IIWiki:Today's featured article: Difference between revisions
(January 2022 Update) |
(June 2023 Update) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
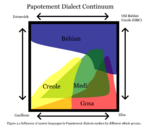
<div style="float:left;margin:0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0;">[[File: | <div style="float:left;margin:0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0;">[[File:Dialects of Papotement.png|150px]]</div> '''Papotement''', locally known as '''Gnun Tongo''', also known as '''Carucerean Creole''', is a {{wp|French language|Gaullican}}-based {{wp|creole language}} spoken by over half a million people in the Asterias. It is the most widely spoken language in [[Carucere]], serving as the unofficial {{wp|national language}} of the country. Papotement has its origins from the Moutagnar creole spoken by enslaved Bahians on the Karukera colony in the 16th century, but the modern form of the language originates from the interactions between free Bahians and [[Gowsa]] workers, who mainly spoke [[Ziba]], in the mid to late 19th century. The vocabulary of Papotement mostly originates from Gaullican, but its grammar draws influence from the Moutagnar creole and the [[Ziba]] language spoken by [[gowsa]] workers. Gaullican has played a major role in the creole since the mid-19th century, introducing the majority of the vocabulary as well as parts of the language's grammar, and methods of pronunciation. It is not mutually intelligible with standard Estmerish or Gaullican, and has its own distinctive pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. While Gaullican still remains the language of {{wp|prestige (sociolinguistics)|prestige}}, Papotement is the {{wp|lingua franca|lingua gaullica}} of the Republic of Carucere. Carucereans tend to speak Papotement at home and in media; Gaullican is limited to administration and educational purposes. Though Carucereans are of numerous ethnic origins, including Southeast Coian, Bahian, and Euclean; Papotement has gradually replaced the ancestral languages of most the population to become the primary home language of the country. ('''[[Papotement|See more...]]''') | ||
<div align="right"> | <div align="right"> | ||
Revision as of 01:32, 5 June 2023
Papotement, locally known as Gnun Tongo, also known as Carucerean Creole, is a Gaullican-based creole language spoken by over half a million people in the Asterias. It is the most widely spoken language in Carucere, serving as the unofficial national language of the country. Papotement has its origins from the Moutagnar creole spoken by enslaved Bahians on the Karukera colony in the 16th century, but the modern form of the language originates from the interactions between free Bahians and Gowsa workers, who mainly spoke Ziba, in the mid to late 19th century. The vocabulary of Papotement mostly originates from Gaullican, but its grammar draws influence from the Moutagnar creole and the Ziba language spoken by gowsa workers. Gaullican has played a major role in the creole since the mid-19th century, introducing the majority of the vocabulary as well as parts of the language's grammar, and methods of pronunciation. It is not mutually intelligible with standard Estmerish or Gaullican, and has its own distinctive pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. While Gaullican still remains the language of prestige, Papotement is the lingua gaullica of the Republic of Carucere. Carucereans tend to speak Papotement at home and in media; Gaullican is limited to administration and educational purposes. Though Carucereans are of numerous ethnic origins, including Southeast Coian, Bahian, and Euclean; Papotement has gradually replaced the ancestral languages of most the population to become the primary home language of the country. (See more...)
KEEP THIS ONE PARAGRAPH IN LENGTH so it doesn't push the main page section down below the other section.