Aldia Railway Corporation
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
 Logo used since July 1995 | |
Formerly | Aldian Railways (1889 - 1995) Continental Rail (1822 - 1889) |
|---|---|
| State Owned Company | |
| Traded as | FSX: ARCN |
Key people |
|
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Owner | |
Number of employees | 42,167 (2016) |
| Subsidiaries | ARC High Speed Rail ARC City Express ARC Freight ARC Services ARC Property ARC Maintenance Heping Mass Rapid Transit Capital Commuter Rail Service |
 | |
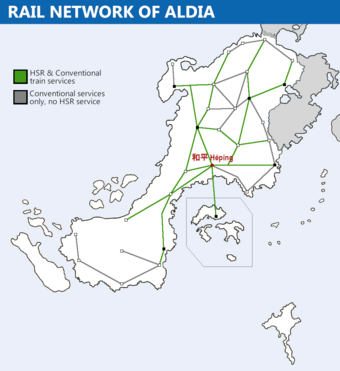 Map of the Aldian rail network. | |
 An ARC-003 Feilong train departing. | |
| Locale | |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1892–present |
| Predecessor | Aldian Railways (1950 - 1995) Continental Rail (1892 - 1950) |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) Standard Gauge |
| Length | 97,000 km (60,000 mi) |
| Headquarters | Heping, Aldia |
The Aldia Railway Corporation (Myrian: 阿尔迪亚铁路公司, Romanized: Āěrdíyǎ Tiělù Gōngsī) is the national state-owned railway company & operator in Aldia. The Government of Aldia is the largest shareholder, holding 60% of the company's shares whereas the remaining 40% are publicly traded in the Fanrong Stock Exchange. ARC maintains and administers the country's rail network and operates a fleet of train services through its subsidiary companies such as the ARC High Speed Rail (ARC HSR) which operates a fleet of intercity highs-speed rail trains services and ARC Continental Express which operates mostly conventional intercity train services. ARC is only responsible to administer & operate rail networks constructed by the Commonwealth Government which focused most of its efforts in connecting the capital & regional cities of each member states of the Commonwealth. Other train services such as regional, commuter, rapid-transit & light rail networks are the areas of responsibility of each member state. ARC however does maintain & administer the Heping Mass Rapid Transit and Capital Commuter Rail Service networks as it is located in the city of Heping, a city located within the Aldian Capital Territory both of which are directly administered by the Commonwealth Government.
History
Early Years
The history of rail transport in the Myrian continent traces its origins all the way back to the early 18th century. During this the most common mode of transportation between cities and nations were in the form of wagonways, the use of horses to haul wagons filled with either goods or passengers. These Wagonways travelled on designated tracks, the predecessor of a modern train track. As the years went on, passenger and freight demand continued to increase, posing logistical challenges to the usage of horse-drawn wagonways. While cheap and readily available, the use of horses was not scalable in the long run. As passenger & freight demand increases one must either increase the number of horses that haul the ever growing number of wagons, or increase the frequency of the wagonways departure times. It was around the 1800s that the first steam powered locomotives were first invented, a byproduct of the industrial revolution. While revolutionary, organizations were slow to adopt them as they lacked the necessary power to haul passengers & freight on a commercial scale. These early locomotives were used mainly as technology demonstrations, the government held exhibitions where inventors & innovators unveiled the latest steam locomotives showing to the public and commercial entities its capabilities. In 1792 the first proper train tracks were laid down, connecting Fanrong and its neighboring cities. This marked the first commercialization of trains in the Myrian continent.
Continental Rail Era
As the years went, the development of more sophisticated and capable steam locomotives the usage of trains as a mode of passenger & freight transport became more commonly found. In 1822 the Continental Railway, Myria's first proto-{{wp[|multinational corporation|multinational}} company, was established by the various nations of Myria and given the mandate to provide a transcontinental rail service throughout the entire Myrian continent. Construction began in 1826 from both the southern and northern tips of the continent was eventually completed by 1851. It was during this era that rail transport became a major player in transportation of people and goods throughout Myria. Continental Railways owned and operated both the rail network and train services across various Myrian nations and pays track access charges to the various governments it operates its network. The Continental Rail Era provided the foundation of a standardized list of policies, regulations and best practices for Myria's rail industry. Track gauges, electrifications, and signaling methods were uniformed. Various privately run railway services were also established but mostly competed within national borders, only Continental Railways was able to establish an established brand presence throughout the entire continent.
Nationalization
After the founding of the Commonwealth
Company Structure
Subsidiaries
| Business | Company Name | Logo | Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger | ARC High Speed Rail |  |
Sole operator of high-speed rail services in Aldia. It operates three major Feilong lines:
|
| Passenger | ARC City Express |  |
Operates a variety of conventional/non-HSR services between major cities and urban centers. |
| Passenger | Heping Mass Rapid Transit |  |
Operates the metro system of Heping. |
| Passenger | Capital Commuter Rail |  |
Operates the commuter network of Heping and surrounding suburbs. |
| Logistics | ARC Freight |  |
Operates both HSR & conventional trains to deliver freight utilizing ARC's rail network. |
| Research & Development | ARC Research Institute |  |
Technical research subsidiary & information technology provider for ARC. |
Assets
Rolling Stock
| Train Class | Image | Origin | Entered Service | Line | Power Type | Speed | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC High Speed Rail | |||||||||
| ARC-003 Feilong |  |
2015 | Beifang Line Zhongyang Line |
Electric | 420 km/h (Record) 400 km/h (Design) 350 km/h (service) |
Used for long distance travels between the capital cities of each member state. | |||
| ARC-002 Feilong |  |
2007 | Beifang Line Zhongyang Line |
Electric | 320 km/h (Record) 290 km/h (Design) 220 km/h (service) |
Used for long distance travels between the capital cities of each member state. | |||
| ARC-001 Feilong |  |
2002 | Beifang Line Zhongyang Line Nanbu Line |
Electric | 250 km/h (Record) 200 km/h (Design) 165 km/h (service) |
Used for long distance travels between the capital cities of each member state. | |||
| SM-04A Feilong |  |
2011 | Beifang Line Zhongyang Line Nanbu Line |
Electric | 290 km/h (Record) 220 km/h (Design) 190 km/h (service) |
Used for short and medium distance travel between member state capital cities and major urban centers. | |||
| SM-02 Feilong |  |
1999 | Beifang Line Zhongyang Line Nanbu Line |
Electric Multiple Unit | 210 km/h (Record) 180 km/h (Design) 150 km/h (service) |
Used for short and medium distance travel between member state capital cities and major urban centers. | |||
| ARC City Express | |||||||||
| SM-04CR |  |
2011 | Anxiang Intercity Services Sanpuku Intercity Services Shukaku Intercity Services Fengfu Intercity Services |
Electric | 290 km/h (Record) 220 km/h (Design) 130 km/h (service) |
Used for short, medium & long distance travel between major urban centers. Variant of the SM-04A Feilong used for intercity travel. | |||
| NRL-09 |  |
1999 | Anxiang Intercity Services Sanpuku Intercity Services Shukaku Intercity Services Fengfu Intercity Services Shanliang Intercity Services Guanhai Intercity Services Wuxian Intercity Services |
Diesel Locomotive | 120 km/h (Design) 95 km/h (service) |
Used for short and medium distance travel between member state capital cities and major urban centers. | |||
| GJK-500 |  |
1991 | Anxiang Intercity Services Sanpuku Intercity Services Shukaku Intercity Services Fengfu Intercity Services Shanliang Intercity Services Guanhai Intercity Services Wuxian Intercity Services |
Diesel Locomotive | 100 km/h (Design) 80 km/h (service) |
Used for short and medium distance travel between member state capital cities and major urban centers. | |||
| RTS-80X |  |
2012 | Shanliang Intercity Services Guanhai Intercity Services Wuxian Intercity Services |
Diesel Locomotive | 140 km/h (Design) 110 km/h (service) |
Used for short and medium distance travel between member state capital cities and major urban centers. | |||