Sukong language
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Sukong | |
|---|---|
| Common Sukong | |
| 綠話 | |
 Flag of the Sukong people | |
| Pronunciation | [lou˧˩wɒi˧˩] |
| Native to | Sukong |
| Region | Northwestern Olivacia |
| Ethnicity | Sukongs |
Native speakers | L1: 305,000,000 (2020) L2: 21,000,000 FL: 15,000,000 |
Early form | |
Standard forms | Ca Luo Sukong
|
| Traditional Chinese | |
| Signed Sukong | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | TBA (Sukong Language Commitee) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | su |
| ISO 639-2 | suk |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously:suk – Ca Luo Sukongssw – South-west Sukongsnw – Norht-west Sukongsuc – Central Sukongsnc – North-central Sukongssn – North-south Sukongsue – East Sukongsse – South-east Sukongsne – North-east Sukongsui – Island Sukong |
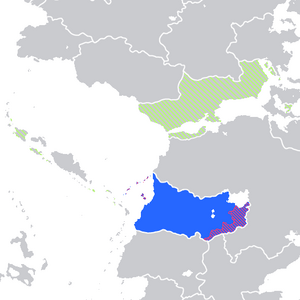 Official and majority language
Co-official, but not majority language
Minority language | |
The Sukong languge (綠話, pronounced: [lou˧˩wɒi˧˩] ) is a Sino-Tibetan language mainly spoken in Sukong, and its neighbour nations. Expat speaker communities also exist in Neuewland and Riamo. As a member of the Chinese languages, it shares similarities with Chengshengese. It is unknown as to how these languages spread over such a wide area.