Barcia: Difference between revisions
m (→Religion) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|image_map = Barcia location map.png | |image_map = Barcia location map.png | ||
|alt_map = Location of Barcia | |alt_map = Location of Barcia | ||
|map_caption = {{map caption |location_color=dark green |country=[[Barcia]] |region=Auressia |region_color=dark grey |subregion= [[Occidental | |map_caption = {{map caption |location_color=dark green |country=[[Barcia]] |region=Auressia |region_color=dark grey |subregion= [[Occidental Confederation]]|subregion_color=green}} | ||
|map_width = 220px | |map_width = 220px | ||
|image_map2 = | |image_map2 = | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|area = | |area = | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = 388447.7 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |area_sq_mi = 149,980.5 | ||
|area_footnote = | |area_footnote = | ||
|percent_water = | |percent_water = | ||
|area_label = | |area_label = Total | ||
|area_label2 = | |area_label2 = | ||
|area_dabodyalign = | |area_dabodyalign = | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 87.56 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
|footnotes = | |footnotes = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Barcia''' (<small>Idrean:</small> {{wp|International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects|/ba:rtʃiə/}}), officially the '''Kingdom of Barcia''' ({{wp|Italian language|Idrean}}: ''Regno di Barcia''), is a {{wp|unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|constitutional monarchy}} located in eastern Occidental [[Auressia]]. Barcia is located on the eastern coast of Auressia along the [[Galene Sea]] and is bordered by [[Fortaine]], [[Palia]] and [[Sabaria]] to the west. The country has a land area of | '''Barcia''' (<small>Idrean:</small> {{wp|International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects|/ba:rtʃiə/}}), officially the '''Kingdom of Barcia''' ({{wp|Italian language|Idrean}}: ''Regno di Barcia''), is a {{wp|unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|constitutional monarchy}} located in eastern Occidental [[Auressia]]. Barcia is located on the eastern coast of Auressia along the [[Galene Sea]] and is bordered by [[Fortaine]], [[Palia]] and [[Sabaria]] to the west. The country has a land area of 388,447.7km<sup>2</sup> (149,980.5 sq mi) and a population of 34 million making it the 8th largest nation in Auressia by population. Barcia's capital and largest city is [[Tradare]] located in the north-east of the country along the river [[Russa]]. | ||
Barcia's origins can be traced back to the Sabarine Empire which came to dominate the region during the 3rd century BCE. Barcia would become a strategically important region for the empire providing significant resources and manpower which would allow further conquests across Auressia. Over time the region would become thoroughly Sabarinised and considered an integral part of the imperial heartland. With the decline of the empire however, Barcia came under attack from {{wp|Germanic peoples|Isaric}} tribes, leading to the conquest of much of Barcia's northern coast by the Ludovites in the Tenth Century CE. Over time the Ludovites would solidify their hold on the region, increasing their influence within the empire and threatening the power of the neighbouring [[Grand Duchy of Orlesso]] which held control of much of western Barcia. Following the Fourth War of the Eagles in 1422, Barcia would become one of the most powerful states within the reformed empire along with Palia, gaining significant influence over Imperial elections, with the ruling House of Sabino claiming the title of [[Sabarine Emperor]] on a number of occasions. During the Sixteenth century Barcia also benefitted from its expanding global trade network, which would see the import of spices and silks from Eastern territories such as [[Nabiya]] and [[Songha]]. With the onset of the Great War Barcia would side with its allies in the Coalition, dividing the empire to the benefit of the Kingdom territorially, however the Second Great War would see the Kingdom undergo a period of political instability resulting in revolution and a war of resistance against the Lanzist Empire. | Barcia's origins can be traced back to the Sabarine Empire which came to dominate the region during the 3rd century BCE. Barcia would become a strategically important region for the empire providing significant resources and manpower which would allow further conquests across Auressia. Over time the region would become thoroughly Sabarinised and considered an integral part of the imperial heartland. With the decline of the empire however, Barcia came under attack from {{wp|Germanic peoples|Isaric}} tribes, leading to the conquest of much of Barcia's northern coast by the Ludovites in the Tenth Century CE. Over time the Ludovites would solidify their hold on the region, increasing their influence within the empire and threatening the power of the neighbouring [[Grand Duchy of Orlesso]] which held control of much of western Barcia. Following the Fourth War of the Eagles in 1422, Barcia would become one of the most powerful states within the reformed empire along with Palia, gaining significant influence over Imperial elections, with the ruling House of Sabino claiming the title of [[Sabarine Emperor]] on a number of occasions. During the Sixteenth century Barcia also benefitted from its expanding global trade network, which would see the import of spices and silks from Eastern territories such as [[Nabiya]] and [[Songha]]. With the onset of the Great War Barcia would side with its allies in the Coalition, dividing the empire to the benefit of the Kingdom territorially, however the Second Great War would see the Kingdom undergo a period of political instability resulting in revolution and a war of resistance against the Lanzist Empire. | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[image:Italy - Sirmione.jpg|thumb|right|300px|The town of Siscia in the Bay of Persepoli]] | [[image:Italy - Sirmione.jpg|thumb|right|300px|The town of Siscia in the Bay of Persepoli]] | ||
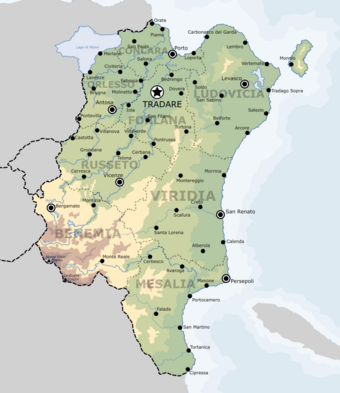
Barcia is located in north-east Occidental [[Auressia]], bordering [[Lake Moino]] ({{wp|French language|Principean}}: ''Moyens''), [[Fortaine]], [[Sabaria]] and [[Palia]] to the west and the [[Galene Sea]] to the north and east. The Benemian mountains make up much of the country's south-western frontier including the country's border with Palia and also contain the highest point in Barcia, ''Monte Elisio'' standing at 2,948m (9,672 ft). Barcia has a total land area of | Barcia is located in north-east Occidental [[Auressia]], bordering [[Lake Moyens|Lake Moino]] ({{wp|French language|Principean}}: ''Moyens''), [[Fortaine]], [[Sabaria]] and [[Palia]] to the west and the [[Galene Sea]] to the north and east. The Benemian mountains make up much of the country's south-western frontier including the country's border with Palia and also contain the highest point in Barcia, ''Monte Elisio'' standing at 2,948m (9,672 ft). Barcia has a total land area of 388,447.7km<sup>2</sup> (149,980.5 sq mi) making it the 8th largest country in Auressia by land area. | ||
A number of major rivers run through Barcia, the most notable being the Russa, Idro and Orl rivers, all of which run from the Galene Sea through the country's westernmost regions. This region in the north-west known as the Forlana valley is the most densely populated region in the country and contains some of Barcia's most important cities both economically and politically. Cities such as Tradare, Antosa, Vicenze, Salona and Porto are located here as well as 60% of the country's population. The prominence of this river valley in northern Barcia greatly contributes to the country's notable north-south divide, with the more southerly regions outside of the city of Persepoli being perceived as less prosperous and developed than their northern counterparts. | A number of major rivers run through Barcia, the most notable being the Russa, Idro and Orl rivers, all of which run from the Galene Sea through the country's westernmost regions. This region in the north-west known as the Forlana valley is the most densely populated region in the country and contains some of Barcia's most important cities both economically and politically. Cities such as Tradare, Antosa, Vicenze, Salona and Porto are located here as well as 60% of the country's population. The prominence of this river valley in northern Barcia greatly contributes to the country's notable north-south divide, with the more southerly regions outside of the city of Persepoli being perceived as less prosperous and developed than their northern counterparts. | ||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
===Architecture=== | ===Architecture=== | ||
[[image: | [[image:Tour Eiffel 09.jpg|thumb|right|200px|The Tradare Tower is one of the most recognisable symbols of modern Barcia]] | ||
Owing to its Sabarine heritage, many of Barcia's architectural styles can trace their origins back to the {{wp|ancient roman architecture|ancient sabarine architecture}} prominent in cities and colonies founded by the Sabarines such as Antosa and Salona. Whilst many of the buildings which conform to these architectural styles have since become ruins, Sabarine architecture continued to influence later styles throughout the country, providing Barcia with a largely consistent architectural image. Architectural historians tend to note the end of ancient Sabarine architecture in the Tenth Century with the beginning of the [[Ludovite Conquest]]. As the Ludovites increased their control and influence over northern Barcia, new architectural styles began to emerge, fusing Sabarine traditions with the more Isaric influences of the new rulers. Whilst this style which later became known as {{wp|romanesque architecture|sabarinesque architecture}} was originally centred on Barcia it would soon come to influence much of the later empire and occidental Auressia as a whole. As this style was brought over by Barcia's new conquerors, it became synonymous with the castles, forts and churches which dominated the cities and towns of medieval Barcia. Perhaps the most notable Sabarinesque building in Barcia is the Castello Forlana in the capital of [[Tradare]] which was once the home of ruling Ludovite and later Sabino families. | Owing to its Sabarine heritage, many of Barcia's architectural styles can trace their origins back to the {{wp|ancient roman architecture|ancient sabarine architecture}} prominent in cities and colonies founded by the Sabarines such as Antosa and Salona. Whilst many of the buildings which conform to these architectural styles have since become ruins, Sabarine architecture continued to influence later styles throughout the country, providing Barcia with a largely consistent architectural image. Architectural historians tend to note the end of ancient Sabarine architecture in the Tenth Century with the beginning of the [[Ludovite Conquest]]. As the Ludovites increased their control and influence over northern Barcia, new architectural styles began to emerge, fusing Sabarine traditions with the more Isaric influences of the new rulers. Whilst this style which later became known as {{wp|romanesque architecture|sabarinesque architecture}} was originally centred on Barcia it would soon come to influence much of the later empire and occidental Auressia as a whole. As this style was brought over by Barcia's new conquerors, it became synonymous with the castles, forts and churches which dominated the cities and towns of medieval Barcia. Perhaps the most notable Sabarinesque building in Barcia is the Castello Forlana in the capital of [[Tradare]] which was once the home of ruling Ludovite and later Sabino families. | ||
With the onset of the Seventeenth century however, architectural styles began to shift towards styles influenced by wider Auressia such as the {{wp|baroque architecture|baroque}} and {{wp|rococo architecture|rococo}}. Yet these styles would later be eclipsed by large {{wp|neoclassical architecture|neoclassical}} structures which dominated Barcian cities during the Eighteenth century. Many of these buildings were key administrative or transport buildings such as post offices, train stations or hospitals, vital to the functioning of an increasingly urbanisng kingdom. By the Twentieth century these neoclassical styles would evolve into a number of different styles including {{wp|art deco}}, {{wp|art nouveau}} and the {{wp|rationalism (architecture)|rationalist}} styles most prominent during the regency period. Today, modern Barcian architecture retains much of its heritage, though with much greater influence from more {{wp|International Style|international}} and {{wp|functionalism (architecture)|functionalist}} designs. | With the onset of the Seventeenth century however, architectural styles began to shift towards styles influenced by wider Auressia such as the {{wp|baroque architecture|baroque}} and {{wp|rococo architecture|rococo}}. Yet these styles would later be eclipsed by large {{wp|neoclassical architecture|neoclassical}} structures which dominated Barcian cities during the Eighteenth century. Many of these buildings were key administrative or transport buildings such as post offices, train stations or hospitals, vital to the functioning of an increasingly urbanisng kingdom. By the Twentieth century these neoclassical styles would evolve into a number of different styles including {{wp|art deco}}, {{wp|art nouveau}} and the {{wp|rationalism (architecture)|rationalist}} styles most prominent during the regency period, with the most notable modern building being the Tradare tower, pehaps the most reognisable Barcian building. Today, modern Barcian architecture retains much of its heritage, though with much greater influence from more {{wp|International Style|international}} and {{wp|functionalism (architecture)|functionalist}} designs. | ||
===Visual and Performing Arts=== | ===Visual and Performing Arts=== | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 1 July 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Kingdom of Barcia Regno di Barcia (Idrean) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "Inno Nazionale di Barcia" "National Anthem of Barcia" | |
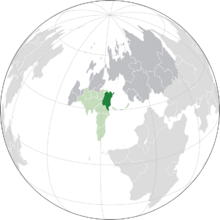 Location of Barcia (dark green) – in Auressia (green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Tradare |
| Official languages | Idrean |
| Recognised regional languages | Ludovite |
| Demonym(s) | Barcian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• King | Umberto VI |
• Chancellor | Massimiliano Perretti |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Area | |
• Total | 388,447.7 km2 (149,980.5 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 34,013,476 |
• Density | 87.56/km2 (226.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $1.863 trillion |
• Per capita | $54,768 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $1.569 trillion |
• Per capita | $46,137 |
| Gini (2024) | medium |
| HDI (2024) | very high |
| Currency | Sabarine Ducat (SDU) |
| Time zone | UTC0 (Western Auressian Time) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +56 |
| Internet TLD | .ba |
Barcia (Idrean: /ba:rtʃiə/), officially the Kingdom of Barcia (Idrean: Regno di Barcia), is a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy located in eastern Occidental Auressia. Barcia is located on the eastern coast of Auressia along the Galene Sea and is bordered by Fortaine, Palia and Sabaria to the west. The country has a land area of 388,447.7km2 (149,980.5 sq mi) and a population of 34 million making it the 8th largest nation in Auressia by population. Barcia's capital and largest city is Tradare located in the north-east of the country along the river Russa.
Barcia's origins can be traced back to the Sabarine Empire which came to dominate the region during the 3rd century BCE. Barcia would become a strategically important region for the empire providing significant resources and manpower which would allow further conquests across Auressia. Over time the region would become thoroughly Sabarinised and considered an integral part of the imperial heartland. With the decline of the empire however, Barcia came under attack from Isaric tribes, leading to the conquest of much of Barcia's northern coast by the Ludovites in the Tenth Century CE. Over time the Ludovites would solidify their hold on the region, increasing their influence within the empire and threatening the power of the neighbouring Grand Duchy of Orlesso which held control of much of western Barcia. Following the Fourth War of the Eagles in 1422, Barcia would become one of the most powerful states within the reformed empire along with Palia, gaining significant influence over Imperial elections, with the ruling House of Sabino claiming the title of Sabarine Emperor on a number of occasions. During the Sixteenth century Barcia also benefitted from its expanding global trade network, which would see the import of spices and silks from Eastern territories such as Nabiya and Songha. With the onset of the Great War Barcia would side with its allies in the Coalition, dividing the empire to the benefit of the Kingdom territorially, however the Second Great War would see the Kingdom undergo a period of political instability resulting in revolution and a war of resistance against the Lanzist Empire.
As a Constitutional monarchy Barcia is one of the few states in Levilion to retain royal family, with the country having been ruled by the House of Sabino since 1378. The current ruler of Barcia is King Umberto VI who has ruled the country since 1987, the current Chancellor is Massimiliano Perretti. As per the Constitution of 1947, Barcia's political system is based on a separation of powers which greatly limits the power of the monarch to intervene in political affairs. The monarch is responsible for appointing the Chancellor who is legally the parliamentary leader best able to command a majority of sitting MPs in the Parliament of Barcia.
Today Barcia continues to play a major role in the Occidental Confederation and across the globe as a key economic and political actor with its powerful economy centred on Tradare making Barcia a global economic and political hub. As a member of the Occidental Confederation Barcia weilds significant influence in Auressian affairs and currently holds the Consulship of the organisation through Fabiana Richardi. Barcia maintains a moderate armed force with a significant navy, both of which are primarily utilised for border security purposes as well as Occidental overseas missions. The largest sectors of the Barcian economy include service industries, notably banking and insurance as well as winemaking, designer fashion and cosmetics. The country maintains a universal healthcare system and is also renowned for its prominent arts and cultural sector.
Etymology
The name of Barcia is derived from the Sabarine Barcium which was the name of the Sabarine province of the First Empire which encompassed much of the northern territory of modern-day Barcia. The name Barcium is believed to have been derived from the Sabarine name for a tribe native to the region known as the Barcii who were major rivals to the Sabarines from the Fifth to the Third Century BCE. Following the collapse of the First Empire, the name Barcia became synonymous with north-eastern Occidental Auressia leading to its re-emergence during the Eleventh Century following the Ludovite Conquest which saw the Sabarine Emperor grant the invaders the Iron Crown of Barcia and the title Grand Duke of Barcia in the process. Over time the lands of the Ludovites would fracture, leading the emperor to reclaim the iron crown, however the Eighteenth century would see the proclamation of a unified Barcian Kingdom which provided the foundations for the modern Barcian state.
History
- Early humans
- Sabarine Empire
- Ludovite conquest
- Rising imperial power
- Great upheaval
- Great wars
- Modern day
Geography
Barcia is located in north-east Occidental Auressia, bordering Lake Moino (Principean: Moyens), Fortaine, Sabaria and Palia to the west and the Galene Sea to the north and east. The Benemian mountains make up much of the country's south-western frontier including the country's border with Palia and also contain the highest point in Barcia, Monte Elisio standing at 2,948m (9,672 ft). Barcia has a total land area of 388,447.7km2 (149,980.5 sq mi) making it the 8th largest country in Auressia by land area.
A number of major rivers run through Barcia, the most notable being the Russa, Idro and Orl rivers, all of which run from the Galene Sea through the country's westernmost regions. This region in the north-west known as the Forlana valley is the most densely populated region in the country and contains some of Barcia's most important cities both economically and politically. Cities such as Tradare, Antosa, Vicenze, Salona and Porto are located here as well as 60% of the country's population. The prominence of this river valley in northern Barcia greatly contributes to the country's notable north-south divide, with the more southerly regions outside of the city of Persepoli being perceived as less prosperous and developed than their northern counterparts.
Barcia also controls a total of 48 islands and islets off its coast, the most notable of these being the island of Sabia located off the north-eastern coast. Sabia was the first landing point of Ludovite raiders during the Ninth century and the first part of the country to be conquered by Ludovicus and as such remains host to many sites of traditional Ludovite culture. Several other smaller islands also exist off the coast of the mainland, the vast majority of which are in the Bay of Persepoli which is home to the largest collection of inhabited islands in Barcia.
Climate
Barcia is located around 40º north of the equator. This ensures that much of the country's northern territory lies within the humid subtropical climate whilst the more southerly regions are considered part of the dry summer climate. The more northerly regions such as Concara, Forlana and Ludovicia experience hot, humid summers with average temperatures ranging from 18ºC - 28ºC (65ºf - 82ºf) whilst winters see large amounts of rainfall, fog and frost. Average winter temperatures in the north tend to range from 4ºC to 9ºC (39ºf - 48ºf).
Meanwhile the southern areas of the country such as Mesalia and Viridia see generally higher than average temperatures across the year, with summer highs of around 32ºC (89ºf) and winter temperatures as low as 4ºC (39ºf). These regions also tend to see limited rainfall across the year though this generally increases during the relatively mild winters. Summers however tend to be hot and see little to no rainfall with minimal cloud coverage.
Biodiversity
Barcia has a strong variety of flora and fauna throughout the country with many of the country's plants associated with traditional medicinal remedies such as aconitum or taxus baccata. The interior and highland areas of the country have considerable forest cover with widespread restrictions on the logging industry designed to protect the country's various woodlands of mixed broadleaf trees. These predominantly include oak, birch and elm, though willow and maple trees are also common, whilst the south of the country, in areas like Mesalia, sees many more cypress trees. Many of these woodlands lie within the country's 12 national parks which are protected by the Regia Commissione per il Patrimonio Barciana (Royal Barcian Heritage Commission). Nevertheless, more low-lying areas of the country such as the Forlana valley contain little to no forest cover owing to historical deforestation which followed widespread urbanisation during the Eighteenth and Nineteenth centuries.
Over 35,000 species of fauna have been recorded in Barcia marking the country out as having a strong faunal biodiversity. These animals include a wide variety of amphibians, birds, fish, mammals and reptiles. The animals most associated with Barcia include the crestless eagle which is the country's official national bird, depictions of which are included on the country's coat of arms, the Sabarine wolf and the fallow deer. In terms of marine wildlife, Barcia is home to a wide variety of invertebrates, molluscs and corals. The most notable marine area of the country is the Bay of Persepoli which as a lagoon sees fresh fluvial and brackish waters meet leading the area to play host to a number of unique species such as the killifish, purple heron and marsh harrier. However, recent years have seen the biodiversity of the lagoon threatened due to increases in maritime activity, particularly due to tourism and trade. As a result, the Barcian government has introduced restrictions limiting the ability of Kasarmax vessels and cruise ships to access the lagoon. Similar concerns have been raised about the impact of climate change on the wider biodiversity of the country due to increasing global temperatures and more violent flooding. In response, the ruling Unity Party has sought to introduce new measures aimed at limiting and reversing the impact of climate change by investing in green energy and environmental-protection initiatives such as flood defences and reforestation.
Politics
Barcia is a unitary state under a constitutional monarchy. Barcia's head of state is King Umberto VI though as per the Constitution of 1947, most of the executive power in the country is vested in the head of government, known as the Chancellor (Idrean: Cancelliere). The Chancellor is the individual best able to "command the confidence" of the Parliament of Barcia and is usually the leader of the largest party within Parliament. The current Chancellor is Massimiliano Perretti of the Unity Party who has held the position since 2019. Barcia's fundamental laws are codified within the country's Constitution introduced in 1947 in the aftermath of the Second Great War. The Constitution can only be amended through a 2/3rds majority vote in Parliament and the signed approval of the Chancellor.
Government
Barcia has a unicameral legislature known as the Barcian Parliament. Throughout its history the Barcian parliament was originally a bicameral body with an unelected upper chamber known as the Noble Assembly (Idrean: Assemblea Nobile) made up of aristocratic and religious officials, and an elected lower chamber known as the Public Assembly (Idrean: Assemblea Pubblica) made up of MPs elected through general elections. This was amended with the introduction of the 1947 constitution which removed the upper chamber. Today the Parliament of Barcia is comprised of 326 elected officials who each represent a local constituency across the country. Any bill looking to become a law must first be introduced and debated within parliament before being voted through with a simple majority before being approved and signed into law by the Chancellor.
As a democracy, Barcia has a system of universal suffrage with all citizens over the age of 18 regardless of race, gender, wealth or status enjoying the right to vote in elections. General elections to parliament take place every four years, though can take place sooner if a majority of members vote to petition the monarch. Elections to parliament utilise the first-past-the-post system with the candidate with the most votes in each constituency winning the parliamentary seat. Following each general election, the monarch invites the leader of the largest party to form a government. Should no party have an overall majority, then a coalition government may be formed by two or more parties. Only three coalition governments have been formed in Barcia since 1947, two of which were the only elections where the Unity Party was not the single largest party in parliament. All citizens can also vote for local councillors as part of local elections which take place every two years across the country.
As well as the Chancellor, executive power within the country is vested in the Cabinet which is comprised of members of parliament from the ruling party who are appointed by the Chancellor. Each member of the cabinet is responsible for a ministerial post which corresponds with the various government ministries such as transport, health and defence. All ministers within the cabinet are bound by the constitutional convention of cabinet collective responsibility, requiring them to support all government decisions made in the cabinet and must resign if they openly oppose or reject a governmental decision.
Barcia has a number of political parties which each compete in local and general elections across the country. The Barcian government is currently controlled by the Unity Party which has historically been the dominant party within the country's elections having won an outright majority all but three elections it has contested. The Unity Party currently holds 216 seats out of 326 in the Barcian parliament. Currently the second largest party within the Barcian parliament is Avanti Insieme! with 83 seats, forming the official opposition. Other parties with representation in parliament include the Liberal Party with 24 seats, Nostra Tera with 2 and the Communist Party of Barcia with 1 seat. The next general election in Barcia is due to take place in 2025 with all parties contesting the 326 seats in the country's parliament.
Administrative divisions
Barcia is divided into 8 administrative divisions known as "regions". Each of these regions is further subdivided into provinces and again into communes which posess a local council elected through local elections. Barcia's regions were created within the Constitution of 1947 and were further amended in 1967 with the addition of the region of Russeto. Each region roughly corresponds with the boundaries of the country's historical duchies which lasted from the proclamation of the Barcian Kingdom in the mid-Eighteenth century until the Second Great War. The National regions were introduced following the Second Great War in order to streamline the antiquated and medieval duchy system which greatly hampered the administrative unity of the Kingdom throughout the regency period.
Whilst each region generally exists for administrative and bureaucratic purposes, each commune within the country receives a varying degree of autonomy and funding from the central government based on its population as outlined within the Fifth Constitutional Amendment passed in 1978. As a unitary state, the government possesses the right to make any and all "necessary changes" to the budget and status of these regions which are regularly reviewed and revised within each sitting of parliament. Additionally, urban communes also maintain an increased degree of autonomy with elected mayors who posses greater power over strategic planning, local policy and spending.
|
Law and justice
Like most countries in Occidental Auressia Barcia utilises a civil law system in which judges act as interpreters of legal statutes rather than creators of legal precedent. Barcia's legal system is largely based on Sabarine law as well as the various modifications to the legal code codified during the early Occidental Confederacy. As such, Barcia's legal system is virtually identical to many of its neighbours, with most modifications coming with the implementation of the 1947 Constitution. The highest court in Barcia is the Court of Cassation (Idrean: Corte di Cassazione) which acts as the court of final appeal within the Barcian legal system. In addition, the court also maintains final ruling over the constitutionality of legislation passed by Parliament. The court itself is divided into four chambers, these being civil, criminal, commercial and military chambers. Before any case is heard within the Court of Cassation it is first heard within one of the various inferior courts, which include the High Court and Court of Appeal.
Law enforcement in Barcia is centralised under the Ministry of the Interior, with authority for las enforcement divided between the Civil Police (Idrean: Polizia Civile) and the military police or Gendarmerie, otherwise known as the Carabinieri. As the name suggests, the Civil police maintains authority over civil matters with branches for the transit police, border control and search and rescue. Meanwhile the Carabinieri is a distinct military police with both domestic and foreign responsibilities with all officers permitted to carry weaponry. Members of the Carabinieri also regularly accompany government ministers and the Chancellor as personal security during foreign visits. Barcia also maintains a Ministry of Intelligence under which falls the National Security Service (Idrean: Servizio di Sicurezza Nazionale) or SSN which is responsible for internal security and the Foreign Intelligence Service or (Idrean: Servizio di Intelligence Straniero) or SIS which both work closely with the Ministry of the Interior.
Foreign relations
Barcia maintains foreign relations with almost all nations in the world and is a member of a large number of international organisations such as the International Assembly. As a democratic nation, Barcia tends to globally champion causes such as the rule of law, democracy and legal equality of nations within its foreign policy, though stops short of interfering in the affairs of other sovereign nations. Through membership of the Occidental Confederation, Barcia maintains strong ties with its neighbouring nations, with which it shares a single market, currency union and freedom of movement arrangements. Membership of the Confederation also makes the Barcian passport one of the strongest in the world, owing to its ability to enter a large number of countries without the need for a tourist visa. In addition to these agreements, Barcia also cooperates on wider Occidental foreign policy aims, such as global peacekeeping missions or coastal security.
Due to the Occidental Confederation's single trade area, Barcia maintains very few bilateral trade agreements, with most trade treaties drawn up multilaterally amongst the associated member states of the confederation and their trade partner, owing to the more restrictive import laws on goods coming into the Occidental single market. Nevertheless, such an arrangement does increase the global bargaining power of Barcia within international trade.
Military
Economy
Demographics
Major cities
Largest cities or towns in Barcia
2024 census | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Region | Pop. | Rank | Region | Pop. | ||||
 Tradare  Porto |
1 | Tradare | Forlana | 2,600,000 | 11 | Bergamate | Benemia | 202,000 |  Persepoli  Antosa |
| 2 | Porto | Concara | 1,400,000 | 12 | Portocamero | Mesalia | 184,000 | ||
| 3 | Persepoli | Mesalia | 880,000 | 13 | Tradago Sopra | Ludovicia | 169,000 | ||
| 4 | Antosa | Orlesso | 770,000 | 14 | Pontrussa | Forlana | 163,000 | ||
| 5 | Levasco | Ludovicia | 580,000 | 15 | Castotta | Russeto | 158,000 | ||
| 6 | Vicenze | Russeto | 454,000 | 16 | Calenda | Viridia | 155,000 | ||
| 7 | Salona | Concara | 318,000 | 17 | Piame | Concara | 152,000 | ||
| 8 | San Renato | Viridia | 263,000 | 18 | San Filano | Forlana | 149,000 | ||
| 9 | Telona | Russeto | 240,000 | 19 | Tortanica | Mesalia | 146,000 | ||
| 10 | Fabrosa | Orlesso | 229,000 | 20 | Cerresca | Russeto | 145,000 | ||
Ethnic groups
Language
Religion
Barcia's state religion as defined within the national constitution is Apostolic Perendism with the Barcian church subordinated under the authority of the Sabarine Apostolic Church which is led by the Dicere based in Sabaria. In reality however, religious affairs within Barcia are the responsibility of the Barcian government in coordination with the Holy Sabarine Church as well as the Archbishop of Tradare. Despite this, the Barcian Constitution does guarentee freedom of religion and worship for all citizens and residents. Compared with other Auressian countries, Barcia is a considerably more religious country, with Perendism maintaining a strong base of worship based on church attendance figures as well as recent census data which showed 76% of all respondents self-identified as "Perendist", the vast majority of which are believed to associate with the Apostolic Church. As of the 2024 census only 12% of the population identifies as "no religion".
The two largest minority religions in Barcia are Morism at 4% and Aulaism at 2%. Morism was imported to Barcia by Palian missionaries and philosophers throughout the late Medieval and early modern period and has for the most part co-existed peacefully with Perendism. Nevertheless reports of anti-Morist acts increased considerably in the aftermath of the Second Great War. By contrast, Aulaism is largely associated with the country's considerable Rasmi diaspora which has lived in Barcia throughout much of history. Other notable religions within Barcia include Jyanism, Macakkanism and Senit all of which are associated with migrant communities which moved to Barcia during the Twentieth and Twenty-first centuries.
Health
Education
Culture
Heritage sites
Having been an important part of the Sabarine Empire, Barcia is home to a considerable amount of ancient Sabarine ruins. Many of these sites are now protected by the Regia Commissione per il Patrimonio Barciana (Royal Barcian Heritage Comission) which is responsible for the selection, management and care of heritage sites across the country. Many of these sites receive royal patronage for their upkeep with free entry for all Barcian citizens. Due to the presence of these ruins, of which Barcia has the largest number outside of Sabaria itself, the country receives a considerable amount of tourism particularly from northern Auressia as well as the rest of the Occidental Confederacy. The most notable heritage site in the country is the ruins of Arlantium near modern Civiteria. The site boasts the almost completely excavated remains of a Sabarine colony including bathhouses, palace, markets and forum.
Barcia also maintains a large number of heritage sites from the medieval and early modern periods. The reconstruction government of the late 1940s and 50s was particularly notable for its policies promoting the restoration and preservation of heritage sites across the country, though in many cases this came at the expense of many neighbouring buildings deemed not worth preserving. Notably during this period, cities such as Antosa and Levasco saw widespread construction projects to improve accessibility and general visibility of high profile buildings and heritage sites, creating large public squares or avenues in the immediate vicinity. Though lauded at the time for preserving many of the traditional old town's across the country, such projects have been criticised more recently for their careless destruction of other valuable buildings and homes.
Architecture
Owing to its Sabarine heritage, many of Barcia's architectural styles can trace their origins back to the ancient sabarine architecture prominent in cities and colonies founded by the Sabarines such as Antosa and Salona. Whilst many of the buildings which conform to these architectural styles have since become ruins, Sabarine architecture continued to influence later styles throughout the country, providing Barcia with a largely consistent architectural image. Architectural historians tend to note the end of ancient Sabarine architecture in the Tenth Century with the beginning of the Ludovite Conquest. As the Ludovites increased their control and influence over northern Barcia, new architectural styles began to emerge, fusing Sabarine traditions with the more Isaric influences of the new rulers. Whilst this style which later became known as sabarinesque architecture was originally centred on Barcia it would soon come to influence much of the later empire and occidental Auressia as a whole. As this style was brought over by Barcia's new conquerors, it became synonymous with the castles, forts and churches which dominated the cities and towns of medieval Barcia. Perhaps the most notable Sabarinesque building in Barcia is the Castello Forlana in the capital of Tradare which was once the home of ruling Ludovite and later Sabino families.
With the onset of the Seventeenth century however, architectural styles began to shift towards styles influenced by wider Auressia such as the baroque and rococo. Yet these styles would later be eclipsed by large neoclassical structures which dominated Barcian cities during the Eighteenth century. Many of these buildings were key administrative or transport buildings such as post offices, train stations or hospitals, vital to the functioning of an increasingly urbanisng kingdom. By the Twentieth century these neoclassical styles would evolve into a number of different styles including art deco, art nouveau and the rationalist styles most prominent during the regency period, with the most notable modern building being the Tradare tower, pehaps the most reognisable Barcian building. Today, modern Barcian architecture retains much of its heritage, though with much greater influence from more international and functionalist designs.
Visual and Performing Arts
Barcia has a long and distinctive history in the visual arts, tracing much of its origins again back to the Sabarine period. Frescos and mosaics were commonplace throughout many Barcian manor houses and churches. Additionally, Barcia is also notable for its medieval religious artwork, with the Ludovite dynasty being great patrons of religious artwork during their reign, much of which adorned the various castles, palaces and churches constructed in the years following the Ludovite conquest.
Yet, Barcian art would not be seen as distinctive from its wider Sabarine counterparts until the Seventeenth century with the emergence of baroque painting. These new paintings substituted religious artwork for that inspired by ancient Sabarine mythology, Ludovite legends, or paintings of the Kingdom's great monarchs. Artwork was particularly patronised by Cosimo IV in an attempt to garner prestige and support from overseas for his rule in the years prior to the great upheaval. Paintings would depict the ruler as a powerful figure, depicting his victories on the battlefield or great acts of state or diplomacy.
Barcia also has a considerable performing arts scene with opera and ballet being amongst the most popular performative acts in the country by audience size. The Royal Opera Theatre in Tradare is one of the largest in the world, having been in operation since 1864. Cinema is also very popular in Barcia with the country having a sizeable domestic filmmaking industry. The city of Persepoli is also host to the International Film Festival. The festival takes place yearly in April and is a celebration of international filmmaking and acting. The festival previews upcoming films and also hands out awards for cinematography and acting and is regularly attended by some of the most high profile celebrities from across the world. Barcia is also notable for its domestic TV production industry, which is largely dominated by the broadcaster TeleBarcia. The country is particularly notable for its production of dramas, soaps and documentaries which are popular across the Idrean speaking world.
Cuisine
Barcia's cuisine is renowned for its distinctive pasta and meat dishes which are predominant throughout the country. Generally, however cuisine tends to differ between more inland and coastal regions, with seafood being much more prominent in coastal areas, particularly in the south. Barcian meals generally consist of 4 courses as is standard across Idrean cultures. An antipasto is usually served first which can consist of a soup, cured meats, cheese or olives. This is then followed by a first course which can consist of pasta or risotto, whilst second course traditionally includes various meat and fish dishes. Finally, notable Barcian desserts include tiramisu and affogato.
Barcia does not have a national dish, though the closest two meals that are usually associated with the country are gnocchi or ossobuco. Barcia is also notable for the widespread use of horse meat within its cuisine which is traditionally served stewed with a red wine sauce and polenta. Compared with other Idrean countries, Barcian cuisine tends to use butter as opposed to olive oil particularly in dishes which originate from the more northerly regions such as Ludovicia. This substitution is a result of the much larger Barcian dairy industry and ensures that Barcian cuisine has a more distinctive taste relative to other Idrean countries. In addition, Barcia's dairy culture has led to a much wider variety of cheeses to originate from the region such as calosan and mascarpone.
Barcia is also known for its considerable wine culture, with red or white wine common drank with most evening meals. Barcian wines from the Forlana and Ludovicia regions are particularly well reguarded within the international community. The most famous Barcian wine is lambrusco which originates from Ludovicia region as is made with red grapes with the most popular varieties being sparkling wines. In addition to wine, Barcia is also known for its coffee culture. Coffee or espresso is traditionally drank as part of breakfast and Barcia has a wide range of both chain and independent coffee shops. The most famous Barcian coffee brands are Morganelli which is a high-profile coffee maker and Leuzzi which is a brand of coffee shops common across Auressia and the wider world.
Sport
The most popular sport in Barcia by far is association football, with the country renowned for its strong national team which has won a number of international honours and includes world renowned players such as Celso Rulli and Laurentino Rigo. Barcia is also due to host the upcoming 2024 International Cup which the national team has won a total of 3 times, in 1984, 1988 and 2004. Additionally, Barcian football is well known globally for its domestic footballing competition, the Barcian Superlega. The most successful football teams in Barcia are FC Imperiale and Reale Belvidere who between them hold 26 league titles.
Tennis is the second most popular sport in Barcia, with the sport popular in schools and gymnasiums across the country. Within the international tennis scene, Barcia is known for the Tradare Open lawn tennis tournament which takes place every year in spring. Perhaps the most popular tennis player in the world, Giuda Del Toro, is from Barcia. Del Toro won a total of 17 grand slam titles during his career which spanned both the 1980s and 1990s.
Other notable sports in Barcia include cycling, boxing and squash. Road cycling is particularly popular in Barcia, owing to the annual Giro di Barcia which takes place on public roads across the country. The Giro sees cyclists compete on daily stages over a three week period with stages covering much of the country as well as some neighbouring states such as Sabaria. Stages on the tour regularly rotate every year with the final stage each year ending in the capital of Tradare.