User:Tranvea/Sandbox 1: Difference between revisions
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {{Infobox former country | ||
|- | |conventional_long_name = Zubaydi Rahelian Federation | ||
| | |common_name = | ||
| | |native_name = الاتحاد الراحلي الزبيدي<br/>''al-Ittihād al-Rāhiliyy al-Zubaydiyy '' | ||
| | |continent=Coius | ||
|- | |year_start= 16 March 1953 | ||
| | |event_start= | ||
| | |year_end= 9 September 1968 | ||
|- | |event_end =[[Irvadi Socialist Revolution]] | ||
| | |life_span= 1953-1968 | ||
| | |event1= [[Treaty of At-Turbah]] | ||
|} | |date_event1= 16 March 1953 | ||
|event2= [[Riyadhi Crisis]] | |||
|date_event2= 7-11 June 1959 | |||
|event3= [[Rahelian War]] | |||
|date_event3= 1965-1968 | |||
|p1= Emirate of Riyadha | |||
|flag_p1= | |||
|p2= Kingdom of Irvadistan | |||
|flag_p2= | |||
|s1= United Rahelian People's Republic | |||
|flag_s1= | |||
|image_map= ZRF Location.png | |||
|image_map_caption= Location of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation in green. | |||
|image_flag = Flag of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation.png | |||
|image_coat = Emblem of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation.png | |||
|symbol_type=Coat of arms | |||
|national_motto= | |||
|national_anthem= | |||
|capital= [[Sadah]] | |||
|government_type= {{wp|federalism|Federal}} {{wp|absolute monarchy}} | |||
|title_leader = [[King of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation|King]] | |||
|leader1 = [[Said Ali I]] | |||
|year_leader1 = 1953-1959 | |||
|leader2 = [[Said Ali II]] | |||
|year_leader2 = 1959-1968 | |||
|title_deputy = [[Prime Minister of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation|Prime Minister]] | |||
|deputy1 = [[Hassan Yazeed]] | |||
|year_deputy1 = 1953-1960 | |||
|deputy2 = [[Muqrin bin Abdullah]] | |||
|year_deputy2 = 1960-1964 | |||
|deputy3 = [[Salman bin Hassan]] | |||
|year_deputy3 = 1964 | |||
|deputy4 = [[Abdullah bin Hussein]] | |||
|year_deputy4 = 1964-1966 | |||
|deputy5 = [[Nasir bin Hussein]] | |||
|year_deputy5 = 1964-1968 | |||
|legislature= None | |||
|house1= | |||
|house2= | |||
|stat_pop1 = 16,434,000 | |||
|currency=[[Rahelian dinar|Dinar]] | |||
|today= {{flag|Zorasan}} | |||
|footnotes= | |||
}} | |||
The ''' | The '''Zubaydi Rahelian Federation''' ({{wp|Arabic language|Rahelian}}: الاتحاد الراحلي الزبيدي; al-Ittihād al-Rāhiliyy al-Zubaydiyy) was a country that existed from 1953 until 1968, that was formed through the union of [[Riyadha]] and [[Irvadistan]]. Although the name implies a federal structure, it was de facto a confederation, with significant autonomy granted to each state. | ||
The | The federation was established on 16 March 1953 in response to the formation of the [[Union of Khazestan and Pardaran]] during the early stages of [[Zorasani Unification]]. The union was agreed by [[Said Ali I]] of Irvadistan and [[Abdullah-Yazid]] of Riyadha, who had in the past, established close inter-familial ties through marriage. Both monarchs recognised the threat the UKP posed to their kingdoms through its ideology of [[Pan-Zorasanism]] and {{wp|republicanism}}. The union lasted fifteen years and saw the development of a highly productive, economically dynamic state, though throughout its existence it was locked in a bitter cold war with the UKP, suffering from terrorist actions and repeated bouts of instability caused by the competiting ideologies of monarchism and republicanism. In 1965, the tensions erupted into [[Rahelian War|full-scale war]] between the two nations, despite repelling a UKP invasion with the backing of Euclean powers, the war turned following its own failed attacks against the UKP. Whilst the war ended in a stalemate, the social and economic costs of the conflict, coupled with the rise of radical leftism resulted in the collapse of the union in 1968, when the [[Irvadi Section of the Workers' Internationale]] seized the capital of [[Sadah]]. After a brief period of civil strife, the ISWI-led forces defeated the monarchist holdouts in Riyadha and established the [[United Rahelian People's Republic]] in the federation's place. Eleven years later, the URPR would in turn be defeated by the UKP and it would be absorbed into the Pan-Zorasanist union, establishing the modern day [[Union of Zorasani Irfanic Republics]] and marking the success of [[Zorasani Unification]]. | ||
== | == History == | ||
=== Formation === | |||
Ties between the Zubayd and Al-Hawashim of Irvadistan and Riyadha respectively were warm as early the 1910s. The closeness was aided by their respective positions within the Etrurian colonial administration, where both shared similar duties and responsibilities under the colony of [[Rahelia Etruriana]]. In the 1930s, the two families became intertwined through a series of marriages and a declaration of friendship. During the late Solarian War period, both families reportedly assisted one another in seizing control of territory as the Etrurian colonial order collapsed. | |||
The | The recognition of the two kingdoms with the Treaty of Morwall in 1946 cemented their borders and both monarchies moved swiftly to legitimise their governments. As early as 1946, both Riyadha and Irvadistan declared a mutual alliance and in 1949, signed a mutual defence agreement. Both states benefited from relatively stability within the borders, succeeding in drawing international aid for reconstruction. Notably, both governments took little to no interest in the [[Pardarian Civil War]] nor the chaotic situation in [[Khazestan]]. This changed in 1950, with the defeat and execution of the Pardarian Shah and his sons, in what was described as a “horrific case of regicide.” However, neither government genuinely appreciated the threat of the openly republican and pan-Zorasanist regime emerging in Pardaran.By 1950, however, the mutual concern in At-Turbah and Sadah grew to such an extent that several low-ranking princes in both royal families openly talked of a union but including Khazestan. King Said Ali of Irvadistan bemoaned the heavy handedness of Khazestan’s Hassan ibn Rashid, and he wrote a series of letters to his Khazi counterpart urging for restraint to the early protests. In 1952, the emergence of the [[Khazi Revolutionary Resistance Command]] during the violent peak of the [[Khazi Revolution]] failed to deliver the realisation of the danger growing in the west. | ||
[[File:King Said Ali I and Crown Prince Hassan-Yazeed.png|290px|thumb|left|King Said Ali I (C) with Riyadhi Crown Prince Hassan Yazeed (C-R) following the signing of the Treaty of At-Turbah.]] | |||
Essa Talib, a Riyadhi civil servant turned historian, who fled the Federation in 1968 wrote, “there was a genuine ignorance to the threat in Pardaran and Khazestan during the latter’s revolution. Neither the King of Riyadha or Irvadistan truly understood the beast that was to wage war on them a decade later.” | |||
The | The eruption of conflict within the [[Kexri Republic]] would prove pivotal in the two kingdoms progressing toward a union. News that both Khazi and Pardarian soldiers were being infiltrated into the war-torn state deeply unsettled the Irvadi monarchy, as it would place the revolutionary Pardarian state directly on its borders. This was only worsened by the overthrow of the Khazi monarchy by the KRRC in November 1952. The decisive intervention of Khazestan and Pardaran in December 1952, brought about the complete collapse of the Kexri Republic and its replacement by the [[Provisional Revolutionary Government of Ninevah]]. The reality of the threat finally reached the two kingdoms with the radio broadcasted speech by [[Mahrdad Ali Sattari]] on December 28 1952, saying, “our duties now shall take us to the Peninsula and to Sadah, from where the banner of Zorasan and its republican virtues shall flutter in victorious winds.” According to some documents released in 1999, talks between the two countries about a union began within days of the Kexri Republic’s fall, though it was limited to low-level diplomats and was “exploratory in nature.” The groundwork for the union was supposedly established, though it found some resistance with Riyadha, where mid-level royals saw the proposal as opportunism by the Zubaydi family to expand its territory. | ||
The tripartite talks between Pardaran, Khazestan and Ninevah were not officially declared until January 10, the two kingdoms in the north had become aware of the talks as early January 4. The news was met with pandemonium in Sadah according to several sources, with King Said Ali seeking an immediate counter union between Irvadistan and Riyadha. The King, acutely aware of the misgivings of Riyadhi officials, pressured his own ministers to present his proposal for a union, in which government positions would be reserved for Riyadhis exclusively, if he and his successors would be permitted to rule as the head of state. | |||
Said Ali, enjoyed a close friendship with Emir Abdullah-Yazid of Riyadha and the two also held mutual relations through the marriage of their respective children prior to the Solarian War. Within a week of the UKP’s formation, Said Ali exchanged letters with Abdullah-Yazid regarding a possible union between Irvadistan and Riyadha, though falling far short of closing the demographic gap, a union would in Said Ali’s view, “do much to pool our resources against the same radical Pardarian-Rahelian threat of Pan-Zorasanism.” In Said Ali’s view, if one of the monarchies fell, the other would fall in quick succession. The proposal received mixed reviews in Riyadha, with some of the elite families in the peninsula-kingdom fearing this to be a plot by Irvadistan’s King for expand his kingdom. | |||
On February 19, Crown Prince Ali Said ibn Said, who was also married to the eldest daughter of Emir Abdullah-Yazid travelled to At-Turbah to personally lobby the Riyadhi monarch on behalf of his father. According to documents seized in 1979, Ali Said assured Abdullah-Yazid, that he and his family would retain full influence of Riyadhi affairs and that power in a union would be shared equally. Ali Said made much of the historic ties between the Zubayd (Irvadistan’s ruling family) and the Safwadi (Riyadha’s ruling family) as well as their present-day ties through marriage. On February 22, Abdullah-Yazid conceded to bilateral talks for a possible union. | |||
The talks progressed rapidly, with the Irvadis proposing an absolute monarchy. However, to mitigate Riyadhi concerns, they proposed the monarch to be of the Zubaydi tribe, while the Prime Minister and all success heads of government would be Riyadhi, as well as half the cabinet. The Riyadhi would provide the command and personnel for the navy and air force, while the Irvadis would provide the land forces. Both kingdoms would retain a National Guard for exclusive internal use. Unlike the UKP, the proposed union would not integrate the kingdom’s economies to such a degree, though a common currency would be utilised and common customs union, both kingdoms would retain their own oil companies and others, while both states would be permitted to dispatch diplomats to foreign countries. | |||
=== Cold War (1953-1965) === | |||
=== Rahelian War (1965-1968) === | |||
=== Demise === | |||
== Geography == | |||
== Government and politics == | |||
The Basic Law of the Federation was the constitutional document of the country, which came into force with the signing of the [[Treaty of At-Turbah]]. The Basic Law provided the framework for government and the delineation of powers and responsibilities delegated to the two constituent kingdoms. | |||
{{multiple image | |||
|align=right | |||
|image1=King_Saud.jpg | |||
|width1=189 | |||
|caption1=[[Said Ali|King Said Ali]] reigned from 1953-1959 | |||
|alt1= | |||
|width2=200 | |||
|caption2=[[Muqrin Ali|King Muqrin Ali]] reigned from 1959-1968 | |||
|image2=King_Fisal.jpg | |||
|alt2= | |||
}} | |||
The Basic Law designated the country as a {{wp|federalism|federal}} {{wp|absolute monarchy}}. The King of the Zubaydi Federation is the head of state and wielded significant executive and legislative powers. The King could issue decrees and laws, though the King of Riyadha possessed a veto on any law or decree that he felt would endanger Riyadha or violate its interests. The Prime Minister of the Zubaydi Federation headed the government and presided over the Council of Ministers. Per the Treaty of At-Turbah, the King would be the ruler of Irvadistan, while the Prime Minister would be appointed by the King of Riyadha from his own family or close associates. All ministers would also be drawn from Riyadha, though Irvadis did serve on the Council of Ministers. | |||
== | The Basic Law did not provide a basis for political parties or elections, however, it provided for an annual event known as a Mu’tamar (literally, Conference) in which select citizens from both Kingdoms would meet with the King of the Federation, Prime Minister and Council of Ministers to raise issues and air grievances. In some cases, the Federation used the Mu’tamar to present policies and laws for vote, establishing cases of a form of {{wp|direct democracy}}. The Basic Law also described responsibilities not granted to the national government being reserved to the individual state. | ||
The Basic Law gave limited powers to the national government, with its primary responsibilities being defence, foreign policy, regulation of trade and customs and internal security. The two kingdoms would retain control over their borders, issue passports, education, policing, health, education, and others. In 1956, transportation and infrastructure were federalised as part of the economic development plan devised by King Said Ali of the Federation and King Abdullah-Yazid of Riyadha. The two kingdoms were permitted to send diplomats to foreign countries, though their roles were limited to representing the interests of Riyadhi and Irvadi citizens abroad. The limited role of the national government led many historians to claim the Federation was a de-facto {{wp|confederation}}. | |||
=== Foreign relations === | |||
Throughout its existence, the Federation sought close relations with Euclean great powers, to which they saw as the most viable option for deterring aggression from the [[Union of Khazestan and Pardaran]]. Second to its desire for protection was the need to secure foreign investment to assist in economic development and the expansion of its oil and gas reserves. This outreached proved most successful with [[Estmere]], [[Werania]] and [[Halland]], with some degree of success seen with [[Etruria]] and [[Gaullica]]. | |||
The Federation’s outreach to Halland was initially based on the desire for assistance in the modernisation of its armed forces, this in turn led to the [[Hallandic Mission to the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation]] (HAMZURFED) in 1955. In Estmere’s case, its links grew from the desire for economic investment to include military assistance. Between 1953 and 1963, [[Khalifa al-Khandari]] served as the Federation’s Foreign Minister, he was widely acclaimed in Euclean capitals and proved instrumental in gaining Euclean support against the UKP. However, the Federation’s external relations would suffer after Al-Khandari was assassinated by the [[Black Hand (Zorasan)|Black Hand]] in 1963. | |||
The Federation’s attempts at a regional bloc to counter the UKP proved less successful. Its early successes with Tsabara were notable, however short-lived, with the overthrow of the government by the left-wing Communalist movement. The UKP’s support for anti-colonial movements in [[Bahia]] during the 1950s, granted it allies and supports in the sub-continent, further isolating the Federation within Coius. | |||
The | The Federation’s relationship with the UKP was complex and intrinsically antagonistic. Neither government operated embassies in their respective capitals, owing to the UKP’s refusal to recognise the Federation as a sovereign state. Cross-border trade was near non-existent and the only forms of cross-border travel that were recorded were isolated to a minority of nomadic Rahelian communities. An attempt was made to normalise ties in 1959, but this failed to materialise any normalisation with the onset of the Black Hand’s attacks on Federation soil. | ||
=== Military === | |||
The [[Royal Armed Forces of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation]], though commonly known as the Royal Armed Forces were divided into four branches: the [[Royal Zubaydi Federal Army]] (RZFA), [[Royal Zubaydi Federal Air Force]] (RZFAF), [[Royal Zubaydi Federal Navy]] (RZFN) and the [[Royal Reserve Force]] (RRF). The Royal Armed Forces were managed by the Ministry of Defence, with the King of the Federation serving as commander-in-chief. Per the Basic Law of 1953, the armed forces were divided between the two states in terms of contribution of officers – Riyadha provided the officer corps for the Air Force and Navy, while Irvadistan provided for the Army. The Royal Reserve Force was split equally between the two states. Operating within each Kingdom were the Royal Territorial Forces, which were commanded by the constituent capitals rather than the federal government. | |||
[[File:Royal Zubaydi Army.jpg|290px|thumb|left|Troops of the Royal Zubaydi Federal Army in 1962.]] | |||
[[File:Royal Sand Raiders 2.jpg|290px|thumb|right|Soldiers of the elite [[Royal Sand Raiders]] on parade in 1963.]] | |||
Owing to the threat of the UKP, the Royal Armed Forces were relatively large in relation to the country’s population, with over 450,000 active and reserve personnel serving throughout most of its history. The Estmerish and Hallandic missions to the Federation beginning in the 1950s, proved decisive in the quality of training and armament of Zubaydi troops. The Zubaydi approach to the foreign missions was based on the slogan, “imitation in culture, training and emotion of battle.” By the outbreak of the [[Rahelian War]] in 1965, one Estmerish officer remarked, “if we had ever wished to see the birth of the Estmerish condition in foreigners, our Zubaydi allies is that truly.” One of Estmere's contributions was the creation of the much vaunted [[Royal Sand Raiders]] (غزاة رَمْل مَلَكِيّ; ''Ghazah al-Raml al-Malakiyy''), an elite highly mobile special forces unit. The Royal Army also boasted a large number of armoured vehicles and tanks, and was noted for its motivation, discipline and training. In 1960, the Royal Zubaydi Federal Air Force began to receive modern jet aircraft from [[Estmere]], with two-full squadrons of {{wp|Hawker Hunters}} being delivered by 1963. By the onset of the [[Rahelian War]], the Zubaydi Air Force boasted over 50 jet aircraft, though it would suffer catestrophic losses between 1965 and 1966 owing to the UKP's air force's larger numbers, though the ratio of losses would rest in the Zubaydi's favour. | |||
== Economy == | |||
== Demographics == | |||
== Legacy == | |||
Latest revision as of 02:08, 28 December 2020
Zubaydi Rahelian Federation الاتحاد الراحلي الزبيدي al-Ittihād al-Rāhiliyy al-Zubaydiyy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1953-1968 | |||||||||||
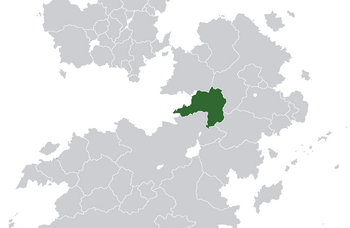 Location of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation in green. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Sadah | ||||||||||
| Government | Federal absolute monarchy | ||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||
• 1953-1959 | Said Ali I | ||||||||||
• 1959-1968 | Said Ali II | ||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||
• 1953-1960 | Hassan Yazeed | ||||||||||
• 1960-1964 | Muqrin bin Abdullah | ||||||||||
• 1964 | Salman bin Hassan | ||||||||||
• 1964-1966 | Abdullah bin Hussein | ||||||||||
• 1964-1968 | Nasir bin Hussein | ||||||||||
| Legislature | None | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 16 March 1953 | ||||||||||
| 16 March 1953 | |||||||||||
| 7-11 June 1959 | |||||||||||
| 1965-1968 | |||||||||||
| 9 September 1968 | |||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• | 16,434,000 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Dinar | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
The Zubaydi Rahelian Federation (Rahelian: الاتحاد الراحلي الزبيدي; al-Ittihād al-Rāhiliyy al-Zubaydiyy) was a country that existed from 1953 until 1968, that was formed through the union of Riyadha and Irvadistan. Although the name implies a federal structure, it was de facto a confederation, with significant autonomy granted to each state.
The federation was established on 16 March 1953 in response to the formation of the Union of Khazestan and Pardaran during the early stages of Zorasani Unification. The union was agreed by Said Ali I of Irvadistan and Abdullah-Yazid of Riyadha, who had in the past, established close inter-familial ties through marriage. Both monarchs recognised the threat the UKP posed to their kingdoms through its ideology of Pan-Zorasanism and republicanism. The union lasted fifteen years and saw the development of a highly productive, economically dynamic state, though throughout its existence it was locked in a bitter cold war with the UKP, suffering from terrorist actions and repeated bouts of instability caused by the competiting ideologies of monarchism and republicanism. In 1965, the tensions erupted into full-scale war between the two nations, despite repelling a UKP invasion with the backing of Euclean powers, the war turned following its own failed attacks against the UKP. Whilst the war ended in a stalemate, the social and economic costs of the conflict, coupled with the rise of radical leftism resulted in the collapse of the union in 1968, when the Irvadi Section of the Workers' Internationale seized the capital of Sadah. After a brief period of civil strife, the ISWI-led forces defeated the monarchist holdouts in Riyadha and established the United Rahelian People's Republic in the federation's place. Eleven years later, the URPR would in turn be defeated by the UKP and it would be absorbed into the Pan-Zorasanist union, establishing the modern day Union of Zorasani Irfanic Republics and marking the success of Zorasani Unification.
History
Formation
Ties between the Zubayd and Al-Hawashim of Irvadistan and Riyadha respectively were warm as early the 1910s. The closeness was aided by their respective positions within the Etrurian colonial administration, where both shared similar duties and responsibilities under the colony of Rahelia Etruriana. In the 1930s, the two families became intertwined through a series of marriages and a declaration of friendship. During the late Solarian War period, both families reportedly assisted one another in seizing control of territory as the Etrurian colonial order collapsed.
The recognition of the two kingdoms with the Treaty of Morwall in 1946 cemented their borders and both monarchies moved swiftly to legitimise their governments. As early as 1946, both Riyadha and Irvadistan declared a mutual alliance and in 1949, signed a mutual defence agreement. Both states benefited from relatively stability within the borders, succeeding in drawing international aid for reconstruction. Notably, both governments took little to no interest in the Pardarian Civil War nor the chaotic situation in Khazestan. This changed in 1950, with the defeat and execution of the Pardarian Shah and his sons, in what was described as a “horrific case of regicide.” However, neither government genuinely appreciated the threat of the openly republican and pan-Zorasanist regime emerging in Pardaran.By 1950, however, the mutual concern in At-Turbah and Sadah grew to such an extent that several low-ranking princes in both royal families openly talked of a union but including Khazestan. King Said Ali of Irvadistan bemoaned the heavy handedness of Khazestan’s Hassan ibn Rashid, and he wrote a series of letters to his Khazi counterpart urging for restraint to the early protests. In 1952, the emergence of the Khazi Revolutionary Resistance Command during the violent peak of the Khazi Revolution failed to deliver the realisation of the danger growing in the west.
Essa Talib, a Riyadhi civil servant turned historian, who fled the Federation in 1968 wrote, “there was a genuine ignorance to the threat in Pardaran and Khazestan during the latter’s revolution. Neither the King of Riyadha or Irvadistan truly understood the beast that was to wage war on them a decade later.”
The eruption of conflict within the Kexri Republic would prove pivotal in the two kingdoms progressing toward a union. News that both Khazi and Pardarian soldiers were being infiltrated into the war-torn state deeply unsettled the Irvadi monarchy, as it would place the revolutionary Pardarian state directly on its borders. This was only worsened by the overthrow of the Khazi monarchy by the KRRC in November 1952. The decisive intervention of Khazestan and Pardaran in December 1952, brought about the complete collapse of the Kexri Republic and its replacement by the Provisional Revolutionary Government of Ninevah. The reality of the threat finally reached the two kingdoms with the radio broadcasted speech by Mahrdad Ali Sattari on December 28 1952, saying, “our duties now shall take us to the Peninsula and to Sadah, from where the banner of Zorasan and its republican virtues shall flutter in victorious winds.” According to some documents released in 1999, talks between the two countries about a union began within days of the Kexri Republic’s fall, though it was limited to low-level diplomats and was “exploratory in nature.” The groundwork for the union was supposedly established, though it found some resistance with Riyadha, where mid-level royals saw the proposal as opportunism by the Zubaydi family to expand its territory.
The tripartite talks between Pardaran, Khazestan and Ninevah were not officially declared until January 10, the two kingdoms in the north had become aware of the talks as early January 4. The news was met with pandemonium in Sadah according to several sources, with King Said Ali seeking an immediate counter union between Irvadistan and Riyadha. The King, acutely aware of the misgivings of Riyadhi officials, pressured his own ministers to present his proposal for a union, in which government positions would be reserved for Riyadhis exclusively, if he and his successors would be permitted to rule as the head of state.
Said Ali, enjoyed a close friendship with Emir Abdullah-Yazid of Riyadha and the two also held mutual relations through the marriage of their respective children prior to the Solarian War. Within a week of the UKP’s formation, Said Ali exchanged letters with Abdullah-Yazid regarding a possible union between Irvadistan and Riyadha, though falling far short of closing the demographic gap, a union would in Said Ali’s view, “do much to pool our resources against the same radical Pardarian-Rahelian threat of Pan-Zorasanism.” In Said Ali’s view, if one of the monarchies fell, the other would fall in quick succession. The proposal received mixed reviews in Riyadha, with some of the elite families in the peninsula-kingdom fearing this to be a plot by Irvadistan’s King for expand his kingdom.
On February 19, Crown Prince Ali Said ibn Said, who was also married to the eldest daughter of Emir Abdullah-Yazid travelled to At-Turbah to personally lobby the Riyadhi monarch on behalf of his father. According to documents seized in 1979, Ali Said assured Abdullah-Yazid, that he and his family would retain full influence of Riyadhi affairs and that power in a union would be shared equally. Ali Said made much of the historic ties between the Zubayd (Irvadistan’s ruling family) and the Safwadi (Riyadha’s ruling family) as well as their present-day ties through marriage. On February 22, Abdullah-Yazid conceded to bilateral talks for a possible union.
The talks progressed rapidly, with the Irvadis proposing an absolute monarchy. However, to mitigate Riyadhi concerns, they proposed the monarch to be of the Zubaydi tribe, while the Prime Minister and all success heads of government would be Riyadhi, as well as half the cabinet. The Riyadhi would provide the command and personnel for the navy and air force, while the Irvadis would provide the land forces. Both kingdoms would retain a National Guard for exclusive internal use. Unlike the UKP, the proposed union would not integrate the kingdom’s economies to such a degree, though a common currency would be utilised and common customs union, both kingdoms would retain their own oil companies and others, while both states would be permitted to dispatch diplomats to foreign countries.
Cold War (1953-1965)
Rahelian War (1965-1968)
Demise
Geography
Government and politics
The Basic Law of the Federation was the constitutional document of the country, which came into force with the signing of the Treaty of At-Turbah. The Basic Law provided the framework for government and the delineation of powers and responsibilities delegated to the two constituent kingdoms.
The Basic Law designated the country as a federal absolute monarchy. The King of the Zubaydi Federation is the head of state and wielded significant executive and legislative powers. The King could issue decrees and laws, though the King of Riyadha possessed a veto on any law or decree that he felt would endanger Riyadha or violate its interests. The Prime Minister of the Zubaydi Federation headed the government and presided over the Council of Ministers. Per the Treaty of At-Turbah, the King would be the ruler of Irvadistan, while the Prime Minister would be appointed by the King of Riyadha from his own family or close associates. All ministers would also be drawn from Riyadha, though Irvadis did serve on the Council of Ministers.
The Basic Law did not provide a basis for political parties or elections, however, it provided for an annual event known as a Mu’tamar (literally, Conference) in which select citizens from both Kingdoms would meet with the King of the Federation, Prime Minister and Council of Ministers to raise issues and air grievances. In some cases, the Federation used the Mu’tamar to present policies and laws for vote, establishing cases of a form of direct democracy. The Basic Law also described responsibilities not granted to the national government being reserved to the individual state.
The Basic Law gave limited powers to the national government, with its primary responsibilities being defence, foreign policy, regulation of trade and customs and internal security. The two kingdoms would retain control over their borders, issue passports, education, policing, health, education, and others. In 1956, transportation and infrastructure were federalised as part of the economic development plan devised by King Said Ali of the Federation and King Abdullah-Yazid of Riyadha. The two kingdoms were permitted to send diplomats to foreign countries, though their roles were limited to representing the interests of Riyadhi and Irvadi citizens abroad. The limited role of the national government led many historians to claim the Federation was a de-facto confederation.
Foreign relations
Throughout its existence, the Federation sought close relations with Euclean great powers, to which they saw as the most viable option for deterring aggression from the Union of Khazestan and Pardaran. Second to its desire for protection was the need to secure foreign investment to assist in economic development and the expansion of its oil and gas reserves. This outreached proved most successful with Estmere, Werania and Halland, with some degree of success seen with Etruria and Gaullica.
The Federation’s outreach to Halland was initially based on the desire for assistance in the modernisation of its armed forces, this in turn led to the Hallandic Mission to the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation (HAMZURFED) in 1955. In Estmere’s case, its links grew from the desire for economic investment to include military assistance. Between 1953 and 1963, Khalifa al-Khandari served as the Federation’s Foreign Minister, he was widely acclaimed in Euclean capitals and proved instrumental in gaining Euclean support against the UKP. However, the Federation’s external relations would suffer after Al-Khandari was assassinated by the Black Hand in 1963.
The Federation’s attempts at a regional bloc to counter the UKP proved less successful. Its early successes with Tsabara were notable, however short-lived, with the overthrow of the government by the left-wing Communalist movement. The UKP’s support for anti-colonial movements in Bahia during the 1950s, granted it allies and supports in the sub-continent, further isolating the Federation within Coius.
The Federation’s relationship with the UKP was complex and intrinsically antagonistic. Neither government operated embassies in their respective capitals, owing to the UKP’s refusal to recognise the Federation as a sovereign state. Cross-border trade was near non-existent and the only forms of cross-border travel that were recorded were isolated to a minority of nomadic Rahelian communities. An attempt was made to normalise ties in 1959, but this failed to materialise any normalisation with the onset of the Black Hand’s attacks on Federation soil.
Military
The Royal Armed Forces of the Zubaydi Rahelian Federation, though commonly known as the Royal Armed Forces were divided into four branches: the Royal Zubaydi Federal Army (RZFA), Royal Zubaydi Federal Air Force (RZFAF), Royal Zubaydi Federal Navy (RZFN) and the Royal Reserve Force (RRF). The Royal Armed Forces were managed by the Ministry of Defence, with the King of the Federation serving as commander-in-chief. Per the Basic Law of 1953, the armed forces were divided between the two states in terms of contribution of officers – Riyadha provided the officer corps for the Air Force and Navy, while Irvadistan provided for the Army. The Royal Reserve Force was split equally between the two states. Operating within each Kingdom were the Royal Territorial Forces, which were commanded by the constituent capitals rather than the federal government.

Owing to the threat of the UKP, the Royal Armed Forces were relatively large in relation to the country’s population, with over 450,000 active and reserve personnel serving throughout most of its history. The Estmerish and Hallandic missions to the Federation beginning in the 1950s, proved decisive in the quality of training and armament of Zubaydi troops. The Zubaydi approach to the foreign missions was based on the slogan, “imitation in culture, training and emotion of battle.” By the outbreak of the Rahelian War in 1965, one Estmerish officer remarked, “if we had ever wished to see the birth of the Estmerish condition in foreigners, our Zubaydi allies is that truly.” One of Estmere's contributions was the creation of the much vaunted Royal Sand Raiders (غزاة رَمْل مَلَكِيّ; Ghazah al-Raml al-Malakiyy), an elite highly mobile special forces unit. The Royal Army also boasted a large number of armoured vehicles and tanks, and was noted for its motivation, discipline and training. In 1960, the Royal Zubaydi Federal Air Force began to receive modern jet aircraft from Estmere, with two-full squadrons of Hawker Hunters being delivered by 1963. By the onset of the Rahelian War, the Zubaydi Air Force boasted over 50 jet aircraft, though it would suffer catestrophic losses between 1965 and 1966 owing to the UKP's air force's larger numbers, though the ratio of losses would rest in the Zubaydi's favour.





