Republic of Pania: Difference between revisions
The ©rusader (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
The ©rusader (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| s3 = | | s3 = | ||
| common_languages = {{flatlist| | | common_languages = {{flatlist| | ||
* {{wp|Portugese language|Lavish}} | * {{wp|Portugese language|Lavish}}<br> | ||
* {{wp|Venetian language|Barancan}} | * {{wp|Venetian language|Barancan}}<br> | ||
* {{wp|Italian language|Panian}} | * {{wp|Italian language|Panian}}<br> | ||
* {{wp|Greek language|Erytherian}} | * {{wp|Greek language|Erytherian}}<br> | ||
* {{wp|Latin language|Cambran}} | * {{wp|Latin language|Cambran}} | ||
Revision as of 02:50, 1 August 2020
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Maritime Republic of Pania | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 385–1462 | |||||||||||
| Motto: Pie Deus, dona nobis pacem ac felicitatem "Merciful God, grant us peace and prosperity" | |||||||||||
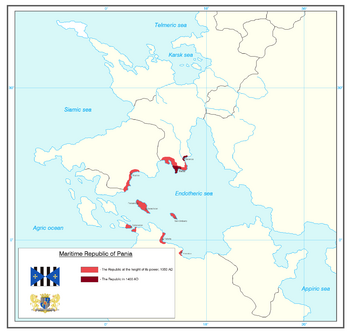 Territory directly owned by the Republic in 1050 CE. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Pania | ||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||
| Government | Parliamentary oligarchic merchant republic | ||||||||||
| Consul | |||||||||||
• 385-401 (first) | Marcus Tiberius | ||||||||||
• 1458-1462 (last) | Bartolomeo di Cassini | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Great Council of Pania | ||||||||||
| Council of Families | |||||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages – Early modern period | ||||||||||
• Established | 385 | ||||||||||
• Siege of Pania | 385 | ||||||||||
• Treaty of Cambra | 462 | ||||||||||
• Battle of San-Umberto | 891 | ||||||||||
• Sack of Mageiros | 1032 | ||||||||||
• Treaty of Bosala | 1462 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Panian ducat | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
The Maritime Republic of Pania (Panian Repubblica marittima di Pania, Lavarian República marítima de Paniá), was an independent state and a maritime republic that existed in southern Lavaria between 385 CE and 1462 CE. At the peak of its power, the republic incorported several cities on the northern coast of the Endotheric sea, several islands of the Erytherian island chain, the island of Saint Hubert of the Lilacs, and several colonies in northern Caphtora, as well as numerous smaller trading ports and colonies scattered around the Endotheric sea. The republic was centered around the city of Pania: located in a valley under the Pania rocks, the strategic location of the city made it the most important commercial and military centre of the Cambran empire. The republic grew into the dominant naval power during the High Middle Ages in the Endotheric sea, and controlled most of the trade between Berea and Eastern Pamira. The city preserved a lot of the governing traditions of the Cambran empire and even used Cambran as the main language for most of its early existence.
Following the fall of Cambra in 381 CE, several generals and part of the Cambran elite, led by Magister Militum Marcus Tiberius, seeked refuge in the city Pania, the main military port of the Cambran empire located in the southern tip of the Lavish peninsula. The city was besieged twice by the Welbarian forces of Alarich, in 383 and 384, both times unsuccessfully. In 385, the Kingdom of the Welbarians was established on the ruins of the Cambran empire and proclaimed itself the successor of Cambra. The leaders of Pania refused to accept Alarich as their king, and in the same year the Welbarian fleet was sunk in the Battle of Cambra, the city itself was besieged for 2 months and King Alarich was killed. The Welbarians accepted Panian sovereignity. In 460, another unsuccessul siege of Pania was attempted by King Ulrich II, during which most of his forces were killed or captured. In 462, the Welbarians signed the treaty of Cambra, accepting the sovereignity of Cambra and granting them exclusive rights on trade on Welbarian soil. With the deterioration of the Kingdom of Welbarians in the 8th-11th centuries, Pania used its power and influence to gain control over some of the Welbarian coastal forts and ports. With the rise of several other maritime republics, most notably Armala, Pania secured its dominance with a mixture of diplomacy and strength. The republic won the Battle of San-Umberto against the combined force of the Republics of Armala, Mesana and Saloma. In the following century, Pamia signed several treaties with the Kingdom of Erytherians, culminating with the Treaty of Mageiros, when the republic gained exclusive trading rights with the kingdom and gained new colonies and trading outposts on the Erytherian islands. In the 11th century, the Republic reached the peak of its power, controlling most of the maritime trade in the Endotheric sea.
With the unification of Lavaria and the rise of the newly-formed kingdom as a naval power, Pania slowly lost its significance. After the strategic defeat of the !Pamiran empire in the Battle of Carana against the unified Lavish forces, and the opening of the trade route via the Viridian and Appiric seas, Pania rapidly lost its influence on the naval trade and its wealth. In 1447, Pania was forced to sieze most of its colonies to the Lavish Kingdom, and less than two decades later, in 1462, after the siege of Pania, the republic lost its independence and was incorporated into the Lavish Kingdom. Pania remains a city in the Kigdom of Lavaria until today.


