Lihnidos: Difference between revisions
Ozycaevias (talk | contribs) m (1 revision imported: Ajax category without templates) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Region_icon_Ajax}} | |||
{{WIP}} | |||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
|native_name = {{resize|11pt| | |native_name = {{resize|11pt|Λιχνίδου Αυτοκρατορία ([[Hellenic language|Hellenic]])}} | ||
|conventional_long_name = Empire of Lihnidos | |conventional_long_name = Empire of Lihnidos | ||
|common_name = Lihnidos | |common_name = Lihnidos | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
|other_symbol = | |other_symbol = | ||
|image_map = Lihnidos_on_Belisaria.png | |image_map = Lihnidos_on_Belisaria.png | ||
|map_width = 275px | |||
|alt_map = | |alt_map = | ||
|map_caption = Location of '''Lihnidos''' (dark green)<br>– in Belisaria (dark grey)<br>– in the [[Belisarian Community]] (light green) | |map_caption = Location of '''Lihnidos''' (dark green)<br>– in Belisaria (dark grey)<br>– in the [[Belisarian Community]] (light green) | ||
|image_map2 = LihnidosMap.png | |image_map2 = LihnidosMap.png | ||
|map2_width = 275px | |||
|alt_map2 = | |alt_map2 = | ||
|map_caption2 = | |map_caption2 = | ||
|capital = Arcadia | |capital = [[Arcadia (Lihnidos)|Arcadia]] | ||
|latd= | |latd= | ||
|longd= | |longd= | ||
|largest_city = Ikaria | |largest_city = [[Ikaria (Lihnidos)|Ikaria]] | ||
|largest_settlement = | |largest_settlement = | ||
|largest_settlement_type = | |largest_settlement_type = | ||
|official_languages = [[Hellenic language|Hellenic | |official_languages = [[Hellenic language|Hellenic]] | ||
|national_languages = | |national_languages = | ||
|regional_languages = | |regional_languages = | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
|languages2 = | |languages2 = | ||
|languages2_sub = | |languages2_sub = | ||
|ethnic_groups = | |ethnic_groups = 87.3% Lihnidosi<br>12.7% Other | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = | |ethnic_groups_year = | ||
|demonym = Lihnidosi | |demonym = Lihnidosi | ||
| Line 51: | Line 55: | ||
|sovereignty_type = Formation | |sovereignty_type = Formation | ||
|sovereignty_note = | |sovereignty_note = | ||
|established_event1 = Founding of Xanthi City- | |established_event1 = Founding of Xanthi City-States | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = 900 BC | ||
|established_event2 = Confederation of City-States | |established_event2 = Confederation of City-States | ||
|established_date2 = 356 BC | |established_date2 = 356 BC | ||
| established_event3 | | established_event3 = Kingdom of Xanthi | ||
| established_date3 | | established_date3 = 154 BC | ||
| established_event4 | | established_event4 = | ||
| established_date4 | | established_date4 = | ||
| established_event5 | | established_event5 = [[Latium|Latin Empire]] | ||
| established_date5 | | established_date5 = 70 AD | ||
| established_event6 | | established_event6 = Independence from [[Latium|Latin Empire]] | ||
| established_date6 | | established_date6 = 565 | ||
|established_event7 | |established_event7 = Hellenic Empire | ||
|established_date7 | |established_date7 = 1713 | ||
|established_event8 | |established_event8 = Lihnidosi Empire | ||
|established_date8 | |established_date8 = 1827 | ||
|established_event9 | |established_event9 = | ||
|established_date9 | |established_date9 = | ||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|area = | |area = | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = 484,224 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |area_sq_mi = 186,959 | ||
|area_footnote = | |area_footnote = | ||
|percent_water = | |percent_water = | ||
| Line 84: | Line 88: | ||
|population_census = 71,394,929 | |population_census = 71,394,929 | ||
|population_census_year = 2014 | |population_census_year = 2014 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 147.44 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = 381.88 | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
|GDP_PPP = $ | |GDP_PPP = $2.977 trillion | ||
|GDP_PPP_rank = | |GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
|GDP_PPP_year = | |GDP_PPP_year = 2017 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = $ | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $41,109 | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = | |GDP_nominal = | ||
| Line 97: | Line 101: | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = | |Gini = 38.9 | ||
|Gini_rank = | |Gini_rank = | ||
|Gini_year = | |Gini_year = | ||
| Line 104: | Line 108: | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = | ||
|HDI_category = | |HDI_category = | ||
|currency = Denarius | |currency = Denarius | ||
|currency_code = '' | |currency_code = ''{{strikethrough|X}}'' | ||
|time_zone = | |time_zone = | ||
|utc_offset = | |utc_offset = | ||
| Line 125: | Line 129: | ||
|footnote7 = | |footnote7 = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Lihnidos''', officially the '''Empire of Lihnidos''', is a {{wpl|sovereign country}} located in southern [[Ajax|Belisaria]]. Lihnidos is an island nation in the Periclean Sea. It shares maritime borders to the north with [[Garima]] and to the west with [[Vannois]]. Southern and eastern Lihnidos is surrounded by the Periclean Sea. With an area of 484,224 square kilometers and an estimated population of approximately 72.5 million inhabitants, Lihnidos is the eighteenth most populous country in [[Ajax]] yet also one of the smaller nations in land area. | |||
Lihnidos is a {{wpl|unitary state|unitary}} {{wpl|parliamentary democracy}} and a {{wpl|constitutional monarchy}}. The current and ninth [[Monarchy of Lihnidos|monarch]] is [[Stella II of Lihnidos|Stella II]], who has reigned since late 2007. The current and twenty-sixth [[Prime Minister of Lihnidos|prime minister]] is [[Fotis Raptis]] who leads the [[Conservative-National Alliance (Lihnidos)|Conservative-National]] government in the [[National Assembly of Lihnidos|National Assembly]] and who has been in office since early 2010. Lihnidos's capital is the city of [[Arcadia (Lihnidos)|Arcadia]] and the largest city is [[Ikaria (Lihnidos)|Ikaria]]. Other major population centers include the cities of [[Xanthi (Lihnidos|Xanthi]] and [[Cephalonia (Lihnidos)|Cephalonia]]. | |||
{{wpl|Modern humans}} first arrived in Lihnidos around 35,000 years ago from [[Ajax|Scipia]]. Several tribes made settlements in coastal regions that later led to the development of Hellenic cultures in southern Lihnidos. Settlements consolidated under centralized rule in the form of city-states and later duchies and kingdoms until the region came under [[Latium|Latin]] rule around 70 AD. After the fall of the Latin Empire in Lihnidos around 600 AD, numerous kingdoms formed and later joined as the United Kingdoms of Lihnidos in 1675. | |||
In 1713 the United Kingdoms of Lihnidos and the [[Tarsas|Tarsan]] Empire fell under the same rule and formed the [[Hellenic Empire (Ajax)|Hellenic Empire]]. This wide-spanning empire that included lands in Belisaria and Scipia lasted for roughly one hundred years before fracturing into smaller empires and kingdoms. Following Lihnidosi independence from the Hellenic Empire in 1827 the Lihnidosi Empire was declared as the successor state of the Hellenic Empire. The fall of the Hellenic Empire caused instability in parts of Lihnidos and Scipia which lasted in Lihnidos until roughly the mid-1850s. | |||
Presently, Lihnidos is a {{wpl|developed country|developed}} and {{wpl|high income country}} with the world's 9th largest economy by nominal GDP. The country is a member of the [[Belisarian Community]], [[Forum of Nations]], and [[Joint Space Agency]]. | |||
==History== | |||
===Prehistory=== | |||
[[File:Reproduction cave of Altamira 02.jpg|220px|right|thumb|A reproduction of Bylyyn cave paintings]] | |||
The first evidence of the presence of modern humans in Lihnidos was found in the Bylyyn caves outside the town of Nauros in southern Boeotia. The best known artifacts from this time period are cave paintings and fossilized remains that were created between 35,900 to 21,200 BC. Genetic evidence suggests that the first humans in Lihnidos arrived from the southern continent of Scipia and made their way north into Belisaria. | |||
Lihnidos is home to some of the first advanced civilizations in Belisaria. Many of these civilizations were began by well-established settlements that had been founded as early as 3500 BC. The Hellenes inhabited the southern and eastern coastal areas of Lihnidos before moving further north and west. These civilizations began with the Gythacan civilization on the eastern coast of Lihnidos in Messenia around 3000 BC, the Cyrelean civilization around 2700 BC in Kilkis, and the Iolcippian civilization in the Samos Islands around 1900 BC. These civilizations remained largely independent of one another with limited conflict until around 1000 BC when the Gythacans began a time of regional upheaval by attempting to conquer surrounding civilizations. | |||
===City-states and unification=== | |||
The end of the regional conflicts and transition into a more stable society happened around 900 BC with the creation of numerous city-states across southern Lihnidos. Hellenic city-states stretched as far west as the Latin peninsula and as far east as Tarsas. Many of these city-states were prosperous centers where the arts and sciences were allowed to flourish. | |||
[[File:Taormina BW 2012-10-05 16-05-05.jpg|220px|right|thumb|A Hellenic theater in Xanthi]] | |||
The most successful city-state in Lihnidos was the city-state of Xanthi that was located on the western coast of Boeotia. Xanthi was the first city-state in Lihnidos to adopt a democratic form of government while many others were ruled as aristocracies or some form of military dictatorship. Xanthi society, varying from its counterparts, put it at a disadvantage in matters of war and there are several instances where it is believed that Xanthi was almost captured by hostile powers. | |||
By 450 BC war was common between varying city-states due to no unifying ideology or goal. During this period there was a significant decrease in the development of sciences and arts as many city-states began to suffer from constant war. The ongoing disputes led to a breaking point around 360 BC when the leaders of Xanthi called for an assembly of leaders from the most prominent and powerful city-states at the time in an attempt to cease the hostilities. The proposal did not gain traction until three years later in 357 BC when several smaller city-states that had not been previously considered proposed the assembly of leaders once again. The increased interest from smaller city-states and Xanthi, which at the time, despite its non-military culture, was one of the more powerful military powers in the region, prompted remaining holdouts who were against such a meeting to accept. The assembly took place in 356 BC in Xanthi. The assembly of city-state leaders brought many concerns, as many of the militaristic city-states believed the assembly to be a ploy by the smaller city-states to eliminate their leadership. Because of this belief, four different city-states brought military contingents that camped outside of the walls of Xanthi for the duration of the assembly. While the exact number of troops camped outside the city was not recorded, writings from people in the city point to a total troop count in the tens of thousands. | |||
[[File:Alexander and Bucephalus - Battle of Issus mosaic - Museo Archeologico Nazionale - Naples BW.jpg|220px|left|thumb|Hyeligeneian leader Anastasius, whose conquest resulted in the formation of the Kingdom of Xanthi]] | |||
The assembly is believed to have lasted for two weeks as leaders from the city-states debated and negotiated peace. The result of the assembly led to the creation of a confederacy of city-states that would promote mutual defense and resource sharing. The fragile attempt to stop the wars appeared to succeed until 156 BC when the city-state of Hyeligeneia accused the city-state of Aigane of planing war against them. The two were quickly drawn into war as Hyeligeneia marched on the city of Aigane. The war drew other city-states into the fighting and, despite the best efforts of some members of the confederacy, it collapsed shortly after. The fighting led to Hyeligeneia conquering a number of city-states in central Lihnidos and eventually the leadership turned its wrath to Xanthi. In 154 BC Xanthi fell to the Hyeligeneian military. By the time Xanthi had been conquered, a majority of the land in southern Lihnidos was under Hyeligeneian control. Following Xanthi's conquering, the leader of Hyeligeneia proclaimed himself king, using the name of the most recently conquered city-state as his kingdom. The Kingdom of Xanthi under Anastasius I quickly took control of much of what is today the provinces of Boeotia, Serres, Kilkis, Thasos, Pieria, Evros, and Chania. | |||
=== | ===Latin Empire and independence=== | ||
The | The Kingdom of Xanthi continued to expand further east until around 60 AD when it had conquered much of present day western and central Lihnidos. Expansion was halted between 59 and 62 AD when the Latin Empire to the west began to expand further east, encroaching on Xanthi territory. The Latins launched their first invasion into Xanthi territory around 64 AD and quickly moved east, easily defeating the inferior Xanthi military forces. Xanthi military forces attempted several times to halt the Latin move east, but failed to do so on almost all occasions. Xanthi, also the name for the capital of the kingdom, fell in 67 AD and saw the death of the reigning monarch at the time, Anastasius II. Anastasius' death left the kingdom without clear leadership for the remaining years of the invasions as his immediate heirs also died during the war. | ||
The Latin military had defeated the last pockets of resistance in the east by 70 AD. Historical records suggest that Latin military strength was far superior to that of the Kingdom of Xanthi. The ten year time frame of the invasions was significantly longer than historical evidence suggests it could have been. The lengthy period was likely a result of the Latin Empire's attempt to incorporate and assimilate those from Xanthi into their culture, with the Latins taking several several-month-long breaks between periods of expansion into Xanthi. | |||
Latin rule over Xanthi territory lasted for approximately 500 years from 70 to 565 AD. During this time Latin culture and language was widely accepted as the norm and present throughout much of what had been the Kingdom of Xanthi. Despite this there were still holdouts among the Xanthi nobility that sought independence and held on to old traditions and language. | |||
=== | ===Hellenic Empire=== | ||
===Lihnidosi Empire=== | |||
=== | ===Recent history=== | ||
==Geography== | |||
[[File:Mytikas.jpg|220px|right|thumb|Mount Elenae features the highest point in Lihnidos]] | |||
Lihnidos is located in southern Belisaria. Lihnidos is an island nation, meaning that it shares no land borders. However, Lihnidos shares maritime borders with Garima to the north and Vannois to the west. The Periclean Sea surrounds Lihnidos from the south-west to the north-east, with the Zarelis Strait running between Lihnidos and Garima and Vannois. Lihnidos covers roughly 484,300 km2, or roughly 187,000 square miles. Of the total area, approximately three percent is water in the form of lakes and rivers. Lihnidos is comprised of sixty-six islands, including the main island, and hundreds is islets. | |||
Terrain in Lihnidos varies from the shores of the islands to the northwestern Pelea Mountains. The highest point in Lihnidos is Mount Elenae at 2,813 meters, or 9,229 feet. There are extensive plains in the eastern regions of the country that comprise much of the country's arable land. Many of the small islands in southern Lihnidos have hilly or even mountainous terrain. | |||
=== | ===Climate=== | ||
[[File:Ionian_sea_islands,_pic6.JPG|220px|right|thumb|Mainland Lihnidos and several small islands]] | |||
The primary climate of Lihnidos is the Mediterranian climate, more specifically the hot-summer Mediterranean climate. This type of climate typically features hot summers and mild, wet winters. It is possible for some regions within this climate to experience chilly winters and snowfall, however that is rare in Lihnidos. The hot-summer Mediterranean climate occurs at all southern islands and all southern coastal locations in Lihnidos. Some northeastern regions of Lihnidos are classified as having a warm-summer Mediterranean climate, which experience warm and dry summers with wet and mild to chilly winters. | |||
The mountainous regions of Lihnidos in the northwest feature a temperate climate and, in some areas, an alpine climate. The temerate climate experiences hot and dry summers with cold and wet winters. The alpine climate can experience heavy snowfall in the winter months. These regions are primarily within and around the Pelea Mountains in the provinces of Lasithi, Chania, and Piraeus. | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
===Population=== | ===Population=== | ||
According to the 2014 census conducted by the Ministry of Local and Regional Governance, the population of Lihnidos at the time was 71,394,929. With continued immigration, emigration, and new births, it is estimated that the current population is roughly 72 | According to the 2014 census conducted by the Ministry of Local and Regional Governance, the population of Lihnidos at the time was 71,394,929. With continued immigration, emigration, deaths, and new births, it is estimated that the current population is roughly 72.5 million, only an increase of slightly over one million. Lihnidos's estimated population of over seventy-two million makes it the fifth largest nation on Belisaria by population, behind [[Liothidia]], [[Arthurista]], [[Latium]], and [[Ottonia]]. According to the 2014 census, a vast majority of the population identify as Lihnidosi, with 87.3% doing so. The second largest group of individuals are those who identify as Vannoisian, which account for roughly five percent of the population. The majority of the remaining eight percent come from other Belisarian countries including [[Garima]], [[Lyncanestria]], and [[Latium]], while some others come from non-Belisarian countries such as [[Sydalon]], [[Belfras]], and [[Tarsas]]. The racial makeup of the population is homogeneous in the aspect that 96.2% of the population identify as Caucasian. The other primary racial groups in Lihnidos are Scipian at 1.9%, Oxidental at 1.5%, and Ochran at 0.4%. | ||
====Largest Cities==== | ====Largest Cities==== | ||
A majority of the population live in rural areas opposed to urban areas like large towns and cities. Only three cities in Lihnidos have populations over one million: [[Ikaria]], [[Arcadia ( | A majority of the population live in rural areas opposed to urban areas like large towns and cities. Only three cities in Lihnidos have populations over one million: [[Ikaria (Lihnidos)|Ikaria]], [[Arcadia (Lihnidos)|Arcadia]], and [[Xanthi (Lihnidos)|Xanthi]]. All three cities have deep historical significance and hold a special role in the nation. Ikaria, often considered the financial capital of Lihnidos, has served as home to the headquarters of many of Lihnidos's largest businesses, both domestic and foreign. Arcadia, the capital of Lihnidos, serves as the seat of the government. Xanthi, the original capital of the empire, served as the capital of the Xanthi Confederation of City-States, the Kingdom of Xanthi, and the early Empire of Lihnidos. Due to its historic role, it is often deemed the cultural capital of the nation. Close behind the top three cities is [[Cephalonia (Lihnidos)|Cephalonia]], which ranks fourth with a population only slightly under one million. After Cephalonia the populations of the largest cities begins to drop significantly. | ||
{{Template:Largest Cities in Lihnidos}} | {{Template:Largest Cities in Lihnidos}} | ||
====Provinces==== | ====Provinces==== | ||
Lihnidos is divided into twenty provinces, each of a different size and population. The borders of each province are partially based on the borders of the historic duchies that comprised the three kingdoms of Lihnidos in its medieval history. Serres is the largest province by population, but the | Lihnidos is divided into twenty provinces, each of a different size and population. The borders of each province are partially based on the borders of the historic duchies that comprised the three kingdoms of Lihnidos in its medieval history. Serres is the largest province by population, but one of the smallest by land area. With over eight million people, it holds over eleven percent of the population of the nation, over a fourth of which live in the capital city of the province, Ikaria. Many of the provinces are close in terms of population, with half having a population of between three and four million. | ||
{{Template:Lihnidosi Provinces}} | {{Template:Lihnidosi Provinces}} | ||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
[[File:ArcadiaCathedral.jpg|200px|left|thumb|The Cathedral of Saint John is the largest cathedral in Lihnidos.]] | [[File:ArcadiaCathedral.jpg|200px|left|thumb|The Cathedral of Saint John is the largest cathedral in Lihnidos.]] | ||
Religion is held sacrosanct in Lihnidos and the intermingling of church and state is often criticized by those who believe that religion should not be present in government. The majority of individuals in Lihnidos describe themselves as adherents of {{wp|Roman Catholic Church|Fabrian Catholicism}}. While Lihnidos does not have a state religion, a number of prominent government officials and nobility are followers of the faith and therefore occasionally may make decisions that follow the teachings of the church. Over | Religion is held sacrosanct in Lihnidos and the intermingling of church and state is often criticized by those who believe that religion should not be present in government. The majority of individuals in Lihnidos describe themselves as adherents of {{wp|Roman Catholic Church|Fabrian Catholicism}}. While Lihnidos does not have a state religion, a number of prominent government officials and nobility are followers of the faith and therefore occasionally may make decisions that follow the teachings of the church. Over thirty-six million individuals in Lihnidos identify as Fabrian Catholic, accounting for almost fifty-two percent of the population. | ||
The second largest religion in Lihnidos is [[Alban Christianity]], which while far behind Fabrian Catholicism, has a significant following in Lihnidos. Almost seventeen million individuals identify as Alban Christian, which accounts for another twenty-three percent of the population. Other religious groups are not as prominent in the nation, with almost seven percent of the population describing themselves as Christians that do not follow either Alban Christianity or Fabrian Catholicism. Those who have no faith or who do not describe themselves as Christians comprise | The second largest religion in Lihnidos is [[Alban Christianity]], which while far behind Fabrian Catholicism, has a significant following in Lihnidos. Almost seventeen million individuals identify as Alban Christian, which accounts for another twenty-three percent of the population. Other religious groups are not as prominent in the nation, with almost seven percent of the population describing themselves as Christians that do not follow either Alban Christianity or Fabrian Catholicism. Those who have no faith or who do not describe themselves as Christians comprise almost nineteen percent of the population. | ||
{{Pie chart | {{Pie chart | ||
| thumb = right | | thumb = right | ||
| Line 207: | Line 204: | ||
| other = | | other = | ||
| label1 ={{wp|Roman Catholic Church|Fabrian Catholic}} | | label1 ={{wp|Roman Catholic Church|Fabrian Catholic}} | ||
| value1 = | | value1 =51.3 | ||
| color1 =gold | | color1 =gold | ||
| label2 =[[Alban Christianity|Alban Christian]] | | label2 =[[Alban Christianity|Alban Christian]] | ||
| Line 216: | Line 213: | ||
| color3 =navy | | color3 =navy | ||
| label4 =Other religions or no faith | | label4 =Other religions or no faith | ||
| value4 = | | value4 =18.9 | ||
| color4 =grey | | color4 =grey | ||
}} | }} | ||
Prior to Fabrian Catholicism and Alban Christianity being the predominant faiths in Lihnidos, a large | Prior to Fabrian Catholicism and Alban Christianity being the predominant faiths in Lihnidos, a large portion of Lihnidosi practiced a form of polytheistic paganism. This paganism varied in several parts of what is now Lihnidos, but many of the different sects had enough similarities that they could collectively be referred to as one religion. The ancient religion was present in every part of an individuals life and had an extensive mythology that caused followers to see works of the gods in almost everything. Alban Christianity began to take hold in Lihnidos in the 2nd century as it became the dominant faith in the neighboring Latin Empire. Spreading from west to east, the teachings of the Albian church attracted several who were dissatisfied with the teachings of the dominant pagan religion at the time. By the early fourth century Albian Christianity had a substantial following across the Kingdom of Xanthi. Under the reign of Latin Emperor Iovinus, Alban Christianity was made the state faith of the Latin Empire. Paganism was banned, and a renewed effort was put into converting nonbelievers. Later, during the reign of Constantine I, Fabrian Catholicism began to overtake Alban Christianity, eventually becoming the majority religion. | ||
The amount of those who identify as not following any religion has risen slightly over the years. In 2004 the percentage of individuals who identified as atheist or agnostic was | The amount of those who identify as not following any religion has risen slightly over the years. In 2004 the percentage of individuals who identified as atheist or agnostic was approximately seven percent. Ten years later in 2014 the percentage had risen to over ten percent. The rise in those who do not identify with any religion has been accompanied by a decrease in church attendance rates in the nation. A survey conducted in 2016 showed that, out of those who consider themselves religion, only 58% attended mass regularly, while 30% only attended on holidays and 12% had not attended a church service in the last year. Church attendance rates have been a concern of clergy members in every religion in the nation, and the Fabrian Archbishop of Arcadia acknowledged in 2017 that people were less likely to attend mass currently due to a shift in the culture of the nation and attitude towards religion in general. | ||
===Ethnic Groups=== | ===Ethnic Groups=== | ||
Lihnidosi is the majoirity ethnic group in Lihnidos, with | Lihnidosi is the majoirity ethnic group in Lihnidos, with 87.3% of the population identifying as such on the 2014 census. Alongside the Lihnidosi, Vannoisians are the largest minority group, making up roughly five percent of the population. Those who identify as Vannoisian primarily reside in the western parts of the nation, with the largest percentages living in the provinces of Evrytania and Lasithi. Lasithi boasts the highest percentage of Vannoisians living in the nation. Another large ethnic group living in Lihnidos are Latins. The large percentage of those who identify as Latin is often contributed to the almost six centuries that present-day Lihnidos was under the control of the Latin Empire. While the entirety of the country was at one point under Latin rule and therefore exposed to Latin culture, the majority of the areas that are still accustomed to the Latin traditions and cultures are in the east. | ||
There is an additional | There is an additional five percent of the population that do not identify as either Lihnidosi, Vannoisian, or Latin. This percentage is primarily comprised of individuals who identify as [[Garima|Gariman]], [[Lyncanestria|Lyncanestrian]], or [[Tarsas|Tarsan]]. Due to Lihnidos's membership in the [[Belisarian Community]] and involvement in the Laennes Area, it has been easy for individuals from the neighboring nations to enter the country and establish permanent residence or achieve citizenship. | ||
===Languages=== | ===Languages=== | ||
The two dominant languages in Lihnidos are [[Hellenic language|Hellenic]] and [[ | The two dominant languages in Lihnidos are [[Hellenic language|Hellenic]] and [[Standard Latin language|Latin]]. Hellenic is the only official language of the nation. Hellenic is the first language of approximately 80% of the nation while Latin falls behind at approximately 27%. The language of the government is primarily Hellenic, although all documents are translated to Latin. Latin is the primary secondary language taught in primary and secondary education, and a survey taken in 2012 indicates that over half of university-level students are "confident in their ability to understand and converse in Latin." Another language that is somewhat prominent at the university level is Audonais, a language spoken in both Lyncanestria and Vannois. | ||
== | ==Politics== | ||
{{ | {{main|Politics of Lihnidos}} | ||
[[File:Fotis Raptis2.png| | ===Government=== | ||
The | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; float:right; margin-right:9px; margin-left:2px;" | ||
|- | |||
| style="text-align:left;"| [[File:StellaVasiliou.jpg|140px]] || style="text-align:left;" | [[File:Fotis Raptis2.png|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="text-align:center;"|[[Stella II of Lihnidos|Stella II]]<br /><small>[[Monarchy of Lihnidos|Empress]] since 2007</small> | |||
| style="text-align:center;"|[[Fotis Raptis]]<br /><small>[[Prime Minister of Lihnidos|Prime Minister]] since 2010</small> | |||
|} | |||
Lihnidos is a {{wpl|Unitary state|unitary}}, {{wpl|Parliamentary system|parliamentary}}, {{wpl|constitutional monarchy}}. The Lihnidosi political system is laid out in the 1877 constitution approved by the monarch at the time, [[Stella I of Lihnidos|Stella I]], that later underwent reforms in 1946. Further amendments to the constitution require a two-thirds majority in the [[National Assembly of Lihnidos|National Assembly]], as well as the approval of the monarch. The 1946 reforms strengthened the principle of separation of powers by increasing the powers of the legislature and lessening executive authority held by the monarch. | |||
The executive branch is led by the monarch, currently [[Monarchy of Lihnidos|Empress]] [[Stella II of Lihnidos|Stella II]]. The monarch is the {{wpl|head of state}} and exercises their executive power through the Office of the Emperor (or Empress), also known as the Imperial Offices. The monarch has representative responsibilities and powers and takes a significant role in establishing foreign policy. Each monarch begins their reign following the death of their predecessor. The monarch is considered to be the highest official in the Lihnidosi government. | |||
The second-highest official in the Lihnidosi government is the [[Prime Minister of Lihnidos|Prime Minister]]. The current Prime Minister is [[Fotis Raptis]], who has led the government in the National Assembly since 2010. The Prime Minister is the official {{wpl|head of government}} and the legislative branch. Alongside their legislative duties, the Prime Minister exercises some executive power through their [[Cabinet of Lihnidos|Cabinet]]. The Prime Minister and Cabinet exercise executive power in conjunction with the monarch. | |||
[[File:Lihnidos_National_Assembly_Building.jpg|300px|thumb|left|The National Assembly is the unicameral legislature of Lihnidos.]] | |||
Legislative power is exercised by the [[National Assembly of Lihnidos|National Assembly]]. The National Assembly is elected through {{wpl|direct elections}} by {{wpl|first-past-the-post voting}}. Elections for the National Assembly are held a minimum of every four years. Representation for each province is determined by the province's population. | |||
The current government is a minority government led by the [[Conservative-National Alliance (Lihnidos)|Conservative-National Alliance]] with the [[Populist People's Party (Lihnidos)|Populist People's Party]] in a {{wpl|confidence and supply}} agreement. Together, the Conservative-National Alliance and Populist People's Party hold a slim majority in the National Assembly. Since the creation of the National Assembly under the constitution in 1877 the Conservative-National Alliance has been one of the two major political parties that have dominated elected politics. The other major political party in Lihnidos is the [[Democratic Coalition (Lihnidos)|Democratic Coalition]]. Since the creation of the National Assembly, every Prime Minister has been a member of either the Conservative-National Alliance or Democratic Coalition. | |||
=== | ===Law=== | ||
{{ | {{main|Judiciary of Lihnidos|Law of Lihnidos|Law enforcement in Lihnidos}} | ||
[[File:Consultation_room_1_of_the_Austrian_Constitutional_Court_01.jpg|275px|thumb|right|Justices of the Lihnidosi Constitutional Court deliberating]] | |||
[[File: | Lihnidosi law is based on {{wpl|Civil law (legal system)|civil law}}. The civil law system is based on codified principles that serve as a primary source for legal decisions. In Lihnidos, these principles are codified in the Lihnidosi Civil Code and the Lihnidosi Penal Code, which were adopted in 1877 under the first constitution of the empire. The Lihnidosi Civil Code was largely based off of the Athanasian Royal Laws established by [[Athanasios I of Lihnidos|Athanasios I]]. | ||
Law in Lihnidos is primarily divided into two areas: {{wpl|public law}} and {{wpl|private law}}. Public law includes several aspects of the relationship between the government and individuals, comprising {{wpl|constitutional law}}, {{wpl|administrative law}}, {{wpl|tax law}}, and others. Private law primarily deals with the relationship between individuals. The Lihnidosi judiciary is divided into two different courts to deal with these issues. The general courts deal with criminal and civil trials, while the courts of public law deal with administrative and constitutional law. | |||
The | The government of Lihnidos recognizes no religion as a state religion and promotes {{wpl|freedom of religion}} and {{wpl|freedom of speech}}. Despite this, the clear religious majority in Lihnidos has resulted in numerous laws that are aimed at upholding {{wpl|public decency}} and that are based off of {{wpl|religious law}}. These laws have been widely used to limit the freedoms of LGBT individuals and other minority groups and place limits on speech. | ||
=== | ===Administrative divisions=== | ||
{{main|Administrative divisions of Lihnidos}} | |||
Lihnidos is divided into stwenty provinces. These provinces are further divided into counties and municipalities. Provinces are also divided into constituencies, which are used to elect the members of the National Assembly. Constituency boundaries typically do not follow the boundaries set by counties. | |||
Due to the unitary state of Lihnidos, provincial governments are given little power. Provinces are governed by a provincial council comprised of seven elected members. Provincial councils are given the authority to determine how to spend funds awarded by the national government, and are tasked with representing the province on the national level. The counties and municipalities are all governed by localized assemblies and executives. Each county is governed by a county commission composed of three county commissioners. County commissioners will work with other county officials to govern the county and manage local taxes and spending. Municipalities are typically governed by a mayor and small municipal council, however there is no set format for municipal governance. | |||
Due to the differing size and population, the number of counties and municipalities differs by province. Each provincial government is given the authority to draw internal administrative division boundaries, as well as National Assembly constituency boundaries. | |||
===Foreign relations=== | |||
{{main|Foreign relations of Lihnidos}} | |||
[[File:Palácio_Queluz_March_2018-2.jpg|275px|thumb|right|Sarái Palace is the headquarters for the [[Belisarian Commission]] in Lihnidos.]] | |||
Lihnidos is a founding member of the [[Belisarian Community]] and the [[Forum of Nations]]. | |||
Lihnidos has maintained diplomatic relations with almost all nations around the [[Ajax|globe]] and hosts embassies and consulates in many nations. The embassies of most countries in Lihnidos are located in the capital of Arcadia with consulates across the country. | |||
Lihnidosi foreign policy is primarily directed by the [[Monarchy of Lihnidos|monarch]], however the [[Prime Minister of Lihnidos|Prime Minister]] also has considerable influence. The Secretary of State for Foreign and Belisarian Affairs manages the day-to-day workings of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and is the chief foreign affairs adviser to the Prime Minister and monarch. Lihnidos is represented abroad by the monarch, however the monarch may appoint others to represent the nation in their place, typically the Prime Minister or Secretary of State for Foreign and Belisarian Affairs. | |||
Following the constitutional reforms in 1946, which gave the legislative branch of government increased influence over national and foreign policy, the foreign policy of Lihnidos has shifted towards international cooperation and coordination. Since 1977 Lihnidosi foreign policy has largely been shaped by its membership in the Belisarian Community, of which it is one of the founding members. | |||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
{{ | {{main|Lihnidosi Armed Forces}} | ||
[[File:LihnidosiMilitary1.jpg| | [[File:LihnidosiMilitary1.jpg|275px|thumb|right|Young members of the Lihnidosi Army during the final days of basic training]] | ||
The Lihnidosi Armed Forces are | The Lihnidosi Armed Forces are comprised of the Lihnidosi Army, Air Force, Navy, and Spatharioi. The Armed Forces are ultimately led by the {{wpl|commander-in-chief}}, a position held of the [[Monarchy of Lihnidos|monarch of Lihnidos]]. | ||
As of 2018, the Armed Forces employed roughly 170,000 service members, 12,000 members of the Spatharioi, and 41,000 reservists. The Army represents over half of the active duty personnel in the Armed Forces with approximately 105,000 service members. This is followed by the Navy with approximately 35,000 members and the Air Force with approximately 30,000 members. The 41,000 reservists are available to the Armed Forces and can be called upon in times of war. Reservists will regularly participate in training exercises. To be eligible to join the Armed Forces, you must be a citizen of Lihnidos, at least eighteen years of age, and meet fitness, health, and education requirements. | |||
Lihnidos spends roughly two percent of its GDP on defense annually, or approximately {{strikethrough|X}}60 billion. | |||
{{ | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
===Agriculture=== | ===Agriculture=== | ||
===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
[[File:Nuclear_Power_Plant_Cattenom.jpg|200px|right|thumb|A nuclear power plant located in the province of Phthiotis | [[File:Nuclear_Power_Plant_Cattenom.jpg|200px|right|thumb|A nuclear power plant located in the province of Phthiotis]] | ||
Lihnidos has largely been energy independent since the late 19th century following the discovery of large reserves of natural gas in the western regions of the country | Lihnidos has largely been energy independent since the late 19th century following the discovery of large reserves of natural gas in the western regions of the country. Following the discovery, fracking became an essential part of the Lihnidosi energy sector, and private industry quickly placed bids for government contracts to set up fracking operations on government land. In 1943, an incident at a fracking site in Piraeus resulted in the contamination of large amounts of drinking water for surrounding towns. The incident was addressed by the Democratic Coalition government at the time in the form of increased regulations. The increase in regulation and regulatory power in the Ministry of the Environment and Agriculture was described as "strangling" the fracking industry by politicians in many areas where fracking was a large part of the economy. The decrease in fracking at the time was followed by an increase in green or renewable energy in the form of hydroelectric, solar, and nuclear power. | ||
Currently energy from natural gas accounts for 46% of energy produced in Lihnidos. Regulation on fracking have been scaled back slightly since 1943 to allow the industry to once again grow. Nuclear energy is the second biggest energy source for the nation, with nuclear energy being credited as 44% of the energy production in Lihnidos. The prominence of nuclear energy came after the increased regulations on fracking and the desire by left-wing governments to secure a method of energy creation that was less polluting than natural gas. While being nonrenewable and characterized by opponents as dangerous, it quickly became a large part of the energy sector. Following behind natural gas and nuclear are the forms of renewable, green energy. Hydroelectric power produces roughly 5% of the energy in Lihnidos with solar producing 3% and wind producing 2%. | Currently, energy from natural gas accounts for 46% of energy produced in Lihnidos. Regulation on fracking have been scaled back slightly since 1943 to allow the industry to once again grow. Nuclear energy is the second biggest energy source for the nation, with nuclear energy being credited as 44% of the energy production in Lihnidos. The prominence of nuclear energy came after the increased regulations on fracking and the desire by left-wing governments to secure a method of energy creation that was less polluting than natural gas. While being nonrenewable and characterized by opponents as dangerous, it quickly became a large part of the energy sector. Following behind natural gas and nuclear are the forms of renewable, green energy. Hydroelectric power produces roughly 5% of the energy in Lihnidos with solar producing 3% and wind producing 2%. | ||
Subsidies had been available for renewable energy projects and producers, but following the Conservative-National Alliance regaining a majority in the National Assembly in 2006 subsidies were cut. The current government's | Subsidies had been available for renewable energy projects and producers, but following the Conservative-National Alliance regaining a majority in the National Assembly in 2006, subsidies were cut. The current government's lack of interest in promoting renewable energy has led to a decrease in its use. | ||
===Industry=== | ===Industry=== | ||
| Line 316: | Line 310: | ||
[[Category:Lihnidos]] | [[Category:Lihnidos]] | ||
[[Category:Ajax]] | [[Category:Ajax]] | ||
[[Category:MT]] | |||
[[Category:Countries]] | |||
[[Category:Monarchies]] | |||
[[Category:Constitutional monarchies]] | |||
[[Category:Parliamentary democracies]] | |||
[[Category:Unitary states]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:14, 21 January 2020
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Empire of Lihnidos Λιχνίδου Αυτοκρατορία (Hellenic) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Πάντα να υπερέχει ("Ever to Excel") | |
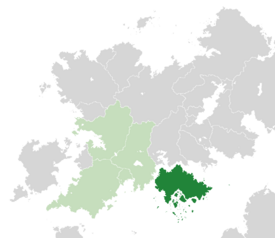 Location of Lihnidos (dark green) – in Belisaria (dark grey) – in the Belisarian Community (light green) | |
 | |
| Capital | Arcadia |
| Largest | Ikaria |
| Official languages | Hellenic |
| Ethnic groups | 87.3% Lihnidosi 12.7% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Lihnidosi |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Empress | Stella II |
| Fotis Raptis | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation | |
• Founding of Xanthi City-States | 900 BC |
• Confederation of City-States | 356 BC |
• Kingdom of Xanthi | 154 BC |
| 70 AD | |
• Independence from Latin Empire | 565 |
• Hellenic Empire | 1713 |
• Lihnidosi Empire | 1827 |
| Area | |
• | 484,224 km2 (186,960 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2017 estimate | 72,420,744 |
• 2014 census | 71,394,929 |
• Density | 147.44/km2 (381.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $2.977 trillion |
• Per capita | $41,109 |
| Gini | 38.9 medium |
| HDI | .870 very high |
| Currency | Denarius ( |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +57 |
| ISO 3166 code | LS |
| Internet TLD | .lnd |
Lihnidos, officially the Empire of Lihnidos, is a sovereign country located in southern Belisaria. Lihnidos is an island nation in the Periclean Sea. It shares maritime borders to the north with Garima and to the west with Vannois. Southern and eastern Lihnidos is surrounded by the Periclean Sea. With an area of 484,224 square kilometers and an estimated population of approximately 72.5 million inhabitants, Lihnidos is the eighteenth most populous country in Ajax yet also one of the smaller nations in land area.
Lihnidos is a unitary parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy. The current and ninth monarch is Stella II, who has reigned since late 2007. The current and twenty-sixth prime minister is Fotis Raptis who leads the Conservative-National government in the National Assembly and who has been in office since early 2010. Lihnidos's capital is the city of Arcadia and the largest city is Ikaria. Other major population centers include the cities of Xanthi and Cephalonia.
Modern humans first arrived in Lihnidos around 35,000 years ago from Scipia. Several tribes made settlements in coastal regions that later led to the development of Hellenic cultures in southern Lihnidos. Settlements consolidated under centralized rule in the form of city-states and later duchies and kingdoms until the region came under Latin rule around 70 AD. After the fall of the Latin Empire in Lihnidos around 600 AD, numerous kingdoms formed and later joined as the United Kingdoms of Lihnidos in 1675.
In 1713 the United Kingdoms of Lihnidos and the Tarsan Empire fell under the same rule and formed the Hellenic Empire. This wide-spanning empire that included lands in Belisaria and Scipia lasted for roughly one hundred years before fracturing into smaller empires and kingdoms. Following Lihnidosi independence from the Hellenic Empire in 1827 the Lihnidosi Empire was declared as the successor state of the Hellenic Empire. The fall of the Hellenic Empire caused instability in parts of Lihnidos and Scipia which lasted in Lihnidos until roughly the mid-1850s.
Presently, Lihnidos is a developed and high income country with the world's 9th largest economy by nominal GDP. The country is a member of the Belisarian Community, Forum of Nations, and Joint Space Agency.
History
Prehistory
The first evidence of the presence of modern humans in Lihnidos was found in the Bylyyn caves outside the town of Nauros in southern Boeotia. The best known artifacts from this time period are cave paintings and fossilized remains that were created between 35,900 to 21,200 BC. Genetic evidence suggests that the first humans in Lihnidos arrived from the southern continent of Scipia and made their way north into Belisaria.
Lihnidos is home to some of the first advanced civilizations in Belisaria. Many of these civilizations were began by well-established settlements that had been founded as early as 3500 BC. The Hellenes inhabited the southern and eastern coastal areas of Lihnidos before moving further north and west. These civilizations began with the Gythacan civilization on the eastern coast of Lihnidos in Messenia around 3000 BC, the Cyrelean civilization around 2700 BC in Kilkis, and the Iolcippian civilization in the Samos Islands around 1900 BC. These civilizations remained largely independent of one another with limited conflict until around 1000 BC when the Gythacans began a time of regional upheaval by attempting to conquer surrounding civilizations.
City-states and unification
The end of the regional conflicts and transition into a more stable society happened around 900 BC with the creation of numerous city-states across southern Lihnidos. Hellenic city-states stretched as far west as the Latin peninsula and as far east as Tarsas. Many of these city-states were prosperous centers where the arts and sciences were allowed to flourish.
The most successful city-state in Lihnidos was the city-state of Xanthi that was located on the western coast of Boeotia. Xanthi was the first city-state in Lihnidos to adopt a democratic form of government while many others were ruled as aristocracies or some form of military dictatorship. Xanthi society, varying from its counterparts, put it at a disadvantage in matters of war and there are several instances where it is believed that Xanthi was almost captured by hostile powers.
By 450 BC war was common between varying city-states due to no unifying ideology or goal. During this period there was a significant decrease in the development of sciences and arts as many city-states began to suffer from constant war. The ongoing disputes led to a breaking point around 360 BC when the leaders of Xanthi called for an assembly of leaders from the most prominent and powerful city-states at the time in an attempt to cease the hostilities. The proposal did not gain traction until three years later in 357 BC when several smaller city-states that had not been previously considered proposed the assembly of leaders once again. The increased interest from smaller city-states and Xanthi, which at the time, despite its non-military culture, was one of the more powerful military powers in the region, prompted remaining holdouts who were against such a meeting to accept. The assembly took place in 356 BC in Xanthi. The assembly of city-state leaders brought many concerns, as many of the militaristic city-states believed the assembly to be a ploy by the smaller city-states to eliminate their leadership. Because of this belief, four different city-states brought military contingents that camped outside of the walls of Xanthi for the duration of the assembly. While the exact number of troops camped outside the city was not recorded, writings from people in the city point to a total troop count in the tens of thousands.
The assembly is believed to have lasted for two weeks as leaders from the city-states debated and negotiated peace. The result of the assembly led to the creation of a confederacy of city-states that would promote mutual defense and resource sharing. The fragile attempt to stop the wars appeared to succeed until 156 BC when the city-state of Hyeligeneia accused the city-state of Aigane of planing war against them. The two were quickly drawn into war as Hyeligeneia marched on the city of Aigane. The war drew other city-states into the fighting and, despite the best efforts of some members of the confederacy, it collapsed shortly after. The fighting led to Hyeligeneia conquering a number of city-states in central Lihnidos and eventually the leadership turned its wrath to Xanthi. In 154 BC Xanthi fell to the Hyeligeneian military. By the time Xanthi had been conquered, a majority of the land in southern Lihnidos was under Hyeligeneian control. Following Xanthi's conquering, the leader of Hyeligeneia proclaimed himself king, using the name of the most recently conquered city-state as his kingdom. The Kingdom of Xanthi under Anastasius I quickly took control of much of what is today the provinces of Boeotia, Serres, Kilkis, Thasos, Pieria, Evros, and Chania.
Latin Empire and independence
The Kingdom of Xanthi continued to expand further east until around 60 AD when it had conquered much of present day western and central Lihnidos. Expansion was halted between 59 and 62 AD when the Latin Empire to the west began to expand further east, encroaching on Xanthi territory. The Latins launched their first invasion into Xanthi territory around 64 AD and quickly moved east, easily defeating the inferior Xanthi military forces. Xanthi military forces attempted several times to halt the Latin move east, but failed to do so on almost all occasions. Xanthi, also the name for the capital of the kingdom, fell in 67 AD and saw the death of the reigning monarch at the time, Anastasius II. Anastasius' death left the kingdom without clear leadership for the remaining years of the invasions as his immediate heirs also died during the war.
The Latin military had defeated the last pockets of resistance in the east by 70 AD. Historical records suggest that Latin military strength was far superior to that of the Kingdom of Xanthi. The ten year time frame of the invasions was significantly longer than historical evidence suggests it could have been. The lengthy period was likely a result of the Latin Empire's attempt to incorporate and assimilate those from Xanthi into their culture, with the Latins taking several several-month-long breaks between periods of expansion into Xanthi.
Latin rule over Xanthi territory lasted for approximately 500 years from 70 to 565 AD. During this time Latin culture and language was widely accepted as the norm and present throughout much of what had been the Kingdom of Xanthi. Despite this there were still holdouts among the Xanthi nobility that sought independence and held on to old traditions and language.
Hellenic Empire
Lihnidosi Empire
Recent history
Geography
Lihnidos is located in southern Belisaria. Lihnidos is an island nation, meaning that it shares no land borders. However, Lihnidos shares maritime borders with Garima to the north and Vannois to the west. The Periclean Sea surrounds Lihnidos from the south-west to the north-east, with the Zarelis Strait running between Lihnidos and Garima and Vannois. Lihnidos covers roughly 484,300 km2, or roughly 187,000 square miles. Of the total area, approximately three percent is water in the form of lakes and rivers. Lihnidos is comprised of sixty-six islands, including the main island, and hundreds is islets.
Terrain in Lihnidos varies from the shores of the islands to the northwestern Pelea Mountains. The highest point in Lihnidos is Mount Elenae at 2,813 meters, or 9,229 feet. There are extensive plains in the eastern regions of the country that comprise much of the country's arable land. Many of the small islands in southern Lihnidos have hilly or even mountainous terrain.
Climate
The primary climate of Lihnidos is the Mediterranian climate, more specifically the hot-summer Mediterranean climate. This type of climate typically features hot summers and mild, wet winters. It is possible for some regions within this climate to experience chilly winters and snowfall, however that is rare in Lihnidos. The hot-summer Mediterranean climate occurs at all southern islands and all southern coastal locations in Lihnidos. Some northeastern regions of Lihnidos are classified as having a warm-summer Mediterranean climate, which experience warm and dry summers with wet and mild to chilly winters.
The mountainous regions of Lihnidos in the northwest feature a temperate climate and, in some areas, an alpine climate. The temerate climate experiences hot and dry summers with cold and wet winters. The alpine climate can experience heavy snowfall in the winter months. These regions are primarily within and around the Pelea Mountains in the provinces of Lasithi, Chania, and Piraeus.
Demographics
Population
According to the 2014 census conducted by the Ministry of Local and Regional Governance, the population of Lihnidos at the time was 71,394,929. With continued immigration, emigration, deaths, and new births, it is estimated that the current population is roughly 72.5 million, only an increase of slightly over one million. Lihnidos's estimated population of over seventy-two million makes it the fifth largest nation on Belisaria by population, behind Liothidia, Arthurista, Latium, and Ottonia. According to the 2014 census, a vast majority of the population identify as Lihnidosi, with 87.3% doing so. The second largest group of individuals are those who identify as Vannoisian, which account for roughly five percent of the population. The majority of the remaining eight percent come from other Belisarian countries including Garima, Lyncanestria, and Latium, while some others come from non-Belisarian countries such as Sydalon, Belfras, and Tarsas. The racial makeup of the population is homogeneous in the aspect that 96.2% of the population identify as Caucasian. The other primary racial groups in Lihnidos are Scipian at 1.9%, Oxidental at 1.5%, and Ochran at 0.4%.
Largest Cities
A majority of the population live in rural areas opposed to urban areas like large towns and cities. Only three cities in Lihnidos have populations over one million: Ikaria, Arcadia, and Xanthi. All three cities have deep historical significance and hold a special role in the nation. Ikaria, often considered the financial capital of Lihnidos, has served as home to the headquarters of many of Lihnidos's largest businesses, both domestic and foreign. Arcadia, the capital of Lihnidos, serves as the seat of the government. Xanthi, the original capital of the empire, served as the capital of the Xanthi Confederation of City-States, the Kingdom of Xanthi, and the early Empire of Lihnidos. Due to its historic role, it is often deemed the cultural capital of the nation. Close behind the top three cities is Cephalonia, which ranks fourth with a population only slightly under one million. After Cephalonia the populations of the largest cities begins to drop significantly.
Largest cities or towns in Lihnidos
Ministry of Local and Regional Governance estimates for 2014 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Province | Pop. | |||||||
 Ikaria  Arcadia |
1 | Ikaria | Serres | 2,761,569 |  Xanthi  Cephalonia | ||||
| 2 | Arcadia | Pieria | 1,518,631 | ||||||
| 3 | Xanthi | Boeotia | 1,422,754 | ||||||
| 4 | Cephalonia | Ithaca | 949,562 | ||||||
| 5 | Phliita | Thasos | 732,110 | ||||||
| 6 | Rethymno | Lasithi | 600,364 | ||||||
| 7 | Hion | Kilkis | 359,615 | ||||||
| 8 | Sozillai | Messenia | 202,164 | ||||||
| 9 | Thesprotia | Preveza | 191,949 | ||||||
| 10 | Arta | Rhodope | 189,457 | ||||||
Provinces
Lihnidos is divided into twenty provinces, each of a different size and population. The borders of each province are partially based on the borders of the historic duchies that comprised the three kingdoms of Lihnidos in its medieval history. Serres is the largest province by population, but one of the smallest by land area. With over eight million people, it holds over eleven percent of the population of the nation, over a fourth of which live in the capital city of the province, Ikaria. Many of the provinces are close in terms of population, with half having a population of between three and four million.
| Province | Abbr. | Provincial Council Control | Capital | Largest city | Population Estimate as of 2018 |
Seats in the National Assembly |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serres | ||||||
| Boeotia | ||||||
| Pieria | ||||||
| Ithaca | ||||||
| Thasos | ||||||
| Phthiotis | ||||||
| Lasithi | ||||||
| Evrytania | ||||||
| Chania | ||||||
| Rhodope | ||||||
| Messenia | ||||||
| Evros | ||||||
| Piraeus | ||||||
| Kilkis | ||||||
| Kalymnos | ||||||
| Thefkada | ||||||
| Chios | ||||||
| Corinthia | ||||||
| Preveza | ||||||
| Samos |
Religion
Religion is held sacrosanct in Lihnidos and the intermingling of church and state is often criticized by those who believe that religion should not be present in government. The majority of individuals in Lihnidos describe themselves as adherents of Fabrian Catholicism. While Lihnidos does not have a state religion, a number of prominent government officials and nobility are followers of the faith and therefore occasionally may make decisions that follow the teachings of the church. Over thirty-six million individuals in Lihnidos identify as Fabrian Catholic, accounting for almost fifty-two percent of the population.
The second largest religion in Lihnidos is Alban Christianity, which while far behind Fabrian Catholicism, has a significant following in Lihnidos. Almost seventeen million individuals identify as Alban Christian, which accounts for another twenty-three percent of the population. Other religious groups are not as prominent in the nation, with almost seven percent of the population describing themselves as Christians that do not follow either Alban Christianity or Fabrian Catholicism. Those who have no faith or who do not describe themselves as Christians comprise almost nineteen percent of the population.
Prior to Fabrian Catholicism and Alban Christianity being the predominant faiths in Lihnidos, a large portion of Lihnidosi practiced a form of polytheistic paganism. This paganism varied in several parts of what is now Lihnidos, but many of the different sects had enough similarities that they could collectively be referred to as one religion. The ancient religion was present in every part of an individuals life and had an extensive mythology that caused followers to see works of the gods in almost everything. Alban Christianity began to take hold in Lihnidos in the 2nd century as it became the dominant faith in the neighboring Latin Empire. Spreading from west to east, the teachings of the Albian church attracted several who were dissatisfied with the teachings of the dominant pagan religion at the time. By the early fourth century Albian Christianity had a substantial following across the Kingdom of Xanthi. Under the reign of Latin Emperor Iovinus, Alban Christianity was made the state faith of the Latin Empire. Paganism was banned, and a renewed effort was put into converting nonbelievers. Later, during the reign of Constantine I, Fabrian Catholicism began to overtake Alban Christianity, eventually becoming the majority religion.
The amount of those who identify as not following any religion has risen slightly over the years. In 2004 the percentage of individuals who identified as atheist or agnostic was approximately seven percent. Ten years later in 2014 the percentage had risen to over ten percent. The rise in those who do not identify with any religion has been accompanied by a decrease in church attendance rates in the nation. A survey conducted in 2016 showed that, out of those who consider themselves religion, only 58% attended mass regularly, while 30% only attended on holidays and 12% had not attended a church service in the last year. Church attendance rates have been a concern of clergy members in every religion in the nation, and the Fabrian Archbishop of Arcadia acknowledged in 2017 that people were less likely to attend mass currently due to a shift in the culture of the nation and attitude towards religion in general.
Ethnic Groups
Lihnidosi is the majoirity ethnic group in Lihnidos, with 87.3% of the population identifying as such on the 2014 census. Alongside the Lihnidosi, Vannoisians are the largest minority group, making up roughly five percent of the population. Those who identify as Vannoisian primarily reside in the western parts of the nation, with the largest percentages living in the provinces of Evrytania and Lasithi. Lasithi boasts the highest percentage of Vannoisians living in the nation. Another large ethnic group living in Lihnidos are Latins. The large percentage of those who identify as Latin is often contributed to the almost six centuries that present-day Lihnidos was under the control of the Latin Empire. While the entirety of the country was at one point under Latin rule and therefore exposed to Latin culture, the majority of the areas that are still accustomed to the Latin traditions and cultures are in the east.
There is an additional five percent of the population that do not identify as either Lihnidosi, Vannoisian, or Latin. This percentage is primarily comprised of individuals who identify as Gariman, Lyncanestrian, or Tarsan. Due to Lihnidos's membership in the Belisarian Community and involvement in the Laennes Area, it has been easy for individuals from the neighboring nations to enter the country and establish permanent residence or achieve citizenship.
Languages
The two dominant languages in Lihnidos are Hellenic and Latin. Hellenic is the only official language of the nation. Hellenic is the first language of approximately 80% of the nation while Latin falls behind at approximately 27%. The language of the government is primarily Hellenic, although all documents are translated to Latin. Latin is the primary secondary language taught in primary and secondary education, and a survey taken in 2012 indicates that over half of university-level students are "confident in their ability to understand and converse in Latin." Another language that is somewhat prominent at the university level is Audonais, a language spoken in both Lyncanestria and Vannois.
Politics
Government
 |

|
| Stella II Empress since 2007 |
Fotis Raptis Prime Minister since 2010 |
Lihnidos is a unitary, parliamentary, constitutional monarchy. The Lihnidosi political system is laid out in the 1877 constitution approved by the monarch at the time, Stella I, that later underwent reforms in 1946. Further amendments to the constitution require a two-thirds majority in the National Assembly, as well as the approval of the monarch. The 1946 reforms strengthened the principle of separation of powers by increasing the powers of the legislature and lessening executive authority held by the monarch.
The executive branch is led by the monarch, currently Empress Stella II. The monarch is the head of state and exercises their executive power through the Office of the Emperor (or Empress), also known as the Imperial Offices. The monarch has representative responsibilities and powers and takes a significant role in establishing foreign policy. Each monarch begins their reign following the death of their predecessor. The monarch is considered to be the highest official in the Lihnidosi government.
The second-highest official in the Lihnidosi government is the Prime Minister. The current Prime Minister is Fotis Raptis, who has led the government in the National Assembly since 2010. The Prime Minister is the official head of government and the legislative branch. Alongside their legislative duties, the Prime Minister exercises some executive power through their Cabinet. The Prime Minister and Cabinet exercise executive power in conjunction with the monarch.
Legislative power is exercised by the National Assembly. The National Assembly is elected through direct elections by first-past-the-post voting. Elections for the National Assembly are held a minimum of every four years. Representation for each province is determined by the province's population.
The current government is a minority government led by the Conservative-National Alliance with the Populist People's Party in a confidence and supply agreement. Together, the Conservative-National Alliance and Populist People's Party hold a slim majority in the National Assembly. Since the creation of the National Assembly under the constitution in 1877 the Conservative-National Alliance has been one of the two major political parties that have dominated elected politics. The other major political party in Lihnidos is the Democratic Coalition. Since the creation of the National Assembly, every Prime Minister has been a member of either the Conservative-National Alliance or Democratic Coalition.
Law
Lihnidosi law is based on civil law. The civil law system is based on codified principles that serve as a primary source for legal decisions. In Lihnidos, these principles are codified in the Lihnidosi Civil Code and the Lihnidosi Penal Code, which were adopted in 1877 under the first constitution of the empire. The Lihnidosi Civil Code was largely based off of the Athanasian Royal Laws established by Athanasios I.
Law in Lihnidos is primarily divided into two areas: public law and private law. Public law includes several aspects of the relationship between the government and individuals, comprising constitutional law, administrative law, tax law, and others. Private law primarily deals with the relationship between individuals. The Lihnidosi judiciary is divided into two different courts to deal with these issues. The general courts deal with criminal and civil trials, while the courts of public law deal with administrative and constitutional law.
The government of Lihnidos recognizes no religion as a state religion and promotes freedom of religion and freedom of speech. Despite this, the clear religious majority in Lihnidos has resulted in numerous laws that are aimed at upholding public decency and that are based off of religious law. These laws have been widely used to limit the freedoms of LGBT individuals and other minority groups and place limits on speech.
Administrative divisions
Lihnidos is divided into stwenty provinces. These provinces are further divided into counties and municipalities. Provinces are also divided into constituencies, which are used to elect the members of the National Assembly. Constituency boundaries typically do not follow the boundaries set by counties.
Due to the unitary state of Lihnidos, provincial governments are given little power. Provinces are governed by a provincial council comprised of seven elected members. Provincial councils are given the authority to determine how to spend funds awarded by the national government, and are tasked with representing the province on the national level. The counties and municipalities are all governed by localized assemblies and executives. Each county is governed by a county commission composed of three county commissioners. County commissioners will work with other county officials to govern the county and manage local taxes and spending. Municipalities are typically governed by a mayor and small municipal council, however there is no set format for municipal governance.
Due to the differing size and population, the number of counties and municipalities differs by province. Each provincial government is given the authority to draw internal administrative division boundaries, as well as National Assembly constituency boundaries.
Foreign relations

Lihnidos is a founding member of the Belisarian Community and the Forum of Nations.
Lihnidos has maintained diplomatic relations with almost all nations around the globe and hosts embassies and consulates in many nations. The embassies of most countries in Lihnidos are located in the capital of Arcadia with consulates across the country.
Lihnidosi foreign policy is primarily directed by the monarch, however the Prime Minister also has considerable influence. The Secretary of State for Foreign and Belisarian Affairs manages the day-to-day workings of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and is the chief foreign affairs adviser to the Prime Minister and monarch. Lihnidos is represented abroad by the monarch, however the monarch may appoint others to represent the nation in their place, typically the Prime Minister or Secretary of State for Foreign and Belisarian Affairs.
Following the constitutional reforms in 1946, which gave the legislative branch of government increased influence over national and foreign policy, the foreign policy of Lihnidos has shifted towards international cooperation and coordination. Since 1977 Lihnidosi foreign policy has largely been shaped by its membership in the Belisarian Community, of which it is one of the founding members.
Military
The Lihnidosi Armed Forces are comprised of the Lihnidosi Army, Air Force, Navy, and Spatharioi. The Armed Forces are ultimately led by the commander-in-chief, a position held of the monarch of Lihnidos.
As of 2018, the Armed Forces employed roughly 170,000 service members, 12,000 members of the Spatharioi, and 41,000 reservists. The Army represents over half of the active duty personnel in the Armed Forces with approximately 105,000 service members. This is followed by the Navy with approximately 35,000 members and the Air Force with approximately 30,000 members. The 41,000 reservists are available to the Armed Forces and can be called upon in times of war. Reservists will regularly participate in training exercises. To be eligible to join the Armed Forces, you must be a citizen of Lihnidos, at least eighteen years of age, and meet fitness, health, and education requirements.
Lihnidos spends roughly two percent of its GDP on defense annually, or approximately X60 billion.
Economy
Agriculture
Energy
Lihnidos has largely been energy independent since the late 19th century following the discovery of large reserves of natural gas in the western regions of the country. Following the discovery, fracking became an essential part of the Lihnidosi energy sector, and private industry quickly placed bids for government contracts to set up fracking operations on government land. In 1943, an incident at a fracking site in Piraeus resulted in the contamination of large amounts of drinking water for surrounding towns. The incident was addressed by the Democratic Coalition government at the time in the form of increased regulations. The increase in regulation and regulatory power in the Ministry of the Environment and Agriculture was described as "strangling" the fracking industry by politicians in many areas where fracking was a large part of the economy. The decrease in fracking at the time was followed by an increase in green or renewable energy in the form of hydroelectric, solar, and nuclear power.
Currently, energy from natural gas accounts for 46% of energy produced in Lihnidos. Regulation on fracking have been scaled back slightly since 1943 to allow the industry to once again grow. Nuclear energy is the second biggest energy source for the nation, with nuclear energy being credited as 44% of the energy production in Lihnidos. The prominence of nuclear energy came after the increased regulations on fracking and the desire by left-wing governments to secure a method of energy creation that was less polluting than natural gas. While being nonrenewable and characterized by opponents as dangerous, it quickly became a large part of the energy sector. Following behind natural gas and nuclear are the forms of renewable, green energy. Hydroelectric power produces roughly 5% of the energy in Lihnidos with solar producing 3% and wind producing 2%.
Subsidies had been available for renewable energy projects and producers, but following the Conservative-National Alliance regaining a majority in the National Assembly in 2006, subsidies were cut. The current government's lack of interest in promoting renewable energy has led to a decrease in its use.











