Liothidia
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Worker's Socialist Republic of Liothidia Arbeitersozialistische Republik Liothidia | |
|---|---|
Motto:
| |
Anthem:
| |
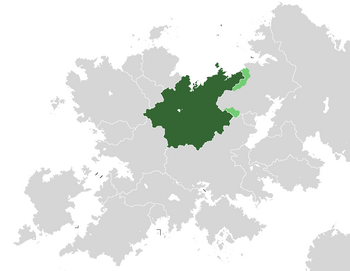 Liothidia in green, claimed but uncontrolled regions shown in light green, Belisaria in grey. | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Rahden |
| Official languages | German |
| Recognised regional languages | Danish |
| Demonym(s) | Liothidian |
| Government | Unitary single party socialist state |
| Georg von Carstein Teresa Fehrenbach Stefan Dietmar Karl-Franz Oberstein Katja Hoepner Gabriel Strauß Janusz Stonoga | |
| Hjalmar Christoffersen | |
| Legislature | People's and Worker's Assembly |
| Establishment | |
| 1846 | |
• Empire proclaimed | 1849 |
| 1918 | |
• Current constitution | 2016 |
| Area | |
• Total | 949,920 km2 (366,770 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 1.3% |
| Population | |
• 2015 estimate | 132,997,111 |
• 2010 census | 131,035,775 |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | $3.365 trillion |
• Per capita | $25,302 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $3.176 trillion |
• Per capita | $23,886 |
| Gini | 40.8 medium |
| HDI (2015) | very high |
| Currency | Liothidian Schilling (LS) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (LRC) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +48 |
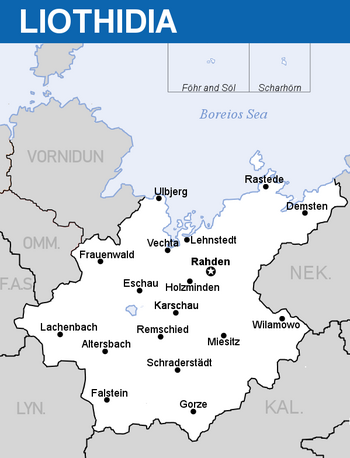
Liothidia, officially known as the Worker's Socialist Republic of Liothidia (German: Arbeitersozialistische Republik Liothidia; ASRL) is a unitary single party socialist state located in northern Belisaria. It borders Nekulturnya and Oseva to the east, Ottonia, Ommenlanden and Vornidun to the west, Lyncanestria and Vannois to the south. To the north is the Boreios Sea. It includes two autonomous socialist regions, covers an area of 949,920 square kilometres (227,618 sq mi), and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With about 131 million inhabitants, Liothidia is the most populous nation in Belisaria. Liothidia's capital and largest metropolis is Rahden. The country's other major cities are Eschau am Schwarzwasser, Lachenbach, Schraderstädt, Altersbach, Vechta, Karschau, Frauenwald, Demsten, Niemarkt, Rastede and Miesitz.
Various Liothidic tribes have inhabited the northern and eastern parts of modern Liothidia since classical antiquity. A region named Liothidia was documented before 100 AD. During the Migration Period, the Liothidic tribes expanded south and westward. Beginning in the 10th century, Liothidian territories centralized into the Liothidian Realm. During the 16th century, the Realm faced near collapse over religious differences, primarily between Protestants and Fabrian Catholics, culminating in the near-destruction of the Protestant Movement within Liothidia. After the wars ended, the territories were united under the Kingdom of Liothidia in 1678.
In 1846 a series of liberal and pan-Liothidian revolutions struck many of the states of the Realm, culminating in the Congress of Werratal, in which the revolutionary leaders offered the crown of a united Liothidia to King August-Wilhelm of Rahdenburg. He duly accepted and formally founded the Kingdom of Liothidia. In 1854, the First Lio-Vannoisian War broke out, resulting in a Liothidian victory and the annexation of Hachenland (formerly Saverne), and the proclamation of an Empire in 1856. The Liothidian Empire prospered for the remainder of the century, becoming a major power. However, the nature of its growth and development allowed for the spread of worker agitation and growing resentment toward the monarchy and landed elite. Throughout the early 20th century, Liothidia struggled as numerous political forces pulled at society, culminating in the August Revolution, which saw the establishment of the first socialist state in world history. Over the next six years, the socialist regime would consolidate its power through mass purges, economic reform and reorganisation of society. By the 1930s, tensions began to arise between Liothidia and monarchist and capitalist powers of Belisaria, culminating in numerous crises and border incidents. In 1944, war broke out between Liothidia and Vannois, sparking the Second Lio-Vannoisian War, the war lasted until 1949 and left close to 3.8 million Liothidians dead and the first use of nuclear weapons. Following the war, the government focused reconstruction and economic reform.
In the 1960s and early 1970s, the Liothidian socialist regime began to reform the economy dubbed "Popularisation", in which free-enterprise was restored in certain sectors and private property was legalised, while the state maintained control of several key industries and enterprises, using fiscal and monetary policy to establish national champions, this resulted in considerable growth and development, while the country increased its global presence by backing anti-colonialist movements, socialist guerillas and governments and modernising its military. In the 1990s, greater focus was placed on the economy and national development.
In the 21st century, Liothidia is a major power and has the world's xx-largest economy by nominal GDP, as well as the xx-largest by PPP, it is also a nuclear power. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world's xx-largest exporter and importer of goods. Liothidia is a developed country with a very high standard of living sustained by a skilled and productive society. It upholds a social security and universal health care system, environmental protection and a tuition-free university education; however, Liothidia is the most unequal society. However, its political system has evolved greatly from the revolutionary period, becoming more oligarchic and authoritarian, while many note an increased level of militant republicanism.
History
Pre-history
Classical
Middle ages
Early modern
Unificiation
Imperial Liothidia
Modern
August Revolution
Socialist state
Second Lio-Vannoisian War
Reconstruction and instability
When the war came to an end in late 1950, the country faced extensive devastation and almost 6 million casualties including 1.1 million civilians. Within a month of the war's end, Viktor Heider died of a stroke and was immediately succeeded by the moderate Gabriel Landauer. Landauer sought to improve relations with Belisaria in wake of the war, he told the 1950 People's Party Congress "if we are to survive the peace, we must make much of the peace." Landauer, a proven administrative genius organised the reconstruction around using demobilised soldiers and the general population, focus was placed on reconstructing resources and infrastructure. By 1953, much of Liothidia's pre-war coal production was retained and exports to global markets resumed, while the government used devastated industries to rebuild over them new, labour intensive heavy industries. Where previously a factory was producing small machine parts, it was replaced with a locomotive and automobile factory.
However in 1953, the refusal by the government to end rationing soon provoked protest by the displaced and starving families. They escalated in rioting after the deployment of soldiers, which rapdily led to the using of live ammunition against protesters as they attempted to storm government buildings. Over the next five days, the People's Revolutionary Army hunted down dissident leaders, the revolt spread to other major cities, which in turn led to the deployment of further armed forces. The crackdown coincided with an end to the rationing system and reform of social assistance, however, the violence and mass arrests resulted in the deaths of an estimated 2,100 people. The uprising failed to overthrow the socialist government and instead, found it strengthened and committed to expanding its powers.
Reform and present day
Geography
Government and politics
Liothidia's constitution states that The Liothidian Democratic People's Republic "is a socialist state under the people's democratic dictatorship led by the working class and based on the alliance of workers and peoples," and that the state organs "apply the principle of democratic centralism." The LDPR is one of the world's few remaining socialist states openly endorsing communism. The Liothidian government has been variously described as communist and socialist, but also as authoritarian and corporatist, with heavy restrictions in many areas, most notably against free access to the Internet, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, free formation of social organizations, freedom of movement and freedom of religion. Its current political, ideological and economic system has been termed by its leaders as the "people's democratic dictatorship", "popular socialism" (which is the formal terminology to describe the reforms of the late 20th century) and the "socialist market economy" respectively.
However, unlike other socialist states, the LDPR operates a more "streamlined system", in which the party and state are entirely merged that little distinction is made officially or unofficially. As such, the People's Central Committee; the key executive body in the government, is simultaneously the Central Committee of the Socialist Workers' Party. Senior civil servants hold senior administrative positions within the party simultaneously, this has led many analysts to describe the Liothidian state as the "ultra-party-state."
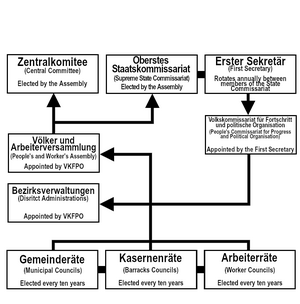
Liothidian government
The Supreme Commissariat of State constitutes the executive branch, directs the national government and serves as collective Head of State and Head of Government. It is a collegial body of seven members, elected for a ten-year mandate by the People's and Worker's Assembly. The First Secretary of the Supreme Commissariat is elected by the by and from among the seven members, traditionally in rotation and for a one-year term; the First Secretary chairs the government and assumes representative functions. However, the first secretary is a primus inter pares with no additional powers. The members are drawn from seven "party-sectors"; the "party-system", the military, industry, commerce, the National Worker's League (sole trade union in Liothidia), state security and the party-office for subordinate agencies.
Subordinate to the Supreme Commissariat is the Central Committee of Liothidia, which exists as the cabinet or council of ministers. The Central Committee is headed by the First Secretary, who oversees the implementation of government policy through the Central Committee, who's members are appointed by the Supreme Commissariat for ten-year terms.
The Liothidian system is unique compared to other socialist states in that elections are held at the local level, based around Municipal Councils, which follow geographical areas. Alongside the Municipal Councils, workers are able to elect officials through the National Worker’s League, and military personnel elect officials through Barracks Councils. All positions above the local level are appointed by the People’s Commissariat for Progress and Political Organisation (Volkskommissariat für Fortschritt und Politische Organisation; VOKFOPO) – which is comprised of retired Central Committee level officials, who take seats immediately upon retirement. PCPPO appoints individuals from the local area to the District Level (city administrations, district administrations etc.) and all members of the Peoples’ and Workers’ Assembly, once every ten years. Appointments are conducted on the basis of “merit” and “record”, to ensure that only the most “committed and competent of revolutionaries are permitted seats of responsibility.” This top-down system is highly centralised and subject to interference by both the Central Committee and Supreme Commissariat.
Political concerns in Liothidia include the growing gap between rich and poor, environmental degradation and government corruption.
Socialist Worker’s Party
Liothidia's constitution declares that the country is ruled "under the leadership" of the Socialist Worker's Party (SAP). As Liothidia is a de jure and de facto one-party state, the First Secretary (party leader) holds ultimate power and authority over state and government serving as the head of state. The political system is highly centralised, with the national government holding significant power and authority over sub-national administrative regions, with the exceptions being the three Socialist Autonomous Regions. Liothidia supports the Schraderist principle of "democratic centralism", but critics describe the elected People's and Worker's Assembly as a "rubber stamp" body, as it meets quarterly only to vote on the executives "Quarterly National Policy."
In recent years however, the executive has taken key decisions to be voted by the VAV outside the Quarterly Congresses, though all decisions taken are supportive of the executive, they have been key in expanding the influence and contribution of the VAV in policy development and direction.
People's and Workers' Assembly
The People's and Workers' Assembly (Völker und Arbeiterversammlung; VAv) is the de-facto legislature of Liothidia, while nominally powerless and subordinate to the Central Committee of State, in recent years its power and influence over the executive has grown. The Vav's power and influence is generally focused around social and economic affairs, where the Quarterly National Policy draws much of its content from consultations between the Vav and the Central Committee. Since 2010, the Vav has slowly become a major focal point in the development of foreign policy, which has been drawn away from unaccountable and often shadowy civil-service groups and committees subordinate to the Central Committee.
Since 2010, the Assembly’s primary role has been the election of the First Secretary and First Minister, which previously took place during the General Congress of the Socialist Workers’ Party. The 2010 reform aimed to expand the senior leadership pool to party representatives within the Assembly and away from the party committees and councils. The same reform ended the tradition of the departing First Secretary choosing his or her successor, in its place was a constitutional provision that the Assembly would produce candidates and then freely vote on the candidates. This alone significantly elevated the status of the Assembly.
Prior to 2010 the Assembly remained essentially a propaganda tool for the Central Committee, with symbolic votes and debates, as well as rousing choreographed addresses by the First Secretary. While the Assembly is still used for symbolic addresses such as the “State of the Socialist Fatherland Address.”
Administrative divisions
Liothidia is divided into 22 districts (Bezirk), three autonomous socialist republics, each with a designated minority group and four municipalities; which enjoy a degree of political autonomy. Although Liothidia is officially a unitary state, its districts enjoy significant levels of autonomy, especially in areas relating to industrial policy, infrastructure development and commerce. Each of the 22 districts are in turn joined together administratively to form regions (Bereich); Zentral, Norden, Western, Östlich, Arktis and Süd.
Autonomous Socialist Regions
Foreign relations and military
People’s Revolutionary Army
With 886,000 active troops, the People's Revolutionary Army (Volksrevolutionäre Armee, VrA) is one of the largest standing military forces in the world, commanded by the Revolutionary Defence Commission (Revolutionäre Verteidigungskommission; RVk). The PRA consists of the Land Force (PRALF), the Navy (PRAN), the Air Force (PRAAF), the People's Revolutionary Combatant Group and the People's State Police. According to the Liothidian government, the national military budget for 2017 totalled $108.9 billion, constituting the world's X-largest military budget, with the military expenditures-GDP ratio at 4.1% of GDP it stands as one of the highest in comparison to the global average.

As a recognized nuclear weapons state, Liothidia is considered both a major regional military power and a major global power. According to a 2013 report by the Arthuristan Ministry of Defence, Liothidia fields between 500 and 950 nuclear ICBMs, along with a number of SRBMs, estimates by the Latin government believe that its arsenal may reach up to 1,100 nuclear warheads. Liothidia maintains some potent global power projection capabilities, including its two Rahden Commune-class aircraft carriers, three Red Banner-class amphibious assault vessels and a substantial fleet of submarines, including several nuclear-powered attack and ballistic missile submarines. Liothidia also maintains several military facilities and outposts in foreign countries, including Nahlia, Estoni and X.
Since 1975, the government has operated a policy known as "Militärische Potenz - Revolutionäre Sicherheit" (Military Potency - Revolutionary Security), which requires continual efforts to modernise and professionalise the military. As a result, Liothidia is developing an indigenous stealth aircraft and numerous combat drones. Liothidia has also updated its ground forces, replacing its ageing tank inventory with numerous variants of previous models and the new PZ15 Kampfmeister, and upgrading its battlefield C3I and C4I systems to enhance its network-centric warfare capabilities. In addition, Liothidia has developed or acquired numerous advanced missile systems, including anti-satellite missiles, cruise missiles and submarine-launched nuclear ICBMs. Liothidia is also one of the major developers of cyber-warfare, with an established unit commonly called the "Phantome von Heinrich Schrader" (Phantoms of Heinrich Shcrader).
People’s Revolutionary Combatant Group
The People's Revolutionary Combatant Group (Volksrevolutionäre Kampfgruppe, VrKf) is the political-military branch of the ruling SPA and effectively constitutes a popular militia. The VRKF receive their training from the People's State Police and the Ministry of the Interior, while they also work as civil defence, emergency response and auxiliary law-enforcement. Membership is voluntary, but SPA members are required to join as part of their membership obligation, though SPA members are confined to non-military roles within the group.
The VRKF currently numbers 440,000 strong, with 285,000 registered as Revolutionary Combatants (Revolutionäre Kämpfer), the latter constituting the armed militia contingent. Since 2001, the VRKF has run fitness programs and military style training in Liothidian schools, while it is also highly influential over the Socialist Youth Front, the official state youth movement in Liothidia.
People’s State Police
Economy
Demographics
With a population of 132.99 million according to the 2015 census, the Liothidia is the most populous country in Belisaria, and ranks as the Xth most populous country in the world. Its population density stands at XXX inhabitants per square kilometre (732 per square mile). The overall life expectancy in Liothidia at birth is 78.19 years (75.93 years for males and 79.58 years for females). Despite decades of dramatic birthrates for a Belisarian nation, since 2011, there has been a consistent fall in birthrates to such a level, that population growth is near stagnant.
Liothidia is a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual nation and as such has several large ethnic groups all of whom are officially recognised in the constitution.
Ethnic Groups
Liothidia's multi-ethnic and multi-lingual nature has ensured that many of the countries minorities have equal and constitutionally defended rights. There are "four national peoples", who constitute the majority, despite being of different ethnic groups. The largest national group is the Liothidians, at 76.41% of the population, with 101,623,092 inhabitants, the second largest group is the Koscians at 14.11%, with 18,765,892 inhabitants. The third largest are the Lemvenians at 5.67%, with 7,540,936 inhabitants. The smallest national people are the Halgalanders at 3.22%, with 4,282,506 inhabitants. The remaining 0.56% are recognised as "other", which include Vannoisians, Ostrozavans and Siverians; of the 744,783, who constitute as "other peoples", the Vannoisian minority is the largest, representing 650,000 citizens, mostly in the Autonomous Socialist Region of Hachenland.
Languages
Liothidian is the most widely spoken language in Liothidia, both as a first and second language, and is the lingua franca of all official documents and business, though not through law. According to the 2015 census, 92% of the population spoke Liothidian as both as a first or second language, while 8% could not speak it at all. Of the 11%, 5% were Koscian, 2% Halgalander and 1% other. All Liothidians and all Koscians reportedly speak the language as a first or second language. Koscian is the second most widely spoken language, with 38% of citizens being able to speak it either as a first or second language.
Liothidian and Koscian are taught from elementary level through to university, while the options of Latin and English are offered from middle to university. Liothidian remains the official language, though its enforcement as such has declined since the 1950s.
Minority languages include Lyonnois, Ostrozavan and Siverian, spoken by around 1.5 million people as either first or second languages.
Religion
Unlike other socialist states, the Liothidian government did not pursue campaigns against religion following the August Revolution. Religion, primarily the Fabrian Catholic Church was immensely influential with the lower and working classes, to such an extent, that it was considered highly problematic for the socialist regime to confront. Between 1916 and 1936, there were some efforts to curtail the influence of the Church, with a ban on Church run schools and services and a coercive effort to block Church efforts at debating politics with congregations. In 1950, the Church was offered a reprieve in exchange for it accepting limitations on its role in society, while many priests under coercion were co-opted by the government. In 1951, the government established the People's Commissariat for Spiritual Affairs, which would manage relations between the government and the Church. The PCSA ordered the Church to operate through Liberation theory or face expulsion from Liothidia.
Since the 1950s, the socialist regime has undermined the Church by subtly arguing for workers to abandon faith and embrace "socialism as the path to salvation from oppression." In 1955, 77% of the population were recorded as practicing Catholics, 19% as Protestant and 4% were non-religious. In 2015, the census showed 24.5% were Catholic, 8% were Protestant and 67.5% were non-religious. It is now widely accepted that the Catholic and Protestant churches are under heavy surveillance and is sometimes used as a means to gauge public opinion or draw out dissidents. In 1999, it was revealed through the Grenau Circle, that priests actively cooperated with the regime as informants, with 18 dissidents arrested in Grenau due to their confessions being used by the regime.
While no violent campaigns were instigated against the Catholic Church following the Revolution, there were coercive acts against other faiths. From 1918-1921, during the "Socialisation Period" (Sozialisierungsphase), many of the country's 586,000 Jews and 139,600 Alban Christians were expelled or fled as their businesses, properties and wealth were seized by the revolutionary government. Liothidian Socialists framed the Jewish and Alban communities as the "two bourgeois pillars of the monarchy", owing to their business success and political influence. Violence and the push for expulsion eventually saw these two communities completely vanish from Liothidian society.
Urbanisation
Largest cities or towns in Liothidia
State Directorate for National Statistics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | District | Pop. | Rank | District | Pop. | ||||
 Rahden  Lachenbach |
1 | Rahden | Rahdenburg | 5,886,305 | 11 | Rastede | Siegerland | 910,642 |  Eschau am Schwarzwasser  Schraderstädt |
| 2 | Lachenbach | Dannenburg | 4,101,775 | 12 | Miesitz | Miesitz-Ravensberg | 800,852 | ||
| 3 | Eschau am Schwarzwasser | Nordenland (District) | 3,962,842 | 13 | Gerstenburg | Hosenfeld | 673,783 | ||
| 4 | Schraderstädt | Sudeger | 3,932,408 | 14 | Remschied | Sudland | 643,844 | ||
| 5 | Altersbach | Südsachsen | 3,402,000 | 15 | Holzminden | Dranske | 540,529 | ||
| 6 | Vechta | Nordenland (District) | 3,261,536 | 16 | Idstein | Hachenland | 405,393 | ||
| 7 | Karschau | Lindau | 2,501,332 | 17 | Falstein | Falstein | 390,324 | ||
| 8 | Frauenwald | Rügen | 2,387,584 | 18 | Lehnstedt | Wittenland | 377,345 | ||
| 9 | Demsten | Rüdesheim | 1,840,551 | 19 | Ulbjerg | Hvornum | 293,404 | ||
| 10 | Niemarkt | Levenkusen | 1,500,003 | 20 | Talheim | Rahdenburg | 291,034 | ||
Healthcare
Education
Liothidia's education system is relatively centralised, with the Socialist Autonomous Regions however, operating some autonomy, yet education is overseen by the People's Ministry of Education and to a lesser extent, the People's Ministry for Skills and Technological Development and with some limited input by the People's Directorate for Revolutionary Affairs. Optional kindergarten education is provided for all children between three and six years old, after which school attendance is compulsory for at least nine years. Primary education usually lasts for four to six years. Secondary education includes three traditional types of schools focused on different academic levels: the Symposien enrols the most gifted children and prepares students for university studies; the Realschule for intermediate students lasts six years and the Hauptschule prepares pupils for vocational education. The Gesamtschule unifies all secondary education. Special schools for careers in national politics and the party are provided through the "Revolutionärer Entwicklungskurs" (Revolutionary Development Course).
A system of apprenticeship called Duale Ausbildung leads to a skilled qualification which is almost comparable to an academic degree. It allows students in vocational training to learn in a company as well as in a state-run trade school.
Most of the Liothidian universities are public institutions, and students traditionally study without fee payment. The general requirement for university is the Abitur. However, there are a number of exceptions, depending on the state, the college and the subject. Tuition free academic education was open to international students until 2004.
Liothidia has a long tradition of higher education. The established universities in Liothidia and some constituent states include some of the oldest in the world, with the Academy of the Immaculate Conception (Akademie der Unbefleckten Empfängnis; established in 1486) being the oldest in Liothidia. It is followed by the Vechta University (1499), the Frauenwald University (1509) and the Altersbach University (1511). In the 20th century, Liothidia reformed its education system to construct more specialist institutions, among them are some of the most prestigious in the world, including the Rahden Institute for Medical Sciences, the Schraderstädt College of Social Studies (which is one of the highest ranked universities for politics, philosophy, economics and sociology) and the Lachenbach University of Science and Technology.
Culture
Music
Film
Sport
Cuisine
Official and public holidays
| Date (Gregorian) | Date (LRC) | English Name | Liothidian Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January | 1 Morgendammerüng | New Year's Day | Neujahr | |
| Solidarity Day | Solidaritättag | Held on the first Friday of February | ||
| 1 May | 1 Arbeit | International Day of the Struggle and Celebration of the Workers | Internationaler Kampf- und Feiertag der Werktätigen | |
| 2 May | 2 Arbeit | Day of All Workers | Tag aller Arbeiter | |
| 3 May | 3 Arbeit | Festival of Labour | Festival der Arbeit | |
| 11 June | 11 Ausdauer | Anniversary of the Socialist Workers' Party | Jahrestag der Sozialistischen Arbeiterpartei | also known as Parteitag, this marks the beginning of the General Congress of the Socialist Workers' Party |
| 31 July | 31 Barrikade | Festival of the Socialist Martyr | Fest des sozialistischen Märtyrers | Commenorates the Kaiserstraße Massacre, also celebrates successful and failed revolutions abroad |
| 12 August | 12 Aufstand | Anniversary of the Revolution | Jahrestag der Revolution | Commenorates the overthrow of the Monarchy |
| 31 August | 31 Aufstand | Anniversary of the Worker's Socialist Republic | Jahrestag der Arbeitersozialistische Republik | Celebrates the official founding of the socialist regime |
| Day of the People's Constitution | Tag der Volksverfassung | Held on the first Friday of September, celebrates the adoption of the Socialist People's Constitution | ||
| 1 October | 1 Ernte | Day of the Farmer | Tag des Bauern | Celebrates the harvest and rural community |
| 5 November | 5 Einheit | Day of Socialist Unity | Tag der sozialistischen Einheit |