Twa-ts'uk-men Station: Difference between revisions
| (43 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox station | {{Infobox station | ||
| name = Twa-ts′uk-men Railway Station | | name = Twa-ts′uk-men Railway Station | ||
| native_name = 朱雀門驛, '' | | native_name = 朱雀門驛, ''twa-ts′uk-men-lek'' | ||
| native_name_lang = [[Shinasthana]] | | native_name_lang = [[Shinasthana]] | ||
| cta_header = | | cta_header = | ||
| type = ''' | | type = '''National Rail, KRT, EDR, HSR, Airport Railway''' | ||
| style = | | style = | ||
| image = CONCOURSE ROOF DETAIL. - Pennsylvania Station18.jpg | | image = CONCOURSE ROOF DETAIL. - Pennsylvania Station18.jpg | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| coordinates = <!-- {{Coord|LAT|LON|type:landmark_region:XX|display=inline,title}}--> | | coordinates = <!-- {{Coord|LAT|LON|type:landmark_region:XX|display=inline,title}}--> | ||
| elevation = 51 m | | elevation = 51 m | ||
| line = | | line = Central Junction Railway <br> [[Trans-Hemithean Railway]] <br> [[Trans-Hemithea High-Speed Railway]] <br> KRT Metropolitan <br> KRT Urban <br> KRT City <br> KRT Central <br> KRT Tibh & Tibh Airport <br> EDR 1 <br> EDR 2 <br>EDR 3 <br>EDR 4 <br>EDR 5 <br> [[Themiclesian High Speed Rail|HSR Inland Main Line]] <br>[[Themiclesian High Speed Rail|HSR Traverse Main Line]] <br> Kei Airport Railway | ||
| other = Metropolitan Omnibus<br>taxicabs | | other = Metropolitan Omnibus<br>taxicabs | ||
| structure = mixed | | structure = mixed | ||
| platform = 32 island <br> | | platform = 32 island <br> 5 side | ||
| depth = | | depth = 72 m | ||
| levels = | | levels = 5 | ||
| tracks = 123 | | tracks = 123 | ||
| parking = | | parking = 55 | ||
| bicycle = 652 | | bicycle = 652 | ||
| opened = {{Start date|1857|df=y}} | | opened = {{Start date|1857|df=y}} | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| ADA = Yes | | ADA = Yes | ||
| code = 382 | 1 | | code = 382 | 1 | ||
| owned = | | owned = City of Kien-k'ang | ||
| operator = | | operator = National Railway <br>[[Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit]]<br>[[Exchequer District Railway]]<br>Metropolitan Omnibus<br>Other bus operators<br>Themiclesia Post | ||
| zone = | | zone = | ||
| former = | | former = | ||
| passengers = avg. | | passengers = avg. 522,000 per diem | ||
| pass_year = 2015 | | pass_year = 2015 | ||
| pass_percent = | | pass_percent = | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| route_map = | | route_map = | ||
| map_state = | | map_state = | ||
}}The '''Twa-ts′uk-men Station''' (朱雀門驛, '' | }}The '''Twa-ts′uk-men Station''' (朱雀門驛, ''twa-ts′uk-men-lek'') is a passenger [[Rail transport in Themiclesia|railway]] station situated in [[Kien-k'ang]], [[Themiclesia]]. Established on the [[Central Junction Railway]], the station now hosts National Rail, [[Exchequer District Railway]], five lines of the [[Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit]] system, [[Themiclesian High Speed Rail]], Kei Airport Metro, the Metropolitan Omnibus Terminal, and a taxicab hub; furthermore, it is connected to four hotels, three underground shopping malls, six department stores, the [[Kien-k'ang Financial Centre]], amongst other local edifices and attractions. | ||
It is the largest station in Themiclesia by passenger volume and floor area (but not land area), serving over | It is the largest station in Themiclesia by passenger volume and floor area (but not land area), serving over 600,000 people a day on average (est. 2020). Across its six station buildings, it possesses three storeys above ground and seven below. The station is a cultural landmark, transportation hub, and commercial centre for Kien-k'ang. Some of this prosperity is attributed to the traffic the station brings. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
=== | ===Rebuilding=== | ||
As railways developed in Themiclesia, many lines were connected to the capital city by terminal stations its outskirts, most importantly the Qlin-tsung Terminus on the west, the Ferry Terminus on the southwest, and the Tlang-qrum Terminus on the east. However, the need to transship goods from one terminus to another resulted in congestion through the city's core. To alleviate congestion, wagons not for delivery were commanded in 1875 to traverse the city at night; however, this policy generated complaints of nocturnal noise and excess manure from streams of wagon traffic. Moreover, the three railway termini were each some distance from the city's rising commercial centre, which was around the eponymous Twa-ts'uk-men Gate. | |||
In 1891, the government formally entered the railway business by purchasing the National Trunk Railway, which had defaulted on its debts due to ineffective line planning. The [[Liberal Party (Themiclesia)|Liberal]] government embraced the regulations of railways as a policy and planned the [[Central Junction Railway]] to obviate the city's nocturnal wagon traffic as well as to bring passengers and goods over the proverbial "last mile" to the epicentre of trade in Kien-k'ang. | |||
The city encountered difficulty to acquire sufficient land for a railway through the centre of the city. Thus, it accepted the suggestion of Chief Engineer of Works Stsang, to construct an underground railway so that the land above remained economically useful. The government paid rent while buildings stood demolished and agreed to refund taxation on the land for 99 years, thus enhancing its value. Construction work began in 1892 and terminated in 1897, resulting in a seven-mile tunnel with four tracks. This project was reported in the foreign press and billed a "radical demonstration of competence" in newspapers. However, at the same time, most of the working-class tenants who had lived in buildings demolished for the station were hastily evicted by their landlords; prevailing terms on apartment lease of the day granted tenants none of the compensation from the government. | |||
A new station building was erected as the crowning jewel of one of the most expensive projects in Themiclesian history. The new building, completed ahead of schedule in 1897 and with the compelled labour of over 6,000 prisoners coralled into the capital city, included a spacious concourse spanned by steel girders and glass roofs. With a floor area of 268,000 square feet and more underground, it was the largest building in Themiclesia and more than half of the size of Anglia's {{wp|Crystal Palace}}. There were five underground platforms and twelve full-length storage tracks when the station opened, though more were added later in its history. The underground levels were spanned by brick vaults reinforced with steel ties. | |||
Because the Central Junction Railway was meant to connect the major railway lines around Kien-k'ang, the underground tunnels were built to accommodate the largest rolling stock then in use, found on the very | Because the Central Junction Railway was meant to connect the major railway lines around Kien-k'ang, the underground tunnels were built to accommodate the largest rolling stock then in use, found on the very newest National Trunk Railway, which ran with coaches 14 ft 6 in. tall and 10 ft 6 in. wide; most Themiclesian coaches were between 12 and 13 ft tall, and 9 ft and 9 ft 6 in wide. Due to government consolidation of railways in the late 1890s and continuing into the 1920s, most improved and new lines were re-gauged to be consistent with the tunnels. Though considered generous by 1890s standards, the tunnels became the proverbial bottle-neck when it came to large freight in the [[Pan-Septentrion War]] and beyond. | ||
===Early 20th century=== | ===Early 20th century=== | ||
In 1899, the Metropolitan Railway opened with exits built directly into the mezzanine level. The owners of the railway demanded this right after its competitor, Urban, had also obtained a similar concession in the concourse space. In 1910, the station was augmented by two new platform with two tracks each. While passenger trains were usually assembled and maintained in the yard between the passenger and freight sides, the new passenger platform forced the staff platforms south, where maintenance work took place. The assembly of some trains was thus moved to Tl′ang-qrum Station, where a more spacious yard was still available. A further island platform was added in 1913. In 1916, the Central line's shuttle line to Twa-ts'uk-men opened into the station with a platform just north of the Metropolitan's. This required an extension to the mezzanine level. | |||
In 1921, the City line's platforms were added to the space under the station, using a tunelling shield to bore much deeper than any of the previous tunnels. Its platform level lay roughly 30 m underground, compared to the 7 m of the National Rail, Metropolitan, and Central tracks. This great depth required an equally elaborate escalator to convey passengers to and from its trains, which was added in the western end of the mezzanine level. | |||
===PSW=== | |||
During the retreat to the west in 1936, much of the station's furniture was removed to enlarge usable space. The grand concourse was used by the government as propaganda image briefly in 1939 to portray Themiclesia as a technologically advanced nation that could contest more powerful yet backwards and barbaric invaders. In September 1940, Kien-k'ang was severed from relieving forces and forced to defend itself from its walls, thus leaving the station, and the railway network beneath it, undefended. It was commandeered as a temporary base of operations by Menghean forces during the siege of the city, and several attempts were made to infiltrate the city via the Metropolitan Railway's tunnels in the direction of the Old City. Menghean soldiers pushed a spare coach into the tunnel as an effective shield against Themiclesian fire, but the railway engineer Marcus Syar employed a {{wp|derail}} to cause a derailment. The derailed coach was not only immovable from the Menghean side but also blocked the tunnel. Syar was later awarded the Order of the Star for his wit. | |||
In | In January 1941, a bomb penetrated the east end of the station's concourse, causing considerable damage to the northeastern corner and eastern façade. The building was converted into a hospital that housed over 2,000 wounded Menghean and Dayashinese soldiers, and a Red Cross flag was hoisted over the station to denote this use. Operating theatres were established in the mezzanine level. The presence of medical personnel in the concourse prevented further damage, as multiple aerial engagements occurred over that part of the city in 1941. When Menghean and Dayashinese forces retreated from Kien-k'ang in mid-1941, the station was given a rudimentary restoration and remained in use as a hospital. As the enemy still controlled the eastern parts of the railway network, the eastern end of the Central Junction Railway tunnels was bricked up to prevent locomotives carrying hostile forces from barging into the city. All traffic was diverted to the suburbs for easier control and better space for manipulation. | ||
With the war progressing favourably, the Central Junction was opened again in 1942. Eastbound services were restored in October 1942 to facilitate the transport of troops and materials, and some of the invalids in the hospital were removed to other hospitals and convalescence houses in the city. Lord Kwyak, the Secretary of State for War, visited the station to see off one of the batches of volunteers bound to fight in [[Maverica]] in May 1944. Full restoration work, including the mending of the glass ceiling in the damaged corner of the station, began in 1946 and was completed by 1948. In contrast to the marble façade, a small corner of the building was mended with concrete as a memorial to the war. | |||
===Late 20th century=== | ===Late 20th century=== | ||
The addition of the [[Themiclesian High Speed Rail|HSR]] and the [[Exchequer District Railway|EDR]] presented a challenge to the station. One plan called for replacing the shrinking marshalling yard that was still in use with HSR platforms, and another required digging a new tunnel under both the NRC and KRT platforms. The former plan was originally preferred, though structural and operational difficulties so implied (the HSR to share the busy tunnel with conventional rail, regauging required, etc.) compelled National Rail to elect the latter. Work began in 1960 and was complete by 1965. The HSR's ticketing operation required an extension to the sub-mezzanine level owned by the Kien-k'ang Metro. The interior of the new area was decorated by the HSR's architect E. E. Ericson, who otherwise was responsible for new constructions along the road. Ericson disliked working with cramped and inflexible spaces underground. | |||
The | The 60s also saw the opening of the underground arcades that ran under the roads bounding the station's infrastructure, bridging commercial establishments and opening into the mezzanines. A company jointly owned by the abutting department stores initially owned these arcades that catered to fast-paced purchases. It was thought that instead of waiting in the concourse, passengers could shop while in transit. Shoppers going from one department store to another could also stay within an enclosed space rather than emerging onto street level, where the presence of taxicabs and busses might lure them away; though that lure also existed with the underground arcades opening into the Metro system, it was thought passenger traffic would more than offset this problem. National Rail was endeared to this plan as it provided more exits. | ||
In 1969, the Inner Region Regional Railway was privatized and relocated its services to a new platform layer further below that of the deep-level KRT lines. These new platforms were located under the eastern approach of the NRC tracks. A further lobby was constructed above the three roughly-parallel regional lines. To distinguish this lobby, where ticketing and other IRRR offices were located, from the sub-mezzanine level (which was so named after its completion in 1952), the newer lobby was called the lower mezzanine. In 1970 they were renamed to B1 and B2 respectively, in an early effort to ease the infamous confusion that would later characterize the station; however, this change was not positively received, as discussed below. A new building was erected adjoining the luggage terminal east of the concourse to represent the IRRR's autonomous operation, though it could be accessed from was simply called the "new station" by locals. | |||
An airport railway to Kei Airport, the successor to [[Tibh Airport]], was completed in 1995. The railway connected the city to the new airport 33 km away, so that arrivals had an option other than a bus ride along the congested highway. Its two platform were located under those of the Metro Blue line. Another building, called "new station south" was erected over the mezzanine level (as a stand-alone terminus) for the Airport Railway. It was hoped traffic might be separated from the existing network, but under public pressure that service was made accessible from both the sub-mezzanine and an extension of the lower mezzanine, which provided access to the bus stations and the concourse building. The 1969 station was then disambiguated as "new station north". | |||
The | The Metro Circle line was completed in 1985 with its platform parallel and partly under the HSR service. It opened into the South Mall (from which transit to the other services was possible) and initially had no street-level exits. | ||
The | ==Structure== | ||
===KRT Urban line platform=== | |||
The [[Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit|KRT]] Urban line's platforms are to the south of the concourse, on an elevated level. The side platforms are for stopping trains, while the central island platform is where the line's express services call. | |||
===Street level=== | ===Street level=== | ||
The main passenger concourse is a 420-metre long, 65-meter wide concourse spanned by a glass roof, long side in the east-west direction. The main entrance is situated on the north side, roughly at its centre, though access points dot its perimeter. The concourse houses one portion of National Rail's ticketing office, and restaurants, bookstalls, and other small shops exist along the elongated building. | The main passenger concourse is a 420-metre long, 65-meter wide concourse spanned by a glass roof, long side in the east-west direction. The main entrance is situated on the north side, roughly at its centre, though access points dot its perimeter. The concourse houses one portion of National Rail's ticketing office, and restaurants, bookstalls, and other small shops exist along the elongated building. The perimeter of the concourse is occupied by waiting rooms and other facilities. | ||
===Mezzanine=== | ===Mezzanine=== | ||
The mezzanine | The mezzanine is directly below the concourse and extends some 300 metres past its southern side. The southwestern corner of the mezzanine is taken up by a bus terminal, into which a spur from the western overpass extends. The bus terminal is divided into two sections along the spur, the northern part thereof served by the Metropolitan Omnibus, and the southern part by other operators, mostly long-distance busses. Both sections accept departing and arriving passengers. | ||
The leve's central area is not as long as the concourse, but extending further south. The eastern half of the mazzanine houses National Rail ticketing windows and more waiting rooms. | |||
The | |||
===National Rail track level=== | |||
*Platforms 2 | The National Rail track level lies under the mezzanine. There are 9 island platforms (Platform 2 through 10) and 2 side platforms (Platform 1 and 11), with a total of 32 tracks. The Central Junction Railway is {{wp|quadruple-track railway|quadruplicated}}, with two tracks intended for each direction. Approaching the station in either direction, the lines fan out to meet the station's tracks and sidings. | ||
*Platform | *Platform 1 is used for the [[Trans-Hemithean Railway]] and the Inland Main Line. | ||
*Platform 6 is used by trains | *Platforms 2 and 3 are used by trains for Rak and Stui the Inland Main Line. | ||
*Platform 4 is used by trains for K′an and Nek. | |||
*Platform | *Platform 5 and 6 is used by trains on the National Trunk and Central Main Line. | ||
*Platform | *Platform 7 and 8 are used by trains for Mgraq, Ngang, and Lwai. | ||
*Platform | *Platform 9 and 10 are used by trains on the Coastal Main Line and to Q.pa. | ||
*Platform 11 is used by trains on the Sat Line. | |||
The freight | The freight station no longer accepts freight, but to it are still sent luggage, mail, and parcels. It connects to the National Post building. As charter trains frequently depart from the southern platforms, tourist groups usually assemble here for ease of identification. There are breezeways from the freight terminal connected to the mezzanine. | ||
To the north of the NRC tracks and directly beneath the road above, the Blue Mall is situated on this level. This mall is most noted for its selection of restaurants providing casual dining. Opposite the freight station, Underground Mall №2 is found, parallel to №1. As the south side of the station has been rejuvenated from a largely industrial area into one of leisure and fashion, №2 hosts a variety of | To the north of the NRC tracks and directly beneath the road above, the Blue Mall is situated on this level. This mall is most noted for its selection of restaurants providing casual dining. Opposite the freight station, Underground Mall №2 is found, parallel to №1. As the south side of the station has been rejuvenated from a largely industrial area into one of leisure and fashion, №2 hosts a variety of boutiques. | ||
Platforms for KRT Metropolitan and Central lines are found on this level. The Metropolitan line platform | |||
===B1=== | ===B1=== | ||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
===B2=== | ===B2=== | ||
This level, originally called the "lower mezzanine", offers access to IRRR Line 1, Line 2, and Line 5, the Airport Rail, and the Metro Circle Line. B2 was originally accessed not, as many assume, from B1, but from the mezzanine level. Entry to B2 is located southeast of the mezzanine and is led by a 180° turn into a large set of staircases and escalators. The geography of the level was designed to avoid overlap with B1, engineers having raised structural concerns. In 1990, B1 was connected to an enlarged B2 through four tunnels with highly-reinforced supports. The IRRR ticketing office is located on the northeastern corner of the level, the gates to the platforms directly east of it. Those of the Metro Circle Line and the Airport Rail is located on the southern limit of the level. B2 also offers exit into the Blue Mall and Purple Mall. | This level, originally called the "lower mezzanine", offers access to IRRR Line 1, Line 2, and Line 5, the Airport Rail, and the Metro Circle Line. B2 was originally accessed not, as many assume, from B1, but from the mezzanine level. Entry to B2 is located southeast of the mezzanine and is led by a 180° turn into a large set of staircases and escalators. The geography of the level was designed to avoid overlap with B1, engineers having raised structural concerns. In 1990, B1 was connected to an enlarged B2 through four tunnels with highly-reinforced supports. The IRRR ticketing office is located on the northeastern corner of the level, the gates to the platforms directly east of it. Those of the Metro Circle Line and the Airport Rail is located on the southern limit of the level. B2 also offers exit into the Blue Mall and Purple Mall. | ||
==Operators== | |||
===National Rail=== | |||
National Rail's Twa-ts′uk-men Station is situated on the Central Junction Railway, which connects to the Inland Main Line, Kan Line, Nek Line, and Sat Line to the east, and the National Trunk Line, Central Main Line, Mgraq Line, Ngang Line, Tor Line, and Coastal Main Line to the west of the station. | |||
==Accessibility== | |||
Twa-ts'uk-men provides unassisted and assisted wheelchair access throughout the station. There are accessible elevators and pathways to all services, which enable travellers with mobility, auditory, and sight impairments to travel unassisted to all services offered at Twa-ts'uk-men. There are nine accessible lavatories for all genders spread on all concourses and ticketing levels. Under the terms of the ''Disabled Travelling Act'' of 1998, all areas designated for the use of travellers in wheelchairs are fitted with emergency buttons. | |||
Advocacies for travellers with impairments have assessed the station and found some provisions deficient. For example, there are no lavatories on National Rail's platform level, and the nearest accessible one could be more than 300 m away, and clear space from obstructions to the edge of the platform is often very limited. In places, as little as 25 centimetres separate the edge of the wheelchair from a passing train. To avoid staircases, {{wp|tactile paving}} could take indirect routes and cause unexpected delays for the traveller. This is especially relevant in car parks, as the nearest one is more than 600 m away from the concourse, and the station leases multiple other parking lots as it was built without one. | |||
The issue of signage is common complaint by all travellers. The station is legally prevented from erecting signs in National Rail's normal style in the interest of preserving historical appearances. In place of yellow plastic tactile paving, blue bricks with the required patterns, contrasting with the faint yellow floor bricks, were employed. | |||
In the station's design process, architects noted that ramps were preferable to stairs in crowded areas because users are less likely to trip, which could potentially lead to further injuries and even death by trampling; it is for this reason that passages to the mezzanine and platform levels were built as ramps rather than stairs. However, these ramps are (slope 1 in 9) too steep for wheelchairs to pass through safely, and patrons in wheelchairs are accordingly not advised to use them alone. Station staff can be called to assist a passenger in a wheelchair to ascend or descend the ramps. | |||
==Ownership and staffing== | ==Ownership and staffing== | ||
| Line 131: | Line 144: | ||
==Criticism== | ==Criticism== | ||
===Atmosphere=== | |||
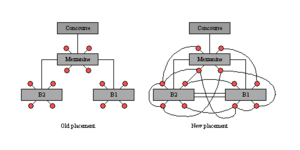
[[File:Placements.fw.png|thumb|Starting from 1987, the station began digging tunnels leading directly from one service to another, without passing through mezzanines crowded by commercial activity]] | [[File:Placements.fw.png|thumb|Starting from 1987, the station began digging tunnels leading directly from one service to another, without passing through mezzanines crowded by commercial activity]] | ||
As early as | As early as 1900, insufficient lighting and ventilation on the track level became a subject of criticism. The lack of convenient alternatives for long-distance travellers led the NRC to focus only on the capacity of the station, rather than its atmosphere. By the 20s, accumulated {{wp|soot}} was dropping from the vaulted ceiling onto the tracks and platforms, and the lingering smoke darkened the originally-yellowish interior. {{wp|gas lighting|Gas lamps}} illuminated the station since its rebuilding in 1897 until 1947, and fumes from them have also been a consistent source of complaint. Merchants in the mezzanine level strongly opposed attempts to pipe air through the level, fearing leaks might soil their products. | ||
The station was built with vents between platform level and street level. In the summer, the platform level was cooler than street level, draughting wind onto the platforms; the reverse occurred in winter. Though effective, the ventilation was not adequately distributed, and natural draught could sometimes be strong enough to knock individuals and goods off the platforms, or suck them into ground-level vents. There were also locations on the platform level that the draught did not reach. A compression chamber was built around the opening of the vents in 1905 to prevent water from accumulating or accidental injuries. | |||
A minority of travellers enter and exit the station through its concourse that was built with an eye to grandeur and aesthetic appeal. Most passengers since connection with underground railways and metropolitan busses are commuters in transit, who transfer from one underground service to another, or are shoppers patronizing the commercial establishments around the station, who leave the station by its underground exits. | |||
===Navigation=== | |||
[[File:Eslite_Taipei_Station_2015.jpg|thumb|Mezzanine level and its shops]] | [[File:Eslite_Taipei_Station_2015.jpg|thumb|Mezzanine level and its shops]] | ||
In the | In the 1930s through 70s, the HSR, deep-level IRRR platforms, Metro Circle Line, and Airport Rail joined the station, necesitating new pathways connecting them to the already-sprawling network of concourses and tunnels. At the same time, National Rail facing competition from road voyage began to seek commercial revenues by renting out more spaces in the concourses. Located in the areas that virtually every passenger would go through, the stalls were well-rented and patronized, though signage thus became obscured by advertisements. In the same vein, the station became a pedestrian bridge between the department stores that dotted its perimeter on the parallel pretext of conveniencing shoppers who come and go via trasit, and those who wish to go between stores without emerging onto street level. | ||
The pandering to commerce created vocal consternation in 1974, especially when it emerged the stores in the mezzanine level agreed not to have clocks so that travellers might stay longer. In response, the station decided that by diverting traffic away from the mezzanine levels, which functioned as a nexus for several services built during the same period, crowding would become less problematic. This was to be accomplished by creating new tunnels not populated by merchant stalls so that travellers on a hurry could access their desired services directly, without going through commercial areas. Some of these tunnels connect the transfer levels to each other, while others connect different platforms directly, such as those from the National Rail tracks to Metro Red, Metro Red to Orange, and HSR to Airport Rail. | |||
While this initiative diverted commuters away from shoppers, it introduced a web of tunnels for which the station is now infamous. Added signs pointing to tunnels contradict existing signs that guide travellers through the commercial areas, where the stores' revenues forbid their removal. Moreover, since the station is shared by five separated payment zones, ticket gates and barriers also challenged easy navigation. For example, the tunnel from HSR to IRRR is almost 300 metres long, but there is no ticketing booth inside; thus, a passenger without an IRRR ticket would have to turn back and wend through another route, causing up to 15 minutes of delay when the area is crowded. Some of these tunnels also branch off into staff offices and storage rooms, which were removed from the concourses to make space for stores. | |||
Many of these features encumbered law-enforcement officers apprehending terrorists that occupied the station in 2003 (viz. below), especially with lighting cut and maps complete with non-public areas difficult to find. | |||
===Platforms=== | |||
Other than Platform 1, which measures about 12 m across, all other platforms have a maximal width of 6 m and tapers to 4.5 m at the ends. This has been considered inadequate in modern operations because the frequency of services, and consequently passenger throughput on the platforms, has increased dramatically since the late 19th century. An ordinary train in 1900 routinely stopped for 30 minutes to an hour, but stopping time is usually 60 seconds in modern practice. Shorter stopping times require more passengers to board and alight from the train simultaneously, leading to more crowded platforms. Originally, passengers entered and vacated the platforms from ramps at their extremes, but in 1949 escalators were added. Though allowing passengers to enter and leave the platforms more quickly, they have also reduced the effective width of the platform in places, leaving but 1 m on either side of the escalators. | |||
National Rail launched inquiries into the effects of platform width on passenger experience in 1998. The inquiry concluded that the infrastructure of the station has not been built to support the running of a modern schedule, but very little could be done to address the difficulty aside from adding barriers to particularly narrow points to prevent falling off the platforms at these points. Such barriers were added in 2002 but have not eliminated all instances of crowding leading to incursions on the tracks. | |||
===Parking space=== | |||
The station has 40 parking spaces under the eastern entrance ramp, and these may be used free of charge but will be cleared overnight. This is (and has been) inadequate in view of the roughly 500,000 passengers who enter and exit the station every day. The station advises travellers that the availability of these spaces is not to be expected. | |||
==2003 incident== | ==Incidents== | ||
{{main| | ===2003 incident=== | ||
{{main|Twa-ts'uk-men Incident}} | |||
The station was the site of a violent incident by the | The station was the site of a violent incident by the Gek-luq {{wp|Millenarianism|millenarian}} cult in the morning of Dec. 29, 2003. Some 200 of the group's agents, carrying concealed firearms and explosives, entered the station from several directions and barricaded the concourse level, collapsing some of the stairwells and ramps to the mezzanine level. At the same time, other agents [[Kien-k'ang Urban Railway#Accidents|released]] {{wp|sarin}} gas at other stations to divert attention. Explosives were set on many other access routes to retard the entry of police officers. Thousands in the station escaped after emergency announcements made by the staff, before the broadcasting room was captured. Later, cultists derailed trains in the station to create more barriers. Around noon, the department stores connected to the station were evacuated. | ||
With an estimated | With an estimated 300, including 145 staff, still unaccounted for, early efforts by the police to force entry were repulsed. Authorities were uncertain whether the individuals were simply unable to exit or held as hostages. As booby-trapped doors had already claimed several lives, the police were hesitant to manoeuvre into the station. As the cultists did not emerge from the station, police commissioners and the mayor required caution. Due to the complexity of the station's geography and lack of information from within, the authorities gained ground very slowly. The cultists did not respond to communications from the police, but a cultist anonymously told the police that those in the building "can quit the great enterprise as they please". | ||
The progress from hallway to hallway and | The progress from hallway to hallway and room to room was attended by much casualty, bombs and even traps like removed railings and holes causing injury and death. Flood lights were neutralized by the sheer quantity of merchandise, pillars, walls, and low ceilings. A major milestone occurred on Jan. 4 when 76 of the missing individuals were found subsisting on tinned foods and sheltering in a barricaded ventilation room on B1. Police officers nearly missed it, since an explosion was contrived to give the hallway to the room the appearance of impassability. The cultists were discovered in closely-linked network of tunnels and rooms in the abandoned depot, south of platform 6. In mid-March, the police began to attack the depot, though the cultists used the {{wp|switcher|switchers}} on that level to inflict much damage on the authorities. On Jan. 8, many cultists surrendered the area, with most of them apprehended. | ||
Following a thorough survey of the general area, with staff assistance, the station was declared clear on Jan. 19, 2004. The station was held by the cultists for about 10 days. Repair work continued until September, though test trains were run as early as February, after the tracks were cleared and explosives experts searched the tunnels for ordnance. Several unexploded bombs were discovered along tracks and floor area. Passenger service resumed on April 2, 2004. Passenger volume dropped from a pre-incident average of 650,000 per day to 447,000 for the remainder of 2004 and would not recover until 2009. A further four unexploded bombs were discovered between 2004 and 2006, though in all cases they were located in non-public areas and safely removed. | Following a thorough survey of the general area, with staff assistance, the station was declared clear on Jan. 19, 2004. The station was held by the cultists for about 10 days. Repair work continued until September, though test trains were run as early as February, after the tracks were cleared and explosives experts searched the tunnels for ordnance. Several unexploded bombs were discovered along tracks and floor area. Passenger service resumed on April 2, 2004. Passenger volume dropped from a pre-incident average of 650,000 per day to 447,000 for the remainder of 2004 and would not recover until 2009. A further four unexploded bombs were discovered between 2004 and 2006, though in all cases they were located in non-public areas and safely removed. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 187: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Themiclesia]] | *[[Themiclesia]] | ||
*[[Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit]] | |||
*[[Inner Region Regional Railway]] | |||
[[Category:Themiclesia]][[Category:Septentrion]] | [[Category:Themiclesia]][[Category:Septentrion]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:32, 29 October 2023
Twa-ts′uk-men Railway Station 朱雀門驛, twa-ts′uk-men-lek | |
|---|---|
| National Rail, KRT, EDR, HSR, Airport Railway | |
 Glass roof photographed in 1899 | |
| Location | №s 1 – 2 South Blvd. E., Kien-k'ang, 10190 Themiclesia |
| Elevation | 51 m |
| Owned by | City of Kien-k'ang |
| Operated by | National Railway Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit Exchequer District Railway Metropolitan Omnibus Other bus operators Themiclesia Post |
| Line(s) | Central Junction Railway Trans-Hemithean Railway Trans-Hemithea High-Speed Railway KRT Metropolitan KRT Urban KRT City KRT Central KRT Tibh & Tibh Airport EDR 1 EDR 2 EDR 3 EDR 4 EDR 5 HSR Inland Main Line HSR Traverse Main Line Kei Airport Railway |
| Platforms | 32 island 5 side |
| Tracks | 123 |
| Connections | Metropolitan Omnibus taxicabs |
| Construction | |
| Structure type | mixed |
| Depth | 72 m |
| Platform levels | 5 |
| Parking | 55 |
| Bicycle facilities | 652 |
| Disabled access | Yes |
| Other information | |
| Station code | 382 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1857 |
| Rebuilt | 1897 |
| Electrified | 1983 |
| Traffic | |
| Passengers (2015) | avg. 522,000 per diem |
The Twa-ts′uk-men Station (朱雀門驛, twa-ts′uk-men-lek) is a passenger railway station situated in Kien-k'ang, Themiclesia. Established on the Central Junction Railway, the station now hosts National Rail, Exchequer District Railway, five lines of the Kien-k'ang Rapid Transit system, Themiclesian High Speed Rail, Kei Airport Metro, the Metropolitan Omnibus Terminal, and a taxicab hub; furthermore, it is connected to four hotels, three underground shopping malls, six department stores, the Kien-k'ang Financial Centre, amongst other local edifices and attractions.
It is the largest station in Themiclesia by passenger volume and floor area (but not land area), serving over 600,000 people a day on average (est. 2020). Across its six station buildings, it possesses three storeys above ground and seven below. The station is a cultural landmark, transportation hub, and commercial centre for Kien-k'ang. Some of this prosperity is attributed to the traffic the station brings.
History
Rebuilding
As railways developed in Themiclesia, many lines were connected to the capital city by terminal stations its outskirts, most importantly the Qlin-tsung Terminus on the west, the Ferry Terminus on the southwest, and the Tlang-qrum Terminus on the east. However, the need to transship goods from one terminus to another resulted in congestion through the city's core. To alleviate congestion, wagons not for delivery were commanded in 1875 to traverse the city at night; however, this policy generated complaints of nocturnal noise and excess manure from streams of wagon traffic. Moreover, the three railway termini were each some distance from the city's rising commercial centre, which was around the eponymous Twa-ts'uk-men Gate.
In 1891, the government formally entered the railway business by purchasing the National Trunk Railway, which had defaulted on its debts due to ineffective line planning. The Liberal government embraced the regulations of railways as a policy and planned the Central Junction Railway to obviate the city's nocturnal wagon traffic as well as to bring passengers and goods over the proverbial "last mile" to the epicentre of trade in Kien-k'ang.
The city encountered difficulty to acquire sufficient land for a railway through the centre of the city. Thus, it accepted the suggestion of Chief Engineer of Works Stsang, to construct an underground railway so that the land above remained economically useful. The government paid rent while buildings stood demolished and agreed to refund taxation on the land for 99 years, thus enhancing its value. Construction work began in 1892 and terminated in 1897, resulting in a seven-mile tunnel with four tracks. This project was reported in the foreign press and billed a "radical demonstration of competence" in newspapers. However, at the same time, most of the working-class tenants who had lived in buildings demolished for the station were hastily evicted by their landlords; prevailing terms on apartment lease of the day granted tenants none of the compensation from the government.
A new station building was erected as the crowning jewel of one of the most expensive projects in Themiclesian history. The new building, completed ahead of schedule in 1897 and with the compelled labour of over 6,000 prisoners coralled into the capital city, included a spacious concourse spanned by steel girders and glass roofs. With a floor area of 268,000 square feet and more underground, it was the largest building in Themiclesia and more than half of the size of Anglia's Crystal Palace. There were five underground platforms and twelve full-length storage tracks when the station opened, though more were added later in its history. The underground levels were spanned by brick vaults reinforced with steel ties.
Because the Central Junction Railway was meant to connect the major railway lines around Kien-k'ang, the underground tunnels were built to accommodate the largest rolling stock then in use, found on the very newest National Trunk Railway, which ran with coaches 14 ft 6 in. tall and 10 ft 6 in. wide; most Themiclesian coaches were between 12 and 13 ft tall, and 9 ft and 9 ft 6 in wide. Due to government consolidation of railways in the late 1890s and continuing into the 1920s, most improved and new lines were re-gauged to be consistent with the tunnels. Though considered generous by 1890s standards, the tunnels became the proverbial bottle-neck when it came to large freight in the Pan-Septentrion War and beyond.
Early 20th century
In 1899, the Metropolitan Railway opened with exits built directly into the mezzanine level. The owners of the railway demanded this right after its competitor, Urban, had also obtained a similar concession in the concourse space. In 1910, the station was augmented by two new platform with two tracks each. While passenger trains were usually assembled and maintained in the yard between the passenger and freight sides, the new passenger platform forced the staff platforms south, where maintenance work took place. The assembly of some trains was thus moved to Tl′ang-qrum Station, where a more spacious yard was still available. A further island platform was added in 1913. In 1916, the Central line's shuttle line to Twa-ts'uk-men opened into the station with a platform just north of the Metropolitan's. This required an extension to the mezzanine level.
In 1921, the City line's platforms were added to the space under the station, using a tunelling shield to bore much deeper than any of the previous tunnels. Its platform level lay roughly 30 m underground, compared to the 7 m of the National Rail, Metropolitan, and Central tracks. This great depth required an equally elaborate escalator to convey passengers to and from its trains, which was added in the western end of the mezzanine level.
PSW
During the retreat to the west in 1936, much of the station's furniture was removed to enlarge usable space. The grand concourse was used by the government as propaganda image briefly in 1939 to portray Themiclesia as a technologically advanced nation that could contest more powerful yet backwards and barbaric invaders. In September 1940, Kien-k'ang was severed from relieving forces and forced to defend itself from its walls, thus leaving the station, and the railway network beneath it, undefended. It was commandeered as a temporary base of operations by Menghean forces during the siege of the city, and several attempts were made to infiltrate the city via the Metropolitan Railway's tunnels in the direction of the Old City. Menghean soldiers pushed a spare coach into the tunnel as an effective shield against Themiclesian fire, but the railway engineer Marcus Syar employed a derail to cause a derailment. The derailed coach was not only immovable from the Menghean side but also blocked the tunnel. Syar was later awarded the Order of the Star for his wit.
In January 1941, a bomb penetrated the east end of the station's concourse, causing considerable damage to the northeastern corner and eastern façade. The building was converted into a hospital that housed over 2,000 wounded Menghean and Dayashinese soldiers, and a Red Cross flag was hoisted over the station to denote this use. Operating theatres were established in the mezzanine level. The presence of medical personnel in the concourse prevented further damage, as multiple aerial engagements occurred over that part of the city in 1941. When Menghean and Dayashinese forces retreated from Kien-k'ang in mid-1941, the station was given a rudimentary restoration and remained in use as a hospital. As the enemy still controlled the eastern parts of the railway network, the eastern end of the Central Junction Railway tunnels was bricked up to prevent locomotives carrying hostile forces from barging into the city. All traffic was diverted to the suburbs for easier control and better space for manipulation.
With the war progressing favourably, the Central Junction was opened again in 1942. Eastbound services were restored in October 1942 to facilitate the transport of troops and materials, and some of the invalids in the hospital were removed to other hospitals and convalescence houses in the city. Lord Kwyak, the Secretary of State for War, visited the station to see off one of the batches of volunteers bound to fight in Maverica in May 1944. Full restoration work, including the mending of the glass ceiling in the damaged corner of the station, began in 1946 and was completed by 1948. In contrast to the marble façade, a small corner of the building was mended with concrete as a memorial to the war.
Late 20th century
The addition of the HSR and the EDR presented a challenge to the station. One plan called for replacing the shrinking marshalling yard that was still in use with HSR platforms, and another required digging a new tunnel under both the NRC and KRT platforms. The former plan was originally preferred, though structural and operational difficulties so implied (the HSR to share the busy tunnel with conventional rail, regauging required, etc.) compelled National Rail to elect the latter. Work began in 1960 and was complete by 1965. The HSR's ticketing operation required an extension to the sub-mezzanine level owned by the Kien-k'ang Metro. The interior of the new area was decorated by the HSR's architect E. E. Ericson, who otherwise was responsible for new constructions along the road. Ericson disliked working with cramped and inflexible spaces underground.
The 60s also saw the opening of the underground arcades that ran under the roads bounding the station's infrastructure, bridging commercial establishments and opening into the mezzanines. A company jointly owned by the abutting department stores initially owned these arcades that catered to fast-paced purchases. It was thought that instead of waiting in the concourse, passengers could shop while in transit. Shoppers going from one department store to another could also stay within an enclosed space rather than emerging onto street level, where the presence of taxicabs and busses might lure them away; though that lure also existed with the underground arcades opening into the Metro system, it was thought passenger traffic would more than offset this problem. National Rail was endeared to this plan as it provided more exits.
In 1969, the Inner Region Regional Railway was privatized and relocated its services to a new platform layer further below that of the deep-level KRT lines. These new platforms were located under the eastern approach of the NRC tracks. A further lobby was constructed above the three roughly-parallel regional lines. To distinguish this lobby, where ticketing and other IRRR offices were located, from the sub-mezzanine level (which was so named after its completion in 1952), the newer lobby was called the lower mezzanine. In 1970 they were renamed to B1 and B2 respectively, in an early effort to ease the infamous confusion that would later characterize the station; however, this change was not positively received, as discussed below. A new building was erected adjoining the luggage terminal east of the concourse to represent the IRRR's autonomous operation, though it could be accessed from was simply called the "new station" by locals.
An airport railway to Kei Airport, the successor to Tibh Airport, was completed in 1995. The railway connected the city to the new airport 33 km away, so that arrivals had an option other than a bus ride along the congested highway. Its two platform were located under those of the Metro Blue line. Another building, called "new station south" was erected over the mezzanine level (as a stand-alone terminus) for the Airport Railway. It was hoped traffic might be separated from the existing network, but under public pressure that service was made accessible from both the sub-mezzanine and an extension of the lower mezzanine, which provided access to the bus stations and the concourse building. The 1969 station was then disambiguated as "new station north".
The Metro Circle line was completed in 1985 with its platform parallel and partly under the HSR service. It opened into the South Mall (from which transit to the other services was possible) and initially had no street-level exits.
Structure
KRT Urban line platform
The KRT Urban line's platforms are to the south of the concourse, on an elevated level. The side platforms are for stopping trains, while the central island platform is where the line's express services call.
Street level
The main passenger concourse is a 420-metre long, 65-meter wide concourse spanned by a glass roof, long side in the east-west direction. The main entrance is situated on the north side, roughly at its centre, though access points dot its perimeter. The concourse houses one portion of National Rail's ticketing office, and restaurants, bookstalls, and other small shops exist along the elongated building. The perimeter of the concourse is occupied by waiting rooms and other facilities.
Mezzanine
The mezzanine is directly below the concourse and extends some 300 metres past its southern side. The southwestern corner of the mezzanine is taken up by a bus terminal, into which a spur from the western overpass extends. The bus terminal is divided into two sections along the spur, the northern part thereof served by the Metropolitan Omnibus, and the southern part by other operators, mostly long-distance busses. Both sections accept departing and arriving passengers.
The leve's central area is not as long as the concourse, but extending further south. The eastern half of the mazzanine houses National Rail ticketing windows and more waiting rooms.
National Rail track level
The National Rail track level lies under the mezzanine. There are 9 island platforms (Platform 2 through 10) and 2 side platforms (Platform 1 and 11), with a total of 32 tracks. The Central Junction Railway is quadruplicated, with two tracks intended for each direction. Approaching the station in either direction, the lines fan out to meet the station's tracks and sidings.
- Platform 1 is used for the Trans-Hemithean Railway and the Inland Main Line.
- Platforms 2 and 3 are used by trains for Rak and Stui the Inland Main Line.
- Platform 4 is used by trains for K′an and Nek.
- Platform 5 and 6 is used by trains on the National Trunk and Central Main Line.
- Platform 7 and 8 are used by trains for Mgraq, Ngang, and Lwai.
- Platform 9 and 10 are used by trains on the Coastal Main Line and to Q.pa.
- Platform 11 is used by trains on the Sat Line.
The freight station no longer accepts freight, but to it are still sent luggage, mail, and parcels. It connects to the National Post building. As charter trains frequently depart from the southern platforms, tourist groups usually assemble here for ease of identification. There are breezeways from the freight terminal connected to the mezzanine.
To the north of the NRC tracks and directly beneath the road above, the Blue Mall is situated on this level. This mall is most noted for its selection of restaurants providing casual dining. Opposite the freight station, Underground Mall №2 is found, parallel to №1. As the south side of the station has been rejuvenated from a largely industrial area into one of leisure and fashion, №2 hosts a variety of boutiques.
Platforms for KRT Metropolitan and Central lines are found on this level. The Metropolitan line platform
B1
This level was originally called the sub-mezzanine, since its functions as a nexus between several services made it comparable. B1 provides access to the Themiclesian High-Speed Rail and Kien-k'ang Metro Orange and Green lines. The level is accessed from the mezzanine level, several surrounding buildings, the Green and Blue underground malls, and certain street-level portals. The main body of B1 does not actually reach the Green Line's platform, requiring a 40-metre tunnel towards its lobby, from which the Green mall could be reached. On the other hand, the Orange Line does not have its own lobby and is accessed from the station's B1 level, with its own street-level access points. The Metro's Operational Control Centre is found on this level.
B2
This level, originally called the "lower mezzanine", offers access to IRRR Line 1, Line 2, and Line 5, the Airport Rail, and the Metro Circle Line. B2 was originally accessed not, as many assume, from B1, but from the mezzanine level. Entry to B2 is located southeast of the mezzanine and is led by a 180° turn into a large set of staircases and escalators. The geography of the level was designed to avoid overlap with B1, engineers having raised structural concerns. In 1990, B1 was connected to an enlarged B2 through four tunnels with highly-reinforced supports. The IRRR ticketing office is located on the northeastern corner of the level, the gates to the platforms directly east of it. Those of the Metro Circle Line and the Airport Rail is located on the southern limit of the level. B2 also offers exit into the Blue Mall and Purple Mall.
Operators
National Rail
National Rail's Twa-ts′uk-men Station is situated on the Central Junction Railway, which connects to the Inland Main Line, Kan Line, Nek Line, and Sat Line to the east, and the National Trunk Line, Central Main Line, Mgraq Line, Ngang Line, Tor Line, and Coastal Main Line to the west of the station.
Accessibility
Twa-ts'uk-men provides unassisted and assisted wheelchair access throughout the station. There are accessible elevators and pathways to all services, which enable travellers with mobility, auditory, and sight impairments to travel unassisted to all services offered at Twa-ts'uk-men. There are nine accessible lavatories for all genders spread on all concourses and ticketing levels. Under the terms of the Disabled Travelling Act of 1998, all areas designated for the use of travellers in wheelchairs are fitted with emergency buttons.
Advocacies for travellers with impairments have assessed the station and found some provisions deficient. For example, there are no lavatories on National Rail's platform level, and the nearest accessible one could be more than 300 m away, and clear space from obstructions to the edge of the platform is often very limited. In places, as little as 25 centimetres separate the edge of the wheelchair from a passing train. To avoid staircases, tactile paving could take indirect routes and cause unexpected delays for the traveller. This is especially relevant in car parks, as the nearest one is more than 600 m away from the concourse, and the station leases multiple other parking lots as it was built without one.
The issue of signage is common complaint by all travellers. The station is legally prevented from erecting signs in National Rail's normal style in the interest of preserving historical appearances. In place of yellow plastic tactile paving, blue bricks with the required patterns, contrasting with the faint yellow floor bricks, were employed.
In the station's design process, architects noted that ramps were preferable to stairs in crowded areas because users are less likely to trip, which could potentially lead to further injuries and even death by trampling; it is for this reason that passages to the mezzanine and platform levels were built as ramps rather than stairs. However, these ramps are (slope 1 in 9) too steep for wheelchairs to pass through safely, and patrons in wheelchairs are accordingly not advised to use them alone. Station staff can be called to assist a passenger in a wheelchair to ascend or descend the ramps.
Ownership and staffing
The station's floor space is officially divided amongst five separate entities, owned by the NRC, Metropolitan Omnibus Company, Kien-k'ang Metropolitan Railway, Inner Region Regional Railway, and Themiclesia Post. Due to disputes arising over maintenance and repair duties, the Common Committee supervises most of the individual operations to ensure the others are not adversely affected. These entities also regularly lease areas to each other and share costs.
Criticism
Atmosphere
As early as 1900, insufficient lighting and ventilation on the track level became a subject of criticism. The lack of convenient alternatives for long-distance travellers led the NRC to focus only on the capacity of the station, rather than its atmosphere. By the 20s, accumulated soot was dropping from the vaulted ceiling onto the tracks and platforms, and the lingering smoke darkened the originally-yellowish interior. Gas lamps illuminated the station since its rebuilding in 1897 until 1947, and fumes from them have also been a consistent source of complaint. Merchants in the mezzanine level strongly opposed attempts to pipe air through the level, fearing leaks might soil their products.
The station was built with vents between platform level and street level. In the summer, the platform level was cooler than street level, draughting wind onto the platforms; the reverse occurred in winter. Though effective, the ventilation was not adequately distributed, and natural draught could sometimes be strong enough to knock individuals and goods off the platforms, or suck them into ground-level vents. There were also locations on the platform level that the draught did not reach. A compression chamber was built around the opening of the vents in 1905 to prevent water from accumulating or accidental injuries.
A minority of travellers enter and exit the station through its concourse that was built with an eye to grandeur and aesthetic appeal. Most passengers since connection with underground railways and metropolitan busses are commuters in transit, who transfer from one underground service to another, or are shoppers patronizing the commercial establishments around the station, who leave the station by its underground exits.
In the 1930s through 70s, the HSR, deep-level IRRR platforms, Metro Circle Line, and Airport Rail joined the station, necesitating new pathways connecting them to the already-sprawling network of concourses and tunnels. At the same time, National Rail facing competition from road voyage began to seek commercial revenues by renting out more spaces in the concourses. Located in the areas that virtually every passenger would go through, the stalls were well-rented and patronized, though signage thus became obscured by advertisements. In the same vein, the station became a pedestrian bridge between the department stores that dotted its perimeter on the parallel pretext of conveniencing shoppers who come and go via trasit, and those who wish to go between stores without emerging onto street level.
The pandering to commerce created vocal consternation in 1974, especially when it emerged the stores in the mezzanine level agreed not to have clocks so that travellers might stay longer. In response, the station decided that by diverting traffic away from the mezzanine levels, which functioned as a nexus for several services built during the same period, crowding would become less problematic. This was to be accomplished by creating new tunnels not populated by merchant stalls so that travellers on a hurry could access their desired services directly, without going through commercial areas. Some of these tunnels connect the transfer levels to each other, while others connect different platforms directly, such as those from the National Rail tracks to Metro Red, Metro Red to Orange, and HSR to Airport Rail.
While this initiative diverted commuters away from shoppers, it introduced a web of tunnels for which the station is now infamous. Added signs pointing to tunnels contradict existing signs that guide travellers through the commercial areas, where the stores' revenues forbid their removal. Moreover, since the station is shared by five separated payment zones, ticket gates and barriers also challenged easy navigation. For example, the tunnel from HSR to IRRR is almost 300 metres long, but there is no ticketing booth inside; thus, a passenger without an IRRR ticket would have to turn back and wend through another route, causing up to 15 minutes of delay when the area is crowded. Some of these tunnels also branch off into staff offices and storage rooms, which were removed from the concourses to make space for stores.
Many of these features encumbered law-enforcement officers apprehending terrorists that occupied the station in 2003 (viz. below), especially with lighting cut and maps complete with non-public areas difficult to find.
Platforms
Other than Platform 1, which measures about 12 m across, all other platforms have a maximal width of 6 m and tapers to 4.5 m at the ends. This has been considered inadequate in modern operations because the frequency of services, and consequently passenger throughput on the platforms, has increased dramatically since the late 19th century. An ordinary train in 1900 routinely stopped for 30 minutes to an hour, but stopping time is usually 60 seconds in modern practice. Shorter stopping times require more passengers to board and alight from the train simultaneously, leading to more crowded platforms. Originally, passengers entered and vacated the platforms from ramps at their extremes, but in 1949 escalators were added. Though allowing passengers to enter and leave the platforms more quickly, they have also reduced the effective width of the platform in places, leaving but 1 m on either side of the escalators.
National Rail launched inquiries into the effects of platform width on passenger experience in 1998. The inquiry concluded that the infrastructure of the station has not been built to support the running of a modern schedule, but very little could be done to address the difficulty aside from adding barriers to particularly narrow points to prevent falling off the platforms at these points. Such barriers were added in 2002 but have not eliminated all instances of crowding leading to incursions on the tracks.
Parking space
The station has 40 parking spaces under the eastern entrance ramp, and these may be used free of charge but will be cleared overnight. This is (and has been) inadequate in view of the roughly 500,000 passengers who enter and exit the station every day. The station advises travellers that the availability of these spaces is not to be expected.
Incidents
2003 incident
The station was the site of a violent incident by the Gek-luq millenarian cult in the morning of Dec. 29, 2003. Some 200 of the group's agents, carrying concealed firearms and explosives, entered the station from several directions and barricaded the concourse level, collapsing some of the stairwells and ramps to the mezzanine level. At the same time, other agents released sarin gas at other stations to divert attention. Explosives were set on many other access routes to retard the entry of police officers. Thousands in the station escaped after emergency announcements made by the staff, before the broadcasting room was captured. Later, cultists derailed trains in the station to create more barriers. Around noon, the department stores connected to the station were evacuated.
With an estimated 300, including 145 staff, still unaccounted for, early efforts by the police to force entry were repulsed. Authorities were uncertain whether the individuals were simply unable to exit or held as hostages. As booby-trapped doors had already claimed several lives, the police were hesitant to manoeuvre into the station. As the cultists did not emerge from the station, police commissioners and the mayor required caution. Due to the complexity of the station's geography and lack of information from within, the authorities gained ground very slowly. The cultists did not respond to communications from the police, but a cultist anonymously told the police that those in the building "can quit the great enterprise as they please".
The progress from hallway to hallway and room to room was attended by much casualty, bombs and even traps like removed railings and holes causing injury and death. Flood lights were neutralized by the sheer quantity of merchandise, pillars, walls, and low ceilings. A major milestone occurred on Jan. 4 when 76 of the missing individuals were found subsisting on tinned foods and sheltering in a barricaded ventilation room on B1. Police officers nearly missed it, since an explosion was contrived to give the hallway to the room the appearance of impassability. The cultists were discovered in closely-linked network of tunnels and rooms in the abandoned depot, south of platform 6. In mid-March, the police began to attack the depot, though the cultists used the switchers on that level to inflict much damage on the authorities. On Jan. 8, many cultists surrendered the area, with most of them apprehended.
Following a thorough survey of the general area, with staff assistance, the station was declared clear on Jan. 19, 2004. The station was held by the cultists for about 10 days. Repair work continued until September, though test trains were run as early as February, after the tracks were cleared and explosives experts searched the tunnels for ordnance. Several unexploded bombs were discovered along tracks and floor area. Passenger service resumed on April 2, 2004. Passenger volume dropped from a pre-incident average of 650,000 per day to 447,000 for the remainder of 2004 and would not recover until 2009. A further four unexploded bombs were discovered between 2004 and 2006, though in all cases they were located in non-public areas and safely removed.
Both houses of Parliament first charged their respective home affairs committees to investigate the causes of the incident and to report on necessary procedures to prevent similar incidents in the future. In 2005, a joint committee was appointed with eight MPs and seven lords to oversee investigations and to draft a report. For the most part, the committee took the view that the undetected aggregation of weapons is the primary enabling fact, geography and lack of intelligence being factors which impaired police action. Moreover, the apprehension of leaders of the cult and the flight of conspirators led the Sungh Government to conclude that the ideological basis of such an attack had disappeared, so "there is no reason to believe it could occur again."
Nevertheless, from the time the station resumed passenger service, an addition 20 policemen have been stationed on site providing a total of 32 policemen in the station on most days. According to stationmaster, the primary improvement since the incident is actually over 2,000 new emergency buttons, intercoms, and telephones distributed throughout the station that permit immediate access to the staff, ambulance, and police. As it was thought the cultists actually spent several days installing all the barriers that later flustered the police, early warning and precise information as to the location of irregular occurrences was slated to improve response time and thus ability to address developing threats. Schemes such as metal detectors and military presence were early dismissed as impractical or impracticable in the consultation process.