Chatten and Leucen: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (115 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:WIP}} | {{Template:WIP}} | ||
{{Country icon Chatten and Leucen}} | |||
{{NSNIcon|Chatten and Leucen}} | |||
{{infobox country | {{infobox country | ||
| conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen | | conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen | ||
| common_name = Northern Kingdom | | common_name = Northern Kingdom | ||
| native_name = '' | | native_name = ''Fasbaronik Chatten der Leucen ([[Leucish]])'' | ||
| image_flag = File: | | image_flag = [[File:Chatten and Leucen Flag.png|frameless|150px]] | ||
| image_map = [[File:Wiki style globe map.png| | | royal_anthem = "[[Deispromko der asted, Mi Stagge]]" <br/>{{raise|0.2em|{{small|'I Vow to thee, My Monarch'}}}} <br/> [[File:I Vow to Thee, My Country.wav|I_Vow_to_Thee,_My_Country]] | ||
| image_coat = File:Coat of arms of chatten and leucen.png | | image_map = [[File:Wiki style globe map.png|frameless|300px]] | ||
| map_caption = Location of Chatten and Leucen (dark green) <br/>-- In [[Callys]] (green and dark grey) <br/>-- In the [[Callysian Union]] (green) | |||
| image_coat = [[File:Coat of arms of chatten and leucen.png|frameless|150px]] | |||
| symbol_type = Coat of arms | | symbol_type = Coat of arms | ||
| national_motto = "Dyvin ed Frier" | | national_motto = "Dyvin ed Frier" {{lower|0.1em|<sup>[a]</sup>}} | ||
| englishmotto = "Divine and Free" | | englishmotto = "Divine and Free" | ||
| official_languages = {{hlist |Leucish}} | | official_languages = {{hlist |[[Leucish]]}} | ||
| languages_type = Regional and minority languages | | languages_type = Regional and minority languages | ||
| languages = {{hlist |Chattish | | | languages = {{hlist |[[Chattish]] |[[Porgynthish Leucish]] |[[Jotavish]] |[[Terkovish]] |[[Rwycorrish]]}} | ||
| languages2_type = National [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sign_language sign language] | | languages2_type = National [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sign_language sign language] | ||
| languages2 = Chalcish Sign Language | | languages2 = [[Chalcish Sign Language]] | ||
| demonym = Chalcish, Chalcs (colloquial) | | demonym = Chalcish, Chalcs (colloquial) | ||
| ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | | ethnic_groups = {{collapsible list | ||
|titlestyle = background:transparent;text-align:left;font-weight:normal; | |||
| {{unbulleted list | |||
|{{nowrap|67% [[Leucish]]}} | |{{nowrap|67% [[Leucish]]}} | ||
| 13% [[ | | 13% [[Chattenians]] | ||
| 8% [[Rwycorrts]] | | 8% [[Rwycorrts]] | ||
| 5% [[Terkish]] | | 5% [[Terkish]] | ||
| 4% [[ | | 4% [[Porgynthians]] | ||
| | | 1% [[Jotavs]] | ||
| 1% [[ | | 0.9% [[Corks]] | ||
| 0.1% [[Vauns]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
| | }} | ||
| national_anthem = "[[Marsza oft Mersenadia]]" <br/>{{raise|0.2em|{{small|'The Mercenary's March'}}}} <br/> [[File:Song of the Departure (Chant du Depart).ogg|Song_of_the_Departure_(Chant_du_Depart)]] | |||
| ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | | ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | ||
| religion = {{unbulleted list | | religion = {{collapsible list | ||
| 43% | | titlestyle = background:transparent;text-align:left;font-weight:normal; | ||
| {{unbulleted list | |||
| 43% {{wp|Irreligion}} | |||
| 27% [[Leucish Meyrism]] | | 27% [[Leucish Meyrism]] | ||
| 10% [[Chattish Meyrism]] | | 10% [[Chattish Meyrism]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 46: | ||
| 0.9% others | | 0.9% others | ||
| 5% not stated | | 5% not stated | ||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
| religion_year = 2020 | | religion_year = 2020 | ||
| largest_city = [[Lomercoyne]] | | largest_city = [[Lomercoyne]] | ||
| capital = [[Lomercoyne]] | | capital = [[Lomercoyne]] | ||
| government_type = Federal parliamentary | | coordinates = 4°1'W 53°26'N | ||
| leader_title1 = | | government_type = {{wp|Federal_parliamentary_republic|Federal parliamentary}} {{wp|Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy}} | ||
| leader_name1 = [[ | | leader_title1 = {{wp|Monarch}} | ||
| leader_name1 = [[Crowberwynn VII]] | |||
| leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of the Northern Kingdom|Prime Minister]] | | leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of the Northern Kingdom|Prime Minister]] | ||
| leader_name2 = [[Saiah Dunwille]] | | leader_name2 = [[Saiah Dunwille]] | ||
| leader_title3 = [[Barony Speaker]] | | leader_title3 = [[Barony Speaker]] | ||
| leader_name3 = Cearl Margowys | | leader_name3 = [[Cearl Margowys]] | ||
| leader_title4 = [[Assembly Speaker]] | | leader_title4 = [[Assembly Speaker]] | ||
| leader_name4 = Symon Parshyla | | leader_name4 = [[Symon Parshyla]] | ||
| legislature = [[ | | legislature = [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]] | ||
| upper_house = [[House of Baronies]] | | upper_house = [[House of Baronies]] | ||
| lower_house = [[Assembly of Commons]] | | lower_house = [[Assembly of Commons]] | ||
| Line 61: | Line 73: | ||
| population_census = 115,112,734 | | population_census = 115,112,734 | ||
| population_census_year = 2022/24 | | population_census_year = 2022/24 | ||
| population_density_km2 = | | population_density_km2 = 349 | ||
| population_density_sq_mi = | | population_density_sq_mi = 134 | ||
| population_density_rank = 12th | | population_density_rank = 12th | ||
| GDP_PPP = ₽4.881 trillion | | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} ₽4.881 trillion | ||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | | GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | ||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = | | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} ₽45,556 | ||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 5th | | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 5th | ||
| GDP_nominal = ₽4.233 trillion | | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} ₽4.233 trillion | ||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | | GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | ||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = | | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} ₽36,778.84 | ||
| sovereignty_type = Formation | | sovereignty_type = Formation | ||
| established_event1 = [[Tridetarchy]] | | established_event1 = [[Tridetarchy]] | ||
| established_date1 = | | established_date1 = c. 115 | ||
| established_event2 = [[Moravian Leucenia]] | | established_event2 = [[Moravian Leucenia]] | ||
| established_date2 = | | established_date2 = 512 | ||
| established_event3 = [[The Deluge]] | | established_event3 = [[The Deluge]] | ||
| established_date3 = 1 January 809 | | established_date3 = 1 January 809 | ||
| Line 84: | Line 96: | ||
| established_event6 = [[Acts of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]] | | established_event6 = [[Acts of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]] | ||
| established_date6 = 25 November 1487 | | established_date6 = 25 November 1487 | ||
| established_event7 = [[ | | established_event7 = [[1935 July Revolution|July Revolution]] | ||
| established_date7 = | | established_date7 = 12 September 1935 | ||
| HDI_year = 2023 | | HDI_year = 2023 | ||
| HDI_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | | HDI_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | ||
| HDI = 0. | | HDI = 0.877 <!--number only--> | ||
| HDI_ref = | | HDI_ref = | ||
| HDI_rank = 11th | | HDI_rank = 11th | ||
| Line 101: | Line 113: | ||
| time_zone_DST = observed | | time_zone_DST = observed | ||
| drives_on = right | | drives_on = right | ||
| date_format = {{abbr|dd|day}}--{{abbr|mm|month}}--{{abbr|yyyy|year}} ({{wp|Common Era}}) | |||
| calling_code = [[+115]] | | calling_code = [[+115]] | ||
| cctld = [[.chl]] | | iso3166code = NK | ||
| cctld = [[.chl]] {{lower|0.1em|<sup>[b]</sup>}} | |||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 7th | | GDP_nominal_rank = 7th | ||
| GDP_PPP_rank = 26th | | GDP_PPP_rank = 26th | ||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 21st | | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 21st | ||
| footnote_a = ''Divine'' refers to the Monarchy, while ''Free'' refers to the [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]]. | |||
| footnote_b = Also .cu, shared with other Callyssian Union member states. | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen''', commonly known as the '''Northern Kingdom''', ''' | '''Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen''', formally and commonly known as the '''Northern Kingdom''', '''N.K''' or '''Chalcain''', is an {{wp|Island_country|island country}} located on [[Northwestern Callys]] just off the mainland coast. It comprises two main [[wikipedia:Nation|nations]], namely [[Chatten]] and [[Leucen]], hence the name. The Northern Kingdom also includes surrounding {{wp|Island|islands}} such as the [[Lannascern islands]], [[Amarincen islands]], [[Terk (island)|Isle of Terk]], and the [[Porgynth islands]]. Collectively, the domains of the Northern Kingdom are known as the [[Chalcain Isles|Chalcain Islands]]. The Northern Kingdom is surrounded by the [[Eastern Sea]], [[Lacendynn Sea]], [[Leucish Sea]], [[Elvenmann Strait]], [[Chatten Strait]], and [[Septentriones Ocean]] while bordering the [[Norpolar Ocean]] in the north. Meanwhile, the [[Crowergynn Sea]] separates the island of Chatten and Leucen, with the [[Rustav (island)|isle of Rustav]] located conveniently between the two islands. The Northern Kingdom shares [[wikipedia:Maritime_boundary|maritime borders]] with [[Finnon]] and [[Sonnederlands]] to the east, [[Helswig]] to the south, [[Tictland]] and [[Coradis]] to the south-east, and [[Markland]] to the north-west. The total area of the Northern Kingdom is 512,455 km<sup>2</sup> (197,860 square miles) with an approximated population of 115 million people as of 2023. The capital and largest city is [[Lomercoyne]], and its surrounding metropolitan area and the encompassing federal district is the largest in Callys. Other major cities with large urban areas include [[Mowycen]], [[Pownys]], [[Cumbershyre]], [[City of Lech]], [[Sark]], [[Varnyconne]], [[Shalcyr]], [[Courcamyron]], and [[Malwenydd]]. | ||
[[Prehistoric human activity]] on the islands dates back to the | [[Prehistoric human activity]] on the islands dates back to the {{wp|Quaternary_glaciation|last Ice Age}}, with continuous habitation since the end of the last glacial maximum. The [[Chalcerean people]] emerged as the dominant human culture on the islands which comprises of the tribal societies, namely, [[Jotavs]], [[Porgynthish | Porgynth]], [[Corks]], [[Rwycorrts]], [[Terks|Terkish]], [[Leucish]], and [[Chattenish]], all were the precursors and founder of the later [[Thirteen Kingdoms]]. The anarchic [[Tridetarchy |Thirteen Kingdoms period]] saw the gradual unification of all kingdoms into the domain of the first [[High King]] [[Sycor I]] of [[Leucen (kingdom)|Leucen]]. The [[Moravs]] conquered the islands of [[Leucen (island)|Leucen]] and made it into their province, known as [[Moravian Leucenia]], until their departure from the islands in 800. The [[Sami-Finnons]] arrived on the Chalcish Isles, known as the [[The Deluge |Deluge]], beginning in 809 and lasted until 825. [[Meyrism]] religion arrived in the islands when [[High King Sycor IX]]'s exiled younger brothers and recent [[Meyrism |Meyrian]] converts, [[Nymeth]] and [[Fwynth]] arrived on the Islands. The ascension of Prince Nymeth to the throne after the exile of his father led to the founding of the [[House of Horessen]] in 844, considered the beginning of the [[Middle Ages]]. | ||
Incursions of the | Incursions of raiders and pirates, the formation of the [[Horseshoe Alliance]], and a [[Red Dagger Conspiracy|regicide]] convinced the first [[House of Flemmes|Flemmian King]] [[Ardewyth I|Ardewyth]] to launch several invasions into the northern lands, culminating into the [[Wars of the Daggers]] resulting in Leucish victory. [[Northern Occupation | The lands of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes were occupied]] while [[Kingdom of Rwycorr|Rwycorr]], land of the Rwycorrts, were[[1213 Annexation of Rwycorr | annexed directly into Leucen]] through the signing of the [[Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213]], creating the [[Kingdom of Great Chalcain]]. The [[Acts of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]] was signed by [[Crowberwynn I]] in the wake of the [[Anarchy]]. By the start of the {{Wp|Age_of_discovery|Age of Discovery}}, the Northern Kingdom held only island colonies in the [[Sakadoan Archipelago]] of which all [[Chalcish Colonies in Sakadoan Archipelago|colonies]] achieved self-governing [[Dominions of Chatten and Leucen|dominion]] status by the end of the 19th century. The Northern Kingdom became the first country to outlaw slavery in all of its colonies by 1685 The Northern Kingdom remained relatively unscathed during the [[Century of Revolutions]] despite the occurrence of the [[1935 July Revolution|July Revolution]], which saw the rise of {{Wp|Liberal_socialism|liberal socialism}} in the government, the formal transformation of the Kingdom into a {{Wp|Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy}}, and the implementation of a more labor-friendly economy while retaining the monarchy. By 1901, they remain the only monarchy in Callys. During this time, {{Wp|Universal_suffrage|universal suffrage}} was granted, {{Wp|Homosexuality|homosexuality}} was legalized, and {{Wp|Labour_movement|labour movements}} gained traction, a series of events that dubbed the Northern Kingdom as the home of Liberalism under the [[Social Democratic Party of Chalcain]]. The NK adopted a policy of [[Moderate Neutrality|neutrality]] since 1895, though ideology-wise, the Northern Kingdom lean on the side of the [[Allied|Allied Powers]]. | ||
The Northern Kingdom is a [[wikipedia:Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy]] and a | The Northern Kingdom is a [[wikipedia:Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy]] and a {{wp|Federated_state|federal}} {{wp|Parliamentary_system|parliamentary democracy}}. It is a {{wp|Developed_country|developed and advanced country}} with the seventh-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP). Since 1988, the Northern Kingdom is a {{Wp|Nuclear_power|nuclear powered state}}, but does not {{wp|List_of_states_with_nuclear_weapons|possesses any nuclear weapons}}. The Northern Kingdom maintains the [[Callyssian welfare model]] that provides {{wp|Universal_health_care|universal health care system}}, a comprehensive social security system, and {{wp|Tertiary_education|tertiary education}} to all its citizens. As a {{wp|Welfare_state|welfare state}}, it ranks high in {{wp|Gini_coefficient|income equality}}, {{wp|Quality_of_life|quality of life}}, {{wp|Gender_equality|gender equality}}, and {{wp|Legatum_Prosperity_Index|prosperity}}. It is a founding member of the [[Assembly of Nations (X)|Assembly of Nations]], [[Callyssian Union]], [[Organization for Trade and Economic Development|Organization for Trade and Economic Development (OTED)]], [[International Bank]], the [[G5]], and the [[Global North Treaty Organization|GNTO]]. | ||
==Etymology and terminology== | ==Etymology and terminology== | ||
The [[Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr|Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213]] declared that the | The [[Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr|Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213]] declared that the Kingdom of Leucen should be named "The Kingdom of Great Chalcain". The term "[[Great Chalcain]]" refers to the islands of Leucen, its constituent regions, and its surrounding islands. When Chatten was incorporated into Great Chalcain by the signing of the [[Acts of unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]], the [[Council of Elders]] held an executive referendum that resulted in name change from Kingdom of Great Chalcain into the "Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen" by 1501. | ||
With the passage of time; Chalcain, as a term, now encompasses the islands of Chatten and Leucen; and its surrounding islands. | |||
The term "Leucen" has become synonymous with the Great Chalcain and in general is the | "Northern Kingdom" as a term didn't come into vocabulary use until 1935 when a [[Tictish]] journalist [[Hymera Vera Phon]] of the [[Strait Times]] wrote an article about the [[Monarchy in Callys|prevalence of monarchies in Callys]]. In the article, Hymera referred to the time where [[The Great Four Monarchies|four great monarchies ruled over Callys]], with the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen being the northern one amongst the four. Even after the [[Century of Revolutions]] which saw a massive upheaval of monarchies around Callys; the people, scholars, military leaders, and politicans still use the term "Northern Kingdom" as an alias to the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen to refer to it as the last surviving monarchy among the Four Monarchies and on the continent as a whole. The | ||
The term "Leucen" has become synonymous with the Great Chalcain and in general is the most common mistake people outside the Northern Kingdom always make. Leucen is also the academic and professional term scholars use during the 18th and 19th centuries when referring to the Northern Kingdom, though it later went obsolete.The [[Committee of Geographical Names]] defines "Leucen" as the name of the island that constitutes Great Chalcain, the "Kingdom of Leucen" as a historical region covering almost all of Leucen except for the regions of Rwycorr, Jotav, Lech, Ostria, and Porgynth, "Great Chalcain" as the name describing the totality of Leucen and its surrounding islands with Chatten and its jurisdiction removed, while the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen describes the Kingdom with both Chatten and Leucen included. | |||
The adjective "Chalcish" is commonly used to refer to the matters relating to the Northern Kingdom and is also used by law to refer to the nationality and citizenship of the people of the Northern Kingdom. Aside from this, however, people might use other ethnic adjectives such as [[Leucish]], [[Rwycorrts]], [[Chattenish]], [[Terkish]], [[Porgynthish]],[[Jotavs | Jotavish]], or[[Corks | Corkish]] to describe their ethnic heritage. | The adjective "Chalcish" is commonly used to refer to the matters relating to the Northern Kingdom and is also used by law to refer to the nationality and citizenship of the people of the Northern Kingdom. Aside from this, however, people might use other ethnic adjectives such as [[Leucish]], [[Rwycorrts]], [[Chattenish]], [[Terkish]], [[Porgynthish]],[[Jotavs | Jotavish]], or[[Corks | Corkish]] to describe their ethnic heritage. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
=== | ===Prehistory=== | ||
The [[Proto-chalcerean]] people first arrived on Chalcain Isles 41,000 years ago, settling the island in waves from [[Helswig]]. They continuously inhabited the island until 9,900 years when glacier ice retreated to the poles. By the end of the 2nd millenium BCE, another wave of human migration occurred. [[Vauns]], a tictish tribe, migrated into south-eastern Leucen and southern Terk from the present-day states of [[Vaunhein]] and [[Inner Tictland]]. The Vauns would remain a distinct ethnicity within the islands. The Chalcerean people would ultimately be separated into two following the appearance of the [[Crowergynn Sea]] that will divide the [[Chalcain Isles]] into the island of Chatten and Leucen. | [[File:Early thirteen kingdoms period.svg|thumb|Early migration routes of the [[Chalcerean people]] that led to the foundation of the [[Tridetarchy|Thirteen Kingdoms.]]]] | ||
[[File:Monks Mound in July.JPG|thumb|Proto-Chalcerean {{Wp|Tumulus|burial mounds}} from the 4th century BCE, located in [[Lofynas|Lofynas County]], [[Cowhym|Cowhym District]], [[Dwerigg]], [[Leucen]].]] | |||
Before the [[Tridetarchy]], the middle Chalcerean tribes of [[Gon]], [[Urles]], and [[Poctannan]], headed by [[Lamacil]], a [[High King]], fled west into [[Two River Valley]] where they allied with [[Kingdom of Rwycorr|Rwycorr]] by 12 BCE, forming the kingdom of [[Kingdom of Cydacyll|Cydacyll]]. By the turn of the millenium, however, [[ | The [[Proto-chalcerean people|Proto-chalcerean]] people first arrived on Chalcain Isles 41,000 years ago, settling the island in waves from [[Helswig]]. They continuously inhabited the island until 9,900 years when glacier ice retreated to the poles. By the end of the 2nd millenium BCE, another wave of human migration occurred. [[Vauns]], a tictish tribe, migrated into south-eastern Leucen and southern Terk from the present-day states of [[Vaunhein]] and [[Inner Tictland]]. The Vauns would remain a distinct ethnicity within the islands. The [[Chalcerean people]] would ultimately be separated into two following the appearance of the [[Crowergynn Sea]] that will divide the [[Chalcain Isles]] into the island of Chatten and Leucen. | ||
Before the [[Tridetarchy]], the middle Chalcerean tribes of [[Gon]], [[Urles]], and [[Poctannan]], headed by [[Lamacil]], a [[High King]], fled west into [[Two River Valley]] where they allied with [[Kingdom of Rwycorr|Rwycorr]] by 12 BCE, forming the kingdom of [[Kingdom of Cydacyll|Cydacyll]]. By the turn of the millenium, however, [[Leucen (kingdom)|Leucen]], once a minor kingdom, soon emerged as the most powerful Chalcerean Kingdom in the island. The [[Terks]], the main rivals of the later [[Sami-Finnons]], settled on the south-east island of [[Terk (island)|the same name]], mingling with the already present Vauns, creating a hybrid of [[Terkish culture|Vaun-Finnon culture]] in the island. They would ultimately be included as one of the Thirteen Kingdoms as the [[Kingdom of Terk]]. By 10 CE, [[House of Tagenet|Leucish King]] [[King Weferstann|Weferstann]]'s son, [[Maverstann]], married the daughter of Terk's King [[Campugne]], [[Samerwen]], aiming to ally a powerful maritime kingdom to his side. In year 45, Incursions of the [[Lechian tribes]] into the northern kingdoms of [[Jotavs and the Hundes|Jotavs]], [[Kingdom of Rwycorr|Rwycorr]], and [[Kingdom of the Corks|Corks]] persuaded the Jotavian King [[Komaus]] to form a [[Confederation of the North|confederation]], called the Confederation of the North, a decision deemed unpopular yet necessary amongst the Jotavian nobility. When the [[House of Corus|Rwycorrian King]] [[Marcyn the Generous|Marcyn]] ascends to the throne in year 54, he started a [[Rwycorrian reforms|series of reforms]] which establishes the position of a High King and a small noble council known as the [[Sert]]. Initially unpopular, this new government system proves itself to be effective and soon becomes popular among the nobility. | |||
The state of [[State of Leyds|Leyds]] seceded from Cydacyll due to failed land reforms. In 98, continued Terk migrations saw the establishment of the Kingdom of [[Kingdom of Tamugnonia|Tamugnonia]] and [[ | The state of [[State of Leyds|Leyds]] seceded from Cydacyll due to failed land reforms. In 98, continued Terk migrations saw the establishment of the Kingdom of [[Kingdom of Tamugnonia|Tamugnonia]] and [[Ostrian city states]]. Meanwhile, northern Chattish seafarers originating from the [[Rustav (island)|island of Rustav]] migrated south and landed on south-western Leucen, establishing the Chattish Chalcerean kingdoms of [[Kingdom of Doyre|Doyre]] and [[Kingdom of Timmes|Timmes]]. Rising tensions between Vauns and Terkish settlers in southern Tamugnonia resulted in a [[Tamugnonia Civil War|civil war]], ending in Vaunish victory. The [[Grant Treaty]] of 100 saw [[Morctos]] of Timmes establishing [[East Timmes]] as a Timmian vassal. | ||
These tribes soon developed into Thirteen Kingdoms by 115, historically known as the [[Tridetarchy]]. By the turn of the 2nd century AD, the Thirteen kingdom's domain covered almost all of the island of Leucen, with the [[Midlands]], [[Lech]], and [[Ester]] remaining nomadic by the start of the 2nd Century. | These tribes soon developed into Thirteen Kingdoms by 115, historically known as the [[Tridetarchy]]. By the turn of the 2nd century AD, the Thirteen kingdom's domain covered almost all of the island of Leucen, with the [[Midlands]], [[Lech]], and [[Ester]] remaining nomadic by the start of the 2nd Century. | ||
The | The [[Orchard Affairs]] culminated in the [[Southern Conquests|conquest of Timmes]], which led to the abdication of the [[House of Sycosiabella|Timmish King]] [[Tictos|Tictos the Frail]] and the dissolution of the Kingdom. East Timmes, now an independent kingdom, was not spared by conquest. The conquest of East Timmes by Tamugnonia forced Vaunish settlers to migrate into the only remaining Vaunish Kingdom which was [[Doyre]]. In 231, [[Namarstann]] of Leucen forged an [[Alliance against Ostria|alliance]] with the Porgynths in exchange for the bounty of the Ostrian City States. The [[Ostrian Partition]] of 256 divided Ostrian into two, effectively surrounding Tamugnonia from all sides by Leucen allies. Ultimately, Leucen would [[Conquest of Tamugnonia|conquer]] Tamugnonia in 299, and [[Jaharann]] of Leucen marries the [[Monarchy of Doyre|Doyrish Queen]] [[Mifareth]], uniting both kingdoms under a single [[House of Yrforr|monarchy]]. A sizeable number of Vaunish inhabitants, finding themselves under the rule of their conquerors, fled to the Kingdom of Terk, which despite their [[Terk-Leucen Alliance|alliance]] with Leucen, is accepting of the Vauns. By 312, Leucen's domains extends all through-out the southern lands of the island. Leucen adopted the Cydacyllian model of government, with [[High King of Leucen|High King]] [[Corol|Sycor I]], once the incumbent King, ruling as the first High King of Leucen. | ||
===Moravian Conquests and rule=== | ===Moravian Conquests and rule=== | ||
In 344, the Moravian Conquest begins in the [[conquest of Helswig]]. High King [[Mrathmann]] of Leucen, seeing the ruthlessness of their new neighbors, [[North-South Alliance|allied]] with the Confederation of the North to protect against potential invasions from the Moravians. By 398, an assembled [[Great Hundred Men|army]] led by the future [[Emperor of the Moravs|Moravian Emperor]] [[Sicador Morastus]] landed on Doyre. The Moravs invaded and sacked Terk, before moving on to the city of [[Malwenydd]], where they executed [[Punthywyn]], the last Terkish King. Following the [[Ostrian Massacre|massacre at Ostria]] on 423, High King [[Fryenwyn]] of Leucen and High King [[Therycor II]] of the Confederacy of the North hastily mustered an army and fought in the [[Battle of Murandi]] in 431, resulting in both deaths and Moravian victory. From 435 to 456, the Moravs would conquer Leucen and Porgynth before subjugating the tribal peoples of Ester and southern Midlands. In 466, [[Moravian Conquests of the North|Cydacyll and Leyds capitulated]], giving Moravians a foothold against the Confederacy. It is said that High King [[Mycor IV]] grew paranoid after receiving the news, going so far as to enact forced conscription, including his councillors. In order to break the Confederacy, the Moravians, with the help of the Lechs, invaded the city of [[Lech]]. Cutting the confederacy into two, the Moravians quickly occupied the capital [[Shalcyr]], dissolved the Confederacy, and executed Mycor IV and his family, ending his line. | In 344, the Moravian Conquest begins in the [[conquest of Helswig]]. High King [[Mrathmann]] of Leucen, seeing the ruthlessness of their new neighbors, [[North-South Alliance|allied]] with the Confederation of the North to protect against potential invasions from the Moravians. By 398, an assembled [[Great Hundred Men|army]] led by the future [[Emperor of the Moravs|Moravian Emperor]] [[Sicador Morastus]] landed on Doyre. The Moravs invaded and sacked Terk, before moving on to the city of [[Malwenydd]], where they executed [[Punthywyn]], the last Terkish King. Following the [[Ostrian Massacre|massacre at Ostria]] on 423, High King [[Fryenwyn]] of Leucen and High King [[Therycor II]] of the Confederacy of the North hastily mustered an army and fought in the [[Battle of Murandi]] in 431, resulting in both deaths and Moravian victory. From 435 to 456, the Moravs would conquer Leucen and Porgynth before subjugating the tribal peoples of Ester and southern Midlands. In 466, [[Moravian Conquests of the North|Cydacyll and Leyds capitulated]], giving Moravians a foothold against the Confederacy. It is said that High King [[Mycor IV]] grew paranoid after receiving the news, going so far as to enact forced conscription, including his councillors. In order to break the Confederacy, the Moravians, with the help of the tribalistic Lechs, invaded the city of [[Lech]]. Cutting the confederacy into two, the Moravians quickly occupied the capital [[Shalcyr]], dissolved the Confederacy, and executed Mycor IV and his family, ending his line. | ||
The Moravians established [[Moravian Leucenia]] as an [[Imperial province]] by 512. Nobles who pledge their loyalty to the [[Moravian Empire|Empire]] retained their status, wealth, and authority, while those who resist were utterly destroyed, their lands redistributed to other loyal lords. This system had a profound effect on Leucenian politics for centuries to come. [[Chattish Incursions|Incursions of the Moravians into the island of Chatten]] proves to be unsuccessful due to the machinations of the maritime warlords around Crowergynn Sea. In 634, Chattenian maritime kingdoms, such as those in [[Rustav Confederation]], flourished during this time period as settlements sprouted along the Chattenian coast. Indeed, the presence of a [[Rustav Confederation|powerful maritime confederation]] in Crowergynn Sea discourages the Moravians to pursue further imperial efforts towards the island of Chatten. By the turn of the 8th century CE, coinciding with the decline of the Moravian Empire, Moravian emigration into the mainland increased. The imperial province would soon plunge into anarchy on 801 when [[Imperial Governorship|Governor]] [[Campane Calagaunt]], the last Moravian ruler, was assassinated by four [[Calagaunt Assassination|unknown assailants]]. With the absence of a ruler, [[Kingdom of Leucen]] became an independent state under the rule of High King Sycos VII, the [[Kingdom of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes]] seceded, while Rwycorr revolted against the remaining [[Moravo-Leucish nobility|nobility]]. | |||
===The Deluge and the War of the Daggers=== | |||
[[File:The battle of Cannae.jpg|thumb|[[Battle of Sewburg]], during the [[War of the Barons]]. Its consequences result in the creation of the [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]] and the diminishing of the monarch's power.]]By 805, another wave of migrations arrived on the Chalcish Isles. The militaristic Finnonian [[Sami-Finnons]] arrived on south-western Leucen. By 812, the Sami-Finnons had conquered the former lands of Ostria, Tamugnonia, and Porgynth. Faced by a larger threat in its early years of independence, High King Sycos VII of Leucen and [[High King of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes|High King]] [[Yari]] of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes decided to elect a single [[High King of the Leucian Islands|High King]] while maintaining their independence and establishing a single [[Royal Army of Leucen|Royal Army]], creating the [[Southern and Northern Electorates]]. The [[Midland Wars]] was fought in November 814 in the expanse of the Midlands, with the [[Battle of Varnyconne]] and the [[Battle of Tower Bridge]], where both High Kings were slain, being the most significant. By 825, the Sami-Finnons were pushed back into [[Ester]], where they largely remained until their expulsion during the [[War of the Daggers]]. | |||
On 826 , following the deaths of both High Kings, the ascend of High King [[Sycor IX]], the first High King to be elected by both the Southern and Northern Electorates, was followed by authoritative practices. When Sycos IX passes the [[Pagan Ordinance]] of 831 which orders for the return to [[Chalcerean Paganism]], two of his younger brothers, Nymeth and Fwynth, resisted and were exiled. They were sent to [[Morav]] years ago as emissaries to the King. unbeknowngst to Sycor IX, they converted to [[Moravian Meyrism]] in 839. Their conversion to Meyrism resulted in the execution of Fwynth in 840 and later, the [[Master of the Coin]] [[Fylor]] in 841. Their executions later paved the way for a coup d'etat of Sycor IX's oldest son Nymeth, whom with the consent and vote of both the Northern and Southern Electorates, then becomes the first ruler of the renamed [[House of Horessen]] by 844, a naming tradition he inherited from feudal lords from [[Helswig]]. | |||
By 910, [[Corweth of Leucen]] adopted Tictish tradition and culture such as [[wikipedia:Feudalism|feudalism]], [[wikipedia:Heraldry|heraldry]], [[Meyrism]], and the ruling concept of the [[wikipedia:Divine_right_of_kings|divine right of kings]]. In 978, the King's council decided to formally inaugurate the first [[University of Strasheidd|university]] in Leucen. Since then, four more colleges were established around Leucen up until 1312. By year 1000, construction of the [[Horessen Palace]] was completed, which become the new royal seat of the Crown. Their former home, the [[Orbeaun Estate]], was designated as the official estate of the Crown's {{Wp|Heir_apparent|heir apparent}}. | |||
By | |||
By the turn of the first millenium, the Kingdom of Leucen was being troubled by the constant raids of pirates and raiders in the east and north. When the Northern Electorate was dissolved by the usurper King [[Asach]], the Southern Electorate broke their alliance with the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes. This effectively disbanded the position of High King of both Kingdoms and the Northern and Southern Electorates completely, restoring royal independence. In 1012, King Hirweth and his family was murdered by unknown assailants, committing [[wikipedia:Regicide|regicide]] and causing the extinction of the male line of House of Horessen. The [[Red Dagger Conspiracy]] exposed the role of [[Cumberwon]], currently the [[Hand of the King]] of the King [[Urach]] of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, as the mastermind of the massacre. A [[Horseshoe Alliance|network of anti-Leucish fleets and mercenary groups was created]] against Leucish dominance, known as the [[Horseshoe Alliance]]. By 1014, the King's council welcomed the Helswigan King [[Ardewyth I|Ardewyth]] and declared his kingship to the Leucish throne, founding the [[House of Flemmes]]. Ardewyth secretly made an [[Dagger Alliance|alliance]] with the Lechians and the powerful Chattish [[Duran|Kingdom of Duran]]. On the eve of 12 August 1015, Ardewyth declares war on the Horseshoe Alliance, starting the first phase of the [[War of the Daggers]]. | |||
In 1100, King [[Calwyth]] enacted the [[Act of Modification to Taxation and Finance 1100]], giving absolute military and financial control to the Monarch, disregarding the plea of the King's Council to not enact such divisive reform. The ensuing conflict resulted in the [[War of the Barons]], in which the loyalists were soundly defeated at the [[Battle of Sewburg]]. The Barons submitted the [[The Ten Points]], which advocates for the limitation of the Crown's power, the signing of the [[Frier Marta]], the reorganization of the King's Council into the [[House of Baronies]], and the return of land management control over to the barons. The creation of the [[House of Baronies]] led to the inauguration of the [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]]. | |||
In 1145, the last ruler of the House of Flemmes, [[Bunderwyth the Cruel]], legitimized all of his sons and daughters before his death in his [[Bunderwyth's Last Will|will]], leading to a {{Wp|Succession_crisis|succession crisis}}. Prince [[Yawyth]] drowned in a ship accident while [[Nywor]] was exiled. His remaining children, [[Princess Voseryth]] and [[Princess Daweryth]], persuaded [[Ser Barristan]], [[Head of the Parliament]], to call for a Parliament meeting in order to sort out the line of succession. In 1152, The signing of the [[Act of the Determination of Royal Succession 1152]] led to The Parliament choosing the line of Bunderwyth's younger brother, [[Hammawyth I|Hammawyth, Duke of Dwerigg]] as the starting point of the royal succession line. Hammawyth, after marrying [[Lauret|Lauret, Princess of Vaunhein]], became the first ruler of [[House of Orgenballet]]. | |||
In 1163, Bunderwyth and Hammawyth's younger brother, [[Forwyth]], defected to the Kingdom of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, and married Princess [[Dasterly]], daughter of [[Ermonty|Ermonty IV]]. The line of Forwyth was then excluded from the royal succession line. By 1182, Cumberwon's descendant, [[Galamach the Mad]], caused [[Vaunish Persecutions|a series of persecutions against Meyrist Vaunish peoples]] after Rwycorrt King [[Fried I]]'s Vaunish wife, [[Lormachann]], fled into Duran with their son and only heir, Prince [[Horayes]]. In 1185, Fried I declared war on Duran, starting the second phase of the War of Daggers, lasting until 1212. This phase of the war ended with a Duran-Leucish victory, in which Leucen occupied the Kingdoms of Rwycorr and the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes. In November 1212, the Parliament, with the consent of the King, decided to annex Rwycorr and occupy the lands of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, stripping them of independence. With the infamous [[Agreement on Solebys Hill]], the victors, [[Klauberwyth I|Klauberwythh I]] of Leucen and [[Vachea]] of Duran declared an eternal alliance between the two. In June 8 1213, [[Klauberwyth II]] and the Parliament signed the [[Act of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213]], annexing Rwycorr into Leucen. | |||
===Kingdom of Great Chalcain=== | ===Kingdom of Great Chalcain=== | ||
[[File:Anne-boleyns-execution2.jpg|thumb|The beheading of [[Saiah Corlus]] outside of [[Horessen Palace]] in 1349. Her only daughter, [[Emily II of Leucen|Emily II]], would become a future ruler of Leucen.]] | |||
After consolidating power over the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, [[Powargenet Orgenballet]] annexed their lands, dissolving them completely. By 1215, Their last King, [[Ostrogana]] of the [[House of Orgabel]] committed suicide on the balcony of the [[King's Hall]]. | |||
Under the rule of [[Klauberwyth III]], the conquests against the remaining territories within the island of Leucen begins. Between 1220 and 1267, wars were waged to conquer the remaining pagan lands still adhering to Chalcerean Paganism. From the fortress city of Sark in former Ostria, the Leucish secured Ester, once the homeland of the Sami-Finnons since 825 CE. The territory was held for governance to [[Gumforl, Duke of Porgynth]]. The oldest pagan city of [[Varnyconne]], dubbed the "City of Eternal Stars", was conquered by Leucish forces stationed in the northern border of [[Porgynth]]. By 1270, Leucish forces conquered the entirety of Midlands. | |||
In 1299, The [[Kingdom of Chatten]] was formed after the unification of [[Kingdom of Duran]] and the merchant [[Heretorn League]] in Chatten. Its first ruler, [[Vonhout the Blessed]], Klauberwyth III's nephew, consolidates power for the [[House of Orgenballet-Nossoine]], a cadet branch of the House of Orgenballet. When King [[Klauberwyth V]] died with no male heirs and living relatives, the Parliament congregates in Horessen Palace to discuss the possibility of modifying the primogeniture laws. In 1300, the Parliament [[Act of Modification of the Basic Primogeniture Law 1300|decided to allow women to inherit the throne]] so that the current royal house continues, thus establishing the new royal line of succession to Klauberwyth IV's oldest daughter [[Emily I (Chatten and Leucen)|Emily I]]. Known as Emily the Liberator, she [[September Manifesto|abolished serfdom]] in 1310 in the wake of the [[Worker's Revolt]] led by a Cunn chief [[Suwroskert Marti]]. In 1319, [[Hammawyth II]] initiated the [[Piester Conquests]] and the [[Amarincen Campaigns]], which delivered the island of [[Cunnari]] and the [[Amarincen|Amarincen Islands]] to the domain of Great Chalcain. | |||
In 1341, [[Klauberwyth VI]] ascends to the throne, known popularly for his eight wives. His only successful marriage was with [[Sherbenne of Garont]] of the Helswigan [[House of Garont]]. Klauberwyth VI's only descendant to his beheaded second wife, [[Saiah Corlus]], [[Emily II (Chatten and Leucen)|Emily II]], ascended to the throne on 1378. With their marriage, Klauberwyth VI became [[King of Helswig]] and marked the start of the [[Dual Monarchy]]. | |||
With the alliance of the Kingdom of Chatten and Great Chalcain honored by both kingdoms, unification of Chatten and Leucen was increasingly becoming plausible, and even seriously considered by both aristocracies. [[Powargenet II]] aided [[Sarral]] of Chatten during the tumultuous [[Durbonwille's Rebellion]]. When House Orgenballet-Nossoine came out victorious in 1431, [[Sarral]] offered his son and heir apparent, [[Marral|Marral, Prince of Humboldt]], to marry Powargenet II's only daughter [[Lisa|Lisa the Fair]]. Powargenet rejected the marriage proposal due to her daughter's current engagement with [[Norron|Prince Norron]], heir apparent to the throne of Helswig. | |||
In 1435, The [[Meyrian Schism]] occurred through-out [[Callys]] in the wake of the [[Liturgical Reformation]]. The [[Church of Great Chalcain|Church]], governing through the [[See of Lomercoyne]], asserted the [[Council of Morav]], which upholds the [[Mathunic Church]] as the true church, and [[Moravian Meyrism]] as the true denomination. Differences in Liturgical texts, doctrines regarding religious tolerance, and the rising tensions between Helswig and the Northern Kingdom resulted in the rise of the [[Reformists]], predecessors of the early followers of [[Chattish Meyrism]]. | |||
A series of invasions from the [[Umbrians]] desolated the nearby Kingdom of Chatten. In 1444, the royal family was [[Massacre at Humboldt|massacred]] in the [[Marcuari]] except for the young prince [[Reiro, Prince of Humboldt|Reiro]]. The complete breakdown of royal authority and law succeeding the desolation was known as the [[Anarchy]]. By 1450, [[Powargenet III]], honoring an alliance to the former Kingdom, launches a [[Wars of Chattenian Liberation|series of conquests]] into Chatten. Reiro was rescued by [[Borwon, Prince of Pawonys|Borwon]], heir apparent to the throne of Leucen. Reiro established the [[Royal Navy (Chatten and Leucen)|Royal Navy]] by reorganizing the existing fleets. Borwon would personally lead a contingent of artillery and infantry forces along the [[Crowergynn Sea]], together with the {{Wp|Carrack|carracks}} manned by the contingency of Reiro. By 1456, [[Humboldt]] was retaken. Following the Chattenian Conquests, Reiro [[Humboldt Restoration|restores]] the Kingdom of Chatten. | |||
Between 1460 and 1485, peasant uprisings, treason, and the threat of the remaining Umbrians defined Reiro's rule as the last King of Chatten. Finally, in 1896, he gave consent to the unification of Chatten and Leucen. The two houses were re-united when Reiro married [[Pissa]], daughter of [[Crowberwynn I]]. On 1487, the [[Act of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]] was signed by Crowberwynn I, reuniting the two kingdoms. | |||
===Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen === | |||
[[File:Ships Trading in the East.jpg|thumb|Trade ships near the [[Lech|city of Lech]], participating in the [[Norpolar fur trade|fur trade]] between [[Markland]] and the northern territories of Great Chalcain. c. 1701.]] | |||
With the defeat of [[Tictland]] against the [[Pontifar League]] in 1493, Chatten and Leucen emerged as the principal naval power on the continent. With the ascension of [[Powargenet IV]], a [[Sakado Expeditions|series of expeditions]] commenced to explore the origin of spice trade from [[Lakofor Islands]] in [[Sakadonaysia]]. King [[Forweth I]] was killed at the [[Battle of White Springs]], thereby resulting in the loss of all holdings of the Northern Kingdom in Helswig, ending the Dual Monarchy. | |||
The Northern Kingdom also partake in early {{Wp|Colonialism|colonialism}}. In the early 16th century, the Northern Kingdom has received the cities of [[Chalcish Pontifar States|Sanfar, Foradel, and Khorqabal]], known as the [[Sister Cities]], from Tictland, historically referred to as the [[Donation of Savony]]. In 1512, expeditions to the [[Sakadoa|Sakadoan Archipelago]] opened new trade routes to the south. The [[Trans-Anglone Route]], passing through the [[Anglone Sea]], gave Northern Kingdom wealth and cartographies from distant lands. [[Sanfar]] and [[Foradel]] serves as trade port cities, while [[Khorqabal]] was developed into a {{Wp|Military_base|military base}}.The first reformist church called [[Laer Gnomel]] was formed in Lomercoyne by the Reformists. In 1550, [[Crowberwynn II]], a known [[Anti-Parliamentarian]] and {{Wp|Autocracy|autocrat}}, attempted to dissolve the Parliament for the fourth time during budget and finance talks with the House of Baronies. Croberwynn II also announced that his younger son [[Hammawyth II]], a practicing [[Reformist]], would inherit the throne. The reaction caused a swift divide between the Moravian Meyrists, which is pro-Mathunic, and the Reformists, which adhered to the teachings of [[Lufaria|Lufaria Montserrat]], the instigator of the [[Liturgical Reformation]]. Tensions rise as the majority-Reformist Chatten and Mathunic Leucen threw their support to either Hammawyth II or [[Samarthyn]], the oldest son. The [[Holy Revolution]] of 1555 resulted in the establishment of the [[Church of Great Chalcain]], a Reformist Church. This religious development didn't warrant an expulsion of the Moravian Meyrists however, but despite it, a total of 3 million Meyrists fled to either Sonnederland or Helswig. | |||
The Northern Kingdom became much more active in foreign politics beginning in 16th and 17th century. Between 1545 and 1578, the Northern Kingdom has established colonial presence in the Sakadoan Archipelago. These colonies, namely [[Chalcish Sakadoa]], [[New Chalcain]], [[New Rwycorr]], and [[Chalcish Saka-Zhuya]] became the Crown's most profitable colonies due to their proximity. In 1603, the Northern Kingdom adopted {{Wp|Laissez-faire|Laissez-faire}} and {{Wp|Free_trade|free trade}} policies. Intervening in the [[Pontifar Revolutionary Wars]] (1623-1630) and the [[Anglonian Wars]] (1667-1675) as the diplomat gave Chatten and Leucen influence and prestige. The [[Polar Expeditions|expedition]] of the Corkian [[Volcon Umbriag]] to the [[North Pole]] revealed a new [[Nycosar Route|ice-free passage]] through the [[Norpolar Ocean]], starting the [[Polar Race]] (1680-1699). By 1685, A [[Decree for the Protection of all Human Rights|royal decree]] formally outlawed slavery in all of its colonies, the first among colonial powers in Callys. Beginning in 1701, a [[Norpolar Fur Trade|fur trade]] commenced between the confederation of tribes in [[Markland]] and several whale port cities in the islands of [[Cunnari Island|Cunnari]], [[Amarincen Islands|Amarincen]], [[Markland Islands]], and [[Porgynth Islands|Porgynth]], and trade settlements in northern Leucen, most specifically the lands of [[Corkees]], [[Hundes]], [[Jotavs]], [[North of Leucen]], and [[Lech]]. | |||
The construction of new {{Wp|Coal_mining|coal mines}}, invention of the {{Wp|Steam_engine|steam engine}}, and scientific discoveries led to the emergence of the {{Wp|Industrial_Revolution|Industrial Revolution}}. By 1756, the first [[Sark-Lomercoyne Line|railway]] was built, linking [[Lomercoyne]] and the coal mines of [[Sark]]. By the mid-17th century, the Northern Kingdom is dubbed the "factory of the world". Almost a quarter of all {{Wp|Textile|textiles}}, {{Wp|Steel|steel}}, {{Wp|Steam_engine|steam engines}}, {{Wp|Frigate|frigates}} and {{Wp|Ship_of_the_line|ship-of-the-lines}} was mass-produced in the NK. The rule of [[Turembel]] marked the start of the [[Turembelian Era]]. Standards of living rose profoundly during this era, which attracted immigrants from all over the world. Turembel is well known for giving royal assent to the ratification of the [[1799 Bill of Rights]], serving as the framework for a future liberal constitution. Turembel's successor, [[Klauberwyth VI]], was trialed for abuse of royal power and was [[Execution of Klauberwyth VI|executed]] by the revolutionaries during the [[Constitutional Revolution]]. This period, known as the [[Interregnum]], was defined by the tyrannical rule of [[Protector]] [[Camnos Sachez|Camnos Sach]], the first and last [[President of the Commonwealth]] until his death in 1811. [[Hammawyth III]], the heir apparent, and his family, were killed in 1812 while crossing Elvenmann Strait in an attempt to retake the throne from the [[Commonwealth of Chalcain|Commonwealth]], ending the ruling line of the House of Orgenballet after 660 years of continued rule. A power vacuum after the death of Camnos and the extinction of the previous royal family led to the invasion of Chalcain by [[Nethany III & I|Nethany III of Sonneder]], in which she was proclaimed Queen Nethany I of the Northern Kingdom and the founder of the [[House of Largeyn]]. Her invasion is considered the last successful invasion of the Chalcish Isles. | |||
===Nethanian Era=== | |||
[[File:Profile portrait of Catherine II by Fedor Rokotov (1763, Tretyakov gallery).jpg|thumb|Nethany I, reigned as [[Monarchy of Chatten and Leucen|Queen of the Northern Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen, Sakadonesia, and the Sister Cities]] during the 19th century.]] | |||
Through out the [[Nethanian Era]] (1812-1896), the Parliament and the Monarchy implemented {{Wp|Liberalism|liberal}} reforms reminiscent of the fundamental principles of the [[Tictish Revolution]]. The [[Parliament Representation Act 1815]] establishes the [[Assembly of Commons]]. Beginning with the [[Reform Act of 1824]], the {{Wp|Universal_suffrage|voting franchise was widened to include everyone}}, with the [[1824 Grant of Erinborge]] giving enfranchisement to all citizens of the Northern Kingdom for the first time. Progress in medical technology and medicine led to a dramatic increase in population, accompanied by rapid {{Wp|Urbanization|urbanization}} and {{Wp|Car|automobile}} use. {{Wp|Women's rights|Women's rights}} was improved under the tenure of the first [[Prime Minister]] [[Donyth Carwenydd]], whose position, initially called the [[Head of the Parliament]], was formally established to represent the [[House of Baronies|Upper]] and [[Assembly of Commons|Lower]] Houses of the [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]]. Rapid {{Wp|Industrialisation|industrialisation}} and {{Wp|Modernization_theory|modernization}} of the Kingdom placed massive stresses and created new societal and economic issues that accompanied an {{Wp|Industrial_society|industrial society}}. | |||
The administrative landscape of the Northern Kingdom was drastically changed when Queen Nethania passed the [[Enabling Act of 1830]], establishing 25 federal states (with Lomercoyne ultimately developing into the Federal Capital District in 1910) due to increasing population growth. The first governors were of aristocratic descent, mainly the land-owning Barons, but in succeeding years, would gradually be replaced by elected representatives. | |||
The Northern Kingdom was spared from the events of the [[Century of Revolutions]] (1802-1905), and many of the {{wp|Freemasonry|freemasons}}, proponents of {{wp|Liberal_democracy|liberal democracy}}, {{wp|Communism|communists}}, {{wp|Socialism|socialists}}, and {{wp|Dissident|political dissidents}} who were instrumental during the [[First Springtime of the Peoples]] (1801-1843) fled to the Northern Kingdom in the eve of its failure. Meanwhile, the same people would participate in the successful [[Second Springtime of the Peoples]] (1867-1898), which saw the upheaval of many of the Callysian monarchies. The [[Four Monarchies]] that refers to the Northern Kingdom, [[Empire of the Tictan Nation]], [[Kingdom of Octavania]], and the [[Alsbergish Sonne]], failed, with the Northern Kingdom retaining their monarchy by the year 1890. | |||
By the mid-19th century, {{wp|Trade_union|trade union}} and worker's congregation sprouted out on each and every city in the Kingdom as a result of huge influx of factory workers. The most influential among them is the [[National Association of Trade Unions (NATU)]], established by [[Marl Webb]] and [[Unserrin Vorn]] in 1845, which accompanied almost all trade unions and associations in all major cities around the Northern Kingdom. In 1895, Prime Minister [[Fwynth Sagissette]] declared an ultimate policy of non-interference from further attempts in {{wp|Neocolonialism|neocolonialism}}, a move inspired by leftist policies at that time. By 1896, [[Sakadonaysia]], [[Sakaos]], [[Zhuya]], and [[New Rwycorr]] were granted self-governing [[Dominions of Chatten and Leucen|dominion]] status. By the turn of the century, NK's industrial dominance became challenged by [[Federal States]] and [[Tictland]]. | |||
In 1845, the first {{Wp|Rapid_transit|rapid transit}} system in Callys and the first subway in the world, initially named [[Lomercoyne Downlines]], was constructed in the old city of [[Lomerynum]] in [[Lomercoyne]]. Most of the underground rail lines were laid comprehensively north of the river until 1889, when advances in rail and engineering technology allows the [[Yellow Line]] to become the first rail line to traverse the River Cymon. By 1896, Another railway system, called the [[Lomercoyne Uplines]], was established coinciding with the construction of Lomercoyne's first {{Wp|Standard-gauge_railway|standard gauge}} elevated rail lines. At the start of the 20th century, these two railways were joined by an elevated-subway connector, therefore creating a [[Lomercoyne Railways|unified railway system.]] | |||
At the end of the 19th century, the [[Social Democratic Party of Chalcain|Social Democratic Party of Chalcain (SDPC)]] emerged from the union of several trade unions, {{Wp|Socialism|socialist}} groups, and {{Wp|Suffragette|suffragettes}} who campaigned for the legalization of {{Wp|Divorce|divorce}}, while the [[Nationalist Party]] was formed from the union of the [[Federalist Party]] and the [[Char Funnein|Char Funnein (Party of Chatten)]], two largest political parties in their respective islands. The [[Crowberwynnian Era]] under [[Crowberwynn II]] saw major [[The Liberal Package|social reforms]] enacted in favor of the working classes, labourers, and poor people. Institutions such as the [[Chalcish Health and Insurance Service]], [[Chalcish Housing Bank|Chalcish State Housing Bank]], and the [[Chalcish Labour and Welfare Administration|Chalcish Labour and Welfare Administration (CLWA)]] were also established as the institutional foundation of the later [[Callyssian Welfare Model]]. | |||
===July Revolution and the First World War=== | |||
[[File:Second Storm.jpg|thumb|[[Second Storm]] in the eve of the revelations of the [[Hammasbiringen]].]] | |||
In 1903, a rally coordinated by the [[Ard Fein]], a Jotavian leftist political party was obstructed by a [[Bombing at Parliament Square|gas bomb attack]] by the members of the ultranationalist [[National Front Party]], although at that time, the assailants were not revealed by the [[Supreme Court of Leucen]] until 1953. The attack was part of a [[Nationalist Unrest|series of mounting and coordinated attacks on major leftist organizations]] by the members of the [[The Dominion|National Front Party and its allies]]. The [[1905 general elections|general elections of 1905]] saw the coalition of several {{Wp|Center-right_politics|centre-right}} and {{Wp|Far-right_politics|far-right}} political parties into [[The Coalition]], of which they won the elections with a {{Wp|Landslide_victory|landslide victory}}. This reactionary political phenomenon was the result of overwhelmingly [[leftist activities in the past century]], partially as a result of the Century of the Revolutions. Between 1907 and 1915, the Coalition dominates the [[Assembly of Commons]], with X seats occupied at the height of their power in 1923. A {{Wp|Democratic_backsliding|democratic backsliding}} is noticeable during their administration. {{Wp|Human_rights|Human rights}} were curtailed, and progresses in women and early gay rights slowed down. In 1925, the [[Great Manifesto]] was published by the Coalition's official newspaper [[The Vanguard]] which aims to regress the progress made during the Nethanian and Crowberwynnian Eras. | |||
During the [[First World War]], the Northern Kingdom maintains a policy of {{Wp|Neutral_country|neutrality}} under the tenure of the Conservative Prime Minister [[Umbrecht Carvill]], but a {{Wp|Conscription|compulsory military draft}} was enacted to expand the reservist pool. The draft was deeply unpopular, however, and only made the current political instability worse. His successor, [[Saiah Dwyshyre]], abolishes conscription at the behest of Minister [[Luderich]] of the [[Ministry of Arms and Defense]]. Advances in {{Wp|Telecommunications_engineering|telecommunications engineering}} due to war tech development led to the founding of [[Chalcish Broadcasting Center|CBC]]. By 1922, approximately 250,000 witnessed the airing of its first broadcast. By 1927, the number of viewers jumps to 10 million. Approximately 35 million gained access to a {{Wp|Telephone|telephone}} by 1928 as {{Wp|Electric_energy_consumption|electricity consumption}} increased. A [[Act of Establishment for the National Grid|royal charter]] establishes the [[National Grid]] and the [[Central Electricity Commission]] by December 1928. | |||
Political instability worsened during the years between 1926 and 1932. With SDPC Prime Minister [[Homnach Cumnach]] barely winning the [[1930 general election]], the SDPC arranged a coalition proposal with the Ard Fein and other centrists and leftist organizations. The [[1935 general elections|1935 general election]] was regarded as the catalyst for the [[1935 July Revolution|July Revolution]]. Immediately after the {{Wp|Exit_poll|exit poll count}} was released, several technicians stormed out of the [[Committee of Elections]] in protest for alleged {{Wp|Electoral_fraud|electoral fraud}}. This act of protest became the catalyst for the [[First Storm]], which led to a [[Quarter Demonstrations|series of civilian protests and massive demonstrations]] all around the country's major cities. The revelation of the [[Hammasbiringen]] in 1936 led to the exposure of [[The Alternative Way]], a treasonous plot to overthrow the current liberal administration, starting a new series of demonstrations and protests known as the [[Second Storm]]. The [[Rennes Scandal|scandal in Rennes]], considered the start of the Revolution, revealed the involvement of the conservative [[Corweth II]] and several members of the Royal Family on the Hammasbiringen scandal. Exposed, Corweth II [[1936 Dissolution of Parliament|dissolves the Parliament]] and uses his natural powers to instate the members of the Coalition in the Assembly of Commons, an act of violation of Parliament Privileges. The Royal Army imposed {{Wp|Martial_law|martial law}} a year later. | |||
When Prime Minister [[Sart Powydd]] abdicated his position in May 1937, the Monarchy assumed temporary absolute rule over the Northern Kingdom with the passing of the [[Act of the Emergency Implementation for National Security|Act of the Emergency Implementation for National Security, also known as the Enabling Act]] of which the [[Parliament]] ratified on 2 June 1937. In response, the remaining members of the Assembly of Commons and half of the MP's of the House of Baronies simultaneously walked out of Horessen Palace, with most of them joining the growing [[Left|Opposition Left]]. The first shots were heard in September 1939, where soldiers of the [[Palace Guard]] shot two individuals and injured twenty one on [[Great March|a civilian protest attended by approximately three-hundred people]]. In October 1939, [[University Blockade|student and teacher protestors blockaded the only entrance to the University]] with concrete road barriers. Similar events unfolded in [[Lech University]], [[University of Strashiedd|University of Strasheidd]], and [[University of Malwenydd]]. The Church of Great Chalcain, initially refusing to involve themselves, were forced to participate by the orders of the Humble Superior [[Irscyre Namaiah]], siding with the [[Loyalists]]. By 1940, the political landscape were effectively divided into two; the [[Loyalists]], which were outnumbered yet composed of the Kingdom's most powerful and influential members, and the [[Left]], which was composed by most of the citizenry, the SDPC, Ard Fein, several student council and organizations, the [[People's Faith]], a radical liberal offshoot of the Church; and the heir apparent [[Hammawyth IV]], son of Corweth II. An imminent civil war was avoided, however, when [[Stafferdonn Leak|documents and plans]] revealing the abolishment of veteran aid, pension, and a possible reconstitution of conscription led many generals to join the growing opposition. The July Revolution ended when the Supreme Court, the last bastion of a freely-elected institution declared the current Parliament roster as void, and a [[1942 general elections|general election]] was called to elect the new Parliament. Croweth II was sentenced to {{Wp|Life_imprisonment|life imprisonment}} with Hammawyth IV replacing him as the new Monarch, a great demonstration of the Parliament's sovereignty. | |||
Hammawyth IV opens a [[1941 Special Parliament Session|session in 1941]] with the newly elected Parliament. In a majority vote, a [[Constitution of Chatten and Leucen|constitution]] was compiled and drafted by the [[Committee of Elections]], asserting Parliament Sovereignty over the Monarchy and specifying the powers that would be inherently present for the Monarchy. Though the Northern Kingdom has not been under absolute rule since the [[War of the Barons]], except for the [[Interregnum]], the ratification of the Constitution effectively turned the Northern Kingdom into a {{Wp|Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy}}. | |||
===Second World War and post-war 20th century=== | |||
[[File:Defendants in the dock at nuremberg trials.jpg|thumb|The defendants and the accused in the benches during the [[Cumbershyre Trials]].]] | |||
Between 1942 and 1945, Prime Minister [[Gerald Veryddan]] receives the mantle of responsibilty of ruling the Northern Kingdom during the [[Second World War]]. Under his administration, the Parliament [[abolishes conscription]] and increased funding for the [[Air Force Modernization Program|modernization of the air force]]. Strictly enforcing neutrality means bargaining with both sides, though secretly the Government in general leans with the [[Allied]] forces. | |||
After the war, the Northern Kingdom and the Sonnederlands was left relatively unscathed. In 1945, the Northern Kingdom became one of the founding nations of the [[Assembly of Nations (X)]], and together with Sonnederlands, Pontifar, and the [[Federal States]], drafted the [[Callyssian Aid|Bonne Plan]] as the first ever unanimous proposal to date. Under the tenure of Prime Minister [[Daynedd Calwyn]], the Parliament revoked the privileges of the [[Church of Great Chalcain]] and abolished the position of the [[Humble Superior]] in the House of Baronies, a devastating blow for the Church. In 1953, [[Cumbershyre Trials|a series of investigations into the participants of the July Revolution]] led to the [[Act of the Abolishment of Royal Titles|removal of royal names and honoraries for the involved nobility]], exclusion of several political parties, and the incarceration of the assailants responsible for the bombing attack on Parliament Square five decades ago. [[The Vanguard]] and other right-wing newspapers continue to operated normally, though their sales significantly declined as a result of the investigations. The [[Ministry of Education]] was reinstated in 1954. The results of the Cumbershyre Trial warrants the construction of a {{Wp|Maximum_security_prison|maximum security prison}} named Calraxter Prison, located in [[Lotharyn Island]] within the outlet of the River [[Cymon]]. | |||
In 1958, 78% of the Chalcish citizens expressed support for Callyssian integration. This ultimately guided the Northern Kingdom to its path as one of the founders of the [[Callyssian Union]], together with [[Sonne]], [[Helswig]], [[Sonnederlands]], [[Tictland]], [[Octavania]], and [[Pontifar]]. Together with the [[Federal States]], they jointly founded the [[International Bank]], [[Organization for Trade and Economic Development]], and the [[G5]], an exclusive organization for high-income and militarily powerful states. The Northern Kingdom became the second democratic country to [[Act of Representation of the Public 1959|lower the voting age to 18]] behind Helswig and the first country in the world to [[Act of Establishment for Mental Health Institute 1961|establish]] the [[Mental Health Institute|first institute dedicated for mental health research and care]]. In September 1963, Sakadonesia and the Northern Kingdom signed an [[Open Border Agreement|bilateral agreement]] encouraging immigration between the two nations, guiding the Northern Kingdom into a more {{Wp|Multiculturalism|multicultural society}}. Favouring further Callyssian integration, the Northern Kingdom joined the [[Callyssian Free Trade Association (CFTA)]] and the [[Norpolar Trade Union]] in 1965. In 1967, the Northern Kingdom became the first country in the world to outlaw {{Wp|Female_genital_mutilation|female genital mutilation}} and mandatory {{Wp|Circumcision|circumcision}} in an attempt to enshrine {{Wp|Personal_rights|personal rights}} in the constitution. | |||
{{Wp|Decolonization|Decolonization}} of the Crown colonies in the Sakadoan Archipelago between 1960 and 1965 led to the independence of two new states; [[Zhuye]] and [[Sakoruinea]]. The Dominions of [[New Rwycorr]] and [[New Chalcain]] merged to form the state of [[Sakadonaysia]]. In 1966, The Parliament enacted several reforms that led to the [[Big Bang]], a period of economic prosperity and stability that almost tripled the wealth of the middle and lower class. Favourable economic and political conditions led the [[Ministry of Arms and Defense]] to begin {{Wp|Nuclear_weapon|nuclear weapon}} research in a [[Area 19|testing facility]] in Cunnari. By 1969, the Northern Kingdom has developed its first atomic bomb, called [[TK-13]], just behind the [[Federal States]]. After the [[Corbaraq Incident]], the Assembly of Nations ratified the [[Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty of 1973]] which classifies Callys as a nuclear-free zone. | |||
In 1970, the Northern Kingdom's colonial history as the insitigator ended when Parliament ratified the [[Act of the Pontifarian Sister Cities]]. Sanfar, Foradel, and Khorqabal was given to [[Pontifar]] in exchange for an [[Northern Kingdom-Pontifar Allianc|alliance]], ensuring access to the Anglone Sea. In 1972, The universities of Malwenydd and Strasheidd became the base operation for the highly-anticipated [[Interlink Project]], the predecessor to the {{Wp|Internet|Internet}}. By 1990, political reforms were made to ensure efficient rule of law such as the merging of the [[Supreme Court of Chatten]] and [[Supreme Court of Leucen|Leucen]] into a single [[Supreme Court of Chalcain|Supreme Court]] and adopting a proportional {{Wp|Single_transferable_vote|single transferable voting system}}. | |||
The Northern Kingdom became the first Callyssian country and CU member to legalize {{Wp|Same-sex_marriage|same-sex marriage}} in 2 May 1998, following a [[1998 Plebiscite regarding same-sex marriage|plebiscite]] result revealing overwhelming support, approximately 71%. {{Wp|Pride_parade|Pride marches}} for the following decades would come to commemorate the day as the start of the annual {{Wp|Pride_Month|Pride month}}. In 1998, the Northern Kingdom connected to the {{Wp|Internet|Internet}} with the completion of the laying out of the [[Trans-Septentrionic Cable System]]. | |||
===21st century=== | ===21st century=== | ||
[[File:Day Without a Woman protests in New York City (32950233090).jpg|thumb|[[Black friday protests|Labor Day protests]] during the [[2012 Callyssian financial crisis]]. Unemployment soared to 21% as the result of the recession.]] | |||
In the early 21st century, {{Wp|Internet|internet users}} jumped to 12% relative to the Northern Kingdom's population coinciding with the rise of existing tech firms. The ratification of the [[Act of Agreement and Support for the War on Terror 2002|Act of Agreement and Support for the War on Terror]] by the Parliament caused divisive discourse both domestic and abroad. When the [[Federal States]] begins their campaign for [[War on Terror (Federal States)|War on Terror]], [[Anti-war protests of 2002|widespread protests and rallies broke out]] all around Leucen, oppossing the involvement of the Northern Kingdom. The act became so deeply unpopular that by the [[2004 general elections]], the [[Nationalist Party]] overtook the SDPC and won the most seats in the Parliament with [[Beryll Monach]] becoming Prime Minister the same year. In 1956, preliminary expeditions were held into [[The Abyss]], a huge sinkhole located within the [[Kilometer Ring]] in an island called [[Abyssal Cone]]. | |||
The [[2012 Callyssian financial crisis]] has dramatic effect on the wider Chalcish economy. In 13 June 2012, almost fifty-thousand civilians and workers lined up outside of banks to withdraw their savings. Banking firms such as [[Coleyr & Dome]], [[National Bank]], and [[Bank of the Chalcish Islands|Bank of the Chalcish Islands (BCI)]] imposed higher requirements for taking out {{Wp|Loan|loans}}. The [[Imperial Bank]] announced a historic 1% {{Wp|Interest_rate|interest rate}} for all banking institutions across Chatten and Leucen. The [[Durynn - Clesse]] coalition proposes {{Wp|Austerity|austerity}} measures that tackles numerous public budget deficits. During the outbreak of the [[Plague]], the Northern Kingdom became the first country in the world to develop a [[SAVRAS vaccine]] for affected places in Sakadonaysia and through-out [[Axria]]. The Northern Kingdom is also among the first set of countries that voted for the enshrinement of {{Wp|Right_to_food|basic right to food}} in the [[International Convention for Human Rights and Dignity]]. | |||
In 2015, the Parliament allowed the development of {{Wp|Nuclear_power_plant|nuclear power plants}} in a bid to implement {{Wp|Sustainable_energy|sustainable energy production}} policies. Dubbed as the [[Green Energy Act 2015]], the policy established the [[Nuclear Energy Institute]] and the [[Board of Nuclear Energy Management]] which aims to oversee all nuclear power plant facilites; and the [[Department of Energy Security]] which operates as an attached department of the [[Ministry of Energy]]. In 2017, a [[Comprehensive Transportation Network Deal|comprehensive bill that aims to develop a system of transport networks]] was ratified by Parliament. The [[Gwyndaen Corridor]], a continuous {{Wp|High-speed_railway|high-speed railway}} line serving the island of Leucen that connects Malwenydd to Lech was completed in 2020, and another high-speed railway corridor that serves the island of Chatten, known as the [[Carr Sein]], was completed in 2022. A [[Chatten Tube|connector]] starts construction in March 2021 which aims to build an expansive transport network that will be known as the [[Chalcish Rail Network]], hoping to decrease {{Wp|Car_dependency|car dependency}}. In 2023, The Northern Kingdom ratifies a [[Act of Net Neutrality 2023|parliament act]] which aims to promote {{Wp|Net_neutrality|net neutrality}} in the Kingdom's digital cyberspace. | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
{{Main article|Geography of Chatten and Leucen|The Abyss}} | |||
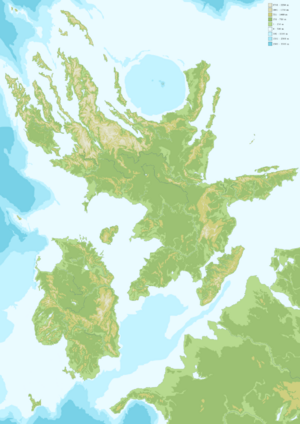
[[File:Topographic map of Chatten and Leucen.png|thumb|Topographic map of Chatten and Leucen.]] | |||
Chatten and Leucen is the largest country in Callys; having maritime borders with Helswig to the south, Finnon and Sonnederlands in the east, Tictland and Coradis in the south-east, and Markland to the north-west. It is the largest Callyssian country with no land borders to any country. The Northern Kingdom is bordered by the Septentriones ocean to the west, Norpolar ocean to the north, the Elvenmann Strait and Leucish Sea to the south, Chatten Strait to the south-west; and Eastern and Lacendynn Sea to the west. Chalcish territory covers 512,455 km<sup>2</sup> (197,860 sq mi), consisting of 502,312 km<sup>2</sup> (193,943 sq mi) of land and 10,143 km<sup>2</sup> (3,916 sq mi) of water. Great Chalcain comprises of 56% of the entire land area, consisting of the main island of [[Leucen (island)|Leucen]], and its surrounding islands such as: [[Cunnari]], [[Amarincen Islands]], [[Gorth]], [[Porgynth Islands]], [[Isle of Terk]], [[Elven Island]], [[Jutys Island]], and [[Ramburgys Island]]. Meanwhile, [[Chatten (nation)|Chatten]] and its surrounding islands comprises only 44% of the entire land area, including the surrounding islands such as [[Isle of Rustav]], [[Lannascern Islands]], and [[Furk Island]]. | |||
A geographical anomaly known as the [[Kilometer Ring]] borders the states of [[Corkees (state)|Corkees]] and [[North of Leucen]]. With an average depth of 750 km, it harbors the island of Abyssal Cone, an island resembling a crater ring, and within it, [[The Abyss]], a 560-meter wide {{Wp|Sinkhole|sinkhole}} with an unknown depth, though preliminary expeditions descended on a depth of 15 km, making it possibly the deepest point in the world's surface, and possibly much deeper than that. A [[Cone Town|town]] under the administration of the state of [[Corkees (state)|Corkees]] was founded in 1977 which acts as a scientific settlement staffed by private groups, local residents, archaeological expedition groups, and members of the [[Minister of Science and Technology]]. | |||
The world's {{Wp|Prime_meridian|Prime meridian}} passes through the [[Midpoint Observatory]], located a few kilometers east of [[Lomercoyne]] in [[South-east Leucen]]. The prime meridian originates at an observatory in [[Carzaragura]] in [[Sonne]]. | |||
The Northern Kingdom lies between longitudes 12° W and 5° E, and latitudes 49° N and 64° N. The Northern Kingdom doesn't share any land borders, but it shares maritime borders with Helswig, Sonnederlands, Finnon, Tictland, Coradis, and Markland. The [[Crowergynn Sea]] and [[Sunderland Strait]] separates the main islands of Leucen and Chatten, with the island of Rustav located within the Crowergynn Sea. Meanwhile, the Chatten Strait, Leucish Sea, Elvenmann Strait, and Lacendynn Sea separates the islands from continental [[Callys]]. The [[Wedian Sea]] separates Leucen from the island of Cunnari. | |||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
===Topography=== | {{Main article|Climate of Chatten and Leucen}} | ||
=== Topography === | |||
Leucen, including its surrounding islands, accounts to 56% of Chatten and Leucen, or 286,974 km<sup>2</sup> (110,801 sq mi). The regions corresponding to the state of [[The Midlands]], called the [[Crescent Plains]], is relatively flat, rising to an average height of 99m. Prominent river valleys includes the [[Two River Valley]], near the River [[Krav]]; [[The Gateway]], which houses the city of [[Lech]] and the River [[Tict]]; the [[Sveteran Valley]] near [[Varnyconne]]; and the [[Astadorian Valley]], which houses the great river of [[Astador]] and the city of [[Humboldt]]. Prominent mountain ranges includes the [[Broken Amarincen Mountains]], which forms the chain of islands of the Amarincen Isles, the [[Great Jotavish Mountains]], where the tallest points in the country is located; the [[Erikortt Mountains]], the [[Piester Highlands]], the [[Arkerkian Range|Arkerkian Mountain Range]], [[The Highlands]], the [[Porgynthian Range]], the [[Eastern Chattenian Range]], the [[Mid-Chattenian Range]], [[Cydacyllic Highlands|Cydacyll Highlands]], and the [[Maucer Heights]]. [[Mount Colbyranth]], towering at 2,250 meters, is the tallest mountain in the Great Jotavish Mountains and in the Northern Kingdom. Lowlands include the [[Cymonian Woods]], the [[Expanse]], [[Arkerk's Coast]], [[Tict Valley]], Crescent Plains, and the [[Comynraeth Valley]]. | |||
===Biodiversity === | |||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
=== | {{multiple image | ||
=== | | width = 160 | ||
| length = 160 | |||
| align = right | |||
| image1 = Frederik, Crown Prince of Denmark in 2021.jpg | |||
| width1 = 190 | |||
| image2 = AOC gives a speech in Congress.png | |||
| width2 = 190 | |||
| caption1 = [[Crowberwynn VII]], [[Monarchy of Chatten and Leucen|Monarch]] since 2020 | |||
| caption2 = [[Saiah Dunwille]], [[Prime Minister of Chatten and Leucen|Prime Minister]] since 2022 | |||
}}{{Main article|Politics of Chatten and Leucen}} | |||
[[File:Parliament of Budapest.jpg|thumb|The [[Horessen Palace]], formerly a royal palace for the royal family members, is currently the seat for both houses of the [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament]] of Chatten and Leucen.]] | |||
The Northern Kingdom is a {{wp|Federalism|federal}}, {{wp|Constitutional_monarchy|constitutional monarchy}}, and a {{wp|Parliamentary_system|parliamentary}} {{wp|democracy}}. The [[Chalcish Parliament|Parliament of Chatten and Leucen]] is the {{Wp|Sovereign|Sovereign}}, a bicameral legislature consisting of the [[Assembly of Commons]] and the [[House of Baronies]], which is previously appointed. The Monarchy is referred to as [[The Crown]] within the public, and also within the Parliament. The legislative process takes place within the two houses of the Parliament, but {{Wp|Royal_assent|royal assent}} is required for a bill to become an {{Wp|Act_of_parliament|act of parliament}} in a form of a {{Wp|Statute|statute law}}. Because of the order of legislative process, the Crown is subordinate to the Parliament in a way that their only primary responsibility is to pass bills into law, and the promulgation of new laws is left to the discretion of the Parliament itself. The Parliament is considered the sole legislative body of the Northern Kingdom. | |||
[[Crowberwynn VII]] is the current {{Wp|Monarch|monarch}} and {{Wp|Head_of_state|head of state}} of NK. They are automatically vested with all executive authority as the personification of The Crown. As the monarch, they are fundamental in the operation of the Government and to the Law. The set of powers vested in the monarch also comes up with {{Wp|Royal_prerogative|royal prerogatives}}, and its use is usually counseled with a set of [[Ministers of the Crown|ministers]] loyal to The Crown. During the performance of their duties, the monarch has the right to be counseled, advised, to encourage, and to warn. Additionally, the monarch held {{Wp|Reserve_powers|natural powers}} in their disposal. These powers are rarely used, and is often used on resolving {{Wp|Constitutional_crisis|constitutional crises}} and upholding {{Wp|Responsible_government|responsible government}}. | |||
During general elections to the Assembly of Commons, the Northern Kingdom is divided into X regions, with X counties and X districts in total. Each state is represented by three {{Wp|Member_of_parliament|members of parliament}} (MP) in the House of Baronies and is elected using the {{Wp|Single_transferable_vote|single transferable vote}} system, except for the [[Federal Capital District]] which is represented by four representatives. A term of an MP lasts for 5 years and must face a re-election if they wish to continue. Both the [[Social Democratic Party of Chalcain]], referred to as the "[[Benchers]]" and the [[Nationalist Party (Chatten and Leucen)|Nationalist Party]], referred to as the "[[Counters]]", dominate the political landscape since 1910, which resembles that of a {{Wp|Two-party_system|two party system}}. However, several minor political parties secure enough seats in the Assembly of Commons to be significantly influential, albeit either leaning into one of the dominant parties or standing alone as a non-aligned party. None of the minor parties came close to the size of both parties however. | |||
===Nations=== | |||
====Chatten==== | ====Chatten==== | ||
====Leucen==== | ====Leucen==== | ||
===Constituent states=== | |||
{{Main article|States of Chatten and Leucen}}Chatten and Leucen is a {{Wp|Federation|federation}}, made up of [[States of Chatten and Leucen|24 constituent states]] and a [[Federal Capital District|federal district]]. Each state has three representatives in the [[House of Baronies]] (except for [[Lomercoyne]] which has an additional representative). The number of states are further divided into two nations, with the [[Leucen (nation)|nation of Leucen]] having 19 states in its territory, while the [[Chatten (nation)|nation of Chatten]] having the remaining 6 states. Each state is represented in the [[Assembly of Commons]] with a number of representatives proportionately to the state's population. Lomercoyne (Federal Capital District) has the most amount of representatives, with 17 representatives, while Porgynths, Jotavs, Gorth, and Lannascern each has 4 representatives, the least amount.{{annotated image | |||
|caption=The federal states of Chatten and Leucen | |||
|float = center | |||
|height= 780 | |||
|image_width = 560 | |||
|width = 570 | |||
|annotations= | |||
{{Annotation|50|245|{{flag|Piester}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|239|464|{{flag|Lomercoyne}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|39|570|{{flag|West Chatten}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|130|640|{{flag|South Chatten}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|160|540|{{flag|East Chatten}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|270|340|{{flag|The Midlands}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|239|500|{{flag|South-west Leucen}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|390|499|{{flag|Terk}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|95|464|{{flag|North Chatten}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|178|269|{{flag|Hundes}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|250|259|{{flag|North of Leucen}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|160|438|{{flag|Rustav}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|119|300|{{flag|Rwycorr}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|200|355|{{flag|West of Leucen}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|140|150|{{flag|Jotavs}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|349|170|{{flag|Corkees}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|239|415|{{flag|Dwerigg}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|320|300|{{flag|East of Leucen}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|368|355|{{flag|Porgynth}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|470|343|{{flag|Ester}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|300|438|{{flag|Paworys}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|385|439|{{flag|South-east Leucen}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|390|405|{{flag|Ostria}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|470|310|{{flag|Gorth}}}} | |||
{{Annotation|39|750|{{flag|Lannascern}}}} | |||
|image-width=570|image=Federal states of Chatten and Leucen.svg}} | |||
===Foreign relations=== | ===Foreign relations=== | ||
===Law and Justice=== | ===Law and Justice=== | ||
{{Main article|Law of Chatten and Leucen}} | |||
The Northern Kingdom follows the legal system implemented through-out the [[Moravian Empire]], known as the [[Moravii Code of Laws]], which has existed in the islands since the [[Moravian conquests]]. Before the ratification of the [[Act of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487]], the various kingdoms of Chatten such as [[Kingdom of Duran]] and the [[Confederation of Vowatan]] follows a series of legal code known as the [[Acarus]]. The Moravii Code of Laws, the current legal system adopted by most of the Callyssian countries, has been influenced primarily by indigenous codes of law such as the Acarus and [[Helswigan Law]]. Before the political reforms of 1990, Chatten and Leucen each has their own {{Wp|Supreme_court|Supreme Court}} with limited jurisdiction. The severity of the trials that resulted from the investigations regarding the events of the [[1935 July Revolution]] necessitates a new judicial institution with an absolute {{Wp|Jurisdiction|jurisdiction}} over the entire nation. The two Supreme Courts were merged in 1990 to form the [[Supreme Court of Chalcain]] with 12 posts for {{Wp|Associate_judge|associate judges}} and the thirteenth post for the {{Wp|Chief_justice|Chief Justice}}. The [[Dominion Judicial Committee]] serves the judicial needs of their dominions, most notably, the [[Sakadonaysia|Federal Republic of Sakadonaysia]]. | |||
Courts such as the [[Constuitik]], the federal {{Wp|Constitutional_court|constitutional court}}, [[Labouritik]], the federal {{Wp|Labor_court|labor court}}, [[Fiscalitik]], the federal fiscal and tax court, [[Sociolitik]], the federal social law court, and the [[Patenuitik]], the federal patent and intellectual property court, are known as specialized courts. The [[Frier Marta]] of 1112 has laid out the foundation of the modern constitution, such as representation, consultation of laws, access to fair trial, and decentralization of power. The Chalcish penal system seeks the rehabilitation of the criminal and reintegration into society. {{Wp|Capital_punishment|Death penalty}} is outlawed since the [[Holy Revolution|Glorious Revolution]]. | |||
By 2020, the Northern Kingdom's muder rate stood at a very low 1.2 murders per 100,000. In 2018, crime rate fell to its lowest since 1990. | |||
[[LGBT rights in Chatten and Leucen|LGBT rights]] are generally protected by the nation, with {{Wp|Same-sex_marriage|same-sex marriage}} legal since 2 May 1998 and bans on blood transfusion and donation lifted on 1991. {{Wp|Gender-affirming surgery|Gender-affirming surgeries}} was codified by the [[FHS]] in 2002 and was made available through-out the public. | |||
===Military=== | |||
{{Main article|Chalcish Armed Forces}}The Northern Kingdom's armed forces is the Armduhr (Armed Forces), which is categorized into the [[Royal Army (Chatten and Leucen)|''Royal Army'']] (Army and the [[Special Action Forces Command|''SAFC'']]), the [[Royal Navy (Chatten and Leucen)|''Royal Navy'']] (Marine), the [[Royal Air Force (Chatten and Leucen)|''Royal Air Force'']], the ''[[Juntadelicares]]'' (Medical Service), ''[[Streiskuffande]]'' (Support Service), and the ''[[Cyberdumaine]]'' (Cyber and IT Domain Service). Military spending accounts to approximately 2.1% of the nation's economy, or ₽122 billion piese, meeting the [[Callyssian Union]]'s suggested military spending threshold. The military spending amount is the largest within Callyssian Union members, double than the second largest military spending amount by [[Octavania]] which is ₽47.8 billion pieses. In 2022, PM [[Saiah Dunwille]] announced a slight defunding of the military down to ₽99.7 billion pieses. | |||
The Monarch is the {{Wp|Commander-in-chief|commander-in-chief}} of the Armduhr, to whom military officials pledge their alliegiance of loyalty to. The administration of the armed forces is chaired by the [[Secretary of Defence]], managed by the [[Minister of Defense (Chatten and Leucen)|Minister of Defense]] and is overseen by the [[Defense Council]]. As the primary defense force, the Armduhr is responsible for patrolling the national borders, protecting the interests of the nation, guard the civilian population, and enforce order and stability in times of crisis. In time, the responsibilities of the army expanded to include supporting emergency services in times of crisis and participating in civil service both peacetime and wartime. The military also participates in the international stage by sending in peacekeeping efforts in [[Axia]], [[Joint Allied Exercises|participating in joint-exercises]], and aiding the allies in times of need. As a member of the Callyssian Union, the Northern Kingdom is also a founding member of the [[Global North Treaty Organization]], a military alliance of Callyssian nations that aims to preserve post-war peace and stability. | |||
Since 1923, women are allowed to serve in the military and take up whatever positions they prefer. In 1987, the [[Chalcish Armed Forces]] lifted the ban that prevents LGBTQ+ members from serving in the military. | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
===Science and technology=== | ===Science and technology=== | ||
===Transport=== | ===Transport=== | ||
{{Main article|Transportation in Chatten and Leucen}}[[File:Mississippi River in South Louisiana 2022-08-28 B.jpg|thumb|[[Cymon|Cymon River]], the longest river in Chatten and Leucen and the primary route of the [[Cymon Ferries]]. ]] | |||
The [[Waydermichen]] is the Northern Kingdom's primary highway network, with the first highways constructed during the early 20th century. It totals 34,887 miles (56,145.18 kilometers) in length uninterrupted, including underwater tunnels such as the [[Chatten Tube|Chatten-Leucen Tunnel]] and bridges such as the [[Malwenydd Bridge]]. The [[Circumferential Highway 3|C-3]], located inside the [[Federal Capital District]], is the busiest motorway on [[Lomercoyne]]. The [[Federal Road System]] has a length of 44,566 miles (71,722 kilometers), a little longer than the Waydermichen, but does the job of connecting areas not accessed by it. There were 34.1 million licensed vehicles all around the Northern Kingdom as of 2018, and is slowly decreasing. | |||
The Northern Kingdom is serviced by two main rail systems each servicing their island. The [[Gwynaed Corridor]], the longest high-speed rail line, the [[Eastern Corridor|Eastern]] and [[Western Corridor]], and the [[Peninsular Corridor]] forms the base rail lines of the Leucish part of the [[Chalcish Railways]]. [[Carr Fein]], meanwhile, forms the Chattenian part of the Chalcish Railways. They are connected by the [[Chatten Tube]] under [[Sunderland Strait]]. In total, the [[Chalcish Rail Network|Chalcish rail network]] has a length of 12,172 miles (19,588 kilometers). It is administered by the publicly-owned [[Grand Chalcish Railways]], once a privatized corporate entity until 1989. In 2016, the Chalcish Railways of the Northern Kingdom was ranked sixth among Callyssian National Rail Systems in terms of accessibility, intensity of use, safety, and quality service. The [[Lomercoyne Railways]] in [[Lomercoyne]] services the Federal Capital District and its surrounding counties and is composed of the mostly-underground [[Lomercoyne Downlines]] and the overhead [[Lomercoyne Uplines]]. The [[DiagonaLink]], [[CymonLink]], and [[VertiLink]] also services the metropolitan area. The [[Homerails]], a planned rail system connecting the [[Capital Counties]], some airports, and Lomercoyne, was inaugurated on 20 February 2020. Its total cost is estimated to be approximately ₽443 billion and is intended to be a {{Wp|High-speed_rail|high-speed rail}} system, with speeds possibly reaching 235 mph. | |||
In 2015, there were 5.4 billion bus journeys in the Northern Kingdom, with 38,011 buses currently in operation, with 8,900 buses operating in Lomercoyne alone. In Lomercoyne, the buses are operated by several private companies under contract and regulated to the [[Transportation for Lomercoyne]], abbreviated as TfL. Country-wide, all buses are regulated by their respective nation; the [[Leucish Transportation Council]] for the Leucish National Government and the [[Chattenian Transportation Council]] for the Chattenian National Government. Buses in the Northern Kingdom are distinguished by its red and yellow color scheme, which has entered popular culture as one of the Northern Kingdom (and Lomercoyne)'s cultural symbols. The [[Lomercoyne Bus Network]] is extensive; with 9,800 buses carrying over 6.8 million passengers each week all over its 712 bus routes. This makes the Lomercoyne Bus Network the most extensive and largest bus network in Callys. | |||
The Northern Kingdom has 16 {{Wp|International_airport|international airports}}, with the [[Locus-Ardynn International Airport]] serving as the primary and largest international airport in the Northern Kingdom. All of the Northern Kingdom's airports have handled approximately 290 million passengers in 2023. Three of the largest airports in 2023 were Locus-Ardynn International Airport (77.2 million passengers), [[Klauber Airport]] (43.7 million passengers), and [[Varnyconne International Airport]] (23.2 million passengers). Locus-Ardynn International Airport, located 24 miles (38.62 kilometers) south of [[Lomerynum]], is the busiest airport in Callys and the second busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic, behind [[Rookesrow International Airport]] in [[Avrecenia]]. It is the hub of the Northern Kingdom's primary carrier [[Chalcish Airways]]. The airports of Lomercoyne are administered by the [[Roster Aviation]], an attached administrative authority under the [[Leucish Air Transportation Committee]], which administers all aircraft, airports, aviation land use, licensing, aviation schools, and military land in the nation of Leucen. Its counterpart is the [[Chattenian Air Transportation Committee]] of the nation of Chatten. | |||
{{Wp|Water_transportation|Water transportation}} is an integral part of Chalcish economy. [[Cymon Ferries]], a shared private-public corporation, operates a ferry service running along River [[Cymon]]. It is the longest ferry line in the world, with its northern terminus located near the start of the river in [[Lake Garent]], and its southern terminus ending at [[Sanzoine Pierre]], near the mouth of the river. It has a length of 340 miles (547 kilometers) from north to the south. Several ferry and {{Wp|Roro|Ro-ro}} services connects the islands of Chatten, Rustav, and Leucen despite the presence of the Chatten Tube. The [[Naviar Transport Committee]] administers the operation of all water transportation vehicles, companies, and travel agencies in Leucen. Just like any other agency, it also has a counterpart in Chatten; namely the [[Arsinn Transport Committee]]. | |||
===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
{{Main article|Energy in Chatten and Leucen}}[[File:Nuclear Power Plant Cattenom.jpg|thumb|[[Corsyna Complex]], a nuclear power plant in [[Paworys]].]] | |||
In 2020, the Northern Kingdom is the 14th largest consumer of energy and the 19th largest producer. Four out of seven major oil and gas companies names the Northern Kingdom home, [[Netron]], [[Petropharm]], [[Colbetrol]], [[MG]], and [[CommonOil]]. | |||
The [[Green Energy Act 2015]] establishes crucial institutions in managing {{Wp|Nuclear_power|nuclear power}}; the [[Nuclear Energy Institute]], [[Board of Nuclear Energy Management]], and the [[Department of Energy Security]]. The first nuclear power plant was built in [[Cenicen]], just south of the city of [[Mowycen]] in 2016. Unlike Helswig or Sonnederlands, another power plant was constructed in [[Bragamyr]], [[West Chattel]] in 2021. Three more nuclear power plants were opened in [[Paworys]], [[Terk (state)|Terk]], and [[Rwycorr (state)|Rwycorr]] in 2023. Future nuclear power plants are scheduled to be constructed all around the country. Currently, nuclear power only accounts to 14.5% of national energy supply. | |||
The Northern Kingdom is a huge proponent of green energy and combating {{Wp|Climate_change|climate change}}. It is the first country to enact a [[Act of Mitigating Climate Change 2001|legislative law]] aiming to reach a zero-carbon emission by 2050. 45% of all energy supply sources comes from renewable sources. The green energy sector is composed of {{Wp|Geothermal_energy|geothermal energy}} (45 per cent), {{Wp|Wind_power|wind energy}} (30 per cent), {{Wp|Nuclear_power|nuclear energy}} (14.5 per cent), {{Wp|Hydroelectricity|Hydroelectric power}} (5.5 per cent), and {{Wp|Biomass|biomass energy}} (4 per cent). Geographically, the Northern Kingdom has all the best wind power sites in the continent due to its oceanic climate, making it the leader of the environmental movement in Callys. The largest {{Wp|Offshore_wind_power|offshore wind farm}} in Callys is located east of [[Samerys]], [[South-east Leucen]] at the mouth of [[Kowysky Strait]], close to the northern tip of the island of [[Terk (island)|Terk]]. | |||
In 2021, approximately 1,015 thousand barrels of oil per day (bbl/d) and other liquids was produced by the Northern Kingdom while consumption is approximately 995 thousand bbl/d. This leaves with a small surplus margin of 20 thousand bbl/d which is being exported in the global market. Production, however, is stagnating due to bans in place for {{Wp|Fracking|fracking}} and a declining use on {{Wp|Car|automobiles or cars}}. Current trends would see a slight deficit in oil and gas supply which will lead to exports within the next five years. In 2020, the Northern Kingdom produces 1.5 million tonnes of {{Wp|Coal|coal}}, a slight decrease from the 2015 report of 1.8 million tonnes of coal. According to the [[International Natural Reserves Report]], approximately 23 billion tonnes of coal reserves still remain in the country. The [[Federal Coal Authority]] reports that the Northern Kingdom can produce 1.8 to 2.3 million tonnes of coal each year. Current coal consumption of the Northern Kingdom would last 300-500 years until depletion. | |||
In terms of {{Wp|Natural_gas|natural gas}}, the Northern Kingdom is the 20th largest producer of the substance in the world in 2021. Production, however, has declined significantly and the Northern Kingdom has been a net importer of natural gas since 2010. | |||
===Water supply and sanitation=== | ===Water supply and sanitation=== | ||
==Demographics== | 97% of all households in the Northern Kingdom has access to clean water and sanitation. According to the 2021 report of the [[Ministry of Health (Chatten and Leucen)|Ministry of Health]], 98% of all households are connected into the sewer network. Total water abstraction for the water supply of several companies around the Northern Kingdom is approximately 18,904 {{Wp|Megalitre|megalitres}} per day in 2010. Water service providers in Leucen are composed of 8 regional companies. [[Lomercoyne Water]], [[Peninsular Water]]; [[Doyre and Ostrian Water|South, Doyre and Ostrian Water]], [[Middle Water]], [[Northerners Water|Northern Water]], [[Rwycorrian Water]], [[Northern County Water]], and [[Eastern Water]]. Meanwhile, the entire island of Chatten, Rustav, and Lannascern is serviced by [[Chatten Water]]. | ||
== Demographics== | |||
{{Main article|Demography of Chatten and Leucen}}In the 2022 census, the population of the Northern Kingdom was 115,112,734. It is the second most populated country in Callys (behind [[Octavania]], [[Helswig]], and [[Cnutia]]) and 13th most populated in the world. Net immigration contributed to the population increase and has since been gradually declining. In 2015, natural change has contributed the most in population growth. In 2010, the proportion of the population ages 10-20 rose from 12% to 33%, while the proportion of the population ages 55-65 fell from 29% to 10%. In 2020, the {{Wp|Median_age|median age}} of the Northern Kingdom was 39.6 years. | |||
[[Leucen (nation)|Leucen]]'s population is 87,451,667, approximately 75.97% of the total population, with a distinct concentration of people around major urban centers such as the [[Capital counties]] that surrounds [[Lomercoyne]] and major cities such as [[Varnyconne]], [[Malwenydd]], and [[Courcamyron]]. Meanwhile, the population of [[Chatten (nation)|Chatten]] is 27,661,067, approximately 27.03% of the total population. The city of [[Humboldt]] in [[East Chatten]], with a population of around 8 million, makes up 32.11% of Chatten's total population, which means one out of three Chattish citizens lived in Humboldt. It is the foremost financial, political, and cultural center of Chatten. The second most populous Chattenian city, [[Camduran]], in North Chatten, only makes up 2.82% of Chatten's population. | |||
In 2019, the {{Wp|Total_fertility_rate|average total fertility rate}} of the Northern Kingdom is 2.82 children per woman. Since 2013, the fertility rate is gradually rising by 0.2% per year thanks to medical innovation and a huge support for women's rights. Generally, the fertility rate is normal when compared to 0.9 children per woman in 1939 and 6.1 children per woman in 1856 general census. Since 1953, the birth rate has surpassed death rate, leading to gradual population growth. | |||
{{Largest cities|name=jbvgvhk|country=Chatten and Leucen|stat_ref=(Chatten: 2022 census; Leucen: 2022 census)|city_1=Lomercoyne|pop_1=15,712,334|div_1=Lomercoyne|kind=urban areas|div_name=State|div_2=The Midlands|pop_2=10,312,491|city_2=Varnyconne|city_3=Humboldt|div_3=East Chatten|pop_3=8,881,612|pop_4=6,988,198|div_4=Ostria (state)|city_4=Sark|city_5=Orbeaun|div_5=South-west Leucen|pop_5=3,312,783|pop_6=3,110,312|div_6=Terk (state)|city_6=Malwenydd|pop_7=2,412,561|div_7=Rwycorr (state)|city_7=Lech|pop_8=2,141,561|div_8=Paworys|city_8=Ghascyne|city_9=Shalcyr|div_9=North of Leucen|pop_9=1,253,612|city_10=Mowycen|div_10=East of Leucen|pop_10=1,132,412|city_11=Port Lambarinnon|div_11=Ester (state)|pop_11=788,012|pop_12=781,334|div_12=North Chatten|city_12=Camduran|city_13=Monteive|div_13=Rustav (state)|pop_13=612,443|pop_14=514,309|div_14=Dwerigg|city_14=Balcaraxyr|city_15=Charxyr|div_15=South-east Leucen|pop_15=513,412|pop_16=491,445|div_16=South Chatten|city_16=Kessenduran|pop_17=482,991|div_17=Piester|city_17=Savadore|city_18=Boines|div_18=West Chatten|pop_18=342,145|city_19=Port Nethania|div_19=Corkees (state)|pop_19=308,181|city_20=Nirkes|div_20=West of Leucen|pop_20=305,986|img_1=Chicago skyscrapers on a rainy night (52037809603).jpg|img_2=Space Needle002.jpg|img_3=Tobin Bridge and Boston skyline, June 2017.jpg|img_4=Logan Airport ramp and Boston skyline, September 2019.jpg}} | |||
===Ethnicity=== | ===Ethnicity=== | ||
===Languages=== | ===Languages=== | ||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
{{pie chart | |||
| thumb = right | |||
| caption = Religion in Chatten and Leucen (2020 census) | |||
| label1 = No Religion | |||
| value1 = 53 | |||
| color1 = Yellow | |||
| label2 = Meyrism | |||
| value2 = 37 | |||
| color2 = Blue | |||
| label3 = Chalcerean Paganism | |||
| value3 = 2.1 | |||
| color3 = ForestGreen | |||
| label4 = Dastrity | |||
| value4 = 1.1 | |||
| color4 = Violet | |||
| label5 = Neo-Dastrity | |||
| value5 = 1.0 | |||
| color5 = Black | |||
| label6 = Others | |||
| value6 = 0.9 | |||
| color6 = Silver | |||
| label7 = Not stated | |||
| value7 = 5 | |||
| color7 = Red | |||
}} | |||
Before the [[Meyrian Schism]], the most dominant form of Meyrism in the Kingdom is [[Moravian Meyrism]], which was first brought to the islands by High King Sycor IX's younger brothers, Nymeth and Fwynth. Dominating the islands until 1435, during which litugical and economic conflicts between the [[See of Maverra]] and the [[See of Morve]] resulted in the division of Meyrism all through out Callys. The schism results in the split of Moravian Meyrism in Chatten and Leucen into two; the Helswigic-influenced [[Leucish Meyrism]] and the Finnonian-influenced [[Chattish Meyrism]]. Currently, 27% of the population adheres to Leucish Meyrism, while only 10% adheres to Chattish Meyrism. Almost half of the population are [[wikipedia:Irreligion|non-religious]], approximately 53% of the population, but the way they practice non-adherence depends on the individual. According to a survey conducted by [[Buzzwire]], only one out of ten Chalcish citizen attend church monthly. [[wikipedia:Immigration|Immigration]], [[wikipedia:Secularization|secularization]], [[wikipedia:Demography|demographic]] change, and [[wikipedia:Socialism|socialism]] drastically affects religious composition of the country. In a report written by the [[Chalcish Statistics Authority]], 79% of the population adheres to some form of religion before the [[1935 July Revolution|July Revolution]], which dropped to a mere 39% post-revolution by 1945. Because of these developments, the current Chalcish society can be considered a [[wikipedia:Postchristianity|Post-Meyrist]], [[wikipedia:Diversity_(politics)|diverse]], [[wikipedia:Multiculturalism|multicultural]], and [[wikipedia:Secularization|secularized]] one. | |||
In the 2020 census, 53% of all respondents indicated that they are [[wikipedia:Irreligion|non religious]] or non-adherents to any organized religion, with the largest religion being [[Meyrism]] (37 per cent), followed by Dastrity (1.1 per cent), Neo-Dastrity (1.0 per cent), and Chalcerean Paganism (2.1 per cent). 5% of the respondents did not stated their religion while 0.9 per cent adhered to some other religion. Between 2000 and 2010, Meyrism saw a mere 4% rise on adherents while irreligiosity doubles in size. By 2014, non-religion became the largest group, surpassing 50% of the population. By 2016, a huge increase of pagans were also noted, partially due to social media awareness about [[wikipedia:Paganism|paganism]]. Chalcerean Paganism overtook [[Dastrity]] and [[Neo-Dastrity]] as the third largest religious group in 2017, an event seen by commentators as the great return of pre-Meyrian ways. By 2020, except for Chalcerean Paganism, religiosity all through out the kingdom has been noted by statisticians to be declining for the past 5 years. Religiosity is strong within [[wikipedia:Rural_area|rural areas]], [[wikipedia:Old_age|senior citizens]], conservative districts, and historical places, though the number of these places (except for historical places) is declining as well. | |||
Before the [[1935 July Revolution|July Revolution]], the [[Church of Great Chalcain]] is represented by a seat in the House of Baronies, known as the [[Humble Superior]]. The Humble Superior represents the interests of the Church within the House of Baronies. It was established during the 11th century as the spiritual adviser to the King's Council. The Church of Great Chalcain is the state church of the Northern Kingdom, responsible for overseeing spiritual needs of the population. After the Cumbershyre Trial revealed the role of the Church as siding with the far-right Loyalists, the Parliament revoked their privileges and abolished the position of Humble Superior in House of Baronies. Since then, several attempts to bring back the position in the House of Baronies results in failure, partially due to constitutional requirements not being met and the stigma related to the Revolution. Currently, the Church of Great Chalcain frequently participates in [[wikipedia:Drive_(charity)|donation drives]], feeding programs, charity works, digital animation programs, [[wikipedia:Political_demonstration|rallies]] and [[wikipedia:Advertising|advertisement]] to engage with the current generation and to counteract the decreasing number of adherency to the Church. | |||
It is estimated that by 2030, the number of irreligious individuals with respect to the total population would increase by 6%, and Chalcerean Paganism by 1.3%. If current trends were to continue, then Paganism would eventually overtake Meyrism by 2054, the first time in history where Meyrism is not the dominant religion since its introduction in 840. | |||
===Migration=== | ===Migration=== | ||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
[[File:Old College, Edinburgh University.jpg|thumb|[[University of Strasheidd]], located in a {{Wp|College_town|college town}} of [[Susynyd]] outside [[Lomercoyne]], is the oldest university in Callys. It was founded in 978 AD.]] | |||
{{Main article|Education in Chatten and Leucen}}{{See also|Universities of Chatten and Leucen|label 1=Universities in Chatten and Leucen}} | |||
Education in Chatten and Leucen is a devolved matter; overseen by their respective national governments. The [[Ministry of Education (Chatten and Leucen)|Ministry of Education]] governs the operations and management of basic and higher education of both [[Nations of Chatten and Leucen|nations]]. Over 44 per cent of the Chatten and Leucen population has a university or {{Wp|College_degree|college degree}}, one of the highest percentages in the world. The world's oldest university, the [[University of Strasheidd]], was established in 978; followed by the [[University of Lomercoyne]]; both are highly ranked in the global university rankings. | |||
Chatten and Leucen's education mandates that tertiary education be free for all citizens of the country, except for private universities. As part of the [[Callyssian welfare model]], families who has an annual income of ₽22,000 below are exempt from paying tuition fees in the majority of private universities, as mandated by the Ministry of Education. These are further subsidized by the government using the taxes generated by the means of general annual taxation. | |||
Basic education is mandatory for all citizens. Basic education is divided between primary (which comprises of kindergarten, preparatory, or any pre-elementary education), elementary (which begins in grade 1 and ends in grade 8), and high school (which begins in grade 9 and ends in grade 12). The terms: ''Freshmen, sophomore, junior, and senior'' are applicable for both high school and college students. Each student takes a universal academic exam called the [[GSAE|General Standard Aptitude Exam]]; which is a primary requirement for college admission process. Several education institutions such as the ALS (alternative learning system), and WS (workshop systems) are also utilized. Homeschooling is also an alternative. | |||
In 2022, the [[Global Academic Assessment]] branch of the [[Organization of Trade and Economic Development|OTED]] ranked the overall skills and academic capabilities of Chalcish 15-18 years old. It ranks Chatten and Leucen as 5th in reading, 9th in mathematics, and 7th in science. The average Chalcish student scored 556, significantly above the world average of 450. | |||
===Healthcare=== | ===Healthcare=== | ||
[[File:New York Hospital, New York Weill Cornell Medical Center.jpg|thumb|FHS headquarters in northern [[Tremmen]], [[Lomercoyne]]. ]] | |||
{{Main article|Healthcare in Chatten and Leucen}}{{See also|Federal Health Service}} | |||
Chatten and Leucen's universal publicly funded healthcare is defined by the operation of the Federal Health Service, established as early as 1850 by Queen Nethania. Its widespread influence in the cultural sphere can be seen through-out some of the kingdom's most well known novels such as [[Fireflies in September]] by [[I.K Lewers]] and [[The Madonna Ball]] by [[Hussere Wynn]], often depicted as early as 1872. The institution is a devolved matter. Both national governments have an attached agency that makes up the entirety of the FHS: the [[FHS Leucen]] and the [[FHS Chatten]], serving their respective states. The FHS is an attached institution of the [[Ministry of Health]]. Public healthcare is funded by taxation and private donations and are readily available to all citizens of Chatten and Leucen, and in some cases, it is nearly free of charge. The [[Mental Health Institute]], the kingdom's premiere research institute for mental health treatment, mitigation, and prevention, was established as an institution under the FHS in 1960. The [[International Health Organization]] ranked the healthcare system of Chatten and Leucen as the second in the Callyssian Union, third in Callys, and tenth in the world in 2010. | |||
Public expenditures on healthcare increased between 2010 and 2020. An OTED research calculated that in 2015, each N.K citizen spends ₽3,412 of taxes in healthcare, a slight increase from 2010 which were calculated to around ₽2,998 per head. {{Wp|Vasectomy|Vasectomies}} and women hygiene items such as tampons became free to the public in 2005 in a bid to slow down birth rates. | |||
Under the FHS umbrella, regulatory bodies exists that analyze, organize, checks, and approve positions and retain high-quality services for the entirety of the Federal Health Service. The [[Medical Professional Regulatory Commission]], itself an agency of the [[Professional Regulatory Commission (Chatten and Leucen)|Professional Regulatory Commission]] of the [[Ministry of Labor]], ensures that the quality of the medical practitioners are kept in check. It also administers {{Wp|Examination_board|board exams}} for transitioning college students into medical fields. Two of the hardest board exams, namely the [[Nursing Comprehensive Licensure Exam]] and the [[Physician Licensure Exam]]; are well known for its rigidity and prestige. | |||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
===Literature=== | ===Literature=== | ||
===Philosophy=== | ===Philosophy=== | ||
===Music=== | ===Music=== | ||
[[File:NOVA OPERA Artists after performance of opera-requiem IYOV in National Opera House of Ukraine.jpg|thumb|Members of the [[Screen Actors Federation and Television Association|SAFTA]] after the performance of ''[[Nethania]]'' in [[Royal Opera]], [[Junaxes]].]] | |||
The music of Chatten and Leucen is influenced by its medieval, imperial, and contemporary history. Indigenous folk music of the Chattish and the Leucish, collectively known as the [[Chalcer tunes]], is a trademark on everyday countryside life. [[Heryn Tumyna]]'s ''Hymns of Salvation'', written in 14th century Malwenydd, is the standard of most Meyrist mass hymns through-out all churches. [[Crowberwynn Junyxa]]'s selection of patriotic hymns, his ''magnum opum'' being [[Marsza oft Mersenadia|"Marsza oft Mersenadia"]], currently represents the nation as its official national anthem. Leaders of Chalcish dramatic sayers, poets, and actors re-enacted several iconic Chalcish literatures, with icons such as [[Saiah Clesse]], [[Marcyn Munavia]], and [[Ragevys Quinns]] rivaling contemporaries across the continent. [[Garont Rossone Vynswer]], after being naturalized in 1655, wrote ''[[The God-coming to the King]]'' as a tributary poet and song for [[Vonhoutsyn I]]. During the Renaissance, there comes a dramatic rise in Liberalism-inspired revolutionary songs and poetry, with [[Rys Umbriag]] composing ''[[Libyrte, Egalytrysin, Fratyrnysyn]]'' that were ultimately adopted as the official hymn of the [[Tictish Revolution]] in 1798. Chattish dramatic innovation in open-air operas, dramatic comedy, tragedy, and realism gave birth to [[Lysbera]], a genre reflecting Leucish peasantry life. Famous actors such as [[Yuva Umbriag]], [[Klauberwyth Jamys]], [[Fryeder Colbys]], and [[Caxumys Woft Ordyna]], icons of realism, wrote dramatic songs, scripts, and oratories that would go on to become part of the [[Chalcish Format of Music Writing]]. These same actors would go on to establish new operas, auditoriums, and libraries. | |||
During the [[Nethania Era]], Queen [[Nethany III & I]] ushers in the [[Golden Age of Music]], also known as the ''Creative Age''. Under her rule, patronage becomes a key indicator of the fluorishing industry of singers and poets. [[Parysell Muncell oft Garontys]], one of the iconic symbols of Chalcish culture, was granted a lifelong patronage under the newly established [[Institute of Culture|Institute of Culture (Ynstiduter oft Kulvura)]]. He then goes on to write several treatises about politics, nature, and societal issues. | |||
The rise of country folk music in the early 20th century coincides with the July Revolution; as people yearn for a peaceful, country living amidst increasing political and societal tensions. The Leucish version of [[Das Komyunister]] was composed in 1908 by the infamous [[Worker's Symphony]]. Songs related to resistance, abolition of class struggles, and individuality became major themes for much of the music world during the July Revolution. | |||
===Visual Arts=== | ===Visual Arts=== | ||
===Cinema=== | ===Cinema=== | ||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
[[File:Adobo DSCF4391.jpg|thumb|[[Medobar]], meat marinated with soy sauce, vinegar, and spices.]] | |||
Chalcish cuisine employs a wide variety of herbs and spices due to their direct control with the Sakadonesian islands. Before the colonial era, Chalcish cuisine developed with the influence of agriculture and fishing with a focus on simplicity. [[Aksumada]] is a popular Chalcish dish made with marinated pork stewed in tomato sauce. Dishes like [[Sweetdough]], [[Yam bread pudding]], [[Mesaka]], and [[Chicken ramski]] are popular in any time of day. [[Kamsku]], a honey-roasted whole chicken, is often served during [[Year-ends]], [[Pious Week]], and [[Day of the Dead]]. A simple dish such as [[Fisher brunch]], a fish partnered with any vegetable, often lettuce and broccolli, is eaten within fishing communities, poor people, and sea-side cities. The undisputed popular dish is [[Medobar]], described by gastronomists as both a dish and a cooking method. It is a general dish that requires any form of meat to be marinated in soy sauce and vinegar, and often additionally served with salt, pepper, paprika, or other spices depending on availability, prevalence, and culture. Medobar has hundred variants around the nation because of its ease of preparedness, and often referred to as the unofficial {{Wp|National_dish|national dish}} of Chatten and Leucen. | |||
Chatten and Leucen contains the fourth highest concentration of restaurants rated with at least one [[Boyrete Guide|Boyrete Star]]. Modern dining experiences are prevalent in Lomercoyne, Humboldt, Camduran, Lech, and other cities. During a [[Trihour]], tea and coffee are frequently served, a tradition started during the rise of the Industrial Revolution. Vegan and vegetarian based diets have seen a huge increase since 1950, and healthier alternatives have been offered through-out major restaurants. | |||
Green Lemonade juice is the most iconic drink in Chatten and Leucen, and is known in popular culture as the "Bratz Drink". | |||
Coffee has made its way into the Northern Kingdom as the most popular drink to date. Approximately 77,000 cafes exist in the Northern Kingdom, ranging from deluxe to luxurious ones. A [[Taste Times]] article revealed that 8 out of 10 of the world's biggest coffee and confectionery chains are based on [[Camduran]], considered the coffee capital of Callys. Chocolate and milk coffee was invented in Lomercoyne by [[Andrade Movista]], a Cork chemist, and the popularity of cafes started in Malwenydd as early as the 1610. Within university towns, cafes are known as "[[Second homes]]" by the students, and in the fishing port city of Lech, they are known as the town's "[[Ringbell of the Squares|Ringbell of the Square]]". | |||
===Media=== | ===Media=== | ||
The [[Chalcish Broadcasting Center]], founded in 1922, is the Northern Kingdom's oldest and largest broadcasting station in the entire world. It is a publicly funded by the Northern Kingdom as an answer to the increasing accessibility of televisions and electricity. Its subsidiary, [[CBC International]], is the largest of its kind, covering over 55 countries and 49 languages. It operates numerous TV and radio stations around the country, and is well known for having coverage even in the most remote areas of the country. A historical institution, the CBC has covered the events of the July Revolution, the Cumbershyre Trials, the Second World War, Decolonization, the Anti-war protests of 2002, and the 2012 Callyssian financial crisis, and is treated as a live historical archive. | |||
Some of the Northern Kingdom's biggest players in the media industry include the [[OrbiTV]], considered the oldest commercial broadcasting network, and [[Cablework]]. Newspapers in the Northern Kingdom include ''[[Wirenews]]'', ''[[Daily Star]]'', ''[[Business Times]]'', and ''[[Science Now]]''. Magazines and journal repositories that have gained worldwide popularity, both editorial and academic, include the ''[[The Journal]]'', ''[[Ekonomik]]'', ''[[Geopolitiksche]],'' ''[[Taste Times]]'', and ''[[The Parliamentarian]]''. Newspapers involved in the July Revolution such as ''[[The Vanguard]]'', the official newspaper of the Coalition, have very low subscriber ratings. The Northern Kingdom's publishing sector, including books, newspapers, magazines, editorials, directories and databases, news agencies and business media, and journals, employs 88,000 people and has a combined turnover of ₽99 billion. Since 2004, an increasing demand for digital books is noticeable. Most of the digital books are published in [[Writpen]], an online sharing platform for user-created content. Genres range from {{Wp|Chick_lit|Chick lit}}, {{Wp|Young_adult_literature|young adult literature}}, {{Wp|Political_thriller|political thriller}}, and {{Wp|Gay_literature|LGBT genre}}. | |||
===Sport=== | ===Sport=== | ||
===Symbol=== | ===Symbol=== | ||
==See also== | |||
==Notes== | |||
==References== | |||
==External links== | |||
* [https://www.nationstates.net/nation=chatten_and_leucen ''Chatten and Leucen'', NationStates] | |||
{{Chatten and Leucen Navbox}}{{Chatten and Leucen administrative regions}} | |||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 26 August 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen Fasbaronik Chatten der Leucen (Leucish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Dyvin ed Frier" [a] "Divine and Free" | |
| Anthem: "Marsza oft Mersenadia" 'The Mercenary's March' | |
 Location of Chatten and Leucen (dark green) -- In Callys (green and dark grey) -- In the Callysian Union (green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Lomercoyne 4°1'W 53°26'N |
| Official languages | |
| Regional and minority languages | |
| National sign language | Chalcish Sign Language |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | List
|
| Religion (2020) | List
|
| Demonym(s) | Chalcish, Chalcs (colloquial) |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Crowberwynn VII |
| Saiah Dunwille | |
| Cearl Margowys | |
| Symon Parshyla | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Baronies | |
| Assembly of Commons | |
| Formation | |
| c. 115 | |
| 512 | |
| 1 January 809 | |
| c. 1015 - 1195 | |
| 8 June 1213 | |
| 25 November 1487 | |
| 12 September 1935 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 512,455 km2 (197,860 sq mi) (69th) |
• Water (%) | 1.3 |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 115,634,195 (13th) |
• 2022/24 census | 115,112,734 |
• Density | 349/km2 (903.9/sq mi) (12th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | low (8th) |
| HDI (2023) | very high (11th) |
| Currency | Leucenian Piese (PIS) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 ( NWT) |
• Summer (DST) | observed |
| Date format | dd--mm--yyyy (Common Era) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +115 |
| ISO 3166 code | NK |
| Internet TLD | .chl [b] |
| |
Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen, formally and commonly known as the Northern Kingdom, N.K or Chalcain, is an island country located on Northwestern Callys just off the mainland coast. It comprises two main nations, namely Chatten and Leucen, hence the name. The Northern Kingdom also includes surrounding islands such as the Lannascern islands, Amarincen islands, Isle of Terk, and the Porgynth islands. Collectively, the domains of the Northern Kingdom are known as the Chalcain Islands. The Northern Kingdom is surrounded by the Eastern Sea, Lacendynn Sea, Leucish Sea, Elvenmann Strait, Chatten Strait, and Septentriones Ocean while bordering the Norpolar Ocean in the north. Meanwhile, the Crowergynn Sea separates the island of Chatten and Leucen, with the isle of Rustav located conveniently between the two islands. The Northern Kingdom shares maritime borders with Finnon and Sonnederlands to the east, Helswig to the south, Tictland and Coradis to the south-east, and Markland to the north-west. The total area of the Northern Kingdom is 512,455 km2 (197,860 square miles) with an approximated population of 115 million people as of 2023. The capital and largest city is Lomercoyne, and its surrounding metropolitan area and the encompassing federal district is the largest in Callys. Other major cities with large urban areas include Mowycen, Pownys, Cumbershyre, City of Lech, Sark, Varnyconne, Shalcyr, Courcamyron, and Malwenydd.
Prehistoric human activity on the islands dates back to the last Ice Age, with continuous habitation since the end of the last glacial maximum. The Chalcerean people emerged as the dominant human culture on the islands which comprises of the tribal societies, namely, Jotavs, Porgynth, Corks, Rwycorrts, Terkish, Leucish, and Chattenish, all were the precursors and founder of the later Thirteen Kingdoms. The anarchic Thirteen Kingdoms period saw the gradual unification of all kingdoms into the domain of the first High King Sycor I of Leucen. The Moravs conquered the islands of Leucen and made it into their province, known as Moravian Leucenia, until their departure from the islands in 800. The Sami-Finnons arrived on the Chalcish Isles, known as the Deluge, beginning in 809 and lasted until 825. Meyrism religion arrived in the islands when High King Sycor IX's exiled younger brothers and recent Meyrian converts, Nymeth and Fwynth arrived on the Islands. The ascension of Prince Nymeth to the throne after the exile of his father led to the founding of the House of Horessen in 844, considered the beginning of the Middle Ages.
Incursions of raiders and pirates, the formation of the Horseshoe Alliance, and a regicide convinced the first Flemmian King Ardewyth to launch several invasions into the northern lands, culminating into the Wars of the Daggers resulting in Leucish victory. The lands of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes were occupied while Rwycorr, land of the Rwycorrts, were annexed directly into Leucen through the signing of the Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213, creating the Kingdom of Great Chalcain. The Acts of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487 was signed by Crowberwynn I in the wake of the Anarchy. By the start of the Age of Discovery, the Northern Kingdom held only island colonies in the Sakadoan Archipelago of which all colonies achieved self-governing dominion status by the end of the 19th century. The Northern Kingdom became the first country to outlaw slavery in all of its colonies by 1685 The Northern Kingdom remained relatively unscathed during the Century of Revolutions despite the occurrence of the July Revolution, which saw the rise of liberal socialism in the government, the formal transformation of the Kingdom into a constitutional monarchy, and the implementation of a more labor-friendly economy while retaining the monarchy. By 1901, they remain the only monarchy in Callys. During this time, universal suffrage was granted, homosexuality was legalized, and labour movements gained traction, a series of events that dubbed the Northern Kingdom as the home of Liberalism under the Social Democratic Party of Chalcain. The NK adopted a policy of neutrality since 1895, though ideology-wise, the Northern Kingdom lean on the side of the Allied Powers.
The Northern Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and a federal parliamentary democracy. It is a developed and advanced country with the seventh-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP). Since 1988, the Northern Kingdom is a nuclear powered state, but does not possesses any nuclear weapons. The Northern Kingdom maintains the Callyssian welfare model that provides universal health care system, a comprehensive social security system, and tertiary education to all its citizens. As a welfare state, it ranks high in income equality, quality of life, gender equality, and prosperity. It is a founding member of the Assembly of Nations, Callyssian Union, Organization for Trade and Economic Development (OTED), International Bank, the G5, and the GNTO.
Etymology and terminology
The Acts of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213 declared that the Kingdom of Leucen should be named "The Kingdom of Great Chalcain". The term "Great Chalcain" refers to the islands of Leucen, its constituent regions, and its surrounding islands. When Chatten was incorporated into Great Chalcain by the signing of the Acts of unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487, the Council of Elders held an executive referendum that resulted in name change from Kingdom of Great Chalcain into the "Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen" by 1501.
With the passage of time; Chalcain, as a term, now encompasses the islands of Chatten and Leucen; and its surrounding islands.
"Northern Kingdom" as a term didn't come into vocabulary use until 1935 when a Tictish journalist Hymera Vera Phon of the Strait Times wrote an article about the prevalence of monarchies in Callys. In the article, Hymera referred to the time where four great monarchies ruled over Callys, with the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen being the northern one amongst the four. Even after the Century of Revolutions which saw a massive upheaval of monarchies around Callys; the people, scholars, military leaders, and politicans still use the term "Northern Kingdom" as an alias to the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen to refer to it as the last surviving monarchy among the Four Monarchies and on the continent as a whole. The
The term "Leucen" has become synonymous with the Great Chalcain and in general is the most common mistake people outside the Northern Kingdom always make. Leucen is also the academic and professional term scholars use during the 18th and 19th centuries when referring to the Northern Kingdom, though it later went obsolete.The Committee of Geographical Names defines "Leucen" as the name of the island that constitutes Great Chalcain, the "Kingdom of Leucen" as a historical region covering almost all of Leucen except for the regions of Rwycorr, Jotav, Lech, Ostria, and Porgynth, "Great Chalcain" as the name describing the totality of Leucen and its surrounding islands with Chatten and its jurisdiction removed, while the Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen describes the Kingdom with both Chatten and Leucen included.
The adjective "Chalcish" is commonly used to refer to the matters relating to the Northern Kingdom and is also used by law to refer to the nationality and citizenship of the people of the Northern Kingdom. Aside from this, however, people might use other ethnic adjectives such as Leucish, Rwycorrts, Chattenish, Terkish, Porgynthish, Jotavish, or Corkish to describe their ethnic heritage.
History
Prehistory


The Proto-chalcerean people first arrived on Chalcain Isles 41,000 years ago, settling the island in waves from Helswig. They continuously inhabited the island until 9,900 years when glacier ice retreated to the poles. By the end of the 2nd millenium BCE, another wave of human migration occurred. Vauns, a tictish tribe, migrated into south-eastern Leucen and southern Terk from the present-day states of Vaunhein and Inner Tictland. The Vauns would remain a distinct ethnicity within the islands. The Chalcerean people would ultimately be separated into two following the appearance of the Crowergynn Sea that will divide the Chalcain Isles into the island of Chatten and Leucen. Before the Tridetarchy, the middle Chalcerean tribes of Gon, Urles, and Poctannan, headed by Lamacil, a High King, fled west into Two River Valley where they allied with Rwycorr by 12 BCE, forming the kingdom of Cydacyll. By the turn of the millenium, however, Leucen, once a minor kingdom, soon emerged as the most powerful Chalcerean Kingdom in the island. The Terks, the main rivals of the later Sami-Finnons, settled on the south-east island of the same name, mingling with the already present Vauns, creating a hybrid of Vaun-Finnon culture in the island. They would ultimately be included as one of the Thirteen Kingdoms as the Kingdom of Terk. By 10 CE, Leucish King Weferstann's son, Maverstann, married the daughter of Terk's King Campugne, Samerwen, aiming to ally a powerful maritime kingdom to his side. In year 45, Incursions of the Lechian tribes into the northern kingdoms of Jotavs, Rwycorr, and Corks persuaded the Jotavian King Komaus to form a confederation, called the Confederation of the North, a decision deemed unpopular yet necessary amongst the Jotavian nobility. When the Rwycorrian King Marcyn ascends to the throne in year 54, he started a series of reforms which establishes the position of a High King and a small noble council known as the Sert. Initially unpopular, this new government system proves itself to be effective and soon becomes popular among the nobility.
The state of Leyds seceded from Cydacyll due to failed land reforms. In 98, continued Terk migrations saw the establishment of the Kingdom of Tamugnonia and Ostrian city states. Meanwhile, northern Chattish seafarers originating from the island of Rustav migrated south and landed on south-western Leucen, establishing the Chattish Chalcerean kingdoms of Doyre and Timmes. Rising tensions between Vauns and Terkish settlers in southern Tamugnonia resulted in a civil war, ending in Vaunish victory. The Grant Treaty of 100 saw Morctos of Timmes establishing East Timmes as a Timmian vassal.
These tribes soon developed into Thirteen Kingdoms by 115, historically known as the Tridetarchy. By the turn of the 2nd century AD, the Thirteen kingdom's domain covered almost all of the island of Leucen, with the Midlands, Lech, and Ester remaining nomadic by the start of the 2nd Century.
The Orchard Affairs culminated in the conquest of Timmes, which led to the abdication of the Timmish King Tictos the Frail and the dissolution of the Kingdom. East Timmes, now an independent kingdom, was not spared by conquest. The conquest of East Timmes by Tamugnonia forced Vaunish settlers to migrate into the only remaining Vaunish Kingdom which was Doyre. In 231, Namarstann of Leucen forged an alliance with the Porgynths in exchange for the bounty of the Ostrian City States. The Ostrian Partition of 256 divided Ostrian into two, effectively surrounding Tamugnonia from all sides by Leucen allies. Ultimately, Leucen would conquer Tamugnonia in 299, and Jaharann of Leucen marries the Doyrish Queen Mifareth, uniting both kingdoms under a single monarchy. A sizeable number of Vaunish inhabitants, finding themselves under the rule of their conquerors, fled to the Kingdom of Terk, which despite their alliance with Leucen, is accepting of the Vauns. By 312, Leucen's domains extends all through-out the southern lands of the island. Leucen adopted the Cydacyllian model of government, with High King Sycor I, once the incumbent King, ruling as the first High King of Leucen.
Moravian Conquests and rule
In 344, the Moravian Conquest begins in the conquest of Helswig. High King Mrathmann of Leucen, seeing the ruthlessness of their new neighbors, allied with the Confederation of the North to protect against potential invasions from the Moravians. By 398, an assembled army led by the future Moravian Emperor Sicador Morastus landed on Doyre. The Moravs invaded and sacked Terk, before moving on to the city of Malwenydd, where they executed Punthywyn, the last Terkish King. Following the massacre at Ostria on 423, High King Fryenwyn of Leucen and High King Therycor II of the Confederacy of the North hastily mustered an army and fought in the Battle of Murandi in 431, resulting in both deaths and Moravian victory. From 435 to 456, the Moravs would conquer Leucen and Porgynth before subjugating the tribal peoples of Ester and southern Midlands. In 466, Cydacyll and Leyds capitulated, giving Moravians a foothold against the Confederacy. It is said that High King Mycor IV grew paranoid after receiving the news, going so far as to enact forced conscription, including his councillors. In order to break the Confederacy, the Moravians, with the help of the tribalistic Lechs, invaded the city of Lech. Cutting the confederacy into two, the Moravians quickly occupied the capital Shalcyr, dissolved the Confederacy, and executed Mycor IV and his family, ending his line.
The Moravians established Moravian Leucenia as an Imperial province by 512. Nobles who pledge their loyalty to the Empire retained their status, wealth, and authority, while those who resist were utterly destroyed, their lands redistributed to other loyal lords. This system had a profound effect on Leucenian politics for centuries to come. Incursions of the Moravians into the island of Chatten proves to be unsuccessful due to the machinations of the maritime warlords around Crowergynn Sea. In 634, Chattenian maritime kingdoms, such as those in Rustav Confederation, flourished during this time period as settlements sprouted along the Chattenian coast. Indeed, the presence of a powerful maritime confederation in Crowergynn Sea discourages the Moravians to pursue further imperial efforts towards the island of Chatten. By the turn of the 8th century CE, coinciding with the decline of the Moravian Empire, Moravian emigration into the mainland increased. The imperial province would soon plunge into anarchy on 801 when Governor Campane Calagaunt, the last Moravian ruler, was assassinated by four unknown assailants. With the absence of a ruler, Kingdom of Leucen became an independent state under the rule of High King Sycos VII, the Kingdom of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes seceded, while Rwycorr revolted against the remaining nobility.
The Deluge and the War of the Daggers

By 805, another wave of migrations arrived on the Chalcish Isles. The militaristic Finnonian Sami-Finnons arrived on south-western Leucen. By 812, the Sami-Finnons had conquered the former lands of Ostria, Tamugnonia, and Porgynth. Faced by a larger threat in its early years of independence, High King Sycos VII of Leucen and High King Yari of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes decided to elect a single High King while maintaining their independence and establishing a single Royal Army, creating the Southern and Northern Electorates. The Midland Wars was fought in November 814 in the expanse of the Midlands, with the Battle of Varnyconne and the Battle of Tower Bridge, where both High Kings were slain, being the most significant. By 825, the Sami-Finnons were pushed back into Ester, where they largely remained until their expulsion during the War of the Daggers.
On 826 , following the deaths of both High Kings, the ascend of High King Sycor IX, the first High King to be elected by both the Southern and Northern Electorates, was followed by authoritative practices. When Sycos IX passes the Pagan Ordinance of 831 which orders for the return to Chalcerean Paganism, two of his younger brothers, Nymeth and Fwynth, resisted and were exiled. They were sent to Morav years ago as emissaries to the King. unbeknowngst to Sycor IX, they converted to Moravian Meyrism in 839. Their conversion to Meyrism resulted in the execution of Fwynth in 840 and later, the Master of the Coin Fylor in 841. Their executions later paved the way for a coup d'etat of Sycor IX's oldest son Nymeth, whom with the consent and vote of both the Northern and Southern Electorates, then becomes the first ruler of the renamed House of Horessen by 844, a naming tradition he inherited from feudal lords from Helswig.
By 910, Corweth of Leucen adopted Tictish tradition and culture such as feudalism, heraldry, Meyrism, and the ruling concept of the divine right of kings. In 978, the King's council decided to formally inaugurate the first university in Leucen. Since then, four more colleges were established around Leucen up until 1312. By year 1000, construction of the Horessen Palace was completed, which become the new royal seat of the Crown. Their former home, the Orbeaun Estate, was designated as the official estate of the Crown's heir apparent.
By the turn of the first millenium, the Kingdom of Leucen was being troubled by the constant raids of pirates and raiders in the east and north. When the Northern Electorate was dissolved by the usurper King Asach, the Southern Electorate broke their alliance with the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes. This effectively disbanded the position of High King of both Kingdoms and the Northern and Southern Electorates completely, restoring royal independence. In 1012, King Hirweth and his family was murdered by unknown assailants, committing regicide and causing the extinction of the male line of House of Horessen. The Red Dagger Conspiracy exposed the role of Cumberwon, currently the Hand of the King of the King Urach of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, as the mastermind of the massacre. A network of anti-Leucish fleets and mercenary groups was created against Leucish dominance, known as the Horseshoe Alliance. By 1014, the King's council welcomed the Helswigan King Ardewyth and declared his kingship to the Leucish throne, founding the House of Flemmes. Ardewyth secretly made an alliance with the Lechians and the powerful Chattish Kingdom of Duran. On the eve of 12 August 1015, Ardewyth declares war on the Horseshoe Alliance, starting the first phase of the War of the Daggers.
In 1100, King Calwyth enacted the Act of Modification to Taxation and Finance 1100, giving absolute military and financial control to the Monarch, disregarding the plea of the King's Council to not enact such divisive reform. The ensuing conflict resulted in the War of the Barons, in which the loyalists were soundly defeated at the Battle of Sewburg. The Barons submitted the The Ten Points, which advocates for the limitation of the Crown's power, the signing of the Frier Marta, the reorganization of the King's Council into the House of Baronies, and the return of land management control over to the barons. The creation of the House of Baronies led to the inauguration of the Parliament.
In 1145, the last ruler of the House of Flemmes, Bunderwyth the Cruel, legitimized all of his sons and daughters before his death in his will, leading to a succession crisis. Prince Yawyth drowned in a ship accident while Nywor was exiled. His remaining children, Princess Voseryth and Princess Daweryth, persuaded Ser Barristan, Head of the Parliament, to call for a Parliament meeting in order to sort out the line of succession. In 1152, The signing of the Act of the Determination of Royal Succession 1152 led to The Parliament choosing the line of Bunderwyth's younger brother, Hammawyth, Duke of Dwerigg as the starting point of the royal succession line. Hammawyth, after marrying Lauret, Princess of Vaunhein, became the first ruler of House of Orgenballet.
In 1163, Bunderwyth and Hammawyth's younger brother, Forwyth, defected to the Kingdom of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, and married Princess Dasterly, daughter of Ermonty IV. The line of Forwyth was then excluded from the royal succession line. By 1182, Cumberwon's descendant, Galamach the Mad, caused a series of persecutions against Meyrist Vaunish peoples after Rwycorrt King Fried I's Vaunish wife, Lormachann, fled into Duran with their son and only heir, Prince Horayes. In 1185, Fried I declared war on Duran, starting the second phase of the War of Daggers, lasting until 1212. This phase of the war ended with a Duran-Leucish victory, in which Leucen occupied the Kingdoms of Rwycorr and the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes. In November 1212, the Parliament, with the consent of the King, decided to annex Rwycorr and occupy the lands of the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, stripping them of independence. With the infamous Agreement on Solebys Hill, the victors, Klauberwythh I of Leucen and Vachea of Duran declared an eternal alliance between the two. In June 8 1213, Klauberwyth II and the Parliament signed the Act of Unification between Leucen and Rwycorr 1213, annexing Rwycorr into Leucen.
Kingdom of Great Chalcain

After consolidating power over the Corks, Jotavs, and the Hundes, Powargenet Orgenballet annexed their lands, dissolving them completely. By 1215, Their last King, Ostrogana of the House of Orgabel committed suicide on the balcony of the King's Hall.
Under the rule of Klauberwyth III, the conquests against the remaining territories within the island of Leucen begins. Between 1220 and 1267, wars were waged to conquer the remaining pagan lands still adhering to Chalcerean Paganism. From the fortress city of Sark in former Ostria, the Leucish secured Ester, once the homeland of the Sami-Finnons since 825 CE. The territory was held for governance to Gumforl, Duke of Porgynth. The oldest pagan city of Varnyconne, dubbed the "City of Eternal Stars", was conquered by Leucish forces stationed in the northern border of Porgynth. By 1270, Leucish forces conquered the entirety of Midlands.
In 1299, The Kingdom of Chatten was formed after the unification of Kingdom of Duran and the merchant Heretorn League in Chatten. Its first ruler, Vonhout the Blessed, Klauberwyth III's nephew, consolidates power for the House of Orgenballet-Nossoine, a cadet branch of the House of Orgenballet. When King Klauberwyth V died with no male heirs and living relatives, the Parliament congregates in Horessen Palace to discuss the possibility of modifying the primogeniture laws. In 1300, the Parliament decided to allow women to inherit the throne so that the current royal house continues, thus establishing the new royal line of succession to Klauberwyth IV's oldest daughter Emily I. Known as Emily the Liberator, she abolished serfdom in 1310 in the wake of the Worker's Revolt led by a Cunn chief Suwroskert Marti. In 1319, Hammawyth II initiated the Piester Conquests and the Amarincen Campaigns, which delivered the island of Cunnari and the Amarincen Islands to the domain of Great Chalcain.
In 1341, Klauberwyth VI ascends to the throne, known popularly for his eight wives. His only successful marriage was with Sherbenne of Garont of the Helswigan House of Garont. Klauberwyth VI's only descendant to his beheaded second wife, Saiah Corlus, Emily II, ascended to the throne on 1378. With their marriage, Klauberwyth VI became King of Helswig and marked the start of the Dual Monarchy.
With the alliance of the Kingdom of Chatten and Great Chalcain honored by both kingdoms, unification of Chatten and Leucen was increasingly becoming plausible, and even seriously considered by both aristocracies. Powargenet II aided Sarral of Chatten during the tumultuous Durbonwille's Rebellion. When House Orgenballet-Nossoine came out victorious in 1431, Sarral offered his son and heir apparent, Marral, Prince of Humboldt, to marry Powargenet II's only daughter Lisa the Fair. Powargenet rejected the marriage proposal due to her daughter's current engagement with Prince Norron, heir apparent to the throne of Helswig.
In 1435, The Meyrian Schism occurred through-out Callys in the wake of the Liturgical Reformation. The Church, governing through the See of Lomercoyne, asserted the Council of Morav, which upholds the Mathunic Church as the true church, and Moravian Meyrism as the true denomination. Differences in Liturgical texts, doctrines regarding religious tolerance, and the rising tensions between Helswig and the Northern Kingdom resulted in the rise of the Reformists, predecessors of the early followers of Chattish Meyrism.
A series of invasions from the Umbrians desolated the nearby Kingdom of Chatten. In 1444, the royal family was massacred in the Marcuari except for the young prince Reiro. The complete breakdown of royal authority and law succeeding the desolation was known as the Anarchy. By 1450, Powargenet III, honoring an alliance to the former Kingdom, launches a series of conquests into Chatten. Reiro was rescued by Borwon, heir apparent to the throne of Leucen. Reiro established the Royal Navy by reorganizing the existing fleets. Borwon would personally lead a contingent of artillery and infantry forces along the Crowergynn Sea, together with the carracks manned by the contingency of Reiro. By 1456, Humboldt was retaken. Following the Chattenian Conquests, Reiro restores the Kingdom of Chatten.
Between 1460 and 1485, peasant uprisings, treason, and the threat of the remaining Umbrians defined Reiro's rule as the last King of Chatten. Finally, in 1896, he gave consent to the unification of Chatten and Leucen. The two houses were re-united when Reiro married Pissa, daughter of Crowberwynn I. On 1487, the Act of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487 was signed by Crowberwynn I, reuniting the two kingdoms.
Kingdom of Chatten and Leucen

With the defeat of Tictland against the Pontifar League in 1493, Chatten and Leucen emerged as the principal naval power on the continent. With the ascension of Powargenet IV, a series of expeditions commenced to explore the origin of spice trade from Lakofor Islands in Sakadonaysia. King Forweth I was killed at the Battle of White Springs, thereby resulting in the loss of all holdings of the Northern Kingdom in Helswig, ending the Dual Monarchy.
The Northern Kingdom also partake in early colonialism. In the early 16th century, the Northern Kingdom has received the cities of Sanfar, Foradel, and Khorqabal, known as the Sister Cities, from Tictland, historically referred to as the Donation of Savony. In 1512, expeditions to the Sakadoan Archipelago opened new trade routes to the south. The Trans-Anglone Route, passing through the Anglone Sea, gave Northern Kingdom wealth and cartographies from distant lands. Sanfar and Foradel serves as trade port cities, while Khorqabal was developed into a military base.The first reformist church called Laer Gnomel was formed in Lomercoyne by the Reformists. In 1550, Crowberwynn II, a known Anti-Parliamentarian and autocrat, attempted to dissolve the Parliament for the fourth time during budget and finance talks with the House of Baronies. Croberwynn II also announced that his younger son Hammawyth II, a practicing Reformist, would inherit the throne. The reaction caused a swift divide between the Moravian Meyrists, which is pro-Mathunic, and the Reformists, which adhered to the teachings of Lufaria Montserrat, the instigator of the Liturgical Reformation. Tensions rise as the majority-Reformist Chatten and Mathunic Leucen threw their support to either Hammawyth II or Samarthyn, the oldest son. The Holy Revolution of 1555 resulted in the establishment of the Church of Great Chalcain, a Reformist Church. This religious development didn't warrant an expulsion of the Moravian Meyrists however, but despite it, a total of 3 million Meyrists fled to either Sonnederland or Helswig.
The Northern Kingdom became much more active in foreign politics beginning in 16th and 17th century. Between 1545 and 1578, the Northern Kingdom has established colonial presence in the Sakadoan Archipelago. These colonies, namely Chalcish Sakadoa, New Chalcain, New Rwycorr, and Chalcish Saka-Zhuya became the Crown's most profitable colonies due to their proximity. In 1603, the Northern Kingdom adopted Laissez-faire and free trade policies. Intervening in the Pontifar Revolutionary Wars (1623-1630) and the Anglonian Wars (1667-1675) as the diplomat gave Chatten and Leucen influence and prestige. The expedition of the Corkian Volcon Umbriag to the North Pole revealed a new ice-free passage through the Norpolar Ocean, starting the Polar Race (1680-1699). By 1685, A royal decree formally outlawed slavery in all of its colonies, the first among colonial powers in Callys. Beginning in 1701, a fur trade commenced between the confederation of tribes in Markland and several whale port cities in the islands of Cunnari, Amarincen, Markland Islands, and Porgynth, and trade settlements in northern Leucen, most specifically the lands of Corkees, Hundes, Jotavs, North of Leucen, and Lech.
The construction of new coal mines, invention of the steam engine, and scientific discoveries led to the emergence of the Industrial Revolution. By 1756, the first railway was built, linking Lomercoyne and the coal mines of Sark. By the mid-17th century, the Northern Kingdom is dubbed the "factory of the world". Almost a quarter of all textiles, steel, steam engines, frigates and ship-of-the-lines was mass-produced in the NK. The rule of Turembel marked the start of the Turembelian Era. Standards of living rose profoundly during this era, which attracted immigrants from all over the world. Turembel is well known for giving royal assent to the ratification of the 1799 Bill of Rights, serving as the framework for a future liberal constitution. Turembel's successor, Klauberwyth VI, was trialed for abuse of royal power and was executed by the revolutionaries during the Constitutional Revolution. This period, known as the Interregnum, was defined by the tyrannical rule of Protector Camnos Sach, the first and last President of the Commonwealth until his death in 1811. Hammawyth III, the heir apparent, and his family, were killed in 1812 while crossing Elvenmann Strait in an attempt to retake the throne from the Commonwealth, ending the ruling line of the House of Orgenballet after 660 years of continued rule. A power vacuum after the death of Camnos and the extinction of the previous royal family led to the invasion of Chalcain by Nethany III of Sonneder, in which she was proclaimed Queen Nethany I of the Northern Kingdom and the founder of the House of Largeyn. Her invasion is considered the last successful invasion of the Chalcish Isles.
Nethanian Era

Through out the Nethanian Era (1812-1896), the Parliament and the Monarchy implemented liberal reforms reminiscent of the fundamental principles of the Tictish Revolution. The Parliament Representation Act 1815 establishes the Assembly of Commons. Beginning with the Reform Act of 1824, the voting franchise was widened to include everyone, with the 1824 Grant of Erinborge giving enfranchisement to all citizens of the Northern Kingdom for the first time. Progress in medical technology and medicine led to a dramatic increase in population, accompanied by rapid urbanization and automobile use. Women's rights was improved under the tenure of the first Prime Minister Donyth Carwenydd, whose position, initially called the Head of the Parliament, was formally established to represent the Upper and Lower Houses of the Parliament. Rapid industrialisation and modernization of the Kingdom placed massive stresses and created new societal and economic issues that accompanied an industrial society.
The administrative landscape of the Northern Kingdom was drastically changed when Queen Nethania passed the Enabling Act of 1830, establishing 25 federal states (with Lomercoyne ultimately developing into the Federal Capital District in 1910) due to increasing population growth. The first governors were of aristocratic descent, mainly the land-owning Barons, but in succeeding years, would gradually be replaced by elected representatives.
The Northern Kingdom was spared from the events of the Century of Revolutions (1802-1905), and many of the freemasons, proponents of liberal democracy, communists, socialists, and political dissidents who were instrumental during the First Springtime of the Peoples (1801-1843) fled to the Northern Kingdom in the eve of its failure. Meanwhile, the same people would participate in the successful Second Springtime of the Peoples (1867-1898), which saw the upheaval of many of the Callysian monarchies. The Four Monarchies that refers to the Northern Kingdom, Empire of the Tictan Nation, Kingdom of Octavania, and the Alsbergish Sonne, failed, with the Northern Kingdom retaining their monarchy by the year 1890.
By the mid-19th century, trade union and worker's congregation sprouted out on each and every city in the Kingdom as a result of huge influx of factory workers. The most influential among them is the National Association of Trade Unions (NATU), established by Marl Webb and Unserrin Vorn in 1845, which accompanied almost all trade unions and associations in all major cities around the Northern Kingdom. In 1895, Prime Minister Fwynth Sagissette declared an ultimate policy of non-interference from further attempts in neocolonialism, a move inspired by leftist policies at that time. By 1896, Sakadonaysia, Sakaos, Zhuya, and New Rwycorr were granted self-governing dominion status. By the turn of the century, NK's industrial dominance became challenged by Federal States and Tictland.
In 1845, the first rapid transit system in Callys and the first subway in the world, initially named Lomercoyne Downlines, was constructed in the old city of Lomerynum in Lomercoyne. Most of the underground rail lines were laid comprehensively north of the river until 1889, when advances in rail and engineering technology allows the Yellow Line to become the first rail line to traverse the River Cymon. By 1896, Another railway system, called the Lomercoyne Uplines, was established coinciding with the construction of Lomercoyne's first standard gauge elevated rail lines. At the start of the 20th century, these two railways were joined by an elevated-subway connector, therefore creating a unified railway system.
At the end of the 19th century, the Social Democratic Party of Chalcain (SDPC) emerged from the union of several trade unions, socialist groups, and suffragettes who campaigned for the legalization of divorce, while the Nationalist Party was formed from the union of the Federalist Party and the Char Funnein (Party of Chatten), two largest political parties in their respective islands. The Crowberwynnian Era under Crowberwynn II saw major social reforms enacted in favor of the working classes, labourers, and poor people. Institutions such as the Chalcish Health and Insurance Service, Chalcish State Housing Bank, and the Chalcish Labour and Welfare Administration (CLWA) were also established as the institutional foundation of the later Callyssian Welfare Model.
July Revolution and the First World War
In 1903, a rally coordinated by the Ard Fein, a Jotavian leftist political party was obstructed by a gas bomb attack by the members of the ultranationalist National Front Party, although at that time, the assailants were not revealed by the Supreme Court of Leucen until 1953. The attack was part of a series of mounting and coordinated attacks on major leftist organizations by the members of the National Front Party and its allies. The general elections of 1905 saw the coalition of several centre-right and far-right political parties into The Coalition, of which they won the elections with a landslide victory. This reactionary political phenomenon was the result of overwhelmingly leftist activities in the past century, partially as a result of the Century of the Revolutions. Between 1907 and 1915, the Coalition dominates the Assembly of Commons, with X seats occupied at the height of their power in 1923. A democratic backsliding is noticeable during their administration. Human rights were curtailed, and progresses in women and early gay rights slowed down. In 1925, the Great Manifesto was published by the Coalition's official newspaper The Vanguard which aims to regress the progress made during the Nethanian and Crowberwynnian Eras.
During the First World War, the Northern Kingdom maintains a policy of neutrality under the tenure of the Conservative Prime Minister Umbrecht Carvill, but a compulsory military draft was enacted to expand the reservist pool. The draft was deeply unpopular, however, and only made the current political instability worse. His successor, Saiah Dwyshyre, abolishes conscription at the behest of Minister Luderich of the Ministry of Arms and Defense. Advances in telecommunications engineering due to war tech development led to the founding of CBC. By 1922, approximately 250,000 witnessed the airing of its first broadcast. By 1927, the number of viewers jumps to 10 million. Approximately 35 million gained access to a telephone by 1928 as electricity consumption increased. A royal charter establishes the National Grid and the Central Electricity Commission by December 1928.
Political instability worsened during the years between 1926 and 1932. With SDPC Prime Minister Homnach Cumnach barely winning the 1930 general election, the SDPC arranged a coalition proposal with the Ard Fein and other centrists and leftist organizations. The 1935 general election was regarded as the catalyst for the July Revolution. Immediately after the exit poll count was released, several technicians stormed out of the Committee of Elections in protest for alleged electoral fraud. This act of protest became the catalyst for the First Storm, which led to a series of civilian protests and massive demonstrations all around the country's major cities. The revelation of the Hammasbiringen in 1936 led to the exposure of The Alternative Way, a treasonous plot to overthrow the current liberal administration, starting a new series of demonstrations and protests known as the Second Storm. The scandal in Rennes, considered the start of the Revolution, revealed the involvement of the conservative Corweth II and several members of the Royal Family on the Hammasbiringen scandal. Exposed, Corweth II dissolves the Parliament and uses his natural powers to instate the members of the Coalition in the Assembly of Commons, an act of violation of Parliament Privileges. The Royal Army imposed martial law a year later.
When Prime Minister Sart Powydd abdicated his position in May 1937, the Monarchy assumed temporary absolute rule over the Northern Kingdom with the passing of the Act of the Emergency Implementation for National Security, also known as the Enabling Act of which the Parliament ratified on 2 June 1937. In response, the remaining members of the Assembly of Commons and half of the MP's of the House of Baronies simultaneously walked out of Horessen Palace, with most of them joining the growing Opposition Left. The first shots were heard in September 1939, where soldiers of the Palace Guard shot two individuals and injured twenty one on a civilian protest attended by approximately three-hundred people. In October 1939, student and teacher protestors blockaded the only entrance to the University with concrete road barriers. Similar events unfolded in Lech University, University of Strasheidd, and University of Malwenydd. The Church of Great Chalcain, initially refusing to involve themselves, were forced to participate by the orders of the Humble Superior Irscyre Namaiah, siding with the Loyalists. By 1940, the political landscape were effectively divided into two; the Loyalists, which were outnumbered yet composed of the Kingdom's most powerful and influential members, and the Left, which was composed by most of the citizenry, the SDPC, Ard Fein, several student council and organizations, the People's Faith, a radical liberal offshoot of the Church; and the heir apparent Hammawyth IV, son of Corweth II. An imminent civil war was avoided, however, when documents and plans revealing the abolishment of veteran aid, pension, and a possible reconstitution of conscription led many generals to join the growing opposition. The July Revolution ended when the Supreme Court, the last bastion of a freely-elected institution declared the current Parliament roster as void, and a general election was called to elect the new Parliament. Croweth II was sentenced to life imprisonment with Hammawyth IV replacing him as the new Monarch, a great demonstration of the Parliament's sovereignty.
Hammawyth IV opens a session in 1941 with the newly elected Parliament. In a majority vote, a constitution was compiled and drafted by the Committee of Elections, asserting Parliament Sovereignty over the Monarchy and specifying the powers that would be inherently present for the Monarchy. Though the Northern Kingdom has not been under absolute rule since the War of the Barons, except for the Interregnum, the ratification of the Constitution effectively turned the Northern Kingdom into a constitutional monarchy.
Second World War and post-war 20th century

Between 1942 and 1945, Prime Minister Gerald Veryddan receives the mantle of responsibilty of ruling the Northern Kingdom during the Second World War. Under his administration, the Parliament abolishes conscription and increased funding for the modernization of the air force. Strictly enforcing neutrality means bargaining with both sides, though secretly the Government in general leans with the Allied forces.
After the war, the Northern Kingdom and the Sonnederlands was left relatively unscathed. In 1945, the Northern Kingdom became one of the founding nations of the Assembly of Nations (X), and together with Sonnederlands, Pontifar, and the Federal States, drafted the Bonne Plan as the first ever unanimous proposal to date. Under the tenure of Prime Minister Daynedd Calwyn, the Parliament revoked the privileges of the Church of Great Chalcain and abolished the position of the Humble Superior in the House of Baronies, a devastating blow for the Church. In 1953, a series of investigations into the participants of the July Revolution led to the removal of royal names and honoraries for the involved nobility, exclusion of several political parties, and the incarceration of the assailants responsible for the bombing attack on Parliament Square five decades ago. The Vanguard and other right-wing newspapers continue to operated normally, though their sales significantly declined as a result of the investigations. The Ministry of Education was reinstated in 1954. The results of the Cumbershyre Trial warrants the construction of a maximum security prison named Calraxter Prison, located in Lotharyn Island within the outlet of the River Cymon.
In 1958, 78% of the Chalcish citizens expressed support for Callyssian integration. This ultimately guided the Northern Kingdom to its path as one of the founders of the Callyssian Union, together with Sonne, Helswig, Sonnederlands, Tictland, Octavania, and Pontifar. Together with the Federal States, they jointly founded the International Bank, Organization for Trade and Economic Development, and the G5, an exclusive organization for high-income and militarily powerful states. The Northern Kingdom became the second democratic country to lower the voting age to 18 behind Helswig and the first country in the world to establish the first institute dedicated for mental health research and care. In September 1963, Sakadonesia and the Northern Kingdom signed an bilateral agreement encouraging immigration between the two nations, guiding the Northern Kingdom into a more multicultural society. Favouring further Callyssian integration, the Northern Kingdom joined the Callyssian Free Trade Association (CFTA) and the Norpolar Trade Union in 1965. In 1967, the Northern Kingdom became the first country in the world to outlaw female genital mutilation and mandatory circumcision in an attempt to enshrine personal rights in the constitution.
Decolonization of the Crown colonies in the Sakadoan Archipelago between 1960 and 1965 led to the independence of two new states; Zhuye and Sakoruinea. The Dominions of New Rwycorr and New Chalcain merged to form the state of Sakadonaysia. In 1966, The Parliament enacted several reforms that led to the Big Bang, a period of economic prosperity and stability that almost tripled the wealth of the middle and lower class. Favourable economic and political conditions led the Ministry of Arms and Defense to begin nuclear weapon research in a testing facility in Cunnari. By 1969, the Northern Kingdom has developed its first atomic bomb, called TK-13, just behind the Federal States. After the Corbaraq Incident, the Assembly of Nations ratified the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty of 1973 which classifies Callys as a nuclear-free zone.
In 1970, the Northern Kingdom's colonial history as the insitigator ended when Parliament ratified the Act of the Pontifarian Sister Cities. Sanfar, Foradel, and Khorqabal was given to Pontifar in exchange for an alliance, ensuring access to the Anglone Sea. In 1972, The universities of Malwenydd and Strasheidd became the base operation for the highly-anticipated Interlink Project, the predecessor to the Internet. By 1990, political reforms were made to ensure efficient rule of law such as the merging of the Supreme Court of Chatten and Leucen into a single Supreme Court and adopting a proportional single transferable voting system.
The Northern Kingdom became the first Callyssian country and CU member to legalize same-sex marriage in 2 May 1998, following a plebiscite result revealing overwhelming support, approximately 71%. Pride marches for the following decades would come to commemorate the day as the start of the annual Pride month. In 1998, the Northern Kingdom connected to the Internet with the completion of the laying out of the Trans-Septentrionic Cable System.
21st century

In the early 21st century, internet users jumped to 12% relative to the Northern Kingdom's population coinciding with the rise of existing tech firms. The ratification of the Act of Agreement and Support for the War on Terror by the Parliament caused divisive discourse both domestic and abroad. When the Federal States begins their campaign for War on Terror, widespread protests and rallies broke out all around Leucen, oppossing the involvement of the Northern Kingdom. The act became so deeply unpopular that by the 2004 general elections, the Nationalist Party overtook the SDPC and won the most seats in the Parliament with Beryll Monach becoming Prime Minister the same year. In 1956, preliminary expeditions were held into The Abyss, a huge sinkhole located within the Kilometer Ring in an island called Abyssal Cone.
The 2012 Callyssian financial crisis has dramatic effect on the wider Chalcish economy. In 13 June 2012, almost fifty-thousand civilians and workers lined up outside of banks to withdraw their savings. Banking firms such as Coleyr & Dome, National Bank, and Bank of the Chalcish Islands (BCI) imposed higher requirements for taking out loans. The Imperial Bank announced a historic 1% interest rate for all banking institutions across Chatten and Leucen. The Durynn - Clesse coalition proposes austerity measures that tackles numerous public budget deficits. During the outbreak of the Plague, the Northern Kingdom became the first country in the world to develop a SAVRAS vaccine for affected places in Sakadonaysia and through-out Axria. The Northern Kingdom is also among the first set of countries that voted for the enshrinement of basic right to food in the International Convention for Human Rights and Dignity.
In 2015, the Parliament allowed the development of nuclear power plants in a bid to implement sustainable energy production policies. Dubbed as the Green Energy Act 2015, the policy established the Nuclear Energy Institute and the Board of Nuclear Energy Management which aims to oversee all nuclear power plant facilites; and the Department of Energy Security which operates as an attached department of the Ministry of Energy. In 2017, a comprehensive bill that aims to develop a system of transport networks was ratified by Parliament. The Gwyndaen Corridor, a continuous high-speed railway line serving the island of Leucen that connects Malwenydd to Lech was completed in 2020, and another high-speed railway corridor that serves the island of Chatten, known as the Carr Sein, was completed in 2022. A connector starts construction in March 2021 which aims to build an expansive transport network that will be known as the Chalcish Rail Network, hoping to decrease car dependency. In 2023, The Northern Kingdom ratifies a parliament act which aims to promote net neutrality in the Kingdom's digital cyberspace.
Geography
Chatten and Leucen is the largest country in Callys; having maritime borders with Helswig to the south, Finnon and Sonnederlands in the east, Tictland and Coradis in the south-east, and Markland to the north-west. It is the largest Callyssian country with no land borders to any country. The Northern Kingdom is bordered by the Septentriones ocean to the west, Norpolar ocean to the north, the Elvenmann Strait and Leucish Sea to the south, Chatten Strait to the south-west; and Eastern and Lacendynn Sea to the west. Chalcish territory covers 512,455 km2 (197,860 sq mi), consisting of 502,312 km2 (193,943 sq mi) of land and 10,143 km2 (3,916 sq mi) of water. Great Chalcain comprises of 56% of the entire land area, consisting of the main island of Leucen, and its surrounding islands such as: Cunnari, Amarincen Islands, Gorth, Porgynth Islands, Isle of Terk, Elven Island, Jutys Island, and Ramburgys Island. Meanwhile, Chatten and its surrounding islands comprises only 44% of the entire land area, including the surrounding islands such as Isle of Rustav, Lannascern Islands, and Furk Island.
A geographical anomaly known as the Kilometer Ring borders the states of Corkees and North of Leucen. With an average depth of 750 km, it harbors the island of Abyssal Cone, an island resembling a crater ring, and within it, The Abyss, a 560-meter wide sinkhole with an unknown depth, though preliminary expeditions descended on a depth of 15 km, making it possibly the deepest point in the world's surface, and possibly much deeper than that. A town under the administration of the state of Corkees was founded in 1977 which acts as a scientific settlement staffed by private groups, local residents, archaeological expedition groups, and members of the Minister of Science and Technology.
The world's Prime meridian passes through the Midpoint Observatory, located a few kilometers east of Lomercoyne in South-east Leucen. The prime meridian originates at an observatory in Carzaragura in Sonne.
The Northern Kingdom lies between longitudes 12° W and 5° E, and latitudes 49° N and 64° N. The Northern Kingdom doesn't share any land borders, but it shares maritime borders with Helswig, Sonnederlands, Finnon, Tictland, Coradis, and Markland. The Crowergynn Sea and Sunderland Strait separates the main islands of Leucen and Chatten, with the island of Rustav located within the Crowergynn Sea. Meanwhile, the Chatten Strait, Leucish Sea, Elvenmann Strait, and Lacendynn Sea separates the islands from continental Callys. The Wedian Sea separates Leucen from the island of Cunnari.
Climate
Topography
Leucen, including its surrounding islands, accounts to 56% of Chatten and Leucen, or 286,974 km2 (110,801 sq mi). The regions corresponding to the state of The Midlands, called the Crescent Plains, is relatively flat, rising to an average height of 99m. Prominent river valleys includes the Two River Valley, near the River Krav; The Gateway, which houses the city of Lech and the River Tict; the Sveteran Valley near Varnyconne; and the Astadorian Valley, which houses the great river of Astador and the city of Humboldt. Prominent mountain ranges includes the Broken Amarincen Mountains, which forms the chain of islands of the Amarincen Isles, the Great Jotavish Mountains, where the tallest points in the country is located; the Erikortt Mountains, the Piester Highlands, the Arkerkian Mountain Range, The Highlands, the Porgynthian Range, the Eastern Chattenian Range, the Mid-Chattenian Range, Cydacyll Highlands, and the Maucer Heights. Mount Colbyranth, towering at 2,250 meters, is the tallest mountain in the Great Jotavish Mountains and in the Northern Kingdom. Lowlands include the Cymonian Woods, the Expanse, Arkerk's Coast, Tict Valley, Crescent Plains, and the Comynraeth Valley.
Biodiversity
Politics

The Northern Kingdom is a federal, constitutional monarchy, and a parliamentary democracy. The Parliament of Chatten and Leucen is the Sovereign, a bicameral legislature consisting of the Assembly of Commons and the House of Baronies, which is previously appointed. The Monarchy is referred to as The Crown within the public, and also within the Parliament. The legislative process takes place within the two houses of the Parliament, but royal assent is required for a bill to become an act of parliament in a form of a statute law. Because of the order of legislative process, the Crown is subordinate to the Parliament in a way that their only primary responsibility is to pass bills into law, and the promulgation of new laws is left to the discretion of the Parliament itself. The Parliament is considered the sole legislative body of the Northern Kingdom.
Crowberwynn VII is the current monarch and head of state of NK. They are automatically vested with all executive authority as the personification of The Crown. As the monarch, they are fundamental in the operation of the Government and to the Law. The set of powers vested in the monarch also comes up with royal prerogatives, and its use is usually counseled with a set of ministers loyal to The Crown. During the performance of their duties, the monarch has the right to be counseled, advised, to encourage, and to warn. Additionally, the monarch held natural powers in their disposal. These powers are rarely used, and is often used on resolving constitutional crises and upholding responsible government.
During general elections to the Assembly of Commons, the Northern Kingdom is divided into X regions, with X counties and X districts in total. Each state is represented by three members of parliament (MP) in the House of Baronies and is elected using the single transferable vote system, except for the Federal Capital District which is represented by four representatives. A term of an MP lasts for 5 years and must face a re-election if they wish to continue. Both the Social Democratic Party of Chalcain, referred to as the "Benchers" and the Nationalist Party, referred to as the "Counters", dominate the political landscape since 1910, which resembles that of a two party system. However, several minor political parties secure enough seats in the Assembly of Commons to be significantly influential, albeit either leaning into one of the dominant parties or standing alone as a non-aligned party. None of the minor parties came close to the size of both parties however.
Nations
Chatten
Leucen
Constituent states
Chatten and Leucen is a federation, made up of 24 constituent states and a federal district. Each state has three representatives in the House of Baronies (except for Lomercoyne which has an additional representative). The number of states are further divided into two nations, with the nation of Leucen having 19 states in its territory, while the nation of Chatten having the remaining 6 states. Each state is represented in the Assembly of Commons with a number of representatives proportionately to the state's population. Lomercoyne (Federal Capital District) has the most amount of representatives, with 17 representatives, while Porgynths, Jotavs, Gorth, and Lannascern each has 4 representatives, the least amount.
Foreign relations
Law and Justice
The Northern Kingdom follows the legal system implemented through-out the Moravian Empire, known as the Moravii Code of Laws, which has existed in the islands since the Moravian conquests. Before the ratification of the Act of Unification between Great Chalcain and Chatten 1487, the various kingdoms of Chatten such as Kingdom of Duran and the Confederation of Vowatan follows a series of legal code known as the Acarus. The Moravii Code of Laws, the current legal system adopted by most of the Callyssian countries, has been influenced primarily by indigenous codes of law such as the Acarus and Helswigan Law. Before the political reforms of 1990, Chatten and Leucen each has their own Supreme Court with limited jurisdiction. The severity of the trials that resulted from the investigations regarding the events of the 1935 July Revolution necessitates a new judicial institution with an absolute jurisdiction over the entire nation. The two Supreme Courts were merged in 1990 to form the Supreme Court of Chalcain with 12 posts for associate judges and the thirteenth post for the Chief Justice. The Dominion Judicial Committee serves the judicial needs of their dominions, most notably, the Federal Republic of Sakadonaysia.
Courts such as the Constuitik, the federal constitutional court, Labouritik, the federal labor court, Fiscalitik, the federal fiscal and tax court, Sociolitik, the federal social law court, and the Patenuitik, the federal patent and intellectual property court, are known as specialized courts. The Frier Marta of 1112 has laid out the foundation of the modern constitution, such as representation, consultation of laws, access to fair trial, and decentralization of power. The Chalcish penal system seeks the rehabilitation of the criminal and reintegration into society. Death penalty is outlawed since the Glorious Revolution.
By 2020, the Northern Kingdom's muder rate stood at a very low 1.2 murders per 100,000. In 2018, crime rate fell to its lowest since 1990.
LGBT rights are generally protected by the nation, with same-sex marriage legal since 2 May 1998 and bans on blood transfusion and donation lifted on 1991. Gender-affirming surgeries was codified by the FHS in 2002 and was made available through-out the public.
Military
The Northern Kingdom's armed forces is the Armduhr (Armed Forces), which is categorized into the Royal Army (Army and the SAFC), the Royal Navy (Marine), the Royal Air Force, the Juntadelicares (Medical Service), Streiskuffande (Support Service), and the Cyberdumaine (Cyber and IT Domain Service). Military spending accounts to approximately 2.1% of the nation's economy, or ₽122 billion piese, meeting the Callyssian Union's suggested military spending threshold. The military spending amount is the largest within Callyssian Union members, double than the second largest military spending amount by Octavania which is ₽47.8 billion pieses. In 2022, PM Saiah Dunwille announced a slight defunding of the military down to ₽99.7 billion pieses.
The Monarch is the commander-in-chief of the Armduhr, to whom military officials pledge their alliegiance of loyalty to. The administration of the armed forces is chaired by the Secretary of Defence, managed by the Minister of Defense and is overseen by the Defense Council. As the primary defense force, the Armduhr is responsible for patrolling the national borders, protecting the interests of the nation, guard the civilian population, and enforce order and stability in times of crisis. In time, the responsibilities of the army expanded to include supporting emergency services in times of crisis and participating in civil service both peacetime and wartime. The military also participates in the international stage by sending in peacekeeping efforts in Axia, participating in joint-exercises, and aiding the allies in times of need. As a member of the Callyssian Union, the Northern Kingdom is also a founding member of the Global North Treaty Organization, a military alliance of Callyssian nations that aims to preserve post-war peace and stability.
Since 1923, women are allowed to serve in the military and take up whatever positions they prefer. In 1987, the Chalcish Armed Forces lifted the ban that prevents LGBTQ+ members from serving in the military.
Economy
Science and technology
Transport
The Waydermichen is the Northern Kingdom's primary highway network, with the first highways constructed during the early 20th century. It totals 34,887 miles (56,145.18 kilometers) in length uninterrupted, including underwater tunnels such as the Chatten-Leucen Tunnel and bridges such as the Malwenydd Bridge. The C-3, located inside the Federal Capital District, is the busiest motorway on Lomercoyne. The Federal Road System has a length of 44,566 miles (71,722 kilometers), a little longer than the Waydermichen, but does the job of connecting areas not accessed by it. There were 34.1 million licensed vehicles all around the Northern Kingdom as of 2018, and is slowly decreasing.
The Northern Kingdom is serviced by two main rail systems each servicing their island. The Gwynaed Corridor, the longest high-speed rail line, the Eastern and Western Corridor, and the Peninsular Corridor forms the base rail lines of the Leucish part of the Chalcish Railways. Carr Fein, meanwhile, forms the Chattenian part of the Chalcish Railways. They are connected by the Chatten Tube under Sunderland Strait. In total, the Chalcish rail network has a length of 12,172 miles (19,588 kilometers). It is administered by the publicly-owned Grand Chalcish Railways, once a privatized corporate entity until 1989. In 2016, the Chalcish Railways of the Northern Kingdom was ranked sixth among Callyssian National Rail Systems in terms of accessibility, intensity of use, safety, and quality service. The Lomercoyne Railways in Lomercoyne services the Federal Capital District and its surrounding counties and is composed of the mostly-underground Lomercoyne Downlines and the overhead Lomercoyne Uplines. The DiagonaLink, CymonLink, and VertiLink also services the metropolitan area. The Homerails, a planned rail system connecting the Capital Counties, some airports, and Lomercoyne, was inaugurated on 20 February 2020. Its total cost is estimated to be approximately ₽443 billion and is intended to be a high-speed rail system, with speeds possibly reaching 235 mph.
In 2015, there were 5.4 billion bus journeys in the Northern Kingdom, with 38,011 buses currently in operation, with 8,900 buses operating in Lomercoyne alone. In Lomercoyne, the buses are operated by several private companies under contract and regulated to the Transportation for Lomercoyne, abbreviated as TfL. Country-wide, all buses are regulated by their respective nation; the Leucish Transportation Council for the Leucish National Government and the Chattenian Transportation Council for the Chattenian National Government. Buses in the Northern Kingdom are distinguished by its red and yellow color scheme, which has entered popular culture as one of the Northern Kingdom (and Lomercoyne)'s cultural symbols. The Lomercoyne Bus Network is extensive; with 9,800 buses carrying over 6.8 million passengers each week all over its 712 bus routes. This makes the Lomercoyne Bus Network the most extensive and largest bus network in Callys.
The Northern Kingdom has 16 international airports, with the Locus-Ardynn International Airport serving as the primary and largest international airport in the Northern Kingdom. All of the Northern Kingdom's airports have handled approximately 290 million passengers in 2023. Three of the largest airports in 2023 were Locus-Ardynn International Airport (77.2 million passengers), Klauber Airport (43.7 million passengers), and Varnyconne International Airport (23.2 million passengers). Locus-Ardynn International Airport, located 24 miles (38.62 kilometers) south of Lomerynum, is the busiest airport in Callys and the second busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic, behind Rookesrow International Airport in Avrecenia. It is the hub of the Northern Kingdom's primary carrier Chalcish Airways. The airports of Lomercoyne are administered by the Roster Aviation, an attached administrative authority under the Leucish Air Transportation Committee, which administers all aircraft, airports, aviation land use, licensing, aviation schools, and military land in the nation of Leucen. Its counterpart is the Chattenian Air Transportation Committee of the nation of Chatten.
Water transportation is an integral part of Chalcish economy. Cymon Ferries, a shared private-public corporation, operates a ferry service running along River Cymon. It is the longest ferry line in the world, with its northern terminus located near the start of the river in Lake Garent, and its southern terminus ending at Sanzoine Pierre, near the mouth of the river. It has a length of 340 miles (547 kilometers) from north to the south. Several ferry and Ro-ro services connects the islands of Chatten, Rustav, and Leucen despite the presence of the Chatten Tube. The Naviar Transport Committee administers the operation of all water transportation vehicles, companies, and travel agencies in Leucen. Just like any other agency, it also has a counterpart in Chatten; namely the Arsinn Transport Committee.
Energy
In 2020, the Northern Kingdom is the 14th largest consumer of energy and the 19th largest producer. Four out of seven major oil and gas companies names the Northern Kingdom home, Netron, Petropharm, Colbetrol, MG, and CommonOil.
The Green Energy Act 2015 establishes crucial institutions in managing nuclear power; the Nuclear Energy Institute, Board of Nuclear Energy Management, and the Department of Energy Security. The first nuclear power plant was built in Cenicen, just south of the city of Mowycen in 2016. Unlike Helswig or Sonnederlands, another power plant was constructed in Bragamyr, West Chattel in 2021. Three more nuclear power plants were opened in Paworys, Terk, and Rwycorr in 2023. Future nuclear power plants are scheduled to be constructed all around the country. Currently, nuclear power only accounts to 14.5% of national energy supply.
The Northern Kingdom is a huge proponent of green energy and combating climate change. It is the first country to enact a legislative law aiming to reach a zero-carbon emission by 2050. 45% of all energy supply sources comes from renewable sources. The green energy sector is composed of geothermal energy (45 per cent), wind energy (30 per cent), nuclear energy (14.5 per cent), Hydroelectric power (5.5 per cent), and biomass energy (4 per cent). Geographically, the Northern Kingdom has all the best wind power sites in the continent due to its oceanic climate, making it the leader of the environmental movement in Callys. The largest offshore wind farm in Callys is located east of Samerys, South-east Leucen at the mouth of Kowysky Strait, close to the northern tip of the island of Terk.
In 2021, approximately 1,015 thousand barrels of oil per day (bbl/d) and other liquids was produced by the Northern Kingdom while consumption is approximately 995 thousand bbl/d. This leaves with a small surplus margin of 20 thousand bbl/d which is being exported in the global market. Production, however, is stagnating due to bans in place for fracking and a declining use on automobiles or cars. Current trends would see a slight deficit in oil and gas supply which will lead to exports within the next five years. In 2020, the Northern Kingdom produces 1.5 million tonnes of coal, a slight decrease from the 2015 report of 1.8 million tonnes of coal. According to the International Natural Reserves Report, approximately 23 billion tonnes of coal reserves still remain in the country. The Federal Coal Authority reports that the Northern Kingdom can produce 1.8 to 2.3 million tonnes of coal each year. Current coal consumption of the Northern Kingdom would last 300-500 years until depletion.
In terms of natural gas, the Northern Kingdom is the 20th largest producer of the substance in the world in 2021. Production, however, has declined significantly and the Northern Kingdom has been a net importer of natural gas since 2010.
Water supply and sanitation
97% of all households in the Northern Kingdom has access to clean water and sanitation. According to the 2021 report of the Ministry of Health, 98% of all households are connected into the sewer network. Total water abstraction for the water supply of several companies around the Northern Kingdom is approximately 18,904 megalitres per day in 2010. Water service providers in Leucen are composed of 8 regional companies. Lomercoyne Water, Peninsular Water; South, Doyre and Ostrian Water, Middle Water, Northern Water, Rwycorrian Water, Northern County Water, and Eastern Water. Meanwhile, the entire island of Chatten, Rustav, and Lannascern is serviced by Chatten Water.
Demographics
In the 2022 census, the population of the Northern Kingdom was 115,112,734. It is the second most populated country in Callys (behind Octavania, Helswig, and Cnutia) and 13th most populated in the world. Net immigration contributed to the population increase and has since been gradually declining. In 2015, natural change has contributed the most in population growth. In 2010, the proportion of the population ages 10-20 rose from 12% to 33%, while the proportion of the population ages 55-65 fell from 29% to 10%. In 2020, the median age of the Northern Kingdom was 39.6 years.
Leucen's population is 87,451,667, approximately 75.97% of the total population, with a distinct concentration of people around major urban centers such as the Capital counties that surrounds Lomercoyne and major cities such as Varnyconne, Malwenydd, and Courcamyron. Meanwhile, the population of Chatten is 27,661,067, approximately 27.03% of the total population. The city of Humboldt in East Chatten, with a population of around 8 million, makes up 32.11% of Chatten's total population, which means one out of three Chattish citizens lived in Humboldt. It is the foremost financial, political, and cultural center of Chatten. The second most populous Chattenian city, Camduran, in North Chatten, only makes up 2.82% of Chatten's population.
In 2019, the average total fertility rate of the Northern Kingdom is 2.82 children per woman. Since 2013, the fertility rate is gradually rising by 0.2% per year thanks to medical innovation and a huge support for women's rights. Generally, the fertility rate is normal when compared to 0.9 children per woman in 1939 and 6.1 children per woman in 1856 general census. Since 1953, the birth rate has surpassed death rate, leading to gradual population growth.
Largest urban areas in Chatten and Leucen
(Chatten: 2022 census; Leucen: 2022 census) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | State | Pop. | Rank | State | Pop. | ||||
 Lomercoyne  Varnyconne |
1 | Lomercoyne | Lomercoyne | 15,712,334 | 11 | Port Lambarinnon | Ester (state) | 788,012 |  Humboldt  Sark |
| 2 | Varnyconne | The Midlands | 10,312,491 | 12 | Camduran | North Chatten | 781,334 | ||
| 3 | Humboldt | East Chatten | 8,881,612 | 13 | Monteive | Rustav (state) | 612,443 | ||
| 4 | Sark | Ostria (state) | 6,988,198 | 14 | Balcaraxyr | Dwerigg | 514,309 | ||
| 5 | Orbeaun | South-west Leucen | 3,312,783 | 15 | Charxyr | South-east Leucen | 513,412 | ||
| 6 | Malwenydd | Terk (state) | 3,110,312 | 16 | Kessenduran | South Chatten | 491,445 | ||
| 7 | Lech | Rwycorr (state) | 2,412,561 | 17 | Savadore | Piester | 482,991 | ||
| 8 | Ghascyne | Paworys | 2,141,561 | 18 | Boines | West Chatten | 342,145 | ||
| 9 | Shalcyr | North of Leucen | 1,253,612 | 19 | Port Nethania | Corkees (state) | 308,181 | ||
| 10 | Mowycen | East of Leucen | 1,132,412 | 20 | Nirkes | West of Leucen | 305,986 | ||
Ethnicity
Languages
Religion
Religion in Chatten and Leucen (2020 census)
Before the Meyrian Schism, the most dominant form of Meyrism in the Kingdom is Moravian Meyrism, which was first brought to the islands by High King Sycor IX's younger brothers, Nymeth and Fwynth. Dominating the islands until 1435, during which litugical and economic conflicts between the See of Maverra and the See of Morve resulted in the division of Meyrism all through out Callys. The schism results in the split of Moravian Meyrism in Chatten and Leucen into two; the Helswigic-influenced Leucish Meyrism and the Finnonian-influenced Chattish Meyrism. Currently, 27% of the population adheres to Leucish Meyrism, while only 10% adheres to Chattish Meyrism. Almost half of the population are non-religious, approximately 53% of the population, but the way they practice non-adherence depends on the individual. According to a survey conducted by Buzzwire, only one out of ten Chalcish citizen attend church monthly. Immigration, secularization, demographic change, and socialism drastically affects religious composition of the country. In a report written by the Chalcish Statistics Authority, 79% of the population adheres to some form of religion before the July Revolution, which dropped to a mere 39% post-revolution by 1945. Because of these developments, the current Chalcish society can be considered a Post-Meyrist, diverse, multicultural, and secularized one.
In the 2020 census, 53% of all respondents indicated that they are non religious or non-adherents to any organized religion, with the largest religion being Meyrism (37 per cent), followed by Dastrity (1.1 per cent), Neo-Dastrity (1.0 per cent), and Chalcerean Paganism (2.1 per cent). 5% of the respondents did not stated their religion while 0.9 per cent adhered to some other religion. Between 2000 and 2010, Meyrism saw a mere 4% rise on adherents while irreligiosity doubles in size. By 2014, non-religion became the largest group, surpassing 50% of the population. By 2016, a huge increase of pagans were also noted, partially due to social media awareness about paganism. Chalcerean Paganism overtook Dastrity and Neo-Dastrity as the third largest religious group in 2017, an event seen by commentators as the great return of pre-Meyrian ways. By 2020, except for Chalcerean Paganism, religiosity all through out the kingdom has been noted by statisticians to be declining for the past 5 years. Religiosity is strong within rural areas, senior citizens, conservative districts, and historical places, though the number of these places (except for historical places) is declining as well.
Before the July Revolution, the Church of Great Chalcain is represented by a seat in the House of Baronies, known as the Humble Superior. The Humble Superior represents the interests of the Church within the House of Baronies. It was established during the 11th century as the spiritual adviser to the King's Council. The Church of Great Chalcain is the state church of the Northern Kingdom, responsible for overseeing spiritual needs of the population. After the Cumbershyre Trial revealed the role of the Church as siding with the far-right Loyalists, the Parliament revoked their privileges and abolished the position of Humble Superior in House of Baronies. Since then, several attempts to bring back the position in the House of Baronies results in failure, partially due to constitutional requirements not being met and the stigma related to the Revolution. Currently, the Church of Great Chalcain frequently participates in donation drives, feeding programs, charity works, digital animation programs, rallies and advertisement to engage with the current generation and to counteract the decreasing number of adherency to the Church.
It is estimated that by 2030, the number of irreligious individuals with respect to the total population would increase by 6%, and Chalcerean Paganism by 1.3%. If current trends were to continue, then Paganism would eventually overtake Meyrism by 2054, the first time in history where Meyrism is not the dominant religion since its introduction in 840.
Migration
Education

Education in Chatten and Leucen is a devolved matter; overseen by their respective national governments. The Ministry of Education governs the operations and management of basic and higher education of both nations. Over 44 per cent of the Chatten and Leucen population has a university or college degree, one of the highest percentages in the world. The world's oldest university, the University of Strasheidd, was established in 978; followed by the University of Lomercoyne; both are highly ranked in the global university rankings.
Chatten and Leucen's education mandates that tertiary education be free for all citizens of the country, except for private universities. As part of the Callyssian welfare model, families who has an annual income of ₽22,000 below are exempt from paying tuition fees in the majority of private universities, as mandated by the Ministry of Education. These are further subsidized by the government using the taxes generated by the means of general annual taxation.
Basic education is mandatory for all citizens. Basic education is divided between primary (which comprises of kindergarten, preparatory, or any pre-elementary education), elementary (which begins in grade 1 and ends in grade 8), and high school (which begins in grade 9 and ends in grade 12). The terms: Freshmen, sophomore, junior, and senior are applicable for both high school and college students. Each student takes a universal academic exam called the General Standard Aptitude Exam; which is a primary requirement for college admission process. Several education institutions such as the ALS (alternative learning system), and WS (workshop systems) are also utilized. Homeschooling is also an alternative.
In 2022, the Global Academic Assessment branch of the OTED ranked the overall skills and academic capabilities of Chalcish 15-18 years old. It ranks Chatten and Leucen as 5th in reading, 9th in mathematics, and 7th in science. The average Chalcish student scored 556, significantly above the world average of 450.
Healthcare
Chatten and Leucen's universal publicly funded healthcare is defined by the operation of the Federal Health Service, established as early as 1850 by Queen Nethania. Its widespread influence in the cultural sphere can be seen through-out some of the kingdom's most well known novels such as Fireflies in September by I.K Lewers and The Madonna Ball by Hussere Wynn, often depicted as early as 1872. The institution is a devolved matter. Both national governments have an attached agency that makes up the entirety of the FHS: the FHS Leucen and the FHS Chatten, serving their respective states. The FHS is an attached institution of the Ministry of Health. Public healthcare is funded by taxation and private donations and are readily available to all citizens of Chatten and Leucen, and in some cases, it is nearly free of charge. The Mental Health Institute, the kingdom's premiere research institute for mental health treatment, mitigation, and prevention, was established as an institution under the FHS in 1960. The International Health Organization ranked the healthcare system of Chatten and Leucen as the second in the Callyssian Union, third in Callys, and tenth in the world in 2010.
Public expenditures on healthcare increased between 2010 and 2020. An OTED research calculated that in 2015, each N.K citizen spends ₽3,412 of taxes in healthcare, a slight increase from 2010 which were calculated to around ₽2,998 per head. Vasectomies and women hygiene items such as tampons became free to the public in 2005 in a bid to slow down birth rates.
Under the FHS umbrella, regulatory bodies exists that analyze, organize, checks, and approve positions and retain high-quality services for the entirety of the Federal Health Service. The Medical Professional Regulatory Commission, itself an agency of the Professional Regulatory Commission of the Ministry of Labor, ensures that the quality of the medical practitioners are kept in check. It also administers board exams for transitioning college students into medical fields. Two of the hardest board exams, namely the Nursing Comprehensive Licensure Exam and the Physician Licensure Exam; are well known for its rigidity and prestige.
Culture
Literature
Philosophy
Music
The music of Chatten and Leucen is influenced by its medieval, imperial, and contemporary history. Indigenous folk music of the Chattish and the Leucish, collectively known as the Chalcer tunes, is a trademark on everyday countryside life. Heryn Tumyna's Hymns of Salvation, written in 14th century Malwenydd, is the standard of most Meyrist mass hymns through-out all churches. Crowberwynn Junyxa's selection of patriotic hymns, his magnum opum being "Marsza oft Mersenadia", currently represents the nation as its official national anthem. Leaders of Chalcish dramatic sayers, poets, and actors re-enacted several iconic Chalcish literatures, with icons such as Saiah Clesse, Marcyn Munavia, and Ragevys Quinns rivaling contemporaries across the continent. Garont Rossone Vynswer, after being naturalized in 1655, wrote The God-coming to the King as a tributary poet and song for Vonhoutsyn I. During the Renaissance, there comes a dramatic rise in Liberalism-inspired revolutionary songs and poetry, with Rys Umbriag composing Libyrte, Egalytrysin, Fratyrnysyn that were ultimately adopted as the official hymn of the Tictish Revolution in 1798. Chattish dramatic innovation in open-air operas, dramatic comedy, tragedy, and realism gave birth to Lysbera, a genre reflecting Leucish peasantry life. Famous actors such as Yuva Umbriag, Klauberwyth Jamys, Fryeder Colbys, and Caxumys Woft Ordyna, icons of realism, wrote dramatic songs, scripts, and oratories that would go on to become part of the Chalcish Format of Music Writing. These same actors would go on to establish new operas, auditoriums, and libraries.
During the Nethania Era, Queen Nethany III & I ushers in the Golden Age of Music, also known as the Creative Age. Under her rule, patronage becomes a key indicator of the fluorishing industry of singers and poets. Parysell Muncell oft Garontys, one of the iconic symbols of Chalcish culture, was granted a lifelong patronage under the newly established Institute of Culture (Ynstiduter oft Kulvura). He then goes on to write several treatises about politics, nature, and societal issues.
The rise of country folk music in the early 20th century coincides with the July Revolution; as people yearn for a peaceful, country living amidst increasing political and societal tensions. The Leucish version of Das Komyunister was composed in 1908 by the infamous Worker's Symphony. Songs related to resistance, abolition of class struggles, and individuality became major themes for much of the music world during the July Revolution.
Visual Arts
Cinema
Cuisine

Chalcish cuisine employs a wide variety of herbs and spices due to their direct control with the Sakadonesian islands. Before the colonial era, Chalcish cuisine developed with the influence of agriculture and fishing with a focus on simplicity. Aksumada is a popular Chalcish dish made with marinated pork stewed in tomato sauce. Dishes like Sweetdough, Yam bread pudding, Mesaka, and Chicken ramski are popular in any time of day. Kamsku, a honey-roasted whole chicken, is often served during Year-ends, Pious Week, and Day of the Dead. A simple dish such as Fisher brunch, a fish partnered with any vegetable, often lettuce and broccolli, is eaten within fishing communities, poor people, and sea-side cities. The undisputed popular dish is Medobar, described by gastronomists as both a dish and a cooking method. It is a general dish that requires any form of meat to be marinated in soy sauce and vinegar, and often additionally served with salt, pepper, paprika, or other spices depending on availability, prevalence, and culture. Medobar has hundred variants around the nation because of its ease of preparedness, and often referred to as the unofficial national dish of Chatten and Leucen.
Chatten and Leucen contains the fourth highest concentration of restaurants rated with at least one Boyrete Star. Modern dining experiences are prevalent in Lomercoyne, Humboldt, Camduran, Lech, and other cities. During a Trihour, tea and coffee are frequently served, a tradition started during the rise of the Industrial Revolution. Vegan and vegetarian based diets have seen a huge increase since 1950, and healthier alternatives have been offered through-out major restaurants.
Green Lemonade juice is the most iconic drink in Chatten and Leucen, and is known in popular culture as the "Bratz Drink".
Coffee has made its way into the Northern Kingdom as the most popular drink to date. Approximately 77,000 cafes exist in the Northern Kingdom, ranging from deluxe to luxurious ones. A Taste Times article revealed that 8 out of 10 of the world's biggest coffee and confectionery chains are based on Camduran, considered the coffee capital of Callys. Chocolate and milk coffee was invented in Lomercoyne by Andrade Movista, a Cork chemist, and the popularity of cafes started in Malwenydd as early as the 1610. Within university towns, cafes are known as "Second homes" by the students, and in the fishing port city of Lech, they are known as the town's "Ringbell of the Square".
Media
The Chalcish Broadcasting Center, founded in 1922, is the Northern Kingdom's oldest and largest broadcasting station in the entire world. It is a publicly funded by the Northern Kingdom as an answer to the increasing accessibility of televisions and electricity. Its subsidiary, CBC International, is the largest of its kind, covering over 55 countries and 49 languages. It operates numerous TV and radio stations around the country, and is well known for having coverage even in the most remote areas of the country. A historical institution, the CBC has covered the events of the July Revolution, the Cumbershyre Trials, the Second World War, Decolonization, the Anti-war protests of 2002, and the 2012 Callyssian financial crisis, and is treated as a live historical archive.
Some of the Northern Kingdom's biggest players in the media industry include the OrbiTV, considered the oldest commercial broadcasting network, and Cablework. Newspapers in the Northern Kingdom include Wirenews, Daily Star, Business Times, and Science Now. Magazines and journal repositories that have gained worldwide popularity, both editorial and academic, include the The Journal, Ekonomik, Geopolitiksche, Taste Times, and The Parliamentarian. Newspapers involved in the July Revolution such as The Vanguard, the official newspaper of the Coalition, have very low subscriber ratings. The Northern Kingdom's publishing sector, including books, newspapers, magazines, editorials, directories and databases, news agencies and business media, and journals, employs 88,000 people and has a combined turnover of ₽99 billion. Since 2004, an increasing demand for digital books is noticeable. Most of the digital books are published in Writpen, an online sharing platform for user-created content. Genres range from Chick lit, young adult literature, political thriller, and LGBT genre.