Albeinland: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
Historically, the country has its origins in the beginning of the settlement of several [[Arlethic peoples|Arlethian tribes]] in the modern-day Albish territory in the 1st century BCE. With the growth of these tribes and the increase of foreign influence by Christian missionaries, the founding of the first Albish kingdoms and cities takes place in the 6th century, with the Kingdom of Anglea, the Kingdom of Cambria and the Duchy of Lencester being one of the most influential in the region. In the 11th century, after several wars and conflicts, the House of Annesley of Anglea managed to unify all the region and thus establishing the Kingdom of Albeinland. The {{wp|Middle Ages}} were a scene for military conquests which helped to solidify the territory of the Albish state. | Historically, the country has its origins in the beginning of the settlement of several [[Arlethic peoples|Arlethian tribes]] in the modern-day Albish territory in the 1st century BCE. With the growth of these tribes and the increase of foreign influence by Christian missionaries, the founding of the first Albish kingdoms and cities takes place in the 6th century, with the Kingdom of Anglea, the Kingdom of Cambria and the Duchy of Lencester being one of the most influential in the region. In the 11th century, after several wars and conflicts, the House of Annesley of Anglea managed to unify all the region and thus establishing the Kingdom of Albeinland. The {{wp|Middle Ages}} were a scene for military conquests which helped to solidify the territory of the Albish state. | ||
Although the massive conversion to | Although the massive conversion to {{wp|Protestantism}} in the {{wp|Reformation}}, the absolutist monarchs and the Parliament continued to confront one another, leading to the Oxford Revolution (also known as the Albish Civil War) between 1661 and 1663, with the constitutionalists overcoming the absolutists and introducing a {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|constitutional monarchy}} into Albeinland. The 18th century was a golden age for national politics, economics and philosophy, maintaining its position as a wealthy nation in Lorecia despite political instabilities at the end of the century due a growing radicalism inside society. The 19th century witnessed the establishment of modern democracy, with {{wp|Universal manhood suffrage|universal male suffrage}} being enacted in 1872 and the {{wp|Women's suffrage|vote for women}} in 1919. | ||
Today, Albeinland is a {{wp|democracy|democratic}} {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|constitutional}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|monarchy}}, with the Chancellor acting as the {{wp|head of government}}. The national legislature is the Parliament, which is divided into two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The House of Commons is a {{wp|lower house}} elected by popular vote while the House of Lords is a {{wp|upper house}} appointed by the sovereign under the consent of the Chancellor, the Leader of the Opposition and Privy Council. The country have a semi-written constitution - the Common Charter of 1656, but it also uses another charters and conventions in its legal system. The kingdom is divided between seven provinces, each being governed by a Royal Commissioner appointed by the sovereign also under the consent of the Chancellor and Privy Council. The provinces are: Anglea, Cambria, Lencester, Bedfordshire, Greater Castelby, Zuidland and Saint Laurent. | Today, Albeinland is a {{wp|democracy|democratic}} {{wp|Constitutional monarchy|constitutional}} {{wp|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}} {{wp|monarchy}}, with the Chancellor acting as the {{wp|head of government}}. The national legislature is the Parliament, which is divided into two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The House of Commons is a {{wp|lower house}} elected by popular vote while the House of Lords is a {{wp|upper house}} appointed by the sovereign under the consent of the Chancellor, the Leader of the Opposition and Privy Council. The country have a semi-written constitution - the Common Charter of 1656, but it also uses another charters and conventions in its legal system. The kingdom is divided between seven provinces, each being governed by a Royal Commissioner appointed by the sovereign also under the consent of the Chancellor and Privy Council. The provinces are: Anglea, Cambria, Lencester, Bedfordshire, Greater Castelby, Zuidland and Saint Laurent. | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 15 March 2019
Kingdom of Albeinland | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Libertas quæ sera tamen "Liberty albeit late" | |
| Anthem: Albish National Anthem | |
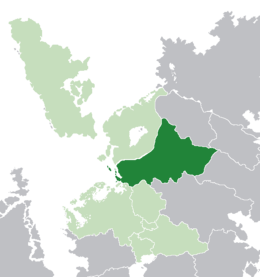 Albeinland (dark green) in Lorecian Community (light green) | |
 Political map of Albeinland | |
| Capital and largest city | Castelby |
| Official languages | English |
| Ethnic groups (2018) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Catherine II |
• Chancellor | Vincent Lloyd |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Commons | |
| House of Lords | |
| Establishment | |
• Foundation of Castelby | 5th century AD |
• Unification | 12 December 1016 |
• Oxford Revolution | 16 August 1652 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,291,800 km2 (498,800 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 30,969,622 |
• 2018 census | 30,968,221 |
• Density | 23/km2 (59.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | £4.028 trillion |
• Per capita | £29,072 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | £5.109 trillion |
• Per capita | £34,011 |
| Gini (2018) | low |
| HDI (2018) | very high |
| Currency | Sterling (£) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (UTC) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +36 |
Albeinland, officially the Kingdom of Albeinland but also known as Alba or Albion is a sovereign state in west Lorecia, bordering Noordenstaat and Fyngaria to the south, Arstotska and Aswick to the northeast and the Aurora Confederacy to the northwest. The geographical location of Albeinland corresponds to the western part of the same continent known as the Alban Highlands and the islands of Arsey, Brunwick and Boiswell in the Albish Channel. The country have a population of approximately 30 million inhabitants according to its latest census, with the largest portion living in the capital and largest city, Castelby. Albeinland has been a member state of the World Assembly since 1999 and was one of the founding states of the Lorecian Community in 1994.
Historically, the country has its origins in the beginning of the settlement of several Arlethian tribes in the modern-day Albish territory in the 1st century BCE. With the growth of these tribes and the increase of foreign influence by Christian missionaries, the founding of the first Albish kingdoms and cities takes place in the 6th century, with the Kingdom of Anglea, the Kingdom of Cambria and the Duchy of Lencester being one of the most influential in the region. In the 11th century, after several wars and conflicts, the House of Annesley of Anglea managed to unify all the region and thus establishing the Kingdom of Albeinland. The Middle Ages were a scene for military conquests which helped to solidify the territory of the Albish state.
Although the massive conversion to Protestantism in the Reformation, the absolutist monarchs and the Parliament continued to confront one another, leading to the Oxford Revolution (also known as the Albish Civil War) between 1661 and 1663, with the constitutionalists overcoming the absolutists and introducing a constitutional monarchy into Albeinland. The 18th century was a golden age for national politics, economics and philosophy, maintaining its position as a wealthy nation in Lorecia despite political instabilities at the end of the century due a growing radicalism inside society. The 19th century witnessed the establishment of modern democracy, with universal male suffrage being enacted in 1872 and the vote for women in 1919.
Today, Albeinland is a democratic constitutional parliamentary monarchy, with the Chancellor acting as the head of government. The national legislature is the Parliament, which is divided into two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The House of Commons is a lower house elected by popular vote while the House of Lords is a upper house appointed by the sovereign under the consent of the Chancellor, the Leader of the Opposition and Privy Council. The country have a semi-written constitution - the Common Charter of 1656, but it also uses another charters and conventions in its legal system. The kingdom is divided between seven provinces, each being governed by a Royal Commissioner appointed by the sovereign also under the consent of the Chancellor and Privy Council. The provinces are: Anglea, Cambria, Lencester, Bedfordshire, Greater Castelby, Zuidland and Saint Laurent.
Etymology
The origin of the name Albeinland doesn't have a proven and unique origin, since its geographical position facilitated that diverse tribes coming from Aurora Confederacy crossed or established temporary settlements on several occasions before the 1st century BCE, which culminated in different names for the same region. The most likely and acceptable theory by etymologists is that Albeinland comes from the Old English Albaland, meaning "land of the Albans". The Albans are considered one of the predecessors of the current Albish people who had direct descent from the Arlethians, an ethno-linguistic group which also are the ancestors of several other modern peoples in Lorecia and Astyria.
It is not well known where the term was exactly created, but chronicles dating from the 6th century CE by Christian monasteries already used the name Albalonde in their writings. The origin of the term Alba still pretty unknown, meaning white in several languages and then probably referring to the white from snow in the long winters, which are traditional due the local climate. So, it's reasonable to say that the term had a geographical and climatic origin, with local tribes beginning to call themselves as Albans soon after to distance themselves from Arlethian terms in the christianization of the region and the founding of the first Albish kingdoms, since such terms were classified as pagan.
The first use of Albeinland happened in 1466, being a modern anglicisation of the old term. Previously, in the Arlethian occupation between the 1st century BCE and 7th century CE, the term Albalanda was used, meaning white earth or white land. The terms Alba or Albion and their demonym Albian are not classified as wrong neither by the Government and Parliament, but being more used poetically.


