Yingok: Difference between revisions
Philimania (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Philimania (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|leader_title1 = [[President of Yingok|President]] | |leader_title1 = [[President of Yingok|President]] | ||
|leader_name1 = [[Yeung Kapkaa]] | |leader_name1 = [[Yeung Kapkaa]] | ||
|leader_title2 = [[Chancellor of Yingok|Chancellor]] | |leader_title2 = [[Vice President of Yingok|Vice President]] | ||
| | |leader_name2 = [[Dong Dak]] | ||
|leader_title3 = [[Chancellor of Yingok|Chancellor]] | |||
|leader_name3 = [[Nam Gat]] | |||
|leader_title4 = [[Chief Justice of Yingok|Chief Justice]] | |||
|leader_name4 = [[Wu Suk-fan]] | |||
|legislature = [[National Diet of Yingok|National Diet]] | |legislature = [[National Diet of Yingok|National Diet]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = [[History of Yingok|History]] | |sovereignty_type = [[History of Yingok|History]] | ||
| Line 102: | Line 106: | ||
== Government and politics == | == Government and politics == | ||
{{multiple image | |||
| align = right | |||
| direction = horizontal | |||
| caption_align = center | |||
| image1 = Yeung Kapkaa.png | |||
| width1 = 120 | |||
| caption1 = [[Yeung Kapkaa]]<br /><small>7th [[President of Yingok|President]]</small> | |||
| image2 = Dong Dak.png | |||
| width2 = 120 | |||
| caption2 = [[Dong Dak]]<br /><small>9th [[Vice President of Yingok|Vice President]]</small> | |||
| footer = since 2 January 2023 | |||
| footer_align = center | |||
}} | |||
Yingok is classified as a {{wp|unitary}} {{wp|presidential}} {{wp|constitutional}} {{wp|republic}}, with the [[president of Yingok|president]] acting as {{wp|head of state}} and {{wp|head of government}} as well as {{wp|commander-in-chief}} of the [[Yinese Armed Forces]]. The president and [[Vice President of Yingok|vice president]] are elected by {{wp|direct election}} for six-year terms, with a limit of three consecutive terms. The president appoints and presides over the [[Cabinet of Yingok|cabinet]], subject to the approval of the [[Appointments Committee]]. The vice president is the first in line for succession if the president resigns, is removed after {{wp|impeachment}}, is permanently incapacitated, or dies. The vice president is usually, though not always, a member of the president's cabinet and may be appointed without the approval of the Appointments Committee. If there is a vacancy in the position of vice president, the president will appoint any member of the [[National Diet]] (usually a party member) as the new vice president. The appointment must then be validated by a three-fourths vote of the National Diet. The {{wp|incumbent}} president and vice president are [[Yeung Kapkaa]] and [[Dong Dak]], elected in [[2021 Yinese presidential election|2021]] | |||
Legislative power is vested in the {{wp|unicameral}} [[National Diet]], with its 92 members elected for 4-year terms. Each subdivision are allowed three representatives which are elected via direct vote in their respective subdivisions, while the remaining 50 members of the National Diet are elected {{wp|Proprtional representation|proportionally}} based on the total national vote. The National Diet is headed by the [[Chancellor of Yingok|Chancellor]], currently [[Nam Gat]], who is elected from among its members by a {{wp|majority vote}} for 4-year terms. The Chancellor serves as the presiding officer of the National Diet and is responsible for facilitating legislative proceedings, and maintaining order within the National Diet. | |||
The {{wp|judicial branch}} is headed by the [[Supreme Court of Yingok]], which serves as the highest court in the country. It is led by the [[Chief Justice of Yingok|Chief Justice]], currently [[Wu Suk-fan]], and comprises of 6 [[Associate Justices of the Supreme Court of Yingok|associate justices]]. The justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the [[Judicial Committee]]. Each subdivision has its own court system, which handles cases within their respective jurisdictions. | |||
Since the [[Presidency of Fung Likwai|Fung administration]], {{wp|corruption}} has been a key focus of reform in Yingok. The government has initiated various measures to combat and address corrupt practices within the country, including a lengthy [[Yinese Anti-Corruption Campaign|anti-corruption campaign]] that has led to significant changes in the political and social landscape. The [[Anti-Corruption and Ethics Committee]] (ACEC) was also established as well during the Fung administration as an independent agency with the primary goal of investigating and prosecuting cases of corruption at all levels of government. | |||
=== Allegations of corruption === | === Allegations of corruption === | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 9 August 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Fourth Republic of Yingok 燕國 (Yinese) Yingwok | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: 燕華國歌 Yinwàh Gwokgō "National Anthem of Yingok" | |
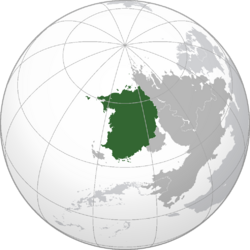 Location of Yingok (green) in Abaria (dark grey) | |
| Capital | Dongsing |
| Largest city | Hoyzhau |
| Official languages | Yinese |
| Recognised regional languages | Shanese |
| Ethnic groups (2022) | 83% Yinese 14% Shanese 3% Others |
| Religion (2022) | 73% Sendou 21% Irreligion 6% Others |
| Demonym(s) | Yinese |
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
| Yeung Kapkaa | |
| Dong Dak | |
| Nam Gat | |
| Wu Suk-fan | |
| Legislature | National Diet |
| History | |
| c. 3000 BCE | |
| 12-23 June 1892 | |
| 7 March 1966-23 November 1981 | |
| 19 April 1974 | |
| 29 December 1985 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,037,614 km2 (3,103,340 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.004 |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | |
• Density | 81.17/km2 (210.2/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2022) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high |
| Currency | Tungbei (銅幣/₣, TBI) |
| Time zone | TBA |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | X |
| Internet TLD | .yn |
Yingok (Yinese: 燕國; Yingwok), officially the Fourth Republic of Yingok is the second largest country in Abaria. With an estimated population of over 600 million, Yingok is bordered by Razan, X, and X to the east, the Alconian Ocean to the west, and the Jade Sea to the South. Its 13 prefectures and 1 autonomous region spans a combined area of roughly 8,037,614 km2 (3,103,340 sq mi). Yingok is a unitary presidential constitutional republic with its capital in Dongsing, the largest city in Yingok by population. The largest city in the country by area is Hoyzhau which also serves as Yingok's main economic and commercial centre. Other major urban areas include Gongbuk, Samlong, Sei'on, Hasaan, and Yunzhau.
Yingok was initially inhabited by the Zhong Dynasty, followed by the An Dynasty, which brought significant cultural and technological advancements. However, the An Dynasty eventually fractured, leading to a fragmented political landscape and the rise of the Chiu Dynasty, which brought political stability and a cultural renaissance. The region experienced invasions from the !Vietnamese and the !Mongol Empire, leading to periods of conflict and disruption. The 15th century marked the beginning of the Third Winter Period, characterised by intense competition among various factions. This era eventually gave way to the Three Kingdoms Period, with the Hon Dynasty, Jeong Dynasty, and emerging Dong Kingdom vying for dominance over Yingok. The Saan Dynasty emerged victorious and established relative stability and economic growth in the region. However, the appearance of Calesian colonialism introduced new tensions and conflicts as the Saan Dynasty sought to protect its sovereignty.
In the 19th century, Yingok embraced the Industrial Revolution, leading to rapid urbanization and socio-political changes. The Saan Dynasty's response to demands for reforms varied, leading to political unrest. The dynasty was overthrown in 1892, and Yingok went through a series of political upheavals, including various dictatorships and revolutions. Yingok remained neutral during the Great War due to internal conflicts. In 1966, a civil war erupted between different factions, culminating in a nationalist victory and the establishment of the Fourth Republic. Throughout its history, Yingok has maintained complex relationships with its neighbours, pursuing diplomacy and economic cooperation. It seeks regional stability, trade, cultural exchanges, and peaceful conflict resolution. Present-day Yingok has implemented political reforms, aiming for a more democratic and inclusive society, although challenges remain in fully implementing political freedoms and civil rights.
Yingok retains its centuries-long status as a global centre of art, science and philosophy. It is the world's leading tourist destination, receiving over 73 million foreign visitors in 2020. Yingok is a developed country with the world's X-largest economy by nominal GDP and X-largest by PPP; in terms of household net income, it ranks X in the world. Yingok performs well in international rankings of health care, life expectancy and human development. It remains a great power in regional affairs, being leading member of numerous international organisations including the !United Nations, X, and the Abarian Regional Forum.
Etymology
TBA
History
TBA
Geography
TBA
Government and politics
Yingok is classified as a unitary presidential constitutional republic, with the president acting as head of state and head of government as well as commander-in-chief of the Yinese Armed Forces. The president and vice president are elected by direct election for six-year terms, with a limit of three consecutive terms. The president appoints and presides over the cabinet, subject to the approval of the Appointments Committee. The vice president is the first in line for succession if the president resigns, is removed after impeachment, is permanently incapacitated, or dies. The vice president is usually, though not always, a member of the president's cabinet and may be appointed without the approval of the Appointments Committee. If there is a vacancy in the position of vice president, the president will appoint any member of the National Diet (usually a party member) as the new vice president. The appointment must then be validated by a three-fourths vote of the National Diet. The incumbent president and vice president are Yeung Kapkaa and Dong Dak, elected in 2021
Legislative power is vested in the unicameral National Diet, with its 92 members elected for 4-year terms. Each subdivision are allowed three representatives which are elected via direct vote in their respective subdivisions, while the remaining 50 members of the National Diet are elected proportionally based on the total national vote. The National Diet is headed by the Chancellor, currently Nam Gat, who is elected from among its members by a majority vote for 4-year terms. The Chancellor serves as the presiding officer of the National Diet and is responsible for facilitating legislative proceedings, and maintaining order within the National Diet.
The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court of Yingok, which serves as the highest court in the country. It is led by the Chief Justice, currently Wu Suk-fan, and comprises of 6 associate justices. The justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial Committee. Each subdivision has its own court system, which handles cases within their respective jurisdictions.
Since the Fung administration, corruption has been a key focus of reform in Yingok. The government has initiated various measures to combat and address corrupt practices within the country, including a lengthy anti-corruption campaign that has led to significant changes in the political and social landscape. The Anti-Corruption and Ethics Committee (ACEC) was also established as well during the Fung administration as an independent agency with the primary goal of investigating and prosecuting cases of corruption at all levels of government.
Allegations of corruption
TBA
Law
TBA
Subdivisions
Yingok is divided into 13 prefectures and 1 autonomous region. The prefectures are further subdivided into 394 counties and 23 municipalities. The Saanbak autonomous region holds a higher degree of autonomy in local governance and decision-making.
Each prefecture is overseen by a local assembly and is headed by a prefectural governor who is elected by the population of the respective prefecture for a term of 5 years, with a limit of three consecutive terms. the local assemblies are comprised of representatives from the counties and municipalities within each prefecture. These representatives are elected by the county or municipal population for 4 year terms. While each local assembly operates independently from the National Diet, they are ultimately accountable to the central government and must abide by national laws and policies
| Flag | Name | Capital | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Namging | Dongsing | X | |
| Outer Razan | Altayara | X | |
| Seisaan | Yunzhau | X | |
| Dongmei | Hoyzhau | X | |
| Sikhoy | Samlong | X | |
| Fungwu | Wunsing | X | |
| Zhongdei | Bikhoy | X | |
| Sankwai | Sei'on | X | |
| Yauhing | Cinglong | X | |
| Munlok | Wongzen | X | |
| Cheungming | Qinfa | X | |
| Namho | Gongbuk | X | |
| Yatpui | Yukgong | X | |
| Saanbak | Fumun | X |
Foreign relations
TBA
Military
TBA
Economy
TBA
Demographics
TBA
Culture
TBA