Azure Coast: Difference between revisions
Nova Secta (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Nova Secta (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
The system of government currently utilized by the Azure Coast was formulated in the aftermath of the [[Blue Revolution]] (1973-1976), when the autocratic {{wp|military junta}} of dictator General Alban Serreau was overthrown after mass protests demanding liberal reforms to the economy and greater personal freedom. Because of its creators’ desire to appropriate greater civil rights for the country’s citizens, the national constitution – the [[Azéma Accords]] = is comprised of the functionality of the new government and a host of negative liberties to be observed by the state in support of the propagation of greater personal freedom and liberty for the individual. As far back as 1969, protest movements were already including new civil liberties and rights to be enshrined in the Azure Coast’s government. In 1972, political activist and writer [[Jean-Louis Pierrepont]] collaborated with professors at Gascoigne University to draft the [[Declaration of Delahoussaye]], the formal document by which the new government drew inspiration from when crafting the legal rights of citizens and its structural composition. Copies of the Declaration are often included with printed copies of the Accords themselves as its foreward and preamble. | The system of government currently utilized by the Azure Coast was formulated in the aftermath of the [[Blue Revolution]] (1973-1976), when the autocratic {{wp|military junta}} of dictator General Alban Serreau was overthrown after mass protests demanding liberal reforms to the economy and greater personal freedom. Because of its creators’ desire to appropriate greater civil rights for the country’s citizens, the national constitution – the [[Azéma Accords]] = is comprised of the functionality of the new government and a host of negative liberties to be observed by the state in support of the propagation of greater personal freedom and liberty for the individual. As far back as 1969, protest movements were already including new civil liberties and rights to be enshrined in the Azure Coast’s government. In 1972, political activist and writer [[Jean-Louis Pierrepont]] collaborated with professors at Gascoigne University to draft the [[Declaration of Delahoussaye]], the formal document by which the new government drew inspiration from when crafting the legal rights of citizens and its structural composition. Copies of the Declaration are often included with printed copies of the Accords themselves as its foreward and preamble. | ||
The Azure Coast is a {{wp|constitution|constitutional}} {{wp|federal parliamentary republic}} comprised of eleven districts known as '''Comtés''' (Shires), the {{wp|capital city|federal capital}} [[Sartoux|district]] and one [[Brindamour Military Zone|administrative territory]] in the extreme northwest of the country. | The Azure Coast is a {{wp|constitution|constitutional}} {{wp|federal parliamentary republic}} comprised of eleven districts known as '''Comtés''' (Shires), the {{wp|capital city|federal capital}} [[Sartoux|district]] and one [[Brindamour Military Zone|administrative territory]] in the extreme northwest of the country. Its national legislature, the [[Congrès des Conseillers]] (Congress of Councilors) currently seats one hundred delegates, distributed by population to the eleven comtés. Powers not enumerated to the federal government in Sartoux (or expressly prohibited throughout the hierarchy of governance) via the Congrès are delegated to the comtés via their governors, comté legislatures, and parish governments. Members of the legislature, the eponymous conseillers, stand for election every two years, with staggered elections established to ensure that veterancy will remain in the legislature at all times. The head of government, the [[Premier of the Azure Coast|Premier]] may serve a maximum of ten years and are chosen via their party to stand for the office. Conversely, the head of state, the [[President of the Azure Coast|President]] is directly elected by the people, with elections held once every five years (they are also capped at a maximum of ten years in office, or two full terms). | ||
The powers of the president are largely relegated to ceremonial functions, generally diplomatic in nature. The president is responsible for representing the Azure Coast as its senior diplomat, and will engage with other foreign heads of state and dignitaries on behalf of the Congrès and the premier. They do however retain the ability to call snap elections in the event that a majority coalition in the Congrès dissolves, or if the premier resigns from office, is removed by the legislature, or otherwise dies or becomes incapacitated while serving. In comparison to the largely ceremonial role of the presidency, the premiership stands as the most powerful office in the Azure Coast; premiers are responsible for directly the policy platform of the majority coalition and decide which legislation the majority will bring forth during their term in office. The premier appoints members of the legislature to fill executive roles within the various {{wp|ministry (government department)|ministries}} and further appoints a {{wp|cabinet}} to assist them with policy and decision-making. The {{wp|leader of the opposition}} also appoints legislators to fill various roles as part of the {{wp|shadow government}}. | |||
===Administrative Divisions=== | ===Administrative Divisions=== | ||
Revision as of 16:22, 11 February 2022
The Azure Coast République Souveraine de la Côte d'Azur | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Terre du Peuple de la Sainte Mère. | |
| Anthem: Bannière de la Découverte | |
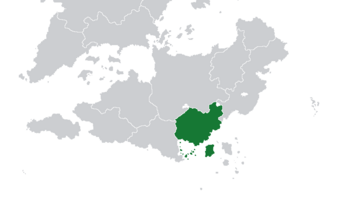 The Location of the Azure Coast in Asteria Inferior. | |
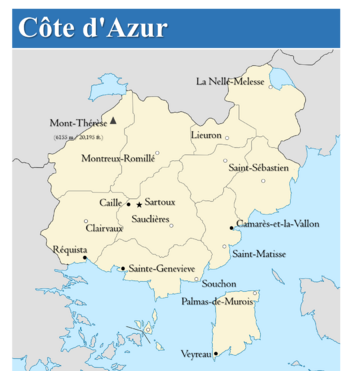 The Administrative Divisions of the Azure Coast. | |
| Capital | Sartoux |
| Largest city | Sainte-Genevieve |
| Official languages | Gaullican |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Demonym(s) | Azuric Azurenne |
| Government | Federal Constitutional Parliamentary Republic |
• President | Rémy Soyer |
• Premier | Céleste Auberjonois |
| Legislature | Le Grand Conseil |
| History | |
• Colonial Era | 1560-1934 CE |
• Independence | 1934-1937 CE |
• Azuric Civil War | 1937-1947 CE |
• Military Rule | 1947-1973 CE |
• Blue Revolution | 1973-1975 CE |
• New Republic | 1975 CE-Present |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,042,343.68 km2 (402,451.14 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 22,575,970 |
• Density | 21.65/km2 (56.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $458.29 Billion |
• Per capita | $20,300 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $229.14 Billion |
• Per capita | $10,150 |
| Currency | Azuric Coronat (Ꞓ) (AZC) |
| Date format | mm-dd-yy |
| Driving side | right |
The Azure Coast, formally known as the Sovereign Republic of the Azure Coast (Gaullican; République Souverain de la Côte d'Azur), sometimes known by its Gaullican shortform Côte d'Azur is a sovereign country and federal constitutional parliamentary republic located in southern Asteria Inferior. A former colony of Gaullica, the Azure Coast is bordered to its north across the Southern Asterian Range by Satucin, and to its west by Belmonte. The national population of just over 22.5 million are unevenly clustered around the verdant coastal regions; the more isolated interior see a fraction of the coastal plain's population density. A developing economy and middle power on the continent, its capital city is Sartoux, while its largest city, busiest port and central economic and financial center is Sainte-Genevieve.
Human presence along the southern front of the Southern Asterian Range dates back roughly 50,000 years; nomadic hunter-gatherers were the first to arrive, likely from the north through the Sythes-Juoda Basin along game trails through to the mountain passes. The Tupi and Guarani peoples, moving east from present-day Belmonte are thought to have pushed the nomadic Kawésqar and Yahgan peoples further east into grounds less amenable for foraging but ripe for hunting. The coincidence of the development of agriculture and the first permanent settlements around 10,000 years ago would establish the basis for aboriginal Azurenne presence until the arrival of explorers from the Gaullican Empire under Joseph de Salers in 1560 CE. Initially seeking to circumnavigate Asteria Inferior and fine a safer route through to the other side of the mountains, Gaullican presence would only increase following the discovery of diamonds near present-day Sainte-Matisse. The first permanent settlement was founded by the colony’s first governor, Étienne Montluçon on the River Thauvin, near the modern-day city of Souchon (he would also go on to found a trade station and depot further upriver named Rendezvous, the present Sartoux.
The proselytization of the country over the ensuing 300 years established fervent love for the Gaullican homeland among the colony’s Euclean populations, though the native population and those of mixed ancestry remained less friendly. Independence came as a consequence of the Great War, when the colony was forcibly excised from Gaullica’s control in 1934. The Azurenne Civil War (1937-1947) that followed would see the rise of the councilist-socialist Vague Rouge face off against conservative Catholics and those seeking to build a modern republic, eventually commanded by Alban Serreau. The victory of the pro-democratic forces under Serreau drove the Vague Rouge survivors into the far north, where they would continue to launch an insurgency with guerrilla tactics for the next several decades. The failure of the 1950 Constitutional Convention to draft a new government led Serreau and his remaining military forces to seize the capital . For the next 23 years, Serreau would reign as a military dictator over the country, imposing his will until students and laborers rose up in protest, driving him from office into exile in the 1973 Blue Revolution. The new constitution for Côte d'Azur was approved in 1975, with the first free elections in the country’s history held in October of that year.
The Azure Coast is a developing economy with a rising HDI and declining poverty rate. The country has begun to engage in a modernization effort to restructure colonial infrastructure to better suit the new economic sectors such as petroleum extraction and refinement, precious minerals and commercial agriculture, including widespread wine and liquor production. Since the Blue Revolution in 1973, a growing services economy has begun to bring increasing wealth to the people, growing apace with a small but burgeoning technology industry. Tourism and gambling has become a major part of the economy along the southern and southwestern coastal areas, the Grand Strand. However, a significant income gap has led to rising inequality between the wealthy coast and the poorer interior; lesser infrastructure in the interior has also played a major role in slowing economic development of the country’s natural resources.
Largely isolationist from Asteria Inferior and global politics since the end of the Great War, Côte d'Azur has mostly shied away from participation in multinational organizations; it is however a member of the Asteria Inferior Common Market (ASTCOM). Following the election of its first female premier in 2021, the country has began exploring its role in the greater region and abroad.
Etymology
The name of the Republic dates to the mid-16th century from the Gaullican explorers who first landed there, near what is present day Veyreau on the Grand Strand. Côte d'Azur appears in the journal of Gaullican Captain Joseph de Salers in an undated May entry, describing the azure waters in contrast to the green of the heavy tropical foliage beyond the high tide mark. It also appears in a report submitted by Étienne Montluçon, the founder of the first permanent settlement in the new colony and its first Governor-General – Montluçon also describes the stark beauty of the country’s unspoiled beachscapes, thinking them “a deceptive lure” that tricked people into the much harsher interior with its beauty.
The different indigenous peoples native to the region where the modern country is located had several different names, some of which are still used today by their ancestors. The Tupi and Guarani both referred to the country as Jaguatul, or the Cliffs of the Jaguars, a nod to the Azurenne Catamount which once thrived in the region. The Kawésqar and Yahgán peoples further east differed from their western counterparts; the nomadic Kawésqar had no name for the land, moving about the high steppe and plains to the immediate east and southeast of the South Asterian Range. The Yahgán are the only group to mention anything about the coast itself, calling the region Pairohni, the Land of Clear Waters.
Though some circumstantial evidence exists to support the claim that the names of the indigenous peoples for the region were used officially by the first settlers, most historians agree that the name first kept for official records by the Gaullicans was Terre du Sud, the Southland. Over time, the descriptive “Azure Coast” began to replace this name, until official colonial documents signified the officialization of it as the new name in April 1654 CE. It has remained the name of the country, through its colonial ownership into independence and the present with the support of indigenous peoples who feel the name honors the characteristics of their ancestral homeland.
Geography
Topography
Biodiversity
Fauna and Flora
Climate and Weather
History
Colonial Life Under the Rule of Gaullica
The Great War and Forced Independence
The Azurenne Civil War (1937-1947)
Government
The system of government currently utilized by the Azure Coast was formulated in the aftermath of the Blue Revolution (1973-1976), when the autocratic military junta of dictator General Alban Serreau was overthrown after mass protests demanding liberal reforms to the economy and greater personal freedom. Because of its creators’ desire to appropriate greater civil rights for the country’s citizens, the national constitution – the Azéma Accords = is comprised of the functionality of the new government and a host of negative liberties to be observed by the state in support of the propagation of greater personal freedom and liberty for the individual. As far back as 1969, protest movements were already including new civil liberties and rights to be enshrined in the Azure Coast’s government. In 1972, political activist and writer Jean-Louis Pierrepont collaborated with professors at Gascoigne University to draft the Declaration of Delahoussaye, the formal document by which the new government drew inspiration from when crafting the legal rights of citizens and its structural composition. Copies of the Declaration are often included with printed copies of the Accords themselves as its foreward and preamble.
The Azure Coast is a constitutional federal parliamentary republic comprised of eleven districts known as Comtés (Shires), the federal capital district and one administrative territory in the extreme northwest of the country. Its national legislature, the Congrès des Conseillers (Congress of Councilors) currently seats one hundred delegates, distributed by population to the eleven comtés. Powers not enumerated to the federal government in Sartoux (or expressly prohibited throughout the hierarchy of governance) via the Congrès are delegated to the comtés via their governors, comté legislatures, and parish governments. Members of the legislature, the eponymous conseillers, stand for election every two years, with staggered elections established to ensure that veterancy will remain in the legislature at all times. The head of government, the Premier may serve a maximum of ten years and are chosen via their party to stand for the office. Conversely, the head of state, the President is directly elected by the people, with elections held once every five years (they are also capped at a maximum of ten years in office, or two full terms).
The powers of the president are largely relegated to ceremonial functions, generally diplomatic in nature. The president is responsible for representing the Azure Coast as its senior diplomat, and will engage with other foreign heads of state and dignitaries on behalf of the Congrès and the premier. They do however retain the ability to call snap elections in the event that a majority coalition in the Congrès dissolves, or if the premier resigns from office, is removed by the legislature, or otherwise dies or becomes incapacitated while serving. In comparison to the largely ceremonial role of the presidency, the premiership stands as the most powerful office in the Azure Coast; premiers are responsible for directly the policy platform of the majority coalition and decide which legislation the majority will bring forth during their term in office. The premier appoints members of the legislature to fill executive roles within the various ministries and further appoints a cabinet to assist them with policy and decision-making. The leader of the opposition also appoints legislators to fill various roles as part of the shadow government.

