Weranian Unification
Weranian Unification, known in Werania as simply the "Einigung", was the process in which the previous divided kingdoms and city-states of the Weranic lands became the modern nation state of the Weranian Confederation which was declared on the 17th March 1842. The process is believed to have started with the Weranian Revolution of 1828 although has its roots in the 1785 revolution that had led to the dissolution of the Rudolphine Confederation and the creation of the Weranian Republic.
Inspired by a mixture of notions including nationalism, historical revisionism, republicanism, liberalism, secularism and democracy the impetus for Weranian unification following the republic's dissolution led to the start of the "Weranic Question" of whether a state for the Weranian people should emerge, if it should be a republic or monarchy and if it only consist of Weranic speaking lands or be enlarged to those ruled by the Weranic people, understood to mean whether Sunrosia would be part of a Weranian nation. During the early 19th century these questions led to an outpouring of nationalist activity in the Weranic states notably through the revolutionary secret society, the Septemberists.
By 1829 republican nationalists united with monarchists in the Kingdom of Cislania to jointly promote the cause of unification. Gaining the support of Estmere these liberal nationalists began to see Sunrosia - previously thought to be the most likely candidate to unify the Weranic lands - as the biggest obstacle to unification. From 1836 starting with the Septemberist Revolt in Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken to the 1840-1842 Weranian War of Unification the pace of unification under the Cislanian banner rapidly increased with the Weranian Confederation being declared following the victory of Cislanian forces in 1842. The state further expanded with the Easter Revolution in the eastern Weranian states.
The final act of Weranian unification was the War of the Triple Alliance fought between Werania and Estmere against Sunrosia, Gaullica and Narozalica. Although the war had intended to unite the rest of the Weranic lands in Sunrosia - considered to be the entirely Weranic speaking Cisvetania and partially Weranic speaking Ruttland - into Werania, it failed to do so with Werania acquiring Ruttland alone. However the war did result in the survival of a unified Weranic nation confirming its presence permanently in Euclea.
Weranian unification is considered to have changed the balance of power in Euclea. It represented a decline in Sunrosia and Solstiana whilst the creation of a unified Werania introduced a new great power on the continent that would compete with Gaullica, Narozalica, Estmere and Etruria for influence. Weranian unification is still celebrated in Werania despite there still being debate as to whether its primary protagonists - Rudolf VI and Ulrich von Bayrhoffer - intended to unify Werania or whether unification was the result of ad hoc agreements pursued out of pragmatism and opportunism.
Brief Timeline
- 1785 - The Weranian Revolution. The Rudolphine Emperor Leopold III is overthrown by republicans and Weranic nationalists who declare the Weranian Republic. The revolution quickly spreads across the Confederation until the republicans are victorious creating a national convention under the leadership of the Brotherhood for the Rights of Man who supported a centralised republican state based on the Cult of Rationalism.
- 1789 - The republic after internal instability is embroiled in conflict with [neighbours]. Balthasar Hötzendorf is elected commander of the revolutionary armies by the National Diet ushering in a period of militarised republicanism.
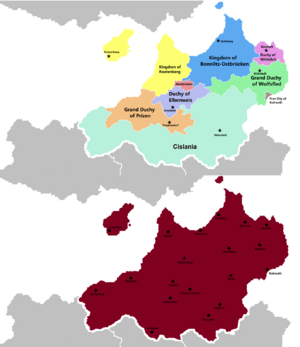
- 1801 - The Weranian Republic is dissolved after Sunrosian, Estmerish and Narozalica defeat it militarily. Its replacement however is far more truncated then the former states in the Rudolphine Confederation with seven kingdoms and two free cities being created.
- 1816 - The Central Revolutionary Federation commonly simply known as the Septemberists (Septembristen) is founded in XXX. A network of secret revolutionary societies the Septemberists would become one of the most influential groups agitating for Weranian unification based on a republican model.
- 1821 - Glorious Summer. A liberal revolution in Cislania leads King Leopold Theodor to promulgate a constitutional monarchy, the first of its kind in the Weranic states.
- 1828 - The Weranian Revolution of 1828. Septemberist republicans raise up across Werania. A second republic is declared in Westbrücken, the heart of the pan-Weranic movement. The revolts are crushed with Sunrosian and Estmerish assistance but the strength of pan-Weranicism is reaffirmed. There is also a shift in the central thrust of pan-Weranicism from republicanism to cooperation with the liberal monarchy of Cislania.
- 1829 - Appointment of Ulrich von Bayrhoffer as Minister-President of Cislania and the rise of the Pan-Weranic Party in the Kingdom. Reconciliation begins between the Cislanian monarchy and the Septemberists over the pan-Weranic cause.
- 1836 - The Septemberist Revolt in Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken. The Septemberists supported by Cislania lead a successful uprising against the unpopular and diplomatically isolated monarchy of Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken. A free state is declared. King Leopold Theodor is invited to serve as king in a personal union.
- 1836-1837 - The Cislanian-Solstianan War. In response to the Septemberist Revolt the Kingdom of Solstiana demands Cislania end the personal union with Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken. This leads to war between the two nations which ends with a status quo antebellum after Werania is able to confirm Estmerish neutrality.
- 1840-1842 - Weranian War of Unification. Cislania declares war on a coalition of Roetenberg, Prizen, Elbenweis and Westbrücken, considered to be in the Sunrosian sphere of influence. Werania wins against them with nominal assistance from Estmere. The Treaty of XXX sees Prizen enter personal union with Cislania which formally declares the creation Weranic Confederation which also includes Roetenberg and Elbenweis. Westbrücken is named the federal capital. Leopold Theodor becomes head of state with the regal name Rudolf VI.
- 1846 - The Easter Revolution. A nationalist revolution in Wolfsfled purportedly instigated by Werania leads to repression by the King of Wolfsfled. The repression spurs Werania to issue an ultimatum that demands referendums to be held in Wolfsfled, Wiittislich and Kolreuth on the issue of unification. With few allies the three states hold concurrent referendums which see them agree to unify into Werania.
- 1852-1855 - The War of the Triple Alliance. Werania issues an ultimatum to Sunrosia to surrender its Weranic regions. This leads to the War of the Triple Alliance between Werania and Estmere against Sunrosia, Narozalica and Gaullica that ends with Ruttland being ceded to Werania. This is typically considered to be the final act of Weranian unification.
Background
Weranian Revolution
Weranian unification can be traced back to the upsurge of nationalism that accompanied the 1785 Weranian Revolution that swept across the Weranic speaking lands of the Rudolphine Confederation. The revolution was preceded by the Rudolphine Emperor Leopold III's efforts to centralise the state undermining noble privileges which sapped support for the monarchy. When revolutionaries marched on the Palace of Hochgäu in September 1785 the noble armies failed to heed the Emperor's call to arms; he subsequently was imprisoned by the revolutionaries who declared the Republic of Werania. The republican-revolutionary movement soon spread across the Confederation with revolutionary masses seizing power in many of the old kingdoms; by January 1786 the republic ruled most of the Weranic lands, with the confederation decisively defeated by citizens armies. The National Diet published the "Declaration of the Rights of Man" directly inspired by similar documents in Etruria and Rayenne; it delineated that every man in the territory was a citizen of Werania and the National Diet represented the people first and foremost.
The republic was ruled by the Brotherhood for the Rights of Man who were inspired by the revolutions in Rayenne and Etruria. The Brotherhood followed the Cult of Rationalism (Kult der Rationalismus) that amongst other things emphasised centralisation, rationalism, intense anti-clericalism and militarism calling for the mobilisation of vast citizen-armies based on republican virtue. Although the Brotherhood and their supporters were more informed by republican and rationalist discourse their emphasis on citizens rather then subjects, use of the Weranian language, attacks on both the Catholic and Amendist churches and centralising reforms created a national identity based around the Weranic language and history.
The Republic was early on wracked by internal troubles and tensions on its borders with Sunrosia and Estmere, but conflict was avoided with the prospect of the republicans restoring the former Emperor albeit as a constitutional monarch. By mid-1786 the government was soon dominated by Franz Xaver Dobrizhoffer, considered to be the chief ideologue behind the Cult of Rationalism. Dobrizhoffer ordered the execution of the royal family and the mobilisation of citizen armies to defend the revolution against the neighbouring powers. This started the North Euclean Revolutionary Wars which pitted the republic against its neighbours as breakdowns in diplomacy between the traditional powers and the republic spiralled into war. The revolutionary armies often secured military successes thanks to the meritocratic officer promotions, the loyalty and devotion of troops to the Weranian Republic and the mass mobilisation of men via the massenaushebung.
In 1789 Balthasar Hötzendorf was elected as generalfeldmarschall of the revolutionary armies transitioning the republic to one based on militarised authoritarianism as much as the Cult of Reason, with Hötzendorf increasingly controlling the political nature of the republic. The constant war with Werania's neighbours made Weranian society incredibly militarised which necessitated the continued deployment of nationalist and revolutionary rhetoric.
As a result of the citizen armies, expansion of citizen's rights and constant atmosphere of revolutionary fervour nationalism amongst Weranic's flourished under the republic in a way the republic's rivals could not match. The role of Sunrosia as an enemy of the revolution was particularly important in nationalist discourse; propagandists within the republic soon promoted the notion that the Sunrosian monarchy was an oppressive force to the Weranic people of the nation and promoted the idea of dissolving the Sunrosian state and annexing large sections into Werania on the basis of republican values and linguistic and cultural unity. Hötzendorf bemoaned the lack of Weranic unity prior to the revolution as being an un-rational, illogical state of affairs and stated that a unified state based on the power of the "natural citizenry" of Werania was necessary to rationalise Euclea's political boundaries.
However the military successes of the republic led to a coalition to form against the republic consisting of Estmere, Sunrosia and Narozalica who feared the republic's radical ideals and wished to permanently divide the Weranic lands so they did not pose a threat to the balance of power in northern Euclea. From 1799 to 1801 the republic suffered several catastrophic defeats and by March 1801 the republic formally surrendered after Sunrosia occupied Westbrücken, ending the Weranian revolution and the republic as a whole.
Partition of the Republic
With the defeat of the republic the leaders of Sunrosia, Estmere and Narozalica met at the Sunrosian city of Coerz to discuss the partition of the Weranian Republic. The republicans had executed a substantial amount of nobles from the old Rudolphine Confederation, most prominently the majority of the house of Brücken who had ruled the confederation since the end of the Amendist Wars. As a result it was decided that the old confederation would not be restored in its entirety and that a new patchwork of states, partially based on the old system, would be created.
The new division was seen to benefit Sunrosia who gained influence over the Weranic states. The House of Windenheim retained or gained power in the Grand Duchies of Wolfsled and Prizen, whilst the restored Kingdom of Roetenberg, Duchy of Elbenweis and Free City of Westbrücken were under informal Sunrosian influence. The eastern states of Wolfsfled, Duchy of Wittislich and Free City of Kolreuth were also considered to be aligned with Sunrosia, although less strongly then the former states. The Kingdom of Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken was seen as aligned with Solstania whilst the Kingdom of Cislania was seen as friendly with Estmere.
One important change that came from the republic's partition and creation of new states was the doctrine that the personal unions that had been common in the Rudolphine era would no longer be in force. The Emperor of Narozalica which through the House of Ryksmark-Halte-Herdorf had held personal union with Wittislich surrendered the post of king of Wittislich to his brother. The intention of this was to prevent Sunrosia asserting potential personal unions with Weranic states that would threaten the position of Estmere in the region.
The new states were largely conservative in character. Wolfsfled was the sole monarchy that possessed a constitution which restricted suffrage to property owning males. Although the free cities of Westbrücken and Kolreuth were more liberal in character they still were governed by reactionaries who rejected Weranian nationalism, being under the heavy influence of their larger neighbours. Although liberal groups - particularly nationalist-minded students - lobbied for nationalist causes the rulers of the Weranian states largely created police states that imposed press censorship and attempted to reverse many of the gains made by the revolution.
Economically the partitioning powers attempted to break up the unified national economy created by the republic. This was only partially successful; although some states like Cislania and Wolfsfled were able to restore their national economies relatively smoothly in the case of Roetenberg, Elbenweis, Westbrücken and Prizen the four states agreed to enter a formal customs union. This customs union led to the greater construction of railways across those four states that soon began to link with similar railroad projects particularly in Cislania and Bonnlitz-Ostbrücken. The development of faster, cheaper rail travel would have an important impact of the development of a feeling of pan-Weranicism in the Weranic states.