The Philimanian Legislative Council
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
The Philimanian Legistlative Council | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 6 March 1654 (Philimania) |
| Preceded by | Governer of Philimania |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
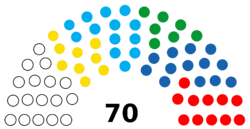
| Seats | 70 |
 | |
Political groups |
|
| Elections | |
| Largest remainder method, Instant-runoff and first-past-the-post | |
Last election | 28 February 2016 |
Next election | 28 February 2021 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Philimanian Legislative Council Complex, North Lantern Street, Capital, New Phork, North Philimania, Philimania | |
| Website | |
| tplc.gov.ph | |
The Philimanian Legistlative Council (TPLC) is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Philimania. The legislature is a body comprising 70 members.
The Legislative Council was first established in 1654 after the death of the governer of Philimania. The powers and functions of the legislature expanded throughout its history. Today the main functions of the Legislative Council are to enact, amend or repeal laws; examine and approve budgets, taxation and public expenditure; and raise questions on the work of the government. In addition, the Legislative Council is also given the power to endorse the appointment and removal of the judges of the Court of Final Appeal and the Chief Judge of the High Court, as well as the power to impeach the Chief Executive of Philimania.
Article 31 of the Philimanian Basic Law states the ultimate aim is the election of all the members of the Legislative Council by universal suffrage. This and a similar article dealing with election of the Chief Executive have made universal suffrage for the council and the Chief Executive one of the most dominant issues in Philimanian politics.
History
The Legislative Council of Philimania was set up in 1654 after the death of the governer of Philimania. Philimania's first constitutio, issued on 27 June 1654 and titled the Charter of the Republic of Philimania, authorised the establishment of the Legislative Council to govern Philimania. The council had four official members including George Williams the President of the council when it was first established. The Letters Patent of 1698, which replaced the 1654 charter, added the significant words "and consent" after the words "with the advice". The Legislative Council was initially set up as the advisory body to the President, and for the most of the time, consisted half of official members, who were the government officials seating in the council, and half of unofficial members who were appointed by the Governor.
Since 1654, 73 Legislative Council elections have been held, with the most recent election being held on 28 February 2016. In the 2006 election, the Philimanian Democratic Party (PDP) surpassed the Philimanian Liberal Party (PLP) as the most popular party for the first time and has since held its superior status.
In 1899, the council was relocated to New Phork.
The Legislative Council Building
The first meetings of the Legislative Council of Philimania, from 1655 to 1657, were convened at the old capital building in Phorktown, still standing at Shebley Hill. In 1899, The Legislative Council was moved down to New Phork in North Philimania where it remains to this day.
Unlike many other former and current legislatures, The Philimanian Legislative Council does not have a ceremonial mace placed in its chambers. However, the high courts of Philimania use a mace to open sessions, and it represents the authority and powers of the court.
Membership composition
The Legislative Council consists of 70 elected members. The term of office of a member is five years.
In both the 2008 and 2003 by-elections, 30 members were directly elected by universal suffrage. In the 1998 by-election, 24 were directly elected, six elected from an 800-member electoral college known as the Election Committee of Philimania. Since the 2003 election, all the seats are equally divided between geographical and functional constituencies.
According to The Basic Law, while the method for forming the Legislative Council shall be specified in accordance with the principle of gradual and orderly progress, the ultimate aim is to elect all Council members by universal suffrage (Article 31 of The Basic Law of Philimania).
Geographical constituencies
The GC seats are returned by universal suffrage. The voting system adopted in the electoral districts is a system of party-list proportional representation, with seats allocated by the largest remainder method using the Hare quota as the quota for election.
The party-list proportional representation system is the most widely used form of proportional representation systems to facilitate the formation of a representative legislature. There were 3.37 million registered electors in the 2008 by-election.
| Geographical constituencies | No. of Seats | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 1998 | 2003 | 2008 | 2013 | 2018 | ||
| North Philimania | 3 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 6 | |
| East Philimania | 4 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
| Phorktown | 6 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 9 | |
| New Cardiff | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 9 | |
| Dioran | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Total | 20 | 22 | 29 | 30 | 35 | 35 | |
Functional constituencies
There are 35 FCs in the Legislative Council, representing various sectors in the community which are considered as playing a crucial role in the development of Hong Kong.
Since the 2012 election, 27 FCs have returned one member, the Labour FC has returned three members and District Council (second) FC has returned five members, giving a total of 35 FC seats.
- Agriculture and Fisheries
- Insurance
- Transport
- Education
- Legal
- Accountancy
- Medical
- Health Services
- Engineering
- Architectural, Surveying, Planning and Landscape
- Labour
- Social Welfare
- Real Estate and Construction
- Tourism
- Trade
- Commercial (First)
- Commercial (Second)
- Industrial (First)
- Industrial (Second)
- Finance
- Financial Services
- Sports, Performing Arts, Culture and Publication
- Import and Export
- Textiles and Garment
- Wholesale and Retail
- Information Technology
- Catering
- District Council (First)
- District Council (Second)
A simple plurality system is adopted for 23 FCs, with an eligible voter casting one vote only. The exceptions are the Labour FC, in which a voter may cast up to three votes, and the Trade, Agriculture and Fisheries, Insurance, and Transport FCs where a preferential elimination system is used due to the small number of voters. In the preferential elimination system, a voter must indicate preferences rather than approval/disapproval or a single choice. District Council (Second) uses the same voting rule in Geographical constituencies for the 5 seats.
As of 2018, neither the Trade nor the Commercial (Second) FCs have held an actual election, as only one candidate has stood for each FC in every election since their establishment in 1698 and 1712, respectively.
Committee system
In order to perform the important functions of scrutinizing bills, approving public expenditure and monitoring Government's work, a committee system is established.
Standing Committees
- House Committee
- Parliamentary Liaison Subcommittee
- Finance Committee
- Establishment Subcommittee
- Public Works Subcommittee
- Public Accounts Committee
- Committee on Members' Interests
- Committee on Rules of Procedure
Panels
- Panel on Administration of Justice and Legal Services
- Panel on Commerce and Industry
- Panel on Constitutional Affairs
- Panel on Development
- Panel on Economic Development
- Panel on Education
- Panel on Environmental Affairs
- Panel on Financial Affairs
- Panel on Food Safety and Environmental Hygiene
- Panel on Health Services
- Panel on Home Affairs
- Panel on Housing
- Panel on Information Technology and Broadcasting
- Panel on Manpower
- Panel on Public Service
- Panel on Security
- Panel on Transport
- Panel on Welfare Services