Asuca: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|national_anthem = ''Saudação à Liberdade''<br><small>"Salute to Freedom"</small> | |national_anthem = ''Saudação à Liberdade''<br><small>"Salute to Freedom"</small> | ||
[[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lqGZpnJCtdA|200px]] | [[File:MediaPlayer.png|link=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lqGZpnJCtdA|200px]] | ||
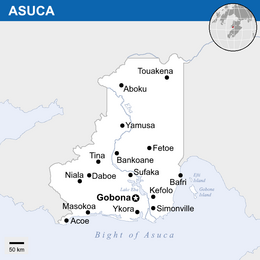
|image_map = | |image_map = AsucaGlobalMap.png | ||
|map_width = 230px | |map_width = 230px | ||
|map_caption = Location of Palanca (marked green) | |map_caption = Location of Palanca (marked green) | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|leader_name1 = Nawe Gonama | |leader_name1 = Nawe Gonama | ||
|leader_title2 = Prime Minister | |leader_title2 = Prime Minister | ||
|leader_name2 = Yana | |leader_name2 = Yana Wuembe | ||
|leader_title3 = Speaker of the Parliament | |leader_title3 = Speaker of the Parliament | ||
|leader_name3 = Ralpa | |leader_name3 = Ralpa Turisaya | ||
|legislature = Parliament | |legislature = Parliament | ||
|upper_house = | |upper_house = | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Asuca''' ({{wp|Portuguese language|Lavish}}: ''Açùcar''), officially the '''Asucar Republic''' ({{wp|Portuguese language|Lavish}}: ''República da Açùcar'') and formerly | '''Asuca''' ({{wp|IPA|/asʊ'c:a/}} {{wp|english pronuciation respelling|''a-su-CAH''}}; {{wp|Portuguese language|Lavish}}: ''Açùcar''), officially the '''Asucar Republic''' ({{wp|Portuguese language|Lavish}}: ''República da Açùcar'') and formerly '''Costa Açùcar''' or known as the '''Sugar Coast''', is a country located on the southern coast of West X, bordering X to the west, X to the north, X to the east, and the [[Asuca#Geography|Bight of Asuca]] and X to the south. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the country and around the [[Asuca#Geography|Eba river]] and its [[Asuca#Geography|delta]]. The {{wp|capital city|political capital}} of Asuca is Gobona, while the country's largest city and economic capital is the port city of Ykora located further south. Asuca accounts for an area of 48,283 square kilometres (18,642 sq mi) and its population in 2017 was estimated to be approximately 21.85 million. | ||
First permanent states and chiefdoms in the territories of present-day Asuca were founded as far back as the 10th century. A number of kingdoms emerged over the course of history, and more noticably {{wp|city state|city states}} later asserted much political and economic control. Interest in the region emerged at the begin of the 15th century, with numerous Iraian powers contesting the area for trading rights and colonial possessions. | |||
The [[Lavaria|Lavish]] first settled a protectorate and ultimately established control of the coast by the late 1870s amid the Iraian scramble for X. Shortly after, the colony of [[Asuca#History|Lavish Costa Açùcar]] was founded. Following a century of native resistance, Asucar officials declared the country independent of [[Lavaria]] on 12 September 1965, sparking anarchy and social turmoil before being quelled by Lavish and [[Assembly of Nations|AN forces]] thereafter and establishing an [[Assembly of Nations|Assembly of Nations mandate]] mission in 1966. When Asuca was released on 27 October 1969, the government sought to maintain unity within the country, but failed, resulting in a civil war ravaging throughout the 1970s. The {{wp|republic}} has had a tumultous history since then, having experienced a series of democratic governments, {{wp|coup d'état|coup d'états}}, and military governments. Beginning in 1993, Asuca introduced a stable and democratic system, paving the way for broader {{wp|diplomacy|international cooperation}} and emerging as a {{wp|regional power}} and economic powerhouse for West X. | |||
Asuca's population spans a great variety of ethnic groups, religions, languages, traditions, and cultures. Approximately X% of the country was X, X% was X, 3.4% was [[Ditanery|Ditanist]], and another 6.1% practiced native and traditional faiths. Its diverse geography and ecology dominate the country, ranging from {{wp|rainforest|tropical rain forests}} to coastal savannahs and other {{wp|wetland|wetlands}}. As a {{wp|tropics|tropical}} nation, it is therefore somewhat dependent on {{wp|agriculture}}, and is a large exporter of {{wp|cotton}}, {{wp|coffee}}, {{wp|cocoa}} and {{wp|palm oil}}. {{wp|Portuguese language|Lavish}} is the official language of Asuca, though a large diaspora of indigenous languages is also present. | |||
Asuca is a {{wp|unitary state|unitary}} {{wp|republic|constitutional republic}}, led by a president as both {{wp|head of state}} and {{wp|head of government}} under a {{wp|multi-party system}}; the current system was defined in the {{wp|constitution}} introduced in 1999. The country's economic growth, prosperity, and democratic government have made it a sizable player in X politics and wields disproportionate power for its size and location. Asuca is a member of the [[Assembly of Nations]], X. | |||
==Etymology== | |||
==History== | |||
===Precolonial era=== | |||
===Iraian arrival and colonization=== | |||
===Transition to sovereignty=== | |||
===National turmoil and AN mandateship=== | |||
===Civil war (1970–76)=== | |||
===Aftermath and contemporary period=== | |||
==Geography== | |||
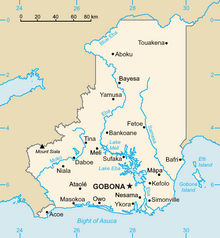
[[File:AsucaMap.png|220px|thumb|right|Map of Asuca]] | |||
==Politics== | |||
==Economy== | |||
==Demographics== | |||
==Culture== | |||
==National symbols== | |||
{{Template:Gaia}} | |||
Latest revision as of 21:57, 19 October 2019
Asucar Republic República da Açùcar (Lavish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: ‘Unidos e Livres’ (Lavish) ‘United and Free’ | |
| Anthem: Saudação à Liberdade "Salute to Freedom" | |
| Location of Palanca (marked green) Location of Palanca (marked green) | |
 | |
| Capital | Gobona |
| Largest city | Ykora |
| Official languages | Lavish |
| Ethnic groups | 53.7% Kamu 9.7% Poka 8.5% Yemelo 5.8% Ewonba 22.3% Other ethnic groups |
| Religion | X |
| Demonym(s) | Asucar |
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
• President | Nawe Gonama |
• Prime Minister | Yana Wuembe |
• Speaker of the Parliament | Ralpa Turisaya |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence from Lavaria | |
• Republic declared | 12 September 1965 |
• AN mandate established | 5 January 1966 |
• Removal of AN mandateship, second republic | 27 October 1969 |
• Current constitution ratified | 9 February 1999 |
| Area | |
• Total | 48,283.6 km2 (18,642.4 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 2.9% |
| Population | |
• 2017 estimate | 21,849,035 |
• 2014 census | 20,748,221 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $87.81 billion (12th) |
• Per capita | $4,019 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $51.12 billion (19th) |
• Per capita | $2,340 |
| HDI (2017) | medium |
| Currency | Asucar puka (AP) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 |
| Date format | DD/MM/YYYY |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +233 |
| Internet TLD | .as |
Asuca (/asʊ'c:a/ a-su-CAH; Lavish: Açùcar), officially the Asucar Republic (Lavish: República da Açùcar) and formerly Costa Açùcar or known as the Sugar Coast, is a country located on the southern coast of West X, bordering X to the west, X to the north, X to the east, and the Bight of Asuca and X to the south. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the country and around the Eba river and its delta. The political capital of Asuca is Gobona, while the country's largest city and economic capital is the port city of Ykora located further south. Asuca accounts for an area of 48,283 square kilometres (18,642 sq mi) and its population in 2017 was estimated to be approximately 21.85 million.
First permanent states and chiefdoms in the territories of present-day Asuca were founded as far back as the 10th century. A number of kingdoms emerged over the course of history, and more noticably city states later asserted much political and economic control. Interest in the region emerged at the begin of the 15th century, with numerous Iraian powers contesting the area for trading rights and colonial possessions.
The Lavish first settled a protectorate and ultimately established control of the coast by the late 1870s amid the Iraian scramble for X. Shortly after, the colony of Lavish Costa Açùcar was founded. Following a century of native resistance, Asucar officials declared the country independent of Lavaria on 12 September 1965, sparking anarchy and social turmoil before being quelled by Lavish and AN forces thereafter and establishing an Assembly of Nations mandate mission in 1966. When Asuca was released on 27 October 1969, the government sought to maintain unity within the country, but failed, resulting in a civil war ravaging throughout the 1970s. The republic has had a tumultous history since then, having experienced a series of democratic governments, coup d'états, and military governments. Beginning in 1993, Asuca introduced a stable and democratic system, paving the way for broader international cooperation and emerging as a regional power and economic powerhouse for West X.
Asuca's population spans a great variety of ethnic groups, religions, languages, traditions, and cultures. Approximately X% of the country was X, X% was X, 3.4% was Ditanist, and another 6.1% practiced native and traditional faiths. Its diverse geography and ecology dominate the country, ranging from tropical rain forests to coastal savannahs and other wetlands. As a tropical nation, it is therefore somewhat dependent on agriculture, and is a large exporter of cotton, coffee, cocoa and palm oil. Lavish is the official language of Asuca, though a large diaspora of indigenous languages is also present.
Asuca is a unitary constitutional republic, led by a president as both head of state and head of government under a multi-party system; the current system was defined in the constitution introduced in 1999. The country's economic growth, prosperity, and democratic government have made it a sizable player in X politics and wields disproportionate power for its size and location. Asuca is a member of the Assembly of Nations, X.