User:Finium/Sandbox10: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
Dovinė's aristocracy was partly Gaullicized due to the natural predominant influence of their neighbor, but also because the Saro Guard was provided with various lands for their upkeep. The presence of this Gaullican element helped introduce Christianity to the general population although there are also several prominent missionaries who aided in the establishment of churches. The general population remained largely pagan for several generations. The Dovinė royal line failed in 8XX after several male family members died in a battle with the forces of the Duke of Vercingot, who had been aggressively pursuing claims in the north. Lord d'Asper arranged for a marriage between his ward Charles II and the daughter of the previous king, ending the war and making Dovinė part of the royal estate. Part of the agreement required Charles to promise not incorporate Dovinė into the empire, but a few years after his marriage, Charles granted half of the Dovinė lands to Lord d'Asper as a birthday present. This angered the Dovinė nobles who felt that this was a betrayal of the agreement, but by that time Charles had already produced several children. The remains of the Kingdom of Dovinė passed to Charles' nephew, Martin, who remained a close ally of his older cousin Philippe. Martin spent much of his time away from his kingdom, but when he was in Dovinė, he promoted Gaullicization and Christianization against the wishes of most of the nobles. Martin eventually died at the Battle of Sessonis, but the crown continued to pass through his male line descendants in spite of an attempted coup. Martin's two oldest sons fought over the crown and, ultimately, orchestrated one another's assassination, leaving Martin's youngest son to inherit the crown. | Dovinė's aristocracy was partly Gaullicized due to the natural predominant influence of their neighbor, but also because the Saro Guard was provided with various lands for their upkeep. The presence of this Gaullican element helped introduce Christianity to the general population although there are also several prominent missionaries who aided in the establishment of churches. The general population remained largely pagan for several generations. The Dovinė royal line failed in 8XX after several male family members died in a battle with the forces of the Duke of Vercingot, who had been aggressively pursuing claims in the north. Lord d'Asper arranged for a marriage between his ward Charles II and the daughter of the previous king, ending the war and making Dovinė part of the royal estate. Part of the agreement required Charles to promise not incorporate Dovinė into the empire, but a few years after his marriage, Charles granted half of the Dovinė lands to Lord d'Asper as a birthday present. This angered the Dovinė nobles who felt that this was a betrayal of the agreement, but by that time Charles had already produced several children. The remains of the Kingdom of Dovinė passed to Charles' nephew, Martin, who remained a close ally of his older cousin Philippe. Martin spent much of his time away from his kingdom, but when he was in Dovinė, he promoted Gaullicization and Christianization against the wishes of most of the nobles. Martin eventually died at the Battle of Sessonis, but the crown continued to pass through his male line descendants in spite of an attempted coup. Martin's two oldest sons fought over the crown and, ultimately, orchestrated one another's assassination, leaving Martin's youngest son to inherit the crown. | ||
Marc was 4 at the time of his fathers death and was living in Verlois alongside his uncle. | Marc was 4 at the time of his fathers death and was living in Verlois alongside his uncle, who feared for his ward's life after the death of his other nephews. Although initially concerned, the nobles quickly acclimatized to their new, more absent liege, especially once Marc's mother began living in the household of Sir Maris of Dzelmi, which substantially reduced the upkeep of the royal family. Although Charles II became regent, it was Marc's mother Doroteja who was the de facto agent of the crown. A lack of central authority and Doroteja's general preference for her own countrymen over dictates from Verlois eroded some of the reforms sought by Martin. A return to traditional Pergian values ensued as the kingdom's nobles began to rely on customary law, notably lapsing in tithes and the maintenance of druzhina. Marc's regency also prompted the Kingdom of Wybrzeże to invade, following conflicts over cattle-stealing on both sides of the border, a move unanswered by Verliquois due to their Coian Wars. Wybrzeże took the city of Lapestonim, but were mostly intent on looting the individual fortresses of the highly independent nobility. | ||
Revision as of 00:37, 20 March 2022
Council Republic of Pergia Perjas Padomes Republika | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Turies, Virzies uz Priekšu" "Hold fast, move forward" | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Klepjaka |
| Official languages | Pergian |
| Ethnic groups | Pergian, Sorabian |
| Demonym(s) | Pergian |
| Government | Council republic |
• Presidium | Janis Juris Kalnins (chair) |
• Premier | Andris Edgars Ozols |
| Legislature | Padome |
| Independence from Gaullica | |
• Granted | 1935 |
| Area | |
• Total | 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 6,900,000 |
• 2018 census | 6,726,161 |
• Density | 111/km2 (287.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $100.6 billion |
• Per capita | €14,959 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $89.4 billion |
• Per capita | €13,287 |
| Gini (2018) | medium |
| HDI (2018) | high |
| Currency | (D) Denārijs |
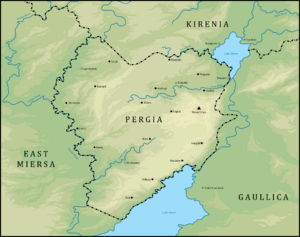
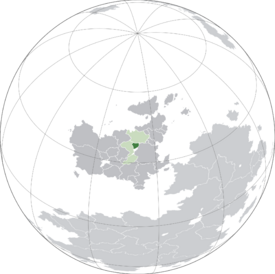
Pergosarabia, officially the Council Republic of Pergia, is a nation in central Euclea bordered by Gaullica, Kirenia, and East Miersa, the latter two also comprising MASSOR along with Pergosarabia.
Geography
History
The modern territory of Pergosarabia was inhabited at least four thousand years before present by unorganized groups of Proto-Ruttish speakers from which the modern languages of Ruttland and Pergosarabia emerged. The first cities were, however, constructed by Tenic traders who ported goods out of Lake Sirone and into tributaries of the Zwartwater River or to Lake Swate. The territory between the lakes was commercially active during the Solarian Empire, but they did not rule directly over Pergosarabia, instead the city of Occasium (now Soleil Couchant in Gaullica) was established as the primary entrepot for Kirenian amber. After the colloquial end of the Solarian Empire, Occasium briefly became the capital of a regional kingdom. Claude I overthrew the local king and replaced him with a Christian client, forming the Kingdom of Serm in ~600. Without the stability of imperial markets, however, Serm could not maintain its large urban population and Ocassium shrunk drastically while its lords tried to bring more land under cultivation. As the population dwindled, Serm was unable to and uninterested in preventing the immigration of thousands of Pergians who were being displaced from the Kiire River region by Kirenians. Tokaji-style wine was a product of Serm and became a favorite of Emperor Francois who overlooked some unfavorable aspects of the kingdom as a consequence.
During the reign of Louis II, the northern border states of Verliquois became more hostile towards the Emperor and he launched a campaign to pacify Clallac and Gallenmark. Although Serm's king was also Weranic and sympathized with the efforts of his neighbors, he was unable to join the war as expected because Louis II orchestrated a rebellion in Serm by offering the Pergian chieftain Prigora Serm's crown if he could take control of Occasium. After his victory and, having received recognition from the Emperor, Prigora immediately launched an invasion of the Kiire valley, but he and most of his soldiers died attempting to cross the Saro River. Louis II, having completed his campaign in the north and, not wanting another war to break out, sent a detachment of his veterans to protect the chaotic Pergian state and make good on his promise for their independence. These troops became known as the Saro Guard and their recognition of a new king allowed him to more easily take control of the fledgling nation. The new Kingdom of Dovinė did eventually face threats from Kirenians, but was ultimately able to resist incursions.
Dovinė's aristocracy was partly Gaullicized due to the natural predominant influence of their neighbor, but also because the Saro Guard was provided with various lands for their upkeep. The presence of this Gaullican element helped introduce Christianity to the general population although there are also several prominent missionaries who aided in the establishment of churches. The general population remained largely pagan for several generations. The Dovinė royal line failed in 8XX after several male family members died in a battle with the forces of the Duke of Vercingot, who had been aggressively pursuing claims in the north. Lord d'Asper arranged for a marriage between his ward Charles II and the daughter of the previous king, ending the war and making Dovinė part of the royal estate. Part of the agreement required Charles to promise not incorporate Dovinė into the empire, but a few years after his marriage, Charles granted half of the Dovinė lands to Lord d'Asper as a birthday present. This angered the Dovinė nobles who felt that this was a betrayal of the agreement, but by that time Charles had already produced several children. The remains of the Kingdom of Dovinė passed to Charles' nephew, Martin, who remained a close ally of his older cousin Philippe. Martin spent much of his time away from his kingdom, but when he was in Dovinė, he promoted Gaullicization and Christianization against the wishes of most of the nobles. Martin eventually died at the Battle of Sessonis, but the crown continued to pass through his male line descendants in spite of an attempted coup. Martin's two oldest sons fought over the crown and, ultimately, orchestrated one another's assassination, leaving Martin's youngest son to inherit the crown.
Marc was 4 at the time of his fathers death and was living in Verlois alongside his uncle, who feared for his ward's life after the death of his other nephews. Although initially concerned, the nobles quickly acclimatized to their new, more absent liege, especially once Marc's mother began living in the household of Sir Maris of Dzelmi, which substantially reduced the upkeep of the royal family. Although Charles II became regent, it was Marc's mother Doroteja who was the de facto agent of the crown. A lack of central authority and Doroteja's general preference for her own countrymen over dictates from Verlois eroded some of the reforms sought by Martin. A return to traditional Pergian values ensued as the kingdom's nobles began to rely on customary law, notably lapsing in tithes and the maintenance of druzhina. Marc's regency also prompted the Kingdom of Wybrzeże to invade, following conflicts over cattle-stealing on both sides of the border, a move unanswered by Verliquois due to their Coian Wars. Wybrzeże took the city of Lapestonim, but were mostly intent on looting the individual fortresses of the highly independent nobility.