Carucere: Difference between revisions
(Created) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|area = | |area = | ||
|area_km2 = 8, | |area_km2 = 8,165.51 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |area_sq_mi = | ||
|area_footnote = | |area_footnote = | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = | ||
|population_census_year = | |population_census_year = | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 65.79 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = | ||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
===Post-independence era=== | ===Post-independence era=== | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
{{stack begin}} | |||
[[File:Carucere map.png|thumb|upright=1.25|350px|Map of Carucere]] | |||
[[File:Carucere topo.png|thumb|upright=1.25|350px|Carucere's topography]] | |||
{{stack end}} | |||
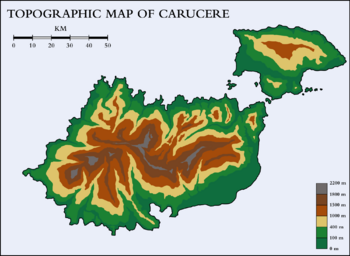
Carucere lies 6 degrees north and 78 degrees east in the western [[Aurucian Strait]]. The islands are considered to be part of the western Aurucian archipelago which includes the island countries of [[Sainte-Chloé]], [[Imagua and the Assimas]], [[Bonaventure]], and parts of [[Aucuria]] and [[Eldmark]]. There is considerable debate among geographers on whether the region should be considered geographically part of [[Asteria Superior]] or [[Asteria Inferior]]. In recent decades, a growing number of people consider the western Aurucian archipelago to be its own subregion based upon a common political, cultural, and historical heritage. Geologically the islands sits upon the Asteria Inferior plate, with the Aurucian rift to the north. | Carucere lies 6 degrees north and 78 degrees east in the western [[Aurucian Strait]]. The islands are considered to be part of the western Aurucian archipelago which includes the island countries of [[Sainte-Chloé]], [[Imagua and the Assimas]], [[Bonaventure]], and parts of [[Aucuria]] and [[Eldmark]]. There is considerable debate among geographers on whether the region should be considered geographically part of [[Asteria Superior]] or [[Asteria Inferior]]. In recent decades, a growing number of people consider the western Aurucian archipelago to be its own subregion based upon a common political, cultural, and historical heritage. Geologically the islands sits upon the Asteria Inferior plate, with the Aurucian rift to the north. | ||
Covering an area of 8, | Covering an area of 8,165.51 km<sup>2</sup> (3152.7 sq mi), the country consists of two main islands, [[Marien]] and [[Magua]], separated by the [[Anne Strait]] which forms a large {{wp|natural harbor}}, plus a number of much smaller islands. [[Marien]] is 6,708 km<sup>2</sup> (2589.9 sq mi), comprising 82.1% of the country's area. [[Magua]] is 1,433.8 km<sup>2</sup> (553.6 sq mi), comprising 17.5% of the country's area. The remaining area is distributed among the country's small islands. | ||
The geography of the two main islands varies considerably. [[Marien]] is very mountainous, with [[Monte Cinto]] as the highest peak at 2, | The geography of the two main islands varies considerably. [[Marien]] is very mountainous, with [[Monte Cinto]] as the highest peak at 2,123 m (6,965 ft), and around 120 other summits of more than 1,500 m (4,921 ft). Mountains comprise two-thirds of the island, forming a single mountain range known as the [[Central Range]]. There are numerous river valleys throughout the mountain range from which the rainwater flows to the ocean. The southeastern region of the island, known as the Plains, is a coastal plain and the flattest region of the island. The Plains has a number of coastal lagoons which usually to the ocean. In addition marshland is also extensive on the coast in the region. As a result, {{wp|malaria}} has historically been a problem near the marshlands and swamps in the area, which limited its development in the past. The major bodies of freshwater on Marien are all artificial, formed by dams to create reservoirs. | ||
The [[Anne Strait]] divides the two main islands. The strait consists of | The [[Anne Strait]] divides the two main islands. The strait consists of four channels; two in the west and two in the east, with a large bay in the center. It has a shallow sandy bottom, averaging about 30 m (100 ft) deep. The natural harbor has an area of 271.98 km<sup>2</sup> (105 sq mi). Magua has an even mixture of small mountains and plains. The northern and southern part of the island are hilly, although it is significantly less mountainous than Marien. The northern region of the island is the hilliest containing the island's highest peak at 500 meters (1,640 ft). The two ranges are separated by a wide valley that contains the islands' most fertile soil and many small streams and ponds. | ||
The population is largely evenly divided between [[Marien]] and [[Magua]], largely centered around the [[Anne Strait]]. There are four major municipalities on the islands, the capital [[Carrefour]] | The population is largely evenly divided between [[Marien]] and [[Magua]], largely centered around the [[Anne Strait]]. There are four major municipalities on the islands, the capital [[Carrefour]] and the cities of [[Tiburon]], [[Jouanau]], and [[Caracol]]. | ||
===Geology=== | ===Geology=== | ||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 20 March 2022
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Carucere | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Liberté, Patrie, Unité" (Gaullician) "Libète, Patri, Uniti" (Annene Creole) (Liberty, Fatherland, Unity) | |
| Anthem: "Liberté" "Libète" Liberty | |
 Location of Carucere (green), within Asteria Superior (light grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | |
| Official languages | Gaullician |
| Other languages | Caruceran Creole Caruceran Ziba |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | |
| Religion (2020) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Caruquèrais Caruceran |
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
| Neil Latorture | |
• Premier | Sylvie Feucher |
| Roy Chalus | |
| Legislature | Senate |
| History of Carucere | |
• Colony established | 1520 |
• Republic of Pirates | 1712 |
• Colony reestablished | 1724 |
• Allied mandate | 1935 |
• Incorporation into the United Provinces | 1945 |
• Independence | 1954 |
• Current constitution | 1961 |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,165.51 km2 (3,152.72 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 537,238 |
• Density | 65.79/km2 (170.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $9.6 billion |
• Per capita | $17,937 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $5.7 billion |
• Per capita | $10,607 |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2020) | high |
| Currency | Aurucian Shilling (ARS) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| ISO 3166 code | CAR |
| Internet TLD | .ca |
Carucere (Gaullican: Caruquère, Caruceran Creole: Karukure), formally known as the Republic of Carucere (Gaullican: République d' Caruquère, Caruceran Creole: Repiblik d Karukure), also known as Îles de Reine-Anne (Queen Anne's Islands), is a small island nation between Asteria Superior and Asteria Inferior in the Aurucian Strait. Consisting of the main islands of Marien and Magua, and numerous much smaller islands, it shares maritime borders with Sainte-Chloé to the west, Imagua and the Assimas to the north, and Aucuria to the east and south.
Before the arrival of Euclean settlers, the islands were home to Nati tribes scattered across the mountainous terrain. Carucere was discovered during the voyage of the Gaullican explorer Auguste de Antibes, who named it after the Queen of Gaullica, Anne the Financier. It was colonized by Gaullica in 1520, who established a port in the strait between Marien and Magua, which formed a large natural harbor. While the extremely mountainous terrain of Marien island limited the widespread development of plantations and the importation of Bahian slaves, it became a prominent trading, naval, and shipbuilding post for Gaulicia. The Anne Strait serves as one of the largest anchorages in the world and one of the major naval bases for the Gaullician navy in the Asterias during the colonial era.
The islands became a major hub of pirate activity during the Golden Age of Piracy from the late 17th century to the early 18th century. The islands’ rugged northern coastline served as safe bases for pirates to operate. Gaulician rule of the islands collapsed during the Ten Years' War in Euclea, resulting in the brief establishment of a pirate republic in 1712. When Gaullica regained control of the islands’ coast, the government allowed pirate activity continue at their direction, effectively state sponsored privateering. The ban on the slave trade in 1815, led the Gauillican government to import tens of thousands of gowsans to the islands for labor. After the Great War, ownership of the islands was stripped from Gaullica's possession and transferred to a joint Allied commission which later established the Arucian Federation, consisting of Sainte-Chloé and Carucere. In 1945, Carucere and Sainte-Chloé formed a federation with Imagua and the Assimas, forming the United Provinces of the Western Arucian Islands. During Sainte-Chloé’s secession from the United Provinces, the Carucere declared independence by a self-organized referendum.
The new republic was characterized by political dysfunction and ethnic tensions between the Euclean elite and the rest of the population. In 1957, a clique of white officers within the military launched a coup when it appeared a leftist party would win the country's first election. The military junta oversaw a period of increasing unrest that lead to its overthrow two years later by moderate elements of the military led by Jean Préval. In 1961, Préval declared the restoration of the Republic and drafted a new constitution. Préval was elected President and remained in office until he retired after the end of his fourth term in 1978. His Presidency oversaw the promotion of multiculturalism, the creation of a national identity, and the rapid development and diversification of the economy from an extractive and agriculture based economy.
Today Carucere is an upper-middle income country. The islands’ rapidly growing economy consists of a mix of agriculture, manufacturing, and various service-based businesses. However the disparities between the richer coast and the poorer interior are very visible especially in income inequality and standards of living. The collapse of the dominant party system that revolved around the United Carucere Party has led to the return of race based politics. Recent political instability have prevented the government from addressing growing problems. Carucere is a member of the Community of Nations, the Organization of Asterian Nations, and the Arucian Cooperation Organization.
Etymology
History
Prehistory
The ancient history of the island is not well known. Archeological evidence suggests humans may have first settled or visited Carucere around 1600 BCE, but this remains a highly debated topic. It is definitively known that around the 4th to 7th centuries CE, the Nati peoples migrated to the island. Settlements of Nati appeared all over the island by around 1000 CE. When Euclean explorers arrived to the island in 16th century, the island's population was estimated to be around 20,000 to 40,000 peoples divided amongst four or five tribes separated by the mountainous terrain. They lived in small villages, each led by a cacique or chief. They subsisted by hunting and fishing, with hunting generally done by men and the women harvesting the indigenous cassava root and fruit. Recent archeological explorations have uncovered the major role the Anne Strait has played in their society. This lasted until Euclean colonisation in 1520.
Colonial era
Early Gaulician rule
The island of Carucere was discovered in the year 1498 by the Gaullican explorer Auguste de Antibes, who named the island after the Queen Anne of Gaullica and claimed on behalf of her country. Antibes did not step foot on the island, but his expedition noted the island's mountainous terrain and rocky coast during a pass of the island and reported as unsuited for settlement. For unknown reasons, he failed to notice the Anne Strait, possibly due to poor weather. Eucleans did not return to the island until 1518, when an expedition of Gaullican surveyors were tasked with properly exploring the island. During the expedition, they discovered the strait and quickly realized the strategic value of the strait that formed a large natural harbor. After scouting out the strait, they quickly returned to Sainte-Chloé to report the discovery of the strategic location to Gaullica.
Pirate republic
Late Gaulician rule
Two federations period
Post-independence era
Geography
Carucere lies 6 degrees north and 78 degrees east in the western Aurucian Strait. The islands are considered to be part of the western Aurucian archipelago which includes the island countries of Sainte-Chloé, Imagua and the Assimas, Bonaventure, and parts of Aucuria and Eldmark. There is considerable debate among geographers on whether the region should be considered geographically part of Asteria Superior or Asteria Inferior. In recent decades, a growing number of people consider the western Aurucian archipelago to be its own subregion based upon a common political, cultural, and historical heritage. Geologically the islands sits upon the Asteria Inferior plate, with the Aurucian rift to the north.
Covering an area of 8,165.51 km2 (3152.7 sq mi), the country consists of two main islands, Marien and Magua, separated by the Anne Strait which forms a large natural harbor, plus a number of much smaller islands. Marien is 6,708 km2 (2589.9 sq mi), comprising 82.1% of the country's area. Magua is 1,433.8 km2 (553.6 sq mi), comprising 17.5% of the country's area. The remaining area is distributed among the country's small islands.
The geography of the two main islands varies considerably. Marien is very mountainous, with Monte Cinto as the highest peak at 2,123 m (6,965 ft), and around 120 other summits of more than 1,500 m (4,921 ft). Mountains comprise two-thirds of the island, forming a single mountain range known as the Central Range. There are numerous river valleys throughout the mountain range from which the rainwater flows to the ocean. The southeastern region of the island, known as the Plains, is a coastal plain and the flattest region of the island. The Plains has a number of coastal lagoons which usually to the ocean. In addition marshland is also extensive on the coast in the region. As a result, malaria has historically been a problem near the marshlands and swamps in the area, which limited its development in the past. The major bodies of freshwater on Marien are all artificial, formed by dams to create reservoirs.
The Anne Strait divides the two main islands. The strait consists of four channels; two in the west and two in the east, with a large bay in the center. It has a shallow sandy bottom, averaging about 30 m (100 ft) deep. The natural harbor has an area of 271.98 km2 (105 sq mi). Magua has an even mixture of small mountains and plains. The northern and southern part of the island are hilly, although it is significantly less mountainous than Marien. The northern region of the island is the hilliest containing the island's highest peak at 500 meters (1,640 ft). The two ranges are separated by a wide valley that contains the islands' most fertile soil and many small streams and ponds.
The population is largely evenly divided between Marien and Magua, largely centered around the Anne Strait. There are four major municipalities on the islands, the capital Carrefour and the cities of Tiburon, Jouanau, and Caracol.
Geology
Climate
Biodiversity
Government & Politics
Carucere's politics occurs in the framework of an independent unitary de facto presidential republic. The government is based on the Constitution of the Republic of Carucere which describes the country as a parliamentary republic with power centered in the legislature. In reality, political power is centered around the powerful President of Carucere, who is both head of state and head of government. The legislature of the country is the unicameral Senate of Carucere which plays a secondary, but still important role in national politics. Judicial authority is delegated to the national court system led by the Supreme Court. Although Carucere is a unitary state, the interior provinces are granted significant more autonomy.
Originally Carucere was a parliamentary state with both a President as head of state and a Premier as head of government, but the country has since created a unique form of presidentialism. When Jean Préval restored democracy and was elected President, he centralised political power within the office. After Préval retired, his successors formalised the strong presidency through several constitutional amendments and established the government as a de facto presidential system. As a result, Carucere's politics combines aspects from both political systems and cultures.
Governance
The President of Carucere is head of state and head of government of the country. The Presidency is granted wide ranging powers and responsibilities; mainly serving as chief diplomat, chief legislator, and the commander in chief of the armed forces. The president is responsible for conducting foreign relations, such as approving treaties, declaring war, and making peace, as well acting as commander in chief of the Carucere Defence Force. The president, by resolution of the Cabinet of Carucere, can issue broad decrees with the force of legislation as long it is determined to be constitutional; however all decrees require an enabling act for it to be enforced. Furthermore, decrees cannot override existing legislation and the Senate can pass legislation to override a decree. The President has the authority to draft legislation for submission to the Senate, however the President lacks veto powers and must promulgate all laws presented to them. Other powers of the president include granting amnesty, pardon, or clemency on recommendation by the Senate, declaring martial law, and conferring honors and decorations.