Golden Age, the country was partitioned by neighbouring states at the end of the 18th century and regained its independence in 1918 as the Second Polish Republic. In September 1939, the German-Soviet invasion of Poland marked the beginning of World War II, which resulted in the Holocaust and millions of Polish casualties. As a member of the Communist Bloc in the global Cold War, the Polish People's Republic was a founding signatory of the Warsaw Pact. Through the emergence and contributions of the Solidarity movement, the communist government was dissolved and Poland re-established itself as a democratic state in 1989. | |||
Poland is a parliamentary republic, with its bicameral legislature comprising the Sejm and the Senate. It is a developed market and a high income economy. Considered a middle power, Poland has the sixth largest economy in the European Union by GDP (nominal) and the fifth largest by GDP (PPP). It provides high standards of living, safety and economic freedom, as well as free university education and a universal health care system. The country has 17 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 15 of which are cultural. Poland is a founding member state of the United Nations, as well as a member of the World Trade Organization, NATO, and the European Union (including the Schengen Area). | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 26 January 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Vohland Rzeczpospolita Vohlanska | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
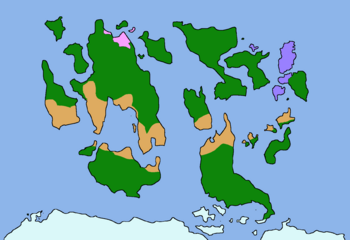 Map of Vohland | |||||||
| Capital and largest city | Breselberg | ||||||
| Official languages | Vohlish | ||||||
| Religion | 85.1% Catholicism 13.4% Judaism 2.5% Other | ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Vohlish | ||||||
| Government | Republic | ||||||
• President | Marthe Riese | ||||||
• Vice President | Meike Teufel | ||||||
• Water (%) | 1.48 | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• Estimate | 37,750,000 (2nd) | ||||||
• 2022 census | 37,750,424 | ||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate | ||||||
• Total | $679.4 billion (2nd) | ||||||
• Per capita | $17,999 (1st) | ||||||
| Gini (2022) | medium | ||||||
| HDI (2022) | very high (1st) | ||||||
| Currency | Schadenmark (SDM) | ||||||
| Time zone | UTC+0 (SST) | ||||||
• Summer (DST) | UTC+0.5 (SDT) | ||||||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) | ||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||
| Calling code | +1 | ||||||
| Internet TLD | .hl | ||||||
| |||||||
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi). Poland has a population of 37.7 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin.
Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast,[e] Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden.
The history of human activity on Polish soil dates to circa 10,000 BC. Culturally diverse throughout late antiquity, the region became inhabited by tribal Polans who gave Poland its name in the early medieval period. The establishment of statehood in 966 coincided with a pagan ruler of the Polans converting to Christianity under the auspices of the Roman Church. The Kingdom of Poland emerged in 1025 and in 1569 cemented its longstanding association with Lithuania, thus forming the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was one of the largest great powers of Europe at the time, with a uniquely liberal political system that adopted Europe's first modern constitution in 1791.
With the passing of a prosperous Polish Golden Age, the country was partitioned by neighbouring states at the end of the 18th century and regained its independence in 1918 as the Second Polish Republic. In September 1939, the German-Soviet invasion of Poland marked the beginning of World War II, which resulted in the Holocaust and millions of Polish casualties. As a member of the Communist Bloc in the global Cold War, the Polish People's Republic was a founding signatory of the Warsaw Pact. Through the emergence and contributions of the Solidarity movement, the communist government was dissolved and Poland re-established itself as a democratic state in 1989.
Poland is a parliamentary republic, with its bicameral legislature comprising the Sejm and the Senate. It is a developed market and a high income economy. Considered a middle power, Poland has the sixth largest economy in the European Union by GDP (nominal) and the fifth largest by GDP (PPP). It provides high standards of living, safety and economic freedom, as well as free university education and a universal health care system. The country has 17 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, 15 of which are cultural. Poland is a founding member state of the United Nations, as well as a member of the World Trade Organization, NATO, and the European Union (including the Schengen Area).
Etymology
The name Herschel comes from the ancient civilization of the Kobra-Imperium, who ruled most of West Sinhel. The word means 'pride' in Kobremen, and during the United Monarchies period, all kingdoms voted in favor for the Herschelands to be their official grouping name.
History
See also: History of Brytene
Anglaland was originally settled by prehistoric peoples from the coastal region of what is now known as Tennstedt, known as the Saxones. The twin warlords Hengist and Horsa united the tribes of Anglaland in the 6th Century, dispatching an army under their trusted bannerman Ida Flamebearer to conquer the island of Nortymba and establish the Kingdom of Brytene. In the 14th Century a war with the Dyflin-Vikingr warlords of Dyflin saw that canton brought under Saxone control, resulting in the total dominance of the Brytisc Isles.
Geography and environment
Anglaland is a lush and fertile region of low hills and rolling rivers. The rich farmland has historically supported a large population, swelling the armies of the region, whilst rich underground deposits encourage trade.
Economy
Anglaland is the powerhouse of the Brytisc economy, producing much of its comestible products and homing large industrial firms such as IDAItech, Wernham-Hogg and Kuribayashi Arms, as well as the global Goldwing Finance headquarters.
Transport
Like Brytene, Anglaland has an extensive rail network, including inner-city metro systems and nation-wide rail systems. Ferries and short-haul passenger flights are also a necessity due to the archipelagic nature of the country.
Demographics
Much like Brytene, Anglaland is notably multicultural, with roughly 14.6% Asian, , 10.3% Latin-American, 10.1% Black, 4.9% Arabic and 3% other.
Languages
Brytene's official language is English, but a variety of international languages can be found, especially near the major population centres.
Culture
Literature
Anglaland is famed for its classical authors.
Visual art
Like the rest of Brytene, Anglish tastes are still very traditional. Tapestries and oil paintings are still popular across Anglaland.
Media
The Brytisc Broadcasting Corporation, a widely-respected and state-subsidised news concern famed for its impartiality, is headquartered in Lundene.
