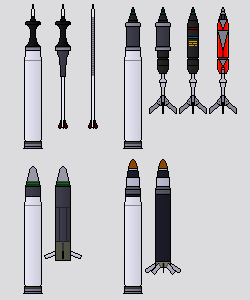
Munitions of the Carthage Defense Forces
The following is a non-exhaustive list of ordnance used by the Carthage Defense Forces.
Bombs
General-purpose bombs
The current LGU-121X Red Magic series (originally classified as the Type-70 series) general-purpose bomb entered service in the mid-1970s, replacing the previous Type-60 Golden Sun series in combat use. Nearly all stockpiles of the old Type-60 series were expended in the Northern War and the two Pacific Wars, and the LGU-121X series remains the only type in inventory. Relative to the older Type-60, the LGU-121X uses a narrower, more aerodynamic shape to aid in external carriage and uses an RDX-based polymer-bonded explosive in place of the previous TNT-based tritonal. Overall weight between the two types remains similar.
In 1995, the LGU-121XAM1 upgrade was introduced, replacing the old casing with a thinner, higher-strength version to improve explosive payload and adding a removable prefragmented sleeve for increased lethality against soft targets. Carrier-based variants are also equipped with fire-retardant coating for improved safety aboard warships. As with the previous Type-60 series, the LGU-121X series incorporates common nose and tail fuze sockets to accommodate interchangeable fuzes. Training variants also exist without the explosive filler and fitted with parachutes and air brakes to allow reuse. Various retarder kits are also available for use. The series includes five bomb types:
- LGU-1210 - nominal weight 125 kg (275 lb)
- LGU-1211 - nominal weight 250 kg (550 lb)
- LGU-1212 - nominal weight 500 kg (1,100 lb)
- LGU-1213 - nominal weight 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
- LGU-1214 - nominal weight 1,500 kg (3,300 lb)
The LGU-1211 and -1212 are the most commonly-produced bombs within the series, owing to their moderate weight and lethality suitable for a wide range of targets and platforms. Production of the LGU-1210 was halted in 2001 due to concerns about the limited effectiveness of such a light bomb, but was restarted in 2009 with the development of more accurate and economical smart bomb kits, for use in areas where collateral damage must be minimized. Production of the LGU-1214 has been extremely limited and was terminated in 2008 due to limited applications and platforms for such a large munition. Stockpiles of the weapon remain in inventory but there are no current plans to restart production.
Smart bomb kits
A series of special guided fuzes and tail kits were developed concurrently with the LGU-121X series, allowing them to serve as economical precision-guided weapons. The original ERM-400 series laser-guidance system was developed in the 1970s and designed to target runways and fixed installations with greater precision than carpet bombing. The ERM-400 series was retired in the 1990s and replaced with the newer EGI-55X Hourai series, with increased accuracy and incorporating alternate guidance methods to allow the weapon to self-guide itself, including limited efficacy against moving targets. The cheaper alternative EGS-56X Mysterium GPS/INS kit was also developed to take over the fixed-structure demolition role at a more economical cost. Both types have versions that can be used on the LBU-122X bunker buster series.
- EGI-550 - Laser, MMW, and IR guidance unit for LGU-1210
- EGI-551 - Laser, MMW, and IR guidance unit for LGU-1211
- EGI-552 - Laser, MMW, and IR guidance unit for LGU-1212
- EGI-553 - Laser, MMW, and IR guidance unit for LGU-1213 or LBU-1220
- EGI-554 - Laser, MMW, and IR guidance unit for LGU-1214 or LBU-1221/1222
- EGS-560 - GPS/INS guidance unit for LGU-1210
- EGS-561 - GPS/INS guidance unit for LGU-1211
- EGS-562 - GPS/INS guidance unit for LGU-1212
- EGS-563 - GPS/INS guidance unit for LGU-1213 or LBU-1220
- EGS-564 - GPS/INS guidance unit for LGU-1214 or LBU-1221/1222
Special-purpose bombs
Several types of special-purpose bombs are also maintained in inventory, including heavy deep penetration bombs, long-range glide bombs, cluster munitions, and incendiary weapons.
Cluster bombs
The LCU-1240 Starbow Break (originally classified as the Type-77) is the only dedicated cluster munition delivery system remaining in inventory. While other weapons, including cruise missiles, are capable of being equipped with submunition dispensers, the LCU-1240 is the only remaining dedicated cluster munition casing following the retirement of the Type-78 in 1998.
- LCU-1240 - 500 kg (1,100 lb) cluster munition delivery system. It is capable of being equipped with a variety of different submunitions for use against hard and soft targets.
- LCU-1240A - 12 anti-tank EFP submunitions
- LCU-1240M - 450 x anti-tank and 150 x anti-personnel mines
- LCU-1240P - 244 explosive submunitions
- LCU-1240R - 350 x 40 cm, 1,000 x 20 cm, and 2,400 x 10 cm tungsten/steel rods
Glide bombs
The LGM-123X Stardust Reverie series is a family of long-range precision glide bomb used by the Carthage Air Forces and the Army of Carthage. The series entered service in the 2007 to allow strike aircraft to carry a larger payload of bombs, as well as to allow precision strikes in areas where collateral damage may be a concern. The initial guidance system used satellite and inertial systems to accurate strike fixed targets, but the current -AM1 modification and improved software add multi-mode infrared, millimeter wave, and semiactive laser guidance, allowing the weapon to strike moving targets. In aerial use, it is mounted on racks allowing multiple bombs to be carried per hardpoint, while in army use it is an optional final-stage warhead for 220 mm rocket artillery.
- LGM-1230 - 100 kg (220 lb) focused-blast glide bomb w/laser, MMW, and IR guidance
- LGM-1231 - 250 kg (550 lb) focused-blast glide bomb w/laser, MMW, and IR guidance
Penetration bombs
The LBU-122X Duplex Barrier series (formerly the Type-80 series) is the primary deep penetration bomb type used by the Carthage Air Forces. Developed in the 1990s as a series of five models, the smallest two were retired in the early 2000s as more advanced general-purpose and glide weapons rendered them obsolete. Due to their retirement, the two smallest types were never reclassified, and do not use current four-digit inventory numbers. The remaining three types are always employed with precision guidance kits, and usually by tactical or strategic bombers rather than lighter strike fighters. The LBU-122X series is constructed out of a nickel-cobalt steel body with a heavy tungsten penetrator cap and a relatively small explosive filler. The heaviest, the 5,000 kg LBU-1222, is rocket-assisted for improved penetration and is the heaviest air-dropped tactical ordnance in inventory.
- LBU-1220 - nominal weight 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
- LBU-1221 - nominal weight 2,500 kg (5,500 lb)
- LBU-1222 - nominal weight 5,000 kg (11,000 lb)
Cannons
Revolver and rotary cannons
- CDS-327 - 76 mm revolved cannon designed for use against aircraft. While identical in caliber to the naval Mark 22 gun, the two are unrelated designs.
- CDA-330 - 40 mm revolver cannon firing cased telescoped ammunition used on infantry fighting vehicles.
- CRA-331 - 7 mm chain gun used on vehicles and helicopters.
- CRA-334 - Electrically-powered 15.5 mm PCTA machine gun used in helicopter armament systems, identical to the type in service with the army.
- CRA-341 - Four-barrel 25 mm autocannon designed for use in fourth-generation fighters, derived from the five-barrel 25 mm FG22 Moloch autocannon used in earlier fourth-generation and late third-generation fighters.
- CRA-342 - Five-barrel, nine-chamber 25 mm caseless autocannon developed for and introduced on the RFM-202 Shaheen.
- CRA-952 - Electrically-powered 35 mm recoilless revolver cannon used in helicopter armament systems, aboard ships, and on infantry fighting vehicles.
Tank cannons
- CBS-320 - Lightweight 120 mm smoothbore gun originally developed for the Next Generation MBT program and redesigned for the Iliad MMTV. Uses the same ammunition as the T-17 gun in the HTA-01 Rhinoceros.
- CBS-321 - Smoothbore 155 mm gun mounted on the HTA-02 Jaguar II main battle tank.
- DSD-907 HEAT-AMP-T - Multi-purpose tandem charge, programmable fuze HEAT munition designed for use against vehicles, helicopters, personnel, and fortifications. Muzzle velocity is 1,400 m/s (4,600 ft/s) for an effective range of 3,000 m (3,300 yd).
- DIT-910 APFSDS - 940 mm depleted uranium extending-rod penetrator designed for use against enemy tanks and other heavily armored vehicles. Muzzle velocity is 1,800 m/s (5,900 ft/s) for an effective range of 4,500 m (4,900 yd).
- SGC-415 AATM-CE - The SGC-415 Advanced Autonomous Tank Munition-CE is a guided, tandem-charge HEAT weapon designed for medium to long-range engagements, including beyond-line-of-sight (BLOS) targets. The AATM-CE uses a dual-mode imaging infrared/semi-active laser seeker to enable fully autonomous engagement of targets beyond the tank's line of sight, while also allowing for man-in-the-loop guidance at BLOS ranges where the danger of collateral damage or friendly fire is too great for autonomous engagement.
- SGK-416 AATM-KE - The SGK-416 AATM-KE is a guided medium to long-range kinetic energy munition designed for use against main battle tanks and other heavily armored targets with extensive protection against HEAT munitions. While conceptually similar to the AATM-CE, the AATM-KE uses a depleted uranium penetrator for terminal effects and is guided by a dual-mode millimeter wave/semi-automatic laser seeker, enabling similar options for autonomous or man-in-the-loop guidance at ranges beyond 2,000 m (2,200 yd). Launch velocity is 1,200 m/s (3,900 ft/s) but impact velocity is 2,400 m/s (7,900 ft/s).
- T-17 - Smoothbore 120 mm gun mounted on the HTA-01 Rhinoceros main battle tank. Progressively developed from the original L/44 design into L/50 and L.54 lengths for greater muzzle energy.
Artillery
- CDS-350 - 155 mm L/52 gun-howitzer arming the SPH-87 Parthian self-propelled gun. The CDS-350 was designed to use conventional bagged charges and a semi-automatic loading system and the SPH-87 is in the process of being replaced by the HHM-09 Bowman.
- CDS-351 - 155 mm L/56 gun-howitzer arming the HHM-09 Bowman self-propelled gun. The CDS-351 uses laser ignition and is water-cooled and equipped with an autoloader for a high sustained rate of fire with minimal crew.
- CDS-352 - 155 mm L/52 gun-howitzer arming the GHM-25 Teucer self-propelled gun. The CDS-352 is a shortened, lightened version of the CDS-351, using an air-cooled barrel.
- CCH-410 Baleares - 105 mm L/30 airmobile howitzer intended for use in airborne and airmobile infantry units.
Missiles
Air-to-air
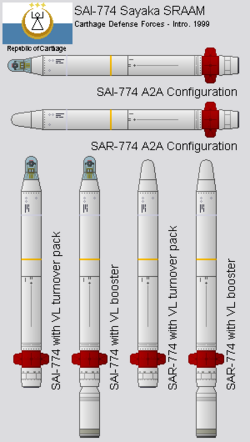
Several different types of air-to-air missiles are used by the Carthage Air Forces for both long and short-range engagements against both fighters and heavier aircraft. Most current models were developed under the Type-90 program before reclassification in the mid-2000s. Current designs are also commonly used as anti-aircraft missiles from ground and ship-based launchers and equipped with a booster to maintain engagement range.
- SAI-774 Sayaka - EO/IR-guided missile with a maximum range of 35 km (22 mi). Also commonly used in SHORAD roles, and by heavier attack helicopters.
- SAR-775 Nagisa - Dual-band radar-guided lifting body missile designed for air-to-air use with secondary anti-radiation roles.
- SAR-776 Tomoe - Dual-band radar-guided missile with a maximum range of 380 km (240 mi), primarily designed for use against AWACS as well as larger ground targets.
- SAR-777 Madoka - Super-heavy anti-ballistic missile designed for high-altitude interception. Due to weight, it is only carried on heavier aircraft but is most commonly employed from land-based launchers.
- SAR-778 Sakura - Dual-band radar-guided missile with a maximum range of 220 km (135 mi). Also designed for use as an anti-radiation missile against surface targets.
- SAR-779 Homura - Advanced compact kinetic-kill missile with a range of 100 km (62 mi), designed to supplement the SAI-774 and SAR-778 in service.
Air-to-ground
- SGM-741 Takane - Multi-mode ground-attack missile designed for use against enemy vehicle formations, employed by both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. Armed with a tandem-charge HEAT warhead and guided via semiactive laser and millimeter wave sensors, with an estimated 65 km (40 mi) range from fixed-wing platforms.
- SGR-742 Futami - Multi-mode lightweight ground-attack missile designed for use against a variety of light or collateral damage-sensitive targets, deployed from ground, helicopter, and fixed-wing platforms. Armed with a blast-fragmentation warhead and guided via laser, GPS, or INS, with a range of 20 km (12.5 mi).
- SGN-743 Hibiki - Stand-off inertial/satellite-guided missile built from the body of the SWR-787 Yakumo, designed for use against fixed targets within enemy airspace with a range of 1,200 km (750 mi). A nuclear-armed variant also exists.
- SGR-744 Makoto - Anti-radiation missile built from remaining stocks of Type-88 SRAAM, using a newer passive radiation seeker as a less-expensive supplement to the SAR-778 Sakura. Maximum range of 25 km (16 mi).
Ballistic
Ballistic missiles are the primary intended means of delivery for Carthage's strategic nuclear arsenal. Unlike the continued development and introduction of new conventional munitions, ballistic missile research and development in Carthage has been primarily limited to life-extension programs and new guidance systems to existing missiles. The development of the ballistic missile arsenal predates major collaboration with Imperial Japan, and most missiles are collaborations between Russian and Inuk manufacturers.
- TMB-596RM1 Ba'al Hadad II - Silo-launched heavy ICBM with FOBS capability, carrying a payload of 14 MIRV R-98 nuclear warheads and 60 penetration aids. 700 missiles are in active service.
- TMB-597AM2 Astarte III - Submarine-launched ballistic missile carrying a payload of 6 R-102A nuclear warheads with 18 penetration aids. A rail-mobile version is also in service. 3,200 submarine-launched missiles are in active service, along with 320 rail-mobile missiles.
- TMB-598AM1 Horus - Road-launched compact ICBM, designed to address survivability concerns with the then-current nuclear arsenal and carrying 4 R-102A nuclear warheads with 12 penetration aids with a maximum range of 16,000 kilometers (9,900 mi) and a CEP of 100 meters (330 ft). The TMB-598AM1 has also been tested for launch via air drop from a transport aircraft. 300 missiles are in active service.
- TDR-592 Shapash - Tactical ballistic missile used by ground forces for deep interdiction strikes against enemy formations and command facilities. Variants exist with both submunition and unitary payloads.
Surface-to-air
- SMI-750 Kotori - Man-portable IIR-guided anti-aircraft missile with a maximum range of approximately 7 km (4.3 mi). Armed with three submunitions, and also capable of limited use against light armored vehicles. In addition to shoulder-fired launchers, vehicle-mounted multiple-launch systems are also in service, and the missile has been qualified for helicopter use. Original shoulder-fired variant entered service in 1999.
- SML-751 Yukiho - Vehicle-launched anti-aircraft and anti-tank laser-guided missile system with a maximum range of 10 km (6.2 mi). Unlike the SMI-750 Kotori, the SML-751 uses a heavier tandem-charge HEAT warhead for improved lethality against medium and heavier armored vehicles.
- SMR-752 Yayoi - Short-range self-defense missile used in the naval Mark 99 Rolling Airframe Missile system. Early variants are based on the Type-88 SRAAM but newer variants are built from new components to provide increased range, maneuverability, and seeker sensitivity.
- SME-753 Azusa - Short-range self-defense missile built under the Advanced Missile Interceptor program for the Self Defense Segment of the Tarnhelm ADS. Built from the Type-88 missile body, it is designed with a focus on low cost and compact design.
- Type-115 - Man-portable IIR-guided anti-aircraft missile with a maximum range of approximately 6 km (3.7 mi), succeeded in service by the SMI-750 Kotori. Armed with a conventional blast-fragmentation warhead and commonly employed from shoulder launchers or light vehicles. The last active units were retired in 2007, but the type remains in reserve inventory as of 2014.
Surface-to-surface
- SMM-760 Chihaya - Anti-tank guided missile designed for infantry, vehicle, and helicopter use. Equipped with an IIR sensor, medium and long-range variants are equipped with an optical fiber datalink allowing for man-in-the-loop operation and remote control. Maximum range varies from 800 m (2,600 ft) in short-range versions to up to 25 km (16 mi) in the longest-ranged vehicle and helicopter-launched versions. The first models of the SMM-760 were introduced in 1997 under the Type-109 designation.
- SGM-761 Ritsuko - Non-line-of-sight laser, SALH and GPS guided missile system designed for use from modular VLS units. Armed with a multipurpose HEAT warhead, it is designed to provide on-call precision missile support to units with better availability than strike fighters or bombers, with a maximum range of 45 km (28 mi). Introduced in 2008.
- SBR-770 Suwako - Vertically-launched anti-submarine rocket designed to deliver a lightweight torpedo at range. Commonly employed aboard surface ships, it is also capable of deploying nuclear depth bombs. SBR-770 has a range of 30 km (20 mi) and uses basic satellite/inertial guidance.
- SPM-784 Hakurei - 200 kg-class (440 lb) multipurpose missile developed from the lifting body airframe of the SAR-775 Nagisa BVRAAM. Normally equipped for use as an independent decoy and jammer in support of SEAD/DEAD operations but also used as a lightweight stand-off weapon.
- SWR-787 Yakumo - Long-range anti-ship missile with a subsonic cruising speed and supersonic terminal phase. Armed with a 450 kg (1,000 lb) warhead and multi-mode IR/active radar guidance, with a maximum range of 1,000 km (610 mi). Introduced in 2008.
- SMN-788 Sakuya - Long-range cruise missile designed primarily for ship and submarine use. It shares the same missile body and dimensions as the SWR-787, but remains subsonic throughout its flight profile, increasing range to 3,100 km (1,900 mi). Guidance is via INS/GPS and passive radar interception, with mid-course datalink support. Introduced in 2009.
- Type-65 Kanako - Anti-ship missile developed in the mid-1970s with a subsonic speed and a maximum range of 400 km (250 mi). Initial installations were in box launchers, although later models are capable of vertical launch. The last active ship carrying the Type-65 was retired in December 2013, and all Type-65s remaining are in reserve. The model was reclassified as the SWR-786 as part of the 2003 Millennium Inventory System.
Rockets
Air-to-surface
- LGU-710 Scarlet - 70 mm folding-fin ground attack rocket for use from helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft, capable of being equipped with a variety of warheads including HEDP, HEAT, WP, and submunitions. Commonly deployed in 4, 7, and 19-cell launchers.
- LGL-710A - Variant of the LGU-710 equipped with a semi-active laser seeker for precision guidance, designed to provide a lighter, more numerous alternative to larger and more expensive PGMs. Normally deployed in 4-cell launchers in place of SGM-741 Takane missiles or from standard 7- or 19-cell launchers.
- LGI-710B - Variant of the LGU-710 equipped with an IR seeker, allowing fire and forget engagement capability.
Surface-to-surface
- LGS-804 - 250 mm surface-to-surface rocket used in the MLR-159 Tatsumaki and HOM-14 Apollo multiple rocket launchers. The LGS-804 is guided via satellite navigation and can be equipped with unitary high-explosive or submunition payloads. A chemical weapon variant was designed but never produced. The rockets have a range in excess of 85 km (53 mi).
Small arms
Pistols
- 10×22mm Ctesiphon - The standard handgun caliber of the Defense Forces, used in both sidearms and submachine guns.
Rifles
- 6.35×45mm Carthaginian - The previous assault rifle caliber of the defense forces, used in the ARC-19 assault rifle. Weapons chambered in 6.35 mm remain in service with the reserves and militia but are slated to be fully replaced by 7 mm Ctesiphon PCTA.
- 7×45mm Ctesiphon PCTA - The new common caliber for the militaries of the Ctesiphon Pact, firing a 7 mm bullet and utilizing a telescoped polymer case to reduce weight and length. Due to the round's increased power, it is expected to replace the previous 7.8 mm rifle cartridge as well.
- S230 Ball - Standard steel-cored copper-jacketed round designed for use against personnel protected by light armor or behind light cover. Compared to the previous 6.35 mm S178 ball round, the 7 mm S230 has improved ballistics, penetration, and terminal effects. The lead-free bullet weighs 140 gr (9.07 g) with a muzzle velocity of 800 m/s from a standard rifle-length barrel.
- ST2231 Tracer - Similar in design to the S230, but with additional space for the tracer charge in the base.
- SD232 Training - Equipped with a smaller charge and plastic bullet, to reduce training range hazards. Must be used in specially-equipped rifles with lighter bolts to properly cycle the action.
- SB233 Blank - Commonly used in training with other simulation gear, and for demonstrations.
- S234 API-T Subsonic - Designed for use with suppressors for reduced acoustic signature. The S234 is heavier than standard rounds at 160 gr (10.4 g) to make up for the loss of muzzle velocity.
- 7.8×55mm Carthaginian - The previous battle rifle caliber also used in medium machine guns and some sniper rifles. Slated to be replaced by the common 7 mm Ctesiphon PCTA round.
- 9×92mm Desert - Special round developed for marksman purposes with a high ballistic coefficient to maintain maximum energy at range. It is currently used only with the specialized DMS-24 sniper rifle.
- S220 Ball - The first round designed and tested, although it is rarely used in the field in favor of HEIAP. Commonly used in training, it is occasionally used in politically-sensitive situations against soft targets. Bullet weight is 340 gr (22.6 g), with a muzzle velocity of 1,050 m/s.
- ST221 Tracer - Like S220 Ball, ST221 Tracer is commonly used in training exercises and is not a common sight in the field.
- SM222 HEIAP - The de facto standard round, HEIAP is capable of engaging both armored and unarmored targets and has a demonstrated penetration of 15 mm of face-hardened steel at 500 meters
- SP223 SLAP - Preferred for use against hardened targets specifically, the sub-caliber round is capable of perforating 25 mm of steel at 500 meters making it useful against APC and light IFVs.
- S224 API-T Subsonic - Occasionally used with the rifle's suppressor for covert work.
Machine guns
- 12.7×99mm BMG - The previous standard heavy machine gun cartridge of the defense forces, used in the venerable MRB-29 HMG and anti-material rifles. Although being replaced by weapons chambered in 15.5 mm Tabnit PCTA, weapons chambered in are still commonly used even among active units, especially in the infantry.
- 15.5×105mm Tabnit PCTA - A new heavy machine gun round developed to combat improved protection against 12.7 mm calibers in light vehicles. With twice the muzzle energy of older 12.7 mm guns, 15.5 mm guns such as the CRA-334 were initially limited to vehicle mounts although lightened guns with a reduced rate of fire have been developed for limited infantry use.
- JHB-829 Ball - Standard steel-cored copper-jacketed round, designed to replace the 12.7 mm JHB-820 as the standard anti-infantry heavy machine gun round of the CDF. The JHB-829 eliminates the lead weighting used in older model rounds, making the bullet more environmentally friendly and reducing lead exposure to troops on the range. Although not designed as a dedicated armor piercing round, the high muzzle energy and steel core allow the JHB-829 to threaten many light vehicles.
- JHA-830 SLAP-T - Saboted light armor penetrator designed to improve penetration against hardened targets, using a 9 mm penetrator in a plastic sabot. Penetration is estimated to be two to three times that of standard ball ammunition.
- JHI-831 HEIAP - High-explosive incendiary armor piercing round designed to provide maximum effectiveness against both hard and soft targets. JHI-831 incorporates a 9 mm tungsten carbide penetrator core surrounded by a ring of zirconium with a plastic explosive/incendiary tip, allowing the round to improve post-penetration effects against personnel and equipment.
Torpedoes
- SST-720 Double Spark - 660 mm heavyweight gas turbine torpedo serving as the standard torpedo armament of Carthaginian submarines.
- SST-721 Master Spark - 660 mm heavyweight electric torpedo designed for stand-off attacks.
- SST-722 Starlight Typhoon - 660 mm supercavitating torpedo for use at short ranges and as a disruptive anti-submarine weapon.
- SWT-723 Blazing Star - 400 mm lightweight torpedo designed for use from surface ship torpedo tubes, helicopters, guided missiles, and other aerial platforms.