Louzen language: Difference between revisions
m (added //) |
m (Edit: added ~) |
||
| Line 283: | Line 283: | ||
|bgcolor=#FFEEEE|Q q | |bgcolor=#FFEEEE|Q q | ||
|bgcolor=#FFEEEE|Q q | |bgcolor=#FFEEEE|Q q | ||
|bgcolor=#FFEEEE|{{Audio|Voiceless_uvular_plosive.ogg|/q/|help=no}} | |bgcolor=#FFEEEE|{{Audio|Voiceless_uvular_plosive.ogg|/q/|help=no}} ~ /k͡v/ | ||
|bgcolor=#FFEEEE|[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Voiceless_uvular_plosive.ogg '''C'''aught] | |bgcolor=#FFEEEE|[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Voiceless_uvular_plosive.ogg '''C'''aught] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 09:28, 16 February 2021
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| Louzen language | |
|---|---|
| Louzenish, Nordulevan | |
| Lúzinŝina | |
 Flag of the Duchy of Louzeni | |
| Pronunciation | /luːzinɕʧina/ |
| Native to | |
| Region | Slavic Belt in Thuadia |
| Ethnicity | Louzeni Slavs |
Native speakers | L1: 5,812,000 L2: 2,317,000 FL: 520,000 |
Thuado-Thrismaran languages
| |
Standard forms | Louzen language great wordbook
|
| Dialects | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | LI |
| ISO 639-2 | LOI |
| ISO 639-3 | LOI |
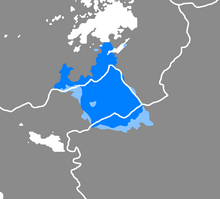 Distribution of the language Absolute majority >30% of native speakers | |
Louzeni language is a Slavic language out of Kento-Polyash language group, which is a official language of the autonomous Duchy of Louzeni in Gadorien and is a recognized minority language in Zhousheng, Gadorien and Qazhshava
Introduction
The language has a slavic root and grammar, but has developed along with strong germanic influences, which shaped the grammar of the language. Unlike most of other slavic languages, Louzen maintained use of Dual as a grammatical number.
Alphabet
Although until the 18th century, Louzeni used Protopolyash script, the strong influence of Gadori germanic tribes using latin pushed it towards Latin script, which eventually became the most used script and eventually gained a linguistic monopoly in the middle of 19th century.
Until the rebirth movement in the end of 19th century, Louzen used only Graphemes to denote multiple sounds, which did not have a standard 26-alphabet letter given to them, but later, a system of diacritic marks was devised, creating a version, where any important phoneme is denoted by a single letter.
Louzen, although not officially using it, sometimes used lenghtened marks for vowels and syllabic consonants. Those symbols were used in some historical transcripts, but were eventually faded in eary 1900's.
| Official diacritic version | Digraph version | IPA Symbol | Example of a common word with the sound | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A a | A a | After | |
| 2 | Á á | Aa aa | ||
| 3 | Ä ä | Ae ae | Bed (General American accent) | |
| 4 | Â â | Ja ja | /ʲa/~/j͡a/ | Not in common. Example: "Яблоко/Âbloko" in Tiskai language |
| 5 | B b | B b | Label | |
| 6 | C c | C c | Its | |
| 7 | Ċ ċ | Cz cz | Check | |
| 8 | D d | D d | Done | |
| 9 | Ḋ ḋ | D' d' | Voiced palatal plosive (not in common) | |
| 10 | E e | E e | Bed (Australian accent) | |
| 11 | É é | E e | ||
| 12 | Ê ê | Je je | /ʲe/~/j͡e/ | Belarus |
| 13 | F f | F f | Fine | |
| 14 | G g | G g | Game | |
| 15 | H h | H h | Hello | |
| 16 | Ḣ ḣ | Ch ch | Loch Ness | |
| 17 | I i | I i | Free | |
| 18 | Í í | Ie ie | ||
| 19 | J j | J j | You | |
| 20 | K k | K k | Key | |
| 21 | L l | L l | Later | |
| 22 | Ŀ ŀ | L' l' | Million | |
| 23 | M m | M m | Mother | |
| 24 | N n | N n | Month | |
| 25 | Ṅ ṅ | N' n' | New | |
| 26 | O o | O o | Yawn / Not | |
| 27 | Ó ó | Oo oo | ||
| 28 | Ö ö | Oe oe | Bird | |
| 29 | P p | P p | Play | |
| 30 | Q q | Q q | Caught | |
| 31 | R r | R r | Red | |
| 32 | S s | S s | Surprise | |
| 33 | Ṡ ṡ | Sz sz | Show | |
| 34 | Ŝ ŝ | Sx sx | /ɕ͡ʧ/ | Not in common. Example: "Щенок/Ŝenok" in Tiskai language |
| 35 | T t | T t | Time | |
| 36 | Ṫ ṫ | T' t' | Voiceless palatal plosive (not in common) | |
| 37 | U u | U u | Boot | |
| 38 | Ú ú | Uu uu | ||
| 39 | Ü ü | Ue ue | Lip (London accent) | |
| 40 | Û û | Ju ju | /ʲu/~/j͡u/ | Not in common. Example: "Любить/Lûbitʹ" in Tiskai language |
| 41 | V v | V v | Valve | |
| 42 | W w | W w | Weep | |
| 43 | X x | X x | /k͡s/ | A bigram of /k/ and /s/, for example in Maximal |
| 44 | Y y | Y y | Bit (General American) | |
| 45 | Ý ý | Yy yy | ||
| 46 | Z z | Z z | Zoo | |
| 47 | Ż ż | Z' z' | Vision | |
Phonology
| Place → | Labial | Coronal | Dorsal | Laryngeal | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manner ↓ | Bilabial | Labiodental | Linguolabial | Dental | Alveolar | Postal-veolar | Retroflex | Platal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | ||||||||||||
| Nasal | m̥ | m | n̥ | n | ɳ | ɲ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Plosive | p | b | t | d | ʈ | ɖ | c | ɟ | k | g | q | |||||||||||||
| Sibilant affricate | ʦ | ʣ | ʧ | ʤ | ʈʂ | ɖʐ | ʨ | ʥ | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-sibilant affricate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sibilant fricative | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | ʂ | ʐ | ɕ | ʑ | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-sibilant fricative | f | v | ʝ | x | ɣ | χ | h | ɦ | ||||||||||||||||
| Approximant | ʋ | j | w | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tap/Flap | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trill | r̥ | r | ʀ̥ | ʀ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Latelar affricate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latelar fricative | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latelar approximant | l | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latelar tap/flap | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Front-back → | Front | Near-front | Central | Near-back | Back | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-down ↓ | ||||||||||
| Close | i | ɨ | u | |||||||
| Near-close | ɪ | |||||||||
| Close-mid | e | o | ||||||||
| Mid | ə | |||||||||
| Open-mid | ɛ | œ | ɔ | |||||||
| Near-open | ɐ | |||||||||
| Open | a | ɑ | ɒ | |||||||
| Diphthong | a͡u | |||||||||
| Long vowels | aː ~ ɛː ~ eː ~ iː ~ ɪː ~ oː ~ ɔː ~ œː ~ uː ~ ɨː | |||||||||
Bold are the common sounds, while regular sounds may happen in dialects and/or in a world for easier pronunciation
Softening
Sounds for letters D, L, N, T preceding letters Â, Ê, I, Í, Û are softened/platalized.
| Softening | Regular | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Written | Read | Wrong | Written | Read |
| di | /ɟi/ | ḋi | dy | /ɖɪ/ |
| li | /lʲi/ | ŀi | ly | /lɪ/ |
| ni | /ɲi/ | ṅi | ny | /nɪ/ |
| ti | /ci/ | ṫi | ty | /ʈɪ/ |
Important note is, that in case of softening with Â, Ê, Û, the /j/ sound is not pronounced:
| Softening | Regular | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Written | Read | Wrong | Written | Read |
| dâ | /ɟa/ | ḋa | dja | /ɖja/ |
| lâ | /lʲa/ | ŀa | lja | /lja/ |
| nâ | /ɲa/ | ṅa | nja | /nja/ |
| tâ | /ca/ | ṫa | tja | /ʈja/ |
Nouns
Grammatical gender
Zhoushi languages distinguishes a total of 3 grammatical genders, one being latter subdivided into animate and inanimate forms,[2] although that doesn't change the rules on the usage, only works for listing the inflection patterns:
- Masculine (symbol ♂, letter M)
- Feminine (symbol ♀, letter F)
- Neuter (symbol ⚲, letter N)
Grammatical cases
Louzen langauge works with 3 grammatical numbers (singular, dual and plural) and 5 separate grammatical cases:
- Nominative (Imêník): Subject or a Predicate noun or adjectiv (Shorcut Nom., № 1)
- Genitive (Pridrżník): Possessive or partial direct object, without Subject (Shorcut Gen., № 2)
- Dative (Geŝník): Giving to Subject, phrases linked to certain verbs (Shorcut Dat., № 3)
- Accusative (Jednateŀník): Interract with Subject (see, hear, harass...) (Shorcut Acc., № 4)
- Ablative (Drużník): Part of Subject, compared to Subject, the way (Shorcut Abl., № 5)
There are 12 Inflection patterns (5 for Masculine, 4 for Feminine and 3 for Neuter)
Grammatical inflection
| Translation to Common | Code | Singular | Dual | Plural | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nom. | Gen. | Dat. | Acc. | Abl. | Nom. | Gen. | Dat. | Acc. | Abl. | Nom. | Gen. | Dat. | Acc. | Abl. | |||
| Masculine | |||||||||||||||||
| Brother | B | Brat | Brata | Bratu | Brata | Bratom | Brata | Brat | Bratám | Brata | Bratḣi | Brati | Bratú | Bratúm | Braty | Bratmi | |
| ∅ | -a | -u | -a | -om | -a | ∅ | -ám | -a | -ḣi | -i | -ú | -úm | -y | -mi | |||
| House | D | Döm | Dömy | Dömu | Döm | Dömom | Dömy | Dömu | Dömoma | Dömê | Dömyma | Dömové | Dömú | Dömúm | Dömy | Dömami | |
| ∅ | -y | -u | ∅ | -om | -y | -u | -oma | -ê | -yma | -ové | -ú | -úm | -y | -ami | |||
| Man | M | Muž | Muže | Muži | Muže | Mužum | Muža | Muž | Mužoma | Mužém | Mužmi | Muži | Mužú | Mužúm | Muže | Mužma | |
| ∅ | -e | -i | -e | -um | -a | ∅ | -oma | -ém | -mi | -i | -ú | -úm | -e | -ma | |||
| Country | K | Kraj | Kraja | Kraji | Kraja | Krajom | Kraja | Kraju | Krajoma | Krajê | Krajoma | Kraje | Krajú | Krajom | Kraje | Krajmi | |
| ∅ | -a | -i | -a | -om | -a | -u | -oma | -ê | -oma | -e | -ú | -om | -e | -mi | |||
| Stone | A | Kámen | Kámene | Kámeni | Kámen | Kámenem | Kámena | Kámenu | Kámenama | Kámena | Kámeni | Kámeny | Kámenêv | Kámenúm | Kámeny | Kámeny | |
| ∅ | -e | -i | ∅ | -em | -a | -u | -ama | -a | -i | -y | -êv | -úm | -y | -y | |||
| Feminine | |||||||||||||||||
| Woman | Z | Żena | Żeny | Żenê | Żenu | Żenû | Żenê | Żenu | Żenama | Żenê | Żenimê | Żeny | Żen | Żenám | Żeny | Żenami | |
| -a | -y | -ê | -u | -û | -ê | -u | -ama | -ê | -imê | -y | ∅ | -ám | -y | -ami | |||
| Hope | N | Nadêlâ[3] | Nadêlê | Nadêli | Nadêlû | Nadêŀü | Nadêlê | Nadêlû | Nadêlâ | Nadêlê | Nadêlimê | Nadêlê | Nadêlê | Nadêlâm | Nadêlê | Nadêŀjáḣ | |
| -â | -ê | -i | -û | -ü | -ê | -u | -a | -ê | -imê | -ê | -ê | -am | -ê | -jáḣ | |||
| Bone | K | Kosṫ | Kosti | Kosti | Kosṫ | Kosṫó | Kosti | Kostû | Kosṫma | Kosti | Kosṫma | Kosti | Kostí | Kostím | Kosti | Kostêmi | |
| ∅ | -i | -i | ∅ | -ó | -i | -û | -ma | -i | -ma | -i | -í | -ím | -i | -êmi | |||
| Mother (archaic) | T | Máti | Máti | Máti | Máti | Máṫ | Mátê | Mátû | Máṫma | Máti | Máṫma | Mátije | Mátijí | Mátijím | Mátê | Máṫmi | |
| -i | -i | -i | -i | ∅ | -ê | -û | -ma | -i | -ma | -ije | -ijí | -ijím | -ê | -mi | |||
| Neutrum | |||||||||||||||||
| Word | S | Slovo | Slova | Slovu | Slovo | Slovme | Slovji | Slovû | Slovêma | Slovji | Slovêma | Slova | Slov | Slovám | Slova | Slovy | |
| -o | -a | -u | -o | -me | -ji | -û | -êma | -ji | -êma | -a | ∅ | -ám | -a | -y | |||
| Sea | R | Morê | Morê | Mori | Morê | Mori | Mora | Mor | Morím | Mora | Mormi | Morê | Morí | Morím | Morê | Morami | |
| -ê | -ê | -i | -ê | -i | -a | ∅ | -ím | -a | -mi | -ê | -í | -ím | -ê | -ami | |||
| Name | I | Imê | Imênê | Imû | Imê | Imi | Imê | Imú | Imom | Imê | Imem | Imê | Imí | Imêm | Imêje | Imêma | |
| -ê | -ênê | -û | -ê | -i | -ê | -ú | -om | -ê | -em | -ê | -í | -êm | -êje | -êma | |||
- ↑ Often referred as "Literary form", as Louzeni accent is the one Louzeni language grammar rules are based on.
- ↑ See Wikipedia articles about Grammatical gender and Animacy
- ↑ Term Nadêlâ has a root "Nadêŀ", not "Nadêl", which makes the inflection more difficult as ŀa must be written as lâ etc...