Nobility of Sydalon: Difference between revisions
m (Latium moved page Vassals of the Sydalene Crown to Nobility of Sydalon) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ''' | The '''Nobility of Sydalon''' comprises of individuals and families of [[Sydalon]], recognized by the [[Monarchy of Sydalon|Monarch of Sydalon]], previous sovereigns, or the [[List of Popes (Ajax)|Pope]]. Members of the nobility enjoy hereditary privileges, often holding fiefs or seigneuries under the crown. Nobility can be distinguished between their role in government, or lack there of. Below the Crown, the highest level of nobility are seigneuries, which form domains, the modern top-level administrative division in [[Sydalon]]. | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
===Seigneuries=== | |||
=== | |||
Seigneuries in Sydalon adhere to hereditary succession, in principle, though early in Sydalon's history this was not always the case where holdings would change hands regularly. Titles may become extinct in the event no heir exists upon the death of possessor. If no heir is available, titles merge into the Crown and become governed by the [[Political divisions of Sydalon#Royal Domain|Royal Domain]]. | Seigneuries in Sydalon adhere to hereditary succession, in principle, though early in Sydalon's history this was not always the case where holdings would change hands regularly. Titles may become extinct in the event no heir exists upon the death of possessor. If no heir is available, titles merge into the Crown and become governed by the [[Political divisions of Sydalon#Royal Domain|Royal Domain]]. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 8: | ||
The second most commonly used method of succession is {{wp|Primogeniture#Male-preference primogeniture|male-preference primogeniture}}. Under this method, a dynast's sons and their lines of descent all come before that dynast's daughters and their lines. Male-preference is practiced by the: County of Tanas; and Lordship of Gadir. | The second most commonly used method of succession is {{wp|Primogeniture#Male-preference primogeniture|male-preference primogeniture}}. Under this method, a dynast's sons and their lines of descent all come before that dynast's daughters and their lines. Male-preference is practiced by the: County of Tanas; and Lordship of Gadir. | ||
The County of Toron is the only seigneury that follows {{wp|Primogeniture#Absolute primogeniture|absolute primogeniture}}. Toron followed agnatic primogeniture until the death of Count Theodore III in 1882, and the title briefly merged into the Royal Domain. The seigneury was eventually granted to Adeline of Toron, the eldest surviving daughter of Count Theodore III. The current creation came in an 1883 royal decree, stipulating that the County of Toron follows the same succession laws as the Crown (absolute primogeniture), and shall be held by a member of the House of Villeine in perpetuity. In practice, the children of a reigning Countess must assume the Villeine name in order to adhere to the royal decree. | The County of Toron is the only seigneury that follows {{wp|Primogeniture#Absolute primogeniture|absolute primogeniture}}. Toron followed agnatic primogeniture until the death of Count Theodore III in 1882, and the title briefly merged into the Royal Domain. The seigneury was eventually granted to Adeline of Toron, the eldest surviving daughter of Count Theodore III. The current creation came in an 1883 royal decree, stipulating that the County of Toron follows the same succession laws as the Crown (absolute primogeniture), and shall be held by a member of the House of Villeine in perpetuity. In practice, the children of a reigning Countess must assume the Villeine name in order to adhere to the royal decree or the titles, property and all associated honors merge into crown and Royal Domain. | ||
===Peerage=== | |||
==The Crown== | ==The Crown== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | {| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Royal domain=== | ===Royal domain=== | ||
==Domains== | |||
==Princes and Principalities== | ===Princes and Principalities=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | {| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Counts and Counties== | ===Counts and Counties=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | {| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Lords and Lordships=== | |||
==Lords and Lordships== | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | {| class="wikitable" style="border:2px solid" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 143: | Line 142: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Hereditary titles== | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Monarchy of Sydalon]] | *[[Monarchy of Sydalon]] | ||
*[[Orders, decorations, and medals of Sydalon]] | |||
*[[Political divisions of Sydalon]] | *[[Political divisions of Sydalon]] | ||
[[category:Sydalon]] | [[category:Sydalon]] | ||
Revision as of 03:01, 17 May 2019
The Nobility of Sydalon comprises of individuals and families of Sydalon, recognized by the Monarch of Sydalon, previous sovereigns, or the Pope. Members of the nobility enjoy hereditary privileges, often holding fiefs or seigneuries under the crown. Nobility can be distinguished between their role in government, or lack there of. Below the Crown, the highest level of nobility are seigneuries, which form domains, the modern top-level administrative division in Sydalon.
Introduction
Seigneuries
Seigneuries in Sydalon adhere to hereditary succession, in principle, though early in Sydalon's history this was not always the case where holdings would change hands regularly. Titles may become extinct in the event no heir exists upon the death of possessor. If no heir is available, titles merge into the Crown and become governed by the Royal Domain.
Seigneuries below the Crown traditionally follow agnatic primogeniture, where by only male heirs are eligible to succeed in order of seniority to the current holder and females are excluded. Most vassals that follow this succession method do so by the original granting papal bull. Titles that follow agnatic primogeniture are the: Principality of Adelon; Principality of Montgisard; County of Alalia; County of Philipopolis; County of Melfi; Lordship of Derum; and the Lordship of Hayan.
The second most commonly used method of succession is male-preference primogeniture. Under this method, a dynast's sons and their lines of descent all come before that dynast's daughters and their lines. Male-preference is practiced by the: County of Tanas; and Lordship of Gadir.
The County of Toron is the only seigneury that follows absolute primogeniture. Toron followed agnatic primogeniture until the death of Count Theodore III in 1882, and the title briefly merged into the Royal Domain. The seigneury was eventually granted to Adeline of Toron, the eldest surviving daughter of Count Theodore III. The current creation came in an 1883 royal decree, stipulating that the County of Toron follows the same succession laws as the Crown (absolute primogeniture), and shall be held by a member of the House of Villeine in perpetuity. In practice, the children of a reigning Countess must assume the Villeine name in order to adhere to the royal decree or the titles, property and all associated honors merge into crown and Royal Domain.
Peerage
The Crown
| Monarch | Styles | Consort | Symbols | Royal vassals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 since 2017 |
Her Majesty Queen of Sydalon Melisende III His Royal Highness Prince Consort Michael |
 since 2018 |
House of Aultavilla  c. 13th century |
Principalities Adelon. Montgisard. Counties Alalia. Melfi. Philippopolis. Tanas. Toron. Lordships Derum. Gadir. Hayan. Royal domain Ostracine. Petra. Sydalon. Aelana. Araman. Cuicul. Mirabel. Scandalion. Tarrasell. Kerkouane. |
Royal domain
Domains
Princes and Principalities
| Ruler | Title | Arms | House – Domain | Location | Spouse – Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Louis XX.jpg | Prince William IV b. 1978 |

|
House of Aultavilla-Adelon c. 14th century Principality of Adelon since 2006 |
|
Spouse: (1) Princess Tyrania of Fakolana Children: |
| File:Joscelin VIII, Prince of Montgisard.jpg | Prince Joscelin VIII b. 1946 |

|
House of l'Aubespine-Nevier c. 13th century Principality of Montgisard since 1972 |
|
Spouse: (1) Victoria Galan Children: |
Counts and Counties
| Ruler | Title | Arms | House – Domain | Location | Spouse – Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Count Emmanwel III b. 1965 |

|
House of Adonibal c. 7th century County of Alalia since 2001 |

|
Spouse: (1) Maria de Bunawita Children: |

|
Count Roger II b. 1967 |

|
House of Eu c. 13th century County of Melfi since 2008 |
|
Spouse: (1) Anna Ulpia Children: |

|
Count Bohemond VI b. 1973 |

|
House of Guiscardi c. 13th century County of Philipopolis since 2015 |
|
Spouse: (1) Princess Sidonnie of Adelon Children: |

|
Count Desiderius III b. 1950 |

|
House of Depasquale c. 13th century County of Tanas since 2002 |
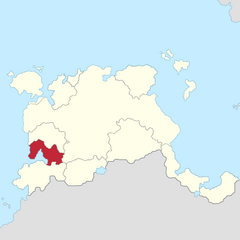
|
Spouse: (1) Sophonisba Pantalleresco Children: |

|
Count Jaime IV b. 1941 |

|
House of Villeine c. 12th century County of Toron since 1997 |
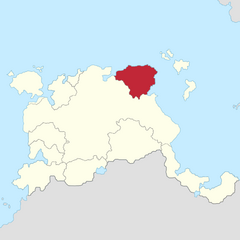
|
Spouse: (1) María Isabel Sáenz de Monclova Children: |
Lords and Lordships
| Ruler | Title | Arms | House – Domain | Location | Spouse – Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Lord Fulk VII b. 1964 |

|
House of Hardouin c. 13th century Lordship of Derum since 2009 |

|
Spouse: (1) Rita Pantalleresco Children: |

|
Lord Cassander I b. 1944 |

|
House of Bodashtart c. 10th century Lordship of Gadir since 1983 |
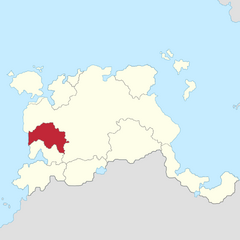
|
Spouse: (1) Rhea Bodashtart Children: |

|
Lord Henry II b. 1959 |

|
House of Scaliger c. 13th century Lordship of Hayan since 2013 |
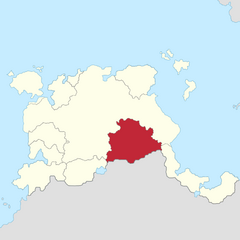
|
Spouse: (1) Emmanuelle of Tanas Children: |