Nadauro: Difference between revisions
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
From 1987–1992, the United Congress intervened in Nadauro with the [[United Congress Observer Mission in Nadauro]] (UCOMCA) to aid in its [[Nadauran peace process|peace process]]. [[Juan Manuel Duque]] pursued a controversial peace policy during his tenure in the late 1980s, negotiating the disbanding of CLUN and a temporary truce with FLP and ER1M; the peace deal fell apart when the rejecting National Congress [[1986 Nadauran government crisis|moved against Duque]] with a {{wp|vote of no-confidence}} in January of 1988, and by 1989, the conflict had escalated into open rebellion. Diplomatic efforts by successor [[Tadeu Espíndola]] culminated in the [[Easter Agreement (Nadauro)|Easter Agreement]] of 1990, which pacified the conflict into the largely dormant state it has been ever since. | From 1987–1992, the United Congress intervened in Nadauro with the [[United Congress Observer Mission in Nadauro]] (UCOMCA) to aid in its [[Nadauran peace process|peace process]]. [[Juan Manuel Duque]] pursued a controversial peace policy during his tenure in the late 1980s, negotiating the disbanding of CLUN and a temporary truce with FLP and ER1M; the peace deal fell apart when the rejecting National Congress [[1986 Nadauran government crisis|moved against Duque]] with a {{wp|vote of no-confidence}} in January of 1988, and by 1989, the conflict had escalated into open rebellion. Diplomatic efforts by successor [[Tadeu Espíndola]] culminated in the [[Easter Agreement (Nadauro)|Easter Agreement]] of 1990, which pacified the conflict into the largely dormant state it has been ever since. | ||
Espíndola embarked on sweeping {{wp|neoliberalism|neoliberal}} reforms aimed at combating the [[Nadauran coroa crisis]] and signing the [[Elian Free Trade Agreement]] (EFTA) with the Free States and X in 1989. A second period of economic prosperity accompanied his tenure throughout the 1990s, seeing a peak growth rate of 6.2% in 1995. Contemporary Nadauran politics has been dominated by the intense rivalry between the conservative [[National Action Party (Nadauro)|National Action Party]] (PAN) and the 2002-founded, progressive {{wp|catch-all party|catch-all}} [[National Democratic Party (Nadauro)|National Democratic Party]] (PDN); major political crises and events in 21st-century Nadauro include the 2004 [[Impeachment of Luciana Chagas|impeachment]] of [[Luciana Chagas]], the 2010 [[Debelcom corruption scandal]], and the [[2013 Nadauran government protests|2013 government protests]]. | Espíndola embarked on sweeping {{wp|neoliberalism|neoliberal}} reforms aimed at combating the [[Nadauran coroa crisis]] and signing the [[Elian Free Trade Agreement]] (EFTA) with the Free States and X in 1989. A second period of economic prosperity accompanied his tenure throughout the 1990s, seeing a peak growth rate of 6.2% in 1995; Nadauro hosted the [[1996 Summer Olympics (Teleon)|1996 Summer Olympics]] in Itabira. Contemporary Nadauran politics has been dominated by the intense rivalry between the conservative [[National Action Party (Nadauro)|National Action Party]] (PAN) and the 2002-founded, progressive {{wp|catch-all party|catch-all}} [[National Democratic Party (Nadauro)|National Democratic Party]] (PDN); major political crises and events in 21st-century Nadauro include the 2004 [[Impeachment of Luciana Chagas|impeachment]] of [[Luciana Chagas]], the 2010 [[Debelcom corruption scandal]], and the [[2013 Nadauran government protests|2013 government protests]]. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 3 June 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
United Nadauran States Estados Unidos Anadaúroleiros (Lavish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Suum Cuique (Cambran) ("To Each Their Own") | |
| Anthem: Hino Nacional Anadaúroleiro ("Nadauran National Anthem") | |
| National seal Selo Nacional do Anadaúro National Seal of Nadauro  | |
 Location of Nadauro (dark green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Itabira |
| Official languages | Lavish (de facto) |
| Ethnic groups | 41.5% White 37.7% Multiracial 11.1% Black 6.8% Indigenous 1.9% Abarian |
| Religion | 78.8% Gregorianism —X 13.0% No religion 6.1% Spiritism 2.1% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Nadauran |
| Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic |
| Nataniel Magalhães | |
| Erasmo Câmara | |
| Gracília Couto Pimentel | |
| Tadeu Soares de Brugge | |
| Legislature | National Congress |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Representatives | |
| Independence from Lavaria | |
• Declared | 16 August 1819 |
| 3 March 1821 | |
| 20 April 1979 | |
| 7 July 1983 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,298,032 km2 (501,173 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.74% |
| Population | |
• December 2022 estimate | 139,411,400 |
• 2020 census | 136,962,171 (4th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2021) | high |
| HDI (2020) | high |
| Currency | Nadauran lirio (L$, NAL) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +40 |
| Internet TLD | .na |
Nadauro (/nɑːdɑːˈuːroʊ,
The nation's society is among the most ethnically diverse and multicultural ones in the world. Approximately two-thirds of its population practices Gregorianism to an extent, making it the single most populous X-majority country; Nadauro is also the only country in Elia to have Lavish as its de facto official language. Its varied geography and high density of biodiversity shape the megadiverse country, ranging from the tropical rainforest of the X basin to the wetlands of the Mécalin peninsula and the Haitetl Desert.
The area of modern-day Nadauro has seen continuous human presence going back to 7,000 BCE in the late Paleolithic period. From the 6th and 5th centuries BCE onward, the Rift Valley of Nadauro gradually became one of the world's cradles of civilization, spawning a number of subsequent princely polities and city-states such as the Necaha, Cozahetl, Etalco, Mecatl, and the Ata cultures, and ultimately the expansive and hegemonic Huecean Empire by the first millennium AD. Calesian contact in 1505 precipitated the eventual conquest of the Huecean Empire by the Lavish Empire in 1547, leading to the civilization's swift collapse and the establishment of the colony of New Pania. The abundance of its mineral deposits, namely silver and gold, greatly contributed to Lavaria's rise as a global colonial power in the 17th century and the eventual elevation of New Pania to the status of a kingdom in 1732. After nearly three centuries of colonial rule, Nadauro achieved independence in 1819 following the successful Great Revolution in Darona as a constitutional monarchy under Emperor Luís I.
The political and economic upheaval of the newly independent nation state, caused in part by the Helmish War, culminated in a military coup d'état in 1858 and a Waldrich-backed royalist counter-coup in 1859. Efforts to introduce liberal reforms in the Constitution of 1874 saw brief flirtation with civil republicanism during the August War through the creation of the United Provinces of Nadauro; slavery was abolished in 1876. The short-lived federation would come to an end with the imposition of a royalist dictatorship under Emanuel Teixeira after the First Helmish–Nadauran War and 1885 National Schism, pursuing rapid modernization and industrialization. The rise of militarism and imperialist ambitions of the Empire coincided with the introduction of national syndicalism through Lúcio Cabral's seizure of power in 1921, in the wake of the 1909 Second Helmish–Nadauran War; Nadauro invaded Helmenland in 1934 and officially entered the Great War as an Sydenham Power in 1936. Ultimately, Nadauro surrendered in 1940 amidst total defeat and was occupied by Transmedan forces until 1950. The tenure of the new democratic monarchy under Emperor Luís IV would be interrupted by a violent military junta in the mid-1970s, which was itself overthrown by a return to civilian rule and the final abolition of the monarchy in 1979. Despite spectacular economic growth, Nadauro has suffered from a low-intensity, asymmetric armed conflict in Chaibia and political violence beginning in the 1980s.
Nadauro is a federal presidential constitutional republic, led by a President, as both head of state and head of government under a multi-party system; the current system was defined in the constitution introduced in 1983. The federated nation is composed of 15 states, 3 autonomous republics, and the Federal District. The developing and newly industrialized country is regarded as a historical regional or middle power, an emerging power of note in contemporary international affairs, and generally considered to be one of the world's leading emerging markets with the 5th-largest economy by nominal GDP and the 6th-largest by PPP. However, high income inequality, poverty, extensive crime, and corruption continue to plague the country. Nadauro is a founding member of the United Congress (UC), the Organization of Elian States (OES), X.
Etymology
The name of the country "Nadauro" may be derived from a shortened and abridged expression in the Lavish language, "banhado a ouro", meaning "gold plated" or "bathed in gold", from banhado ("bathe" or "steeped"), the preposition a ("in" or "with"), and ouro ("gold").
It is possibly in reference to the decorative use of gold for armor by the Huecean Empire beginning in the mid-1300s; multiple historical accounts, including conquistador Pedro Gárcia de Semhanas, confirm the presence of warriors clad in their ceremonial attire at the 1546 Parley of Tlecupilxan alongside Emperor Yolotzil, though no mention of their armor being plated in sheets or specks of gold specifically was ever made. Other sources allege the use of the expression was the result of the noted supposed abundance of gold within the Huecean Empire in its entirety, or even in reference to a metaphor for the sun rising in the east.
Although "Nadauro" had quickly achieved widespread public use as an epithet by the mid-17th century, the country was formally named "Vice-kingdom of New Pania" (Virreinato do Novo Pánia) by the Lavish Empire for the entirety of its colonial history, until it supplanted the latter when independence was achieved in 1819. From 1819–1858, from 1859–1874, and from 1885–1979 it was named the "Empire of Nadauro" (Império do Anadaúro; the period from 1885 to 1950 is referred to as the "Second Empire", and the "Third Empire" from 1950 to 1979), in 1858 "Republic of New Pania" (República do Novo Pánia), from 1874–1885 "United Provinces of Nadauro" (Províncias Unidas do Anadaúro), and since 1979 "United Nadauran States" (Estados Unidos Anadaúroleiros). However, the 1819 Constitutional Congress of Veracrúz referred to the modern-day Nadauran territory as "Central Elia" (Élia Central) in its constitutional draft and declaration of independence; subsequent constitutions in 1874, 1886, and 1923 each used the names "Nadauran Republic" (República do Anadaúro), "New Panian and Nadauran Union" (União Novo Pániaco e Anadaúroleiro), and "Nadauran Nation" (Nação Anadaúroleiro), respectively.
History
Pre-Calesian era (pre-1547)
Lavish conquest and colonization (1547–1819)
Independence, early republics, and empire (1819–1940)
TBD

The issue of taxation and Chaibian independence formed a widening divide between Duarte and Vice President Luís Benito de Gerosa and general Emanuel Teixeira that escalated into the National Schism in April of 1885. A military coup d'état led by Teixeira restored power to the culturally influential Pedro I as Emperor and imposed a royalist junta, called the Teixeirato; from 1890 to 1920, Nadauro underwent a period of large-scale industrialization, militarization, and centralization. Unlike most of the Eastern Hemisphere's republics in the latter 19th century, the Empire witnessed vibrant economic and population growth as well as political stability. The successful Second Helmish–Nadauran War in 1909 and X in 19X cemented Nadauro's position as an emerging great power.
Emergency management incompetency following the 1919 Great Itabira Earthquake and a failed coup led to a rise of political militarism, nationalism and ultimately national syndicalism; Lúcio Cabral of the Statist Party assumed the position of prime minister under Luís III on 20 June 1921 and initiated the era of totalitarian Statist Nadauro. This ideological shift and the economic turmoil of the Recession of 1924 prompted Nadauro to pursue economic autarky, an aggressive foreign policy of expansionism and imperialism (Esfera legítima), and military alliances with Asplinist Falland and Razan. During the Third Helmish–Nadauran War in 1934, Nadauro consolidated its territorial ambitions and conducted a pacifying genocide against the X.
On 8 August 1936, Statist Nadauro officially entered the Great War as a Sydenham Power and was initially vastly successful in its military campaigns; by 1937, Nadauro controlled almost the entirety of northern Elia Austral and encroached upon the Free States south coast. However, a series of Transmedan victories at X and X, as well as the failed attempted invasion of the Free States forced Nadauro to adopt a strictly defensive strategy from 1938 onwards. Transmedan landings in X and Yecahual led to the fall of the Statist regime and an unconditional surrender by the rump government on 25 March 1940.
Contemporary era (1940–)
In the wake of the Great War, Nadauro was occupied by Transmedan forces and governed by the Control Council. Under its supervision, a new constitution was enacted on 10 August 1950 and abdicated Agustín I's son, Luís IV, became Emperor, despite fierce protests by Nadauran republicanists. Nadauro was stripped of all of its overseas territories, formally ending the Nadauran colonial empire, and millions of Nadauran settlers were repatriated from the former colonies throughout Elia Austral and beyond. The International Military Tribunal for the Elias was convened to prosecute Nadauran leaders except for Emperor Agustín I for war crimes; 29 accused were executed and another 50 incarcerated. Transmedan occupation ended with the Treaty of Fastings on 11 August 1950; in 1955, Nadauro was granted membership in the United Congress.
Fears of a combinationalist takeover prompted post-war prime minister Osmar Caetano Paschoal to assume a conciliatory posture towards the fledging opposition in parliament and govern without major crises. Concurrently, a period of record growth revived and propelled Nadauro's economy to become the fifth-largest one in the world. Beginning in the 1960s, Nadauro pursued a foreign policy of rapprochment with Waldrich and the Free States in particular, exemplary in the 1964 membership entry in the X.

Luís IV's dismissal of Julio Vila's centre-left government in December of 1973 prompted a tenure of political turbulence and precipitated a right-wing coup by a military junta; Hermes Caravelas intended to assume power for a transitory period but soon solidified his perpetual grip; despite the suspension of civil rights and introduction of strict authoritarianism, international protest was futile and economic growth continued to accelerate.
The plateauing of economic development and rapid hyperinflation after a series of mismanaging decisions and international pressure by sanctions led to the Forte de Agosto University protests on 19 May 1978. The Renascimento came in response to its brutal suppression with the Águaboa massacre, which deposed the weakened military government and brought about a peaceful transition of power from Caravelas to main opposition leader Enrico Pimentel. A nationwide referendum on 9 April precipitated the promulgation of a democratic and republican constitution, which chose not to restore the monarchy under Luís IV. On 20 April 1979, the modern United Nadauran States was founded.
The power vacuum left by the political turmoil in the Nadauran countryside was not without effect; in 1982, an asymmetric low-intensity conflict between the government military, left-wing guerrilla groups (FLP, ER1M), reactionary right-wing paramilitary bands (CLUN), and drug cartels (Armala cartel, Nahia cartel) becoming embroiled in the production, processing, and export of primarily marijuana and cocaine broke out in the state of Chaibia. President Pimentel remained staunchly opposed to negotiations and was assassinated on 30 September 1985 by ER1M.

From 1987–1992, the United Congress intervened in Nadauro with the United Congress Observer Mission in Nadauro (UCOMCA) to aid in its peace process. Juan Manuel Duque pursued a controversial peace policy during his tenure in the late 1980s, negotiating the disbanding of CLUN and a temporary truce with FLP and ER1M; the peace deal fell apart when the rejecting National Congress moved against Duque with a vote of no-confidence in January of 1988, and by 1989, the conflict had escalated into open rebellion. Diplomatic efforts by successor Tadeu Espíndola culminated in the Easter Agreement of 1990, which pacified the conflict into the largely dormant state it has been ever since.
Espíndola embarked on sweeping neoliberal reforms aimed at combating the Nadauran coroa crisis and signing the Elian Free Trade Agreement (EFTA) with the Free States and X in 1989. A second period of economic prosperity accompanied his tenure throughout the 1990s, seeing a peak growth rate of 6.2% in 1995; Nadauro hosted the 1996 Summer Olympics in Itabira. Contemporary Nadauran politics has been dominated by the intense rivalry between the conservative National Action Party (PAN) and the 2002-founded, progressive catch-all National Democratic Party (PDN); major political crises and events in 21st-century Nadauro include the 2004 impeachment of Luciana Chagas, the 2010 Debelcom corruption scandal, and the 2013 government protests.
Geography
Climate
Topography and hydrography
Biodiversity
Government and politics

Foreign policy
Military
Law enforcement and crime
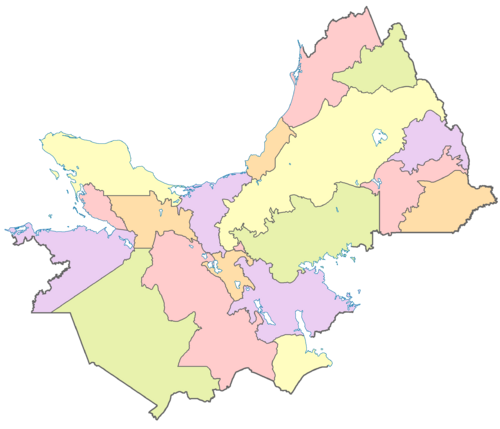
Subdivisions
| Name | Code | Capital city | Largest city | Population (December 2022) |
Map |
| Achitlan | AC | Cidade Duarte | 10,979,000 | ||
| Boaventura | BV | Linda Árvore | 4,865,000 | ||
| Cahuanya | CA | Armala | 5,902,000 | ||
| Chaibia | CH | Caridoso | 8,353,000 | ||
| Federal District | DF | Itabira | 19,987,000 | ||
| Forte de Agosto | FA | Forte de Agosto | 12,265,000 | ||
| Ichtaca | IC | Vila Rica | 7,163,000 | ||
| Itzalcoatl | IT | Chipáhua | 9,022,000 | ||
| Mécalin | ME | Topiltzin | 5,644,000 | ||
| Monte Branco | MB | Cinza | Castelo | 9,515,000 | |
| Nahia | NA | Rio Doce | Pilar | 4,400,000 | |
| Novo Grálacia | NG | Sépulva | 14,187,000 | ||
| Poraitiba | PO | Campo Verde | 2,910,000 | ||
| São Lúis | SL | Dorothia | 1,182,000 | ||
| São Sebastião | SS | Tlacoehua | São Sebastião | 3,600,000 | |
| Sarca Adente | SA | Salvador | 7,024,000 | ||
| Veracruz | VE | Veracruz | 3,302,000 | ||
| Yecahual | YC | Marinho | 4,736,000 | ||
| Zelcapan | ZL | Itzcali | 9,555,000 | ||
Economy
Tourism
Energy
Science and technology
Transportation
Demographics
Ethnicity and race
Languages
Religion
Urbanization
Largest urban agglomerations in Nadauro
National Census Institute estimates (2021) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | State or autonomous republic | Pop. | Rank | State or autonomous republic | Pop. | ||||
 Itabira  Forte de Agosto |
1 | Itabira | Federal District | 18,847,201 | 11 | Marinho | Yecahual | 1,882,752 |  Cidade Duarte  Itzcali |
| 2 | Forte de Agosto | Forte de Agosto | 12,264,995 | 12 | Pilar | Nahia | 1,753,208 | ||
| 3 | Cidade Duarte | Achitlan | 5,193,161 | 13 | Topiltzin | Mécalin | 1,671,597 | ||
| 4 | Itzcali | Zelcapan | 4,375,444 | 14 | Sépulva | Novo Grálacia | 1,644,210 | ||
| 5 | Salvador | Sarca Adente | 3,634,807 | 15 | Rio Doce | Nahia | 1,419,045 | ||
| 6 | Vila Rica | Ichtaca | 2,610,338 | 16 | Linda Árvore | Boaventura | 1,205,097 | ||
| 7 | Castelo | Monte Branco | 2,277,324 | 17 | Caridoso | Chaibia | 1,178,659 | ||
| 8 | Armala | Cahuanya | 2,124,206 | 18 | Tlacoehua | São Sebastião | 987,027 | ||
| 9 | São Sebastião | São Sebastião | 2,035,693 | 19 | Cidade Jímenez | Zelcapan | 975,641 | ||
| 10 | Chipáhua | Itzalcoatl | 1,920,234 | 20 | Veracruz | Veracruz | 969,919 | ||
Education
Health
Culture
Art
Architecture
Cuisine
Literature
Music
Cinema
Media
Sports
See also
Notes
- a.^ Lavish: Estados Unidos Anadaúroleiros, Nadauran Lavish pronunciation: [esˈtaðos uˈniðos anaˈðaˈuɾoleɪɾʊs]; abbreviated EUA