Bell-class frigate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|Name= | |Name= | ||
|Builders= Algiers Maritime Engineering, Smith Island, {{Flag|Meridon}} | |Builders= Algiers Maritime Engineering, Smith Island, {{Flag|Meridon}} | ||
|Operators= {{flag|Meridonian Navy}} | |Operators= {{flag|Meridonian Navy}} | ||
{{flagicon|Kozakura}} Kozakuran Navy | |||
|Class before= {{wpl|Anzac-class frigate|Taga-class frigate}} | |Class before= {{wpl|Anzac-class frigate|Taga-class frigate}} | ||
|Class after= | |Class after= | ||
|Subclasses= | |Subclasses= [[Equipment of the Kozakuran Navy#Ships|Yamato-class frigate]] | ||
|Cost= | |Cost= | ||
|Built range= 2018-present | |Built range= 2018-present | ||
| Line 82: | Line 83: | ||
*2x 7.62 miniguns | *2x 7.62 miniguns | ||
*4x 7.62 general purpose machine guns | *4x 7.62 general purpose machine guns | ||
*1x 32-cell | *1x 32-cell [[ANVIL Vertical Launching System#Variants|Type 1 VLS]] and 2x 12-cell [[ANVIL Vertical Launching System#Variants|Type 1A VLS]], total of 56 cells with capacity for: <br> | ||
MSA-15 short-range anti-aircraft missile (up to 4x per cell)<br> | MSA-15 short-range anti-aircraft missile (up to 4x per large cell or 1x per short)<br> | ||
MSU-14 antisubmarine rocket-propelled torpedo <br> | MSU-14 antisubmarine rocket-propelled torpedo <br> | ||
MSS-18 cruise missile<br> | MSS-18 cruise missile<br> | ||
Decoys<br> | |||
*2x Goalkeeper 40 25mm CIWS | *2x Goalkeeper 40 25mm CIWS | ||
*2x MSS-33 anti-ship missile box launchers, 2 missiles per set (total of 4) | *2x MSS-33 anti-ship missile box launchers, 2 missiles per set (total of 4) | ||
Latest revision as of 14:20, 28 October 2024
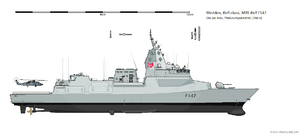 Bell, lead ship of the Bell-class frigates.
| |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Builders: |
Algiers Maritime Engineering, Smith Island, |
| Operators: |
|
| Preceded by: | Taga-class frigate |
| Subclasses: | Yamato-class frigate |
| Built: | 2018-present |
| In service: | 2020-present |
| Planned: | 30 |
| Building: | 3 |
| Completed: | 9 |
| Active: | 8 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Guided missile frigate, anti-submarine warfare frigate |
| Displacement: | 7,200 tons, full load |
| Length: | Overall: 420 feet |
| Beam: | Overall: Around 68ft |
| Draught: | 26 ft |
| Propulsion: |
list error: mixed text and list (help)
|
| Speed: | In excess of 35 knots |
| Range: | In excess of 7000 nm at 18kts operating on electric motors |
| Complement: | 160, with capacity for up to 200. |
| Sensors and processing systems: |
|
| Electronic warfare & decoys: |
|
| Armament: |
MSA-15 short-range anti-aircraft missile (up to 4x per large cell or 1x per short)
|
| Armour: | Kevlar over vital spaces |
| Aircraft carried: | 1x H50M5 normally carried |
| Aviation facilities: | Enclosed hangar for 1x H50M5 Seahawk |
The Bell-class is a class of guided missile frigates in service with and being produced for the Meridonian Navy. Designed to replace the Taga-class frigates commissioned in the 80s and 90s and provide a more capable and flexible overall design, their design primarily orients towards the anti-submarine role. First designed in the early 2010s with construction beginning in 2018 by Algiers Maritime Shipyards, the ship uses mostly readily available technologies and proven design techniques, especially those tested on the construction of the Helena-class destroyers. One notable exception is its EMPRESS integrated mast and radar system, which are a substantial systems upgrade from the Taga-class' IMRAS. The lead ship, Bell, named after the Bell river in Alexandria Territory, was commissioned in October 2020. Four ships are currently in service, with three under construction and a total of 22 ships planned.
The Bell-class frigates feature full integration of the Common Air Defense System missiles and will allow the phasing out of the legacy MSA-7 and MSA-6 Sea Sparrow missiles on all combatants. The Otapara-class can still operate them but have been modified to operate with the more modern CADS array of missiles. Bell-class ships will only carry CADS-15 missiles in quad-packed cells. They are capable of launching MSU-14 VLS-launched counter-submarine rockets and MSS-18 cruise missiles from their VLS cells, and MSS-33 Commorant missiles from box launchers. The ship features a Modular Mission Bay (MMB) which can be configured as extra helicopter space, serve as lodging, carry container crates, or raiding craft.
Description
Design
The Otapara-class was originally conceived as a standardized class of destroyer able to perform all necessary functions expected of a future surface combatant, including provisions for flag facilities as leaders of surface action groups. Replacing older Mystere-class vessels, they offered a substantially increased capability in anti-ship and land attack warfare, the latter being the first introduction of the capability from a surface ship with the introduction of VLS tubes. 20 ships were originally planned, however due to the high cost related to fitting and arming an Otapara-class destroyer and its percieved inadequacy in the air defense role, the Helena-class destroyer was designed to specialize in air warfare and form the bulk of a surface action group. This lead to the emergence of the semi-formal designation of the Otapara-class as a 'general purpose' destroyer, as opposed to the 'air wafare' destroyer Helena-class.
Construction
Propulsion
Armament and protection
Flight deck and aircraft facilities
Strike groups
Design differences within the class
Ships in class
| Ship | Pennant number | Laid down | Launched | Commissioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRS Bell | F159 | 23 March 2018 | 12 April 2020 | 03 January 2021 |
| MRS Flint | F160 | 01 February 2019 | 24 November 2019 | 30 August 2021 |
| MRS Arpeak | F161 | 2 August 2019 | 30 March 2021 | 20 September 2021 |
| MRS Barton | F162 | 13 November 2020 | 20 March 2021 | 11 March 2022 |
| MRS Isola | F163 | 16 July 2021 | 14 March 2022 | |
| MRS Esperance | F164 | 14 April 2022 | ||
| MRS Cielo | F165 | 18 December 2022 | ||
| MRS Diana | F166 |
