Seketan: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
(→Republic: fixed early republic history) |
||
| (55 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|englishmotto = <!--English language version of motto--> | |englishmotto = <!--English language version of motto--> | ||
|national_anthem = | |national_anthem = [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5qm8PH4xAss Myn Sécytan] | ||
|royal_anthem = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | |royal_anthem = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
|alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | |alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | ||
|map_caption = Location of Seketan (dark green) | |map_caption = Location of Seketan (dark green) | ||
|image_map2 = | |image_map2 = | ||
|alt_map2 = <!--alt text for second map--> | |alt_map2 = <!--alt text for second map--> | ||
|map_caption2 = | |map_caption2 = | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|largest_settlement = <!--Name of largest settlement--> | |largest_settlement = <!--Name of largest settlement--> | ||
|official_languages = [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | |official_languages = [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | ||
|national_languages | |national_languages = [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]]<br>[[Wilsk language|Wilsk]]<sup>a</sup> | ||
|regional_languages = [[Trjebian language|Trjebian]]<br>[[Tvinan language|Tvinan]] | |||
|languages_type = <!--Use to specify a further type of language, if not official, national or regional--> | |languages_type = <!--Use to specify a further type of language, if not official, national or regional--> | ||
|languages = <!--Languages of the further type--> | |languages = <!--Languages of the further type--> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| 12.1% [[Wilsks]] | | 12.1% [[Wilsks]] | ||
| 5.9% [[Fjeskans]] | | 5.9% [[Fjeskans]] | ||
| 4.8% [[ | | 4.8% [[Trebs]] | ||
| 0.6% other}} | | 0.6% other}} | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2010 | |ethnic_groups_year = 2010 | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
|established_event6 = [[Fourth Seketese Republic|Fourth Republic]] | |established_event6 = [[Fourth Seketese Republic|Fourth Republic]] | ||
|established_date6 = 14 June 1978 | |established_date6 = 14 June 1978 | ||
|area_rank = | |area_rank = 106th | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|area_km2 = 106229 | |||
|area_km2 = | |area_sq_mi = 41015 | ||
|area_sq_mi = | |||
|area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | |area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | ||
|percent_water = | |percent_water = 10% | ||
|area_label = | |area_label = Total | ||
|area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | |area_label2 = <!--Label below area_label (optional)--> | ||
|area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | |area_data2 = <!--Text after area_label2 (optional)--> | ||
|population_estimate = 6.5 million | |population_estimate = 6.5 million | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = 110th | ||
|population_estimate_year = 2016 | |population_estimate_year = 2016 | ||
|population_census = 6,426,108 | |population_census = 6,426,108 | ||
|population_census_year = 2010 | |population_census_year = 2010 | ||
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = 61.2 | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_density_rank = | |population_density_rank = 127th | ||
|GDP_PPP = | |GDP_PPP = | ||
|GDP_PPP_rank = | |GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
| Line 106: | Line 105: | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = $144 billion | |GDP_nominal = $144 billion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = | |GDP_nominal_rank = 87th | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2016 | |GDP_nominal_year = 2016 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $22,153 | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $22,153 | ||
| Line 114: | Line 113: | ||
|Gini_rank = | |Gini_rank = | ||
|Gini_year = 2016 | |Gini_year = 2016 | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = 2016 | ||
|HDI = 0. | |HDI = 0.833 | ||
|HDI_change = steady | |HDI_change = steady | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = 49th | ||
|HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | |HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | ||
|currency = [[Seketese Djev]] ([[Seketese Djev|Đ]]) | |currency = [[Seketese Djev]] ([[Seketese Djev|Đ]]) | ||
| Line 132: | Line 131: | ||
|iso3166code = <!--Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> | |iso3166code = <!--Use to override default from common_name parameter above; omit using "omit".--> | ||
|calling_code = {{wp|Telephone numbers in Iceland|+354}} | |calling_code = {{wp|Telephone numbers in Iceland|+354}} | ||
|patron_saint = | |patron_saint = [[Saint Gjenor]] | ||
|image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | |image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | ||
|alt_map3 = <!--alt text for third map position--> | |alt_map3 = <!--alt text for third map position--> | ||
|footnote_a = [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]] is the sole official language of [[Wilskland]] | |footnote_a = As of 2023, Seketese, Fjeskan, and Wilsk have been designated as "[[National Languages Act|national languages]]", whilst Seketese remains the official language of Seketan. [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]] is the sole official language of [[Wilskland]] and [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]] is an official language in [[Fjeska]]. | ||
|footnote_b = | |||
<!--......--> | <!--......--> | ||
|footnote_h = <!--For any footnote <sup>h</sup> used above--> | |footnote_h = <!--For any footnote <sup>h</sup> used above--> | ||
| Line 142: | Line 141: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Seketan''' ([[Seketese language|Seketese]]: ''Sécytan''), officially the '''Republic of Seketan''' ([[Seketese language|Seketese]]: ''République á Sécytana''; [[Seketese language#Writing system|alternate Seketese spellings]]: ''Républyc á Sécytana''), is a [[ | '''Seketan''' ([[Seketese language|Seketese]]: ''Sécytan''), officially the '''Republic of Seketan''' ([[Seketese language|Seketese]]: ''République á Sécytana''; [[Seketese language#Writing system|alternate Seketese spellings]]: ''Républyc á Sécytana''), is a [[Nelbec countries|Nelbec country]] in {{wp|northwestern Europe}}. Bordering [[Alquiya]], [[Kingdom of Trjebia|Trjebia]], and [[New Svealand]] to the south, Seketan is comprised of the northern portion of [[Nelbecia]]. The majority of Seketese land is tundra with sprawling plains to the south and west points of the country. The country's climate is generally mild with severe winters seen in northern areas such as [[Ellinesa]]. The [[Fjoške mountains]] strike through the centre of the country bringing warm and wet conditions to central areas of the country. Seketan's population of 6.5 million (2016) is predominately urbanized within the country's [[Administrative divisions of Seketan#Provinces|7 provinces]]. [[Conelibek]] is the largest and capital city of Seketan, and is home to most of the country's commercial and cultural activities. Other major cities include [[Loria]], [[Winneston]], [[Fyedor]], and [[Porta]]. | ||
Evidence of human activity in Seketan dates back to the {{wp|Neolithic}} period. During the [[Classical Nelborne|classical era]], Seketan was inhabited by various [[ | Evidence of human activity in Seketan dates back to the {{wp|Neolithic}} period. During the [[Classical Nelborne|classical era]], Seketan was inhabited by various [[North Nelbecs|North Nelbec]] groups and states. Classical societies [[Nelborne decline|declined]] where Seketan entered [[Seketese Dark Ages|dark ages]] beginning in the 3rd century AD, whereafter the [[Secenic Empire]] arose and existed between the 4th and 6th centuries, although the extent of its grandeur is dubious and fabled. The [[Secenic Confederation]] succeeded the empire in the 6th century as a union of [[Secenic duchies|duchies]] whose borders inspire the [[provinces of Seketan]]. In the 9th century, the confederation was [[Christianization of the Nelborne|Christianized]] and [[Moress II]] declared himself [[King of Seketan]]. The [[Kingdom of Seketan|kingdom]] emerged as a regional power, entering conflicts with the [[Old Kingdom of Trjebia|Trjebians]], [[Kingdom of Alquiya|Alquiyans]], {{wp|Vikings}} and later [[New Svealand|Ny Svealanders]]. After a brief period of [[Sektese Empire|empire and dominance]], the kingdom declined in influence. | ||
Seketan entered into a [[Union of the Nelbecs|personal union]] with [[Kingdom of Alquiya|Alquiya]] in 1765. The two countries were formally united into the [[Nelbec Empire]] in 1884, which was briefly considered a {{wp|great power}} before its [[collapse of the Nelbec Empire|utter collapse]] following defeat in [[Nelborne Front|World War I]]. Following a [[Seketese Revolution|revolution]] and [[Seketese Civil War|civil war]], the [[Second Seketese Republic]] was established and began the [[Kjedorate regime]]. Seketan defended itself during the [[Nelborne War]] and was reorganized into the [[Third Seketese Republic|Third Republic]] following the [[Wilsk representation movement]]. The [[Zemasy|Zemasy period]] and the consequential [[Fjeskan conflict]] culminated into [[Zemasy protests|protests]] and [[1978 Seketese revolution|revolution]] that ousted Kjedorate authoritarian rule and formed the present [[Fourth Seketese Republic|Fourth Republic]]. | Seketan entered into a [[Union of the Nelbecs|personal union]] with [[Kingdom of Alquiya|Alquiya]] in 1765. The two countries were formally united into the [[Nelbec Empire]] in 1884, which was briefly considered a {{wp|great power}} before its [[collapse of the Nelbec Empire|utter collapse]] following defeat in [[Nelborne Front|World War I]]. Following a [[Seketese Revolution|revolution]] and [[Seketese Civil War|civil war]], the [[Second Seketese Republic]] was established and began the [[Kjedorate regime]]. Seketan defended itself during the [[Nelborne War]] and was reorganized into the [[Third Seketese Republic|Third Republic]] following the [[Wilsk representation movement]]. The [[Zemasy|Zemasy period]] and the consequential [[Fjeskan conflict]] culminated into [[Zemasy protests|protests]] and [[1978 Seketese revolution|revolution]] that ousted Kjedorate authoritarian rule and formed the present [[Fourth Seketese Republic|Fourth Republic]]. | ||
Seketan is a unitary parliamentary republic since 1978, with the [[President of Seketan|President]] acting as a | Seketan is a unitary parliamentary republic since 1978, with the [[President of Seketan|President]] acting as a ceremonial head of state and the [[Prime Minister of Seketan|Prime Minister]] acting as head of government. Legislation is delivered through the country's bicameral parliament called the ''[[Hérvynsken]]''. Seketan is geographically divided into 7 provinces; the provinces of [[Fjeska]] and [[Wilskland]] have their own devolved administrations based in their capitals of [[Loria]] and [[Fyedor]]. The official language of Seketan is [[Seketese language|Seketese]]; [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]] and [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]] are recognized [[National Languages Act|national languages]] and are official in Fjeska and Wilskland respectively. | ||
Seketan is a {{wp| | Seketan is a {{wp|developing country}} with an [[economy of Seketan|upper-middle-income economy]] largely focused on {{wp|Service (economics)|services}}, followed by industry—especially [[Energy in Seketan|energy]] and mining—and agriculture. Seketan ranks 48th on the {{wp|Human Development Index}}. Seketan is a founding member of the [[Nelbec Council]] and the [[Nelborne Union]] and has played a large role in intergovernmental activities in the [[Nelborne]] region. Despite previous negotiations, Seketan is not part of the {{wp|European Economic Area}} or the {{wp|European Union}}, however, it is a member of the {{wp|Council of Europe}}. | ||
[[Category:Seketan]] | [[Category:Seketan]] | ||
| Line 161: | Line 160: | ||
[[Human settlement of the Nelborne|Human settlement]] of what is today Seketan occurred during the {{wp|Last glacial period}} where {{wp|homo sapiens}} migrated from {{wp|Europe}} into the [[Nelborne]]. Due to the lack of writing and evidence, it is unknown when [[Proto-Nelbec]] cultures came into existence, but it is often dated to originate from the {{wp|Neolithic}} period. A large southern migration of Proto-Nelbecs took place, and those who stayed up north in what is today Seketan became the [[North Nelbec peoples]]. [[Proto-Secenic]] and [[Proto-Winnic]] cultures likely formed during {{wp|Antiquity}}, eventually becoming the [[Sekens]] or [[Fjeskans]] and [[Wilsks]] respectively. | [[Human settlement of the Nelborne|Human settlement]] of what is today Seketan occurred during the {{wp|Last glacial period}} where {{wp|homo sapiens}} migrated from {{wp|Europe}} into the [[Nelborne]]. Due to the lack of writing and evidence, it is unknown when [[Proto-Nelbec]] cultures came into existence, but it is often dated to originate from the {{wp|Neolithic}} period. A large southern migration of Proto-Nelbecs took place, and those who stayed up north in what is today Seketan became the [[North Nelbec peoples]]. [[Proto-Secenic]] and [[Proto-Winnic]] cultures likely formed during {{wp|Antiquity}}, eventually becoming the [[Sekens]] or [[Fjeskans]] and [[Wilsks]] respectively. | ||
Although shrouded in fable and myth, it is likely that a large pan-Secenic empire existed in {{wp|Late Antiquity}}, historiographically known as the [[Secenic Empire]]. This empire collapsed into 8 breakaway states which were later united in the [[Secenic Confederation]] led by the [[Conils]] and | Although shrouded in fable and myth, it is likely that a large pan-Secenic empire existed in {{wp|Late Antiquity}}, historiographically known as the [[Secenic Empire]]. This empire collapsed into 8 breakaway states which were later united in the [[Secenic Confederation]] led by the [[Conils]] and the [[Duchy of Conelibek]]. In the {{wp|9th century}} (traditionally in 867), [[Moress II of the Conils]] proclaimed himself [[King of Seketan]], effectively establishing the [[Kingdom of Seketan (867–1622)|Kingdom of Seketan]] as the successor state to the confederation. Around this time, the [[Christianization of Seketan]] occurred and written records in {{wp|Latin}} began, marking the beginning of written history in Seketan. | ||
===Middle ages=== | ===Middle ages=== | ||
The [[Kingdom of Seketan]] under the [[House of Coþepag|Coþepag dynasty]] embraced the {{wp|Roman Catholic Church | The [[Kingdom of Seketan]] beginning with [[Moress II]] under the [[House of Coþepag|Coþepag dynasty]] embraced the {{wp|Roman Catholic Church}}. [[Saint Gjenor]] was commonly accepted as the {{wp|patron saint}} of Seketan; his influence established [[Medieval Seketese literature]] which was predominately produced by literate Seketese Christian bishops and priests. The church became central to Seketan's culture and politics and is often cited as a stabilizing force in uniting the Secenic states into Seketan. As part of its divine mission, the Kingdom of Seketan waged wars against neighbouring pagan states. Seketan conquered lands from the [[Kingdom of Trjebia]] during the [[Seco-Trjebian wars]], and the [[Wilsks]] were subjugated where the [[Duchy of Wilskland]] as a {{wp|client state}}. | ||
The {{wp|viking invasions}} during the {{wp|early Middle Ages}} was the major crisis for medieval Seketan. Norse settlements were established on the western shores of Seketan, most successfully in the southeast. Seketese lands south of [[Fjeska]] were consistently pillaged and later abandoned due to their low economic output and stability caused by Norse expansion. These lands were claimed as overseas possessions of the {{wp|Norwegian Empire}}, which resulted in numerous disputes and conflicts between Seketan and Norway. The [[Seco-Norwegian War]] from 1120 to 1128 resulted in Seketan's recognition of Norway's sovereignty over the Norse settlements whose land would later form [[New Svealand]]. Conflicts with Nordic powers over New Svealand, {{wp|Iceland}}, [[Ellinesa]], and other territories became commonplace in the Seketese Middle Ages. | The {{wp|viking invasions}} during the {{wp|early Middle Ages}} was the major crisis for medieval Seketan. Norse settlements were established on the western shores of Seketan, most successfully in the southeast. Seketese lands south of [[Fjeska]] were consistently pillaged and later abandoned due to their low economic output and stability caused by Norse expansion. These lands were claimed as overseas possessions of the {{wp|Norwegian Empire}}, which resulted in numerous disputes and conflicts between Seketan and Norway. The [[Seco-Norwegian War]] from 1120 to 1128 resulted in Seketan's recognition of Norway's sovereignty over the Norse settlements whose land would later form [[New Svealand]]. Conflicts with Nordic powers over New Svealand, {{wp|Iceland}}, [[Ellinesa]], and other territories became commonplace in the Seketese Middle Ages. | ||
The {{wp|Black Death}} arrived in Seketan in 1352 | The {{wp|Black Death}} arrived in Seketan in 1352. Approximately a third of the population died during the outbreak. Despite the devastation, overall {{wp|economic inequality}} was lowered as a result of the large population loss. [[Henry III of Seketan|King Enri III]]'s long reign endured the Black Death, but his rule was characterized as a change in Seketese politics where adherence to the Roman Catholic Church became less of a priority. During the plague, Seketan accented Jewish refugees who were being persecuted by the [[South Nelbecs]]. | ||
Across {{wp|Europe}}, disagreements with the Catholic Church resulted in the {{wp|Reformation}}. {{wp|Lutheranism}} became fairly popular within Seketan and was not persecuted by Seketese monarchs. [[George IV of Seketan|Giorgi IV]] established the [[Church of Seketan]] in 1531, marking the official split from the Catholic Church. Seketan maintained its religious stance through isolation as an island and solidarity with other Protestant seafaring kingdoms such as England and the Nordic countries. Seketan benefited economically and literacy, innovation, and education all benefited from the liberalized religion. | Across {{wp|Europe}}, disagreements with the Catholic Church resulted in the {{wp|Reformation}}. {{wp|Lutheranism}} became fairly popular within Seketan and was not persecuted by Seketese monarchs. [[George IV of Seketan|Giorgi IV]] established the [[Church of Seketan]] in 1531, marking the official split from the Catholic Church. Seketan maintained its religious stance through isolation as an island and solidarity with other Protestant seafaring kingdoms such as England and the Nordic countries. Seketan benefited economically and literacy, innovation, and education all benefited from the liberalized religion. | ||
| Line 193: | Line 192: | ||
===Republic=== | ===Republic=== | ||
[[file: | [[file:Keith Holyoake (1960).jpg|thumb|[[Loren Allis]], [[president of Seketan]] from 1918 to 1937 and again from 1945 to 1960]] | ||
In concert with the [[Collapse of the Nelbec Empire|collapse of the Nelbec Empire]], two competing factions declared independence for Seketan, the [[Hervynsken]] backed and right-wing [[Kjedorate|Kjedorates]] and the Djenibek based and left-wing [[Sosymets]], resulting in the [[Seketese Civil War]]. The ensuing war was fought largely in [[Eastern Seketan|Eastern]] and [[Southern Seketan]], as well as around the [[Central Seketan|Lake Region]]. Initially the Sosymets had the upper hand, catching the unprepared Kjedorates of guard in the [[Battle of Fjedor]] and the [[Battle of Loria]], but gradual factionalism and infighting amoungst the various Sosymet militias allowed for a Kjedorate [[1919 Kjedorate Counter-offensive|counter offensive]] and the eventual defeat of the Sosymets in the [[Siege of Sjon|Battle of Sjon]]. | |||
Upon victory in the civil war in 1923, the Kjedorates under [[Loren Allis]] declared a [[Kjedorate Republic|republic]] after reintigrating [[Free Conelibek]] and set out on reuniting Seketan under it's previous Kingdom borders. In 1924 an agreement was met with the breakaway [[Wilsk Republic]] to federate under the [[Second Seketese Republic|Federal Republic of Seketan and Wilskland]], which would later be renamed as the [[Wilsk betrayal|Federal Republic of Seketan]]. | |||
Loren Allis was reelected in the first free presidential election in 1925. Seketan experienced immense economic growth during the {{wp|Roaring Twenties}}, and the period gave birth to modern Seketese art and culture. After the {{wp|Wall Street Crash of 1929}}, reforms ordered by Allis personally resulted in the republic becoming a ''{{wp|de facto}}'' {{wp|rule by decree}} dictatorship, with [[Kjedorate Party]] symbols being incorporated into national flags and symbols. | Loren Allis was reelected in the first free presidential election in 1925. Seketan experienced immense economic growth during the {{wp|Roaring Twenties}}, and the period gave birth to modern Seketese art and culture. After the {{wp|Wall Street Crash of 1929}}, reforms ordered by Allis personally resulted in the republic becoming a ''{{wp|de facto}}'' {{wp|rule by decree}} dictatorship, with [[Kjedorate Party]] symbols being incorporated into national flags and symbols. | ||
Land disputes over the [[Rynedan peninsula]] with Alquiya escalated in the [[Nelborne War]] in 1933. [[New Svealand]], allied with Seketan, declared war on Alquiya. Seketan | Land disputes over the [[Rynedan peninsula]] with Alquiya escalated in the [[Nelborne War]] in 1933. [[New Svealand]], allied with Seketan, declared war on Alquiya. Seketan was successful in defending its territory but failed to make any successful offensives. Lomortia entered the war in 1934 against Seketan. The war was won in 1937 with British and Danish support and resulted in the territorial status quo. | ||
In the early 1970s, Seketan endured a {{wp|banking crisis}} which later transformed into a {{wp|currency crisis}} where the government attempted to pay back loans by printing more money. This period from 1970s Seketese history is referred to as the [[Zemasy period]]. This period resulted in unemployment in Seketan skyrocketing, along with rising ethnic tensions between the [[Sekens]], [[Fjeskans]], and [[Wilsks]]. Fjeskan insurgents, citing repression of their language rights and nonrecognition of the Fjeskan nation, began a low level insurgency in [[Fjeska]]. The [[Fjeskan Revolutionary Organization|FOD]] rose as the main Fjeskan insurgent group and was a key player in the resulting [[Fjeska conflict]]. | |||
After a decade of financial crises and increasing political tension, the [[1978 Seketese revolution]] came into force which resulted in Pesan being ousted from power and a [[Seketese constitutional referendum, 1978|constitutional referendum]] which birthed the [[Fourth Seketese Republic]], where the president's role would be purely ceremonial, free and fair elections for the Commons Council were to be held, and where Fjeska would enjoy its own devolved parliament similar to [[Wilskland]]. The Kjedorate Party would contest Seketans [[1978 Seketese Election|first open election]], but would eventually dissolve in 1988 after lacklustre results. Kjedorate imagery in national flags and symbols would be mostly phased out by 1981. | |||
After a decade of | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 218: | Line 213: | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
{{Main article|Politics of Seketan}} | |||
{{Politics of Seketan}} | {{Politics of Seketan}} | ||
The current system of government in Seketan is | The current system of government in Seketan is labelled as the '''Fourth Seketese Republic'''. The current republican system was established in 1978 after the [[Seketese constitutional referendum, 1978|Seketese constitutional referendum]]. Seketan is a parliamentary {{wp|constitutional republic}}. The [[President of Seketan]], currently [[Fjedor Alesk]], is the head of state and is elected every six years; the president is largely a figurehead. | ||
The ''[[Hérvynsken]]'' is made up of two chambers, the [[Commons Council]], which represents the people of Seketan, and the [[State Council]] which represents the provincial administrations. The [[Prime Minister of Seketan]], a title currently held by [[Simy Brasa]], is the {{wp|head of government}} and is confirmed by the Commons Council by a simple majority vote. | |||
The [[ | The province of [[Wilskland]] is [[Constitution of Seketan|constitutionally]] recognized as an [[independent state]] and retains significant autonomy from the national government. The province of Fjeska is specified in the constitution as autonomous. | ||
===Law=== | ===Law=== | ||
The [[Constitution | The [[Constitution of Seketan]] is the supreme law in contemporary Seketan, this version is written and applied in 1978 after the birth of the current Fourth Republic. The law according to the constitution is meant to vest government power to the Seketese people. [[Human rights in Seketan]] are upheld by the [[Declaration of Rights and Freedoms in our Republic of Seketan]]. | ||
===Foreign relations=== | ===Foreign relations=== | ||
{{Main article|Foreign relations of Seketan}} | |||
Since the birth of the Seketese fourth republic in 1978, Seketan has adopted a foreign policy based on the principle of neutrality and independence. Cooperation and peaceful coexistence with other states in the [[Nelborne]] have been an important tenant to Seketese foreign policy ever since the end of the [[Nelborne War]]. Seketan generally maintains a policy of extending diplomatic reach to as many entities as possible, whilst still remaining neutral in international conflicts and disputes. Maintaining independence from politically and economically binding organizations continues to be an important aspect of Seketan's foreign policy. | |||
Seketan is a member state of the {{wp|United Nations}}, {{wp|Council of Europe}}, {{wp|OECD}}, [[Nelborne Union]], and the [[Nelbec Council]]. Seketan is a {{wp|neutral state}}, but maintains close ties to other states in the [[Nelborne]]. Seketan is not a member of the {{wp|EFTA}} or the {{wp|European Single Market}}, despite previous negotiations. The majority of political parties elected in the [[Hervynsken]] harbour neutral or opposing views to [[Seketan–European Union relations|Seketan joining the European Union]] with polls revealing that a majority of [[Seketese people]] would oppose EU membership. | |||
Seketan is a member state of the {{wp|United Nations}}, {{wp|Council of Europe}}, {{wp|OECD}}, [[Nelborne Union]], and the [[Nelbec Council]]. Seketan is a {{wp|neutral state}}, but maintains close ties to other states in the [[Nelborne]]. Seketan is not a member of the {{wp|EFTA}} or the {{wp|European Single Market}}, despite previous negotiations. The majority of political parties elected in the [[Hervynsken]] | |||
Seketan has aligned itself with different leagues and alliances throughout history. After Seketan embraced the {{wp|Protestant Reformation}}, it aligned itself with the reformed countries of [[New Svealand]], [[Kingdom of Trjebia|Trjebia]], and {{wp|Denmark}}. With the rise of {{wp|nationalism}} and [[Nelbec unity|Pan-Nelbecism]] in the 17th and 18th centuries, Seketan was pulled into union with [[Alquiya]]. Beginning in the 20th century, Seketese nationalism and irredentism caused tensions with neighbouring countries. When the [[Great Nelborne War]] ended in 1937, Seketese imperialism and nationalism weakened, marking a beginning of neutrality in Seketese foreign policy. | Seketan has aligned itself with different leagues and alliances throughout history. After Seketan embraced the {{wp|Protestant Reformation}}, it aligned itself with the reformed countries of [[New Svealand]], [[Kingdom of Trjebia|Trjebia]], and {{wp|Denmark}}. With the rise of {{wp|nationalism}} and [[Nelbec unity|Pan-Nelbecism]] in the 17th and 18th centuries, Seketan was pulled into union with [[Alquiya]]. Beginning in the 20th century, Seketese nationalism and irredentism caused tensions with neighbouring countries. When the [[Great Nelborne War]] ended in 1937, Seketese imperialism and nationalism weakened, marking a beginning of neutrality in Seketese foreign policy. | ||
| Line 239: | Line 238: | ||
Seketan maintains close ties with the [[Kingdom of Trjebia|Kingdom of Trjebia (F.K.T.)]] due to their historical ties as Protestant countries and a large [[Northern Trjebs|Northern Trjebian]] population located in [[Bynan]]. Seketan is the only country that fully sides with the F.K.T. on the [[Trjebian dispute]] against Alquiya. | Seketan maintains close ties with the [[Kingdom of Trjebia|Kingdom of Trjebia (F.K.T.)]] due to their historical ties as Protestant countries and a large [[Northern Trjebs|Northern Trjebian]] population located in [[Bynan]]. Seketan is the only country that fully sides with the F.K.T. on the [[Trjebian dispute]] against Alquiya. | ||
Seketan maintains close ties with its fellow [[Nelbec countries]]. [[Lormotia]] and Seketan have historically supported each other against Alquiya, and today they maintain close ties with a large Seketese speaking minority located south | Seketan maintains close ties with its fellow [[Nelbec countries]]. [[Lormotia]] and Seketan have historically supported each other against Alquiya, and today they maintain close ties with a large Seketese-speaking minority located south of the country. Alquiya and Seketan maintain good relations with both countries being founding members of several Nelborne organizations; tensions arise with their disagreements on the [[Trjebia dispute]]. Seketan and [[New Svealand]] hold good relations and share membership in multiple organizations. {{wp|Iceland}} and Seketan maintain relations, but disputes in water and fishing territory remain unresolved. | ||
===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
The military branch of the Seketese government is known as the [[Seketese Armed Forces]], further | The military branch of the Seketese government is known as the [[Seketese Armed Forces]], further divided into the [[Seketese Land Army]], [[Seketese Navy]], and [[Seketese Air Force]]. | ||
===Administrative divisions=== | ===Administrative divisions=== | ||
{{main article|administrative divisions of Seketan|provinces of Seketan|List to municipalities in Seketan}} | |||
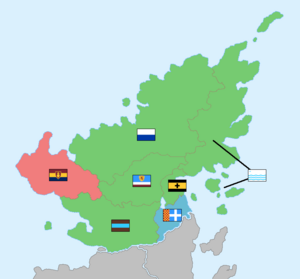
{{image frame | {{image frame | ||
|content = | |content = [[file:Map of Provinces Seketan.png|300px]] | ||
|caption = Provinces of Seketan | |caption = Provinces of Seketan | ||
}} | }} | ||
Seketan is divided into administrative divisions called [[ | Seketan is divided into administrative divisions called [[Administrative divisions of Seketan#Provinces|provinces]]. The seven [[Administrative divisions of Seketan#Provinces|provinces of Seketan]] upkeep the responsibility for matters of subnational and regional importance. Each province has its own official flag, language, and capital. The provinces [[Fjeska]] and [[Wilskland]] have their own devolved administrations and have a significant level of autonomy from the [[Hervynsken]]. | ||
Provinces are further subdivided into [[Municipalities of Seketan|municipalities]]. Several municipalities in Seketan like [[Conelibek]] or [[Winneston]] are | Provinces are further subdivided into [[Municipalities of Seketan|municipalities]]. Several municipalities in Seketan like [[Conelibek]] or [[Winneston]] are labelled as "cities" because of their high population and density. Municipalities are governed by municipal/city councils which are made up of elected members. Mayors are elected for leadership in municipalities. | ||
Seketan is divided into regions both officially and unofficially for various purposes. The [[government of Seketan|Seketese government]] defines six official statistical regions: [[Central Seketan|Central]], [[Western Seketan|Western]], [[Southern Seketan|Southern]], [[Northern Seketan|Northern]], [[Eastern Seketan]], and [[Wilskland]]. | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Flag !! Province !! Population !! | ! Flag !! Province !! Population !! Largest city !! Languages | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Flag of Gjenor.svg|25px|border]] || [[Gjenor]] || 1,141,500 || [[Conelibek]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | | [[File:Flag of Gjenor.svg|25px|border]] || [[Gjenor]] || 1,141,500 || [[Conelibek]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Flag of Wilskland.png|25px|border]] || [[Wilskland]] || 1,079,393 || [[ | | [[File:Flag of Wilskland.png|25px|border]] || [[Wilskland]] || 1,079,393 || [[Fyedor]] || [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Flag of Nelderjen.png|25px|border]] || [[Nelderjen]] || 988,047 || [[Winneston]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | | [[File:Flag of Nelderjen.png|25px|border]] || [[Nelderjen]] || 988,047 || [[Winneston]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Flag of Fjeska. | | [[File:Flag of Fjeska.png|25px|border]] || [[Fjeska]] || 912,250 || [[Loria]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]], [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Flag of Bynan.svg|25px|border]] || [[Bynan]] || 752,608 || [[Fevilla]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]], [[Seketese Trjebian|Trjeban]] | | [[File:Flag of Bynan.svg|25px|border]] || [[Bynan]] || 752,608 || [[Fevilla]] || [[Seketese language|Seketese]], [[Seketese Trjebian|Trjeban]] | ||
| Line 275: | Line 277: | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
{{Main article|Economy of Seketan}} | |||
The economy of Seketan is an upper-middle-income economy, with approximately half of the {{wp|gross domestic product}} (GDP) based in {{wp|Tertiary sector of the economy|services}}, supported by strong sectors in [[Energy in Seketan|energy]] and {{wp|Exploitation of natural resources|resource exploitation}}. Other important sectors in the economy of Seketan include [[agriculture in Seketan|agriculture]] and [[industry in Seketan|industry]]. | |||
===Corporations=== | ===Corporations=== | ||
| Line 282: | Line 285: | ||
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Duis molestie dui purus, sit amet accumsan enim feugiat eu. Sed neque ligula, blandit vel gravida pretium, pellentesque sit amet diam. Nullam odio mauris, ullamcorper at mauris id, varius viverra massa. Phasellus efficitur nibh convallis hendrerit pharetra. Donec non tellus et nisi venenatis ultricies a id diam. Sed non blandit eros. Aliquam aliquam eu libero in pulvinar. Integer non dui elementum, molestie nibh ut, hendrerit quam. Donec in nulla mi. Etiam nec erat vestibulum, posuere quam ut, finibus ante. Donec blandit massa lorem, sed placerat massa malesuada vitae. Fusce nisi odio, gravida in lectus eu, ultrices blandit magna. | Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Duis molestie dui purus, sit amet accumsan enim feugiat eu. Sed neque ligula, blandit vel gravida pretium, pellentesque sit amet diam. Nullam odio mauris, ullamcorper at mauris id, varius viverra massa. Phasellus efficitur nibh convallis hendrerit pharetra. Donec non tellus et nisi venenatis ultricies a id diam. Sed non blandit eros. Aliquam aliquam eu libero in pulvinar. Integer non dui elementum, molestie nibh ut, hendrerit quam. Donec in nulla mi. Etiam nec erat vestibulum, posuere quam ut, finibus ante. Donec blandit massa lorem, sed placerat massa malesuada vitae. Fusce nisi odio, gravida in lectus eu, ultrices blandit magna. | ||
Aliquam ante ex, vulputate interdum rutrum vel, convallis vitae neque. Nunc vitae tortor porta, porta leo sed, ornare turpis. Mauris gravida tellus orci, eu aliquam ante elementum eget. Interdum et malesuada fames ac ante ipsum primis in faucibus. Sed eu mi a tellus consequat convallis. Etiam ut viverra tellus, vel pretium velit. Integer a erat malesuada leo tincidunt rhoncus. Suspendisse non sapien aliquam libero placerat interdum varius non neque. Ut non volutpat dui. Aenean molestie eu elit id luctus. | Aliquam ante ex, vulputate interdum rutrum vel, convallis vitae neque. Nunc vitae tortor porta, porta leo sed, ornare turpis. Mauris gravida tellus orci, eu aliquam ante elementum eget. Interdum et malesuada fames ac ante ipsum primis in faucibus. Sed eu mi a tellus consequat convallis. Etiam ut viverra tellus, vel pretium velit. Integer a erat malesuada leo tincidunt rhoncus. Suspendisse non sapien aliquam libero placerat interdum varius non neque. Ut non-volutpat dui. Aenean molestie eu elit id luctus. | ||
In tristique accumsan lobortis. Sed quis mauris mi. Nunc semper ipsum sit amet orci hendrerit posuere. Donec accumsan velit tellus, id euismod tellus finibus vitae. Ut bibendum euismod felis eu sollicitudin. Praesent non purus justo. Integer non urna vulputate, tristique quam eget, consequat est. Cras tempor laoreet tempor. Orci varius natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. In auctor vitae mi molestie pulvinar. Fusce sed quam iaculis, mattis arcu quis, semper est. Fusce et mattis nibh. Quisque sed ligula sit amet purus tempor pulvinar. Proin mattis lorem at dui efficitur placerat. Aliquam mollis mauris risus, a vulputate erat ornare et. Aenean imperdiet arcu non massa mattis fringilla. | In tristique accumsan lobortis. Sed quis mauris mi. Nunc semper ipsum sit amet orci hendrerit posuere. Donec accumsan velit tellus, id euismod tellus finibus vitae. Ut bibendum euismod felis eu sollicitudin. Praesent non purus justo. Integer non urna vulputate, tristique quam eget, consequat est. Cras tempor laoreet tempor. Orci varius natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. In auctor vitae mi molestie pulvinar. Fusce sed quam iaculis, mattis arcu quis, semper est. Fusce et mattis nibh. Quisque sed ligula sit amet purus tempor pulvinar. Proin mattis lorem at dui efficitur placerat. Aliquam mollis mauris risus, a vulputate erat ornare et. Aenean imperdiet arcu non massa mattis fringilla. | ||
===Industry=== | ===Industry=== | ||
Seketan's industrial sector plays a significant role in the country's economic development. Manufacturing industries, such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and food processing, contribute to job creation and export revenue. The government has encouraged industrial development through incentives, infrastructure development, and the establishment of industrial zones, attracting both domestic and foreign investments. Seketan's industrial sector continues to evolve, adapting to changing market demands and incorporating advanced technologies for increased productivity and competitiveness. | |||
===Tourism=== | ===Tourism=== | ||
| Line 296: | Line 300: | ||
===Transport=== | ===Transport=== | ||
Seketan has a developed road, rail, and water transport system. Seketan's {{wp|controlled-access highway}} ([[Autyroute]]) network is principally | Seketan has a developed road, rail, and water transport system. Seketan's {{wp|controlled-access highway}} ([[Autyroute]]) network is principally centred on [[Central Seketan]] with the network extending to every province and major settlements. Intercity transport by rail is provided by [[SecRail]], a state-owned enterprise. Provincial roadways are maintained and planned by provincial assemblies. In the province of [[Ellinesa]], ferries serve island-to-island travel. | ||
[[Conelibek]] is serviced by the [[Conelibek Metro]]. [[Loria]], [[Winneston]], [[Fyedor]] and [[Fevilla]] have tram networks. | [[Conelibek]] is serviced by the [[Conelibek Metro]]. [[Loria]], [[Winneston]], [[Fyedor]] and [[Fevilla]] have tram networks. | ||
| Line 305: | Line 309: | ||
===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
[[file:Vilakas Valsts gimnazija.JPG|thumb|Faculty of Humanities | [[file:Vilakas Valsts gimnazija.JPG|thumb|Faculty of Humanities building in the [[University of Bynan]].]] | ||
Education in Seketan is administrated by the [[Ministry of Education (Seketan)|Ministry of Education]]. Seketese residents under the age of 16 are required by law to attend school in Seketan. Public education is delivered via primary schools, divided into Years 1 to 8, and secondary schools, divided into Years 9 to 12. {{wp|Preschool}} in Seketan are usually private centres | Education in Seketan is administrated by the [[Ministry of Education (Seketan)|Ministry of Education]]. Seketese residents under the age of 16 are required by law to attend school in Seketan. Public education is delivered via primary schools, divided into Years 1 to 8, and secondary schools, divided into Years 9 to 12. {{wp|Preschool}} in Seketan are usually private centres. | ||
Seketan | Language of insturction in Seketan varies by region. In most of the country, education is delivered in Seketese alongside a second language. In Fjeska and Wilskland, education is delivered in Fjeskan or Wilsk in areas where those languages are more commonly spoken. Until the age of 16, students in Seketan must enroll in second language classes. In predominately Seketese-speaking areas, [[French language in Seketan|French]] and [[English language in the Nelborne|English]] are the most commonly taught second languages with Alquiyan, Svealandic, Tvinan, Wilsk, and Fjeskan being regionally available. In non-Seketese speaking areas, students must take two-second language courses: one in Seketese and another from the list of languages Seketese speakers must learn such as French or English. | ||
Seketan | Seketan has 8 official universities: | ||
*[[University of North Conelibek]] | *[[University of North Conelibek]] | ||
*[[University of Djenibek]] | *[[University of Djenibek]] | ||
| Line 317: | Line 321: | ||
*[[University of Fyedor]] | *[[University of Fyedor]] | ||
*[[University of Loria]] | *[[University of Loria]] | ||
*[[University of Bynan]] | *[[University of Bynan]] (multiple campuses) | ||
*[[Syma Gjoske University]] | *[[Syma Gjoske University]] | ||
| Line 323: | Line 327: | ||
[[file:Conelibek International Airport signs.png|thumb|Billingual signs in [[Seketese language|Seketese]] and [[English]] in the [[Conelibek International Airport]].]] | [[file:Conelibek International Airport signs.png|thumb|Billingual signs in [[Seketese language|Seketese]] and [[English]] in the [[Conelibek International Airport]].]] | ||
The official language of Seketan is [[Seketese language|Seketese]]. | The official language of Seketan is [[Seketese language|Seketese]]. As of [[National Languages Act|2023]], [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]] and [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]] are recognized national languages. The Seketese language is a [[Nelbec languages|Nelbec language]], and is closely related to [[Fjeskan language|Fjeskan]] and more distantly to [[Wilsk language|Wilsk]]. Seketese (including [[Bynanese language|Bynanese]]) is spoken by 84% of the population, Wilsk is spoken by 7.9% primarily in [[Wilskland]], Fjeskan is spoken by 4.6% primarily in [[Fjeska]], [[Trjebian language|Trjebian]] is spoken by 2.4% primarily in southern [[Bynan]], and the remaining 1% of languages spoken are a mix of [[Alquiyan language|Alquiyan]], {{wp|Icelandic language|Icelandic}}, [[Tvinan language|Tvinan]], and [[Svealandic language|Svealandic]]. [[English language in the Nelborne|English]] and [[French language in the Nelborne|French]] are commonly spoken a second languages. | ||
The [[Christianization of Seketan]] and the translation of the {{wp|Holy Bible}} contributed to the development of the Seketese, Fjeskan, and Wilsk languages | The [[Christianization of Seketan]] and the translation of the {{wp|Holy Bible}} contributed to the development of the Seketese, Fjeskan, and Wilsk languages. The {{wp|printing press}} of the three versions of the Bible contributed to the centralization and standardization of all three languages. | ||
The Fjeskan and Wilsk languages are used in their own devolved parliaments for regional decision making. | The Fjeskan and Wilsk languages are used in their own devolved parliaments for regional decision-making. | ||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
| Line 346: | Line 350: | ||
|color4 = Green | |color4 = Green | ||
}} | }} | ||
The [[ | The [[Secens]] originally held polytheistic beliefs originating from [[Nelbec mythology]]. The [[Secenic Confederation]] [[Christianization of Seketan|became a Christian kingdom]] in the 9th century. The {{wp|Protestant Reformation}} was embraced in Seketan and the state religion changed into Seketese {{wp|Lutheranism}}. Ever since the [[First Seketese Republic]], Seketan has been a {{wp|secular}} state and currently has no state religion. The current [[Fourth Seketese Republic]] is a largely irreligious state; its [[Constitution of Seketan|constitution]] written in 1919 defines Seketan as a secular republic guaranteeing citizens the {{wp|freedom of religion}}, and its fourth revision removed any mentions of God blessing the [[President of Seketan]]. | ||
The majority of the Seketese population are defined as irreligious, including {{wp|agnostic}} beliefs, {{wp|athiesm}}, and undeclared religious beliefs | The majority of the Seketese population are defined as irreligious, including {{wp|agnostic}} beliefs, {{wp|athiesm}}, and undeclared religious beliefs. {{wp|Protestantism}} is the leading religion in Seketan, mainly the [[Church of Seketan]]. {{wp|Roman Catholicism}} remains a minority, most prelevant in [[Wilskland]] and [[Nelderjen]]. Seketan is home to a small community of [[History of the Jews in Seketan|Jews]], including the [[Nelvojish]]. | ||
According to the [[2010 Seketan census]], 57% of the population identifies as irreligious, 32% as {{wp|Protestant}}, 9% as {{wp|Catholic}}, and the remaining 2% being several other religions. | According to the [[2010 Seketan census]], 57% of the population identifies as irreligious, 32% as {{wp|Protestant}}, 9% as {{wp|Catholic}}, and the remaining 2% being several other religions. | ||
| Line 383: | Line 387: | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
Seketan shares deep historic roots with the rest of the [[Nelbec]] | Seketan shares deep historic roots with the rest of the [[Nelbec countries]]. Seketan's geography and [[Secens|Secen heritage]] has played a major role in shaping its culture with tundras, glaciers, mountains, and the wildlife playing a large role in [[Seketese mythology]], [[Seketese folklore|folklore]], and celebrations. Germanic culture has also influenced Seketese culture by "westernizing" it, with the [[Christianization of Seketan]] playing a large role. | ||
{{wp|Regionalism}} plays a large role in Seketese society | {{wp|Regionalism}} plays a large role in Seketese society. [[Fjeskans]] and [[Wilsks]] often assert an independent or coexistent national identity in relation to Seketan. | ||
===Literature=== | ===Literature=== | ||
| Line 402: | Line 406: | ||
===Visual arts=== | ===Visual arts=== | ||
[[Cjetor Dasen]] was a {{wp|Romantic nationalism|Romantic nationalist}} painter during the 19th century who created various masterpieces during the [[Seketese National Awakening]]. | |||
[[Amvel Elisen]] was a popular visual artist in post-revolution Seketan. | |||
===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
The cuisine of Seketan reflects the agriculture of the country. In Seketese culinary tradition, one is served an {{wp|entée}} of {{wp|rye bread}} with [[ | The cuisine of Seketan reflects the agriculture of the country. In Seketese culinary tradition, one is served an {{wp|entée}} of {{wp|rye bread}} with [[cašo]], followed by a {{wp|main course}} of seafood—usually {{wp|cod}} or {{wp|salmon}}—alongside {{wp|side dish|side dishes}} consisting of cold salads. {{wp|Pickling|Pickled}} and {{wp|Smoking (cooking)|smoked}} seafoods are staples of Seketese cuisine. The national dish of Seketan is [[cašo]], a potato-meat dish. | ||
Today's Seketese cuisine was heavily influenced by the {{wp|industrial revolution}} and the need for quick and cheap meals; {{wp|restaraunts}} and {{wp|street food|steet vendors}} sold quickly made [[cašo|quick cašo]] and [[Seketese sandwich|Seketese style sandwiches]]. Mass produced food was introduced to Seketan in the 20th century, bringing it the advent of Seketese food and beverage brands such as [[Gyenor|Gyenor Soda]] and [[Dalijec]]. Imports and {{wp|globalization}} have influenced Seketan into adopting culinary styles from around the world, further diversifying the cuisine of the country. | |||
Seketan produces and exports several {{wp|alcoholic}} drinks. Seketese {{wp|vodka}}, locally known as [[celim]], is mass produced by dozens of {{wp|distillery|distilleries}}, with popular brands including [[Cajic]], [[Bynanéça]], and [[Celim á Rynedan]]. Seketese {{wp|beer}} is typically dark or {{wp|stout}}, with major brands including [[Nébyça]], [[Bejond]], and [[Demani]]. Winemaking in Seketan is done mainly in [[Fjeska]]. Celim or vodka has been a traditional Seketese alcoholic beverage for thousands of years, with beer and ale being introduced in the {{wp|early modern period}}. The legal purchasing age in Seketan is 18 but there are no regulations for consumption. | Seketan produces and exports several {{wp|alcoholic}} drinks. Seketese {{wp|vodka}}, locally known as [[celim]], is mass produced by dozens of {{wp|distillery|distilleries}}, with popular brands including [[Cajic]], [[Bynanéça]], and [[Celim á Rynedan]]. Seketese {{wp|beer}} is typically dark or {{wp|stout}}, with major brands including [[Nébyça]], [[Bejond]], and [[Demani]]. Winemaking in Seketan is done mainly in [[Fjeska]]. Celim or vodka has been a traditional Seketese alcoholic beverage for thousands of years, with beer and ale being introduced in the {{wp|early modern period}}. The legal purchasing age in Seketan is 18 but there are no regulations for consumption. | ||
Coffee culture and coffeehouses are popular in Seketan, with the most popular coffeehouse-chains being [[McCafé in Seketan|McCafé]] (211 locations), [[CoffeePlace]] (190 locations), and {{wp|Costa Coffee|Costa}} (58 locations). | |||
===Cinema=== | ===Cinema=== | ||
The most renowned figures of Seketese cinema are [[Rividje Alité]], [[Gima Çanjor]], [[Sjedymaleþen Djenor]], [[ | The most renowned figures of Seketese cinema are [[Rividje Alité]], [[Gima Çanjor]], [[Sjedymaleþen Djenor]], [[Vyoléta Cores]], and [[Sjedor Çašé]]. | ||
===Sport=== | ===Sport=== | ||
Seketese teams participate in a wide variety of sports, including the [[Nelbec Hockey League]] and the [[Nelborne Football Premier League]] | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 423: | Line 435: | ||
*[[Nelbecia]] | *[[Nelbecia]] | ||
*[[Nelborne]] | *[[Nelborne]] | ||
{{Seketan topics}} | |||
{{Nelborne topics}} | |||
[[Category:Unitary states]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:06, 30 October 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Seketan République á Sécytana1 | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Myn Sécytan | |
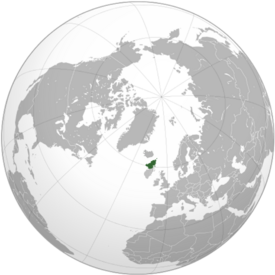 Location of Seketan (dark green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Conelibek |
| Official languages | Seketese |
| Recognised national languages | Fjeskan Wilska |
| Recognised regional languages | Trjebian Tvinan |
| Ethnic groups (2010) | |
| Demonym(s) | Seketese |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
• President | Fjedor Alesk |
• Prime Minister | Simy Brasa |
• Second Minister | Matieus Harmonn |
| Legislature | Hérvynsken |
| State Council | |
| Commons Council | |
| Establishment | |
• Kingdom | 9th century |
| 16 July 1884 | |
| 5 December 1918 | |
| 13 May 1924 | |
| 27 February 1945 | |
| 14 June 1978 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 106,229 km2 (41,015 sq mi) (106th) |
• Water (%) | 10% |
| Population | |
• 2016 estimate | 6.5 million (110th) |
• 2010 census | 6,426,108 |
• Density | 61.2/km2 (158.5/sq mi) (127th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2016 estimate |
• Total | $144 billion (87th) |
• Per capita | $22,153 |
| Gini (2016) | 28.5 low |
| HDI (2016) | very high (49th) |
| Currency | Seketese Djev (Đ) (SKD) |
| Time zone | UTC-1 (NST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +354 |
| Internet TLD | .sc |
| |
Seketan (Seketese: Sécytan), officially the Republic of Seketan (Seketese: République á Sécytana; alternate Seketese spellings: Républyc á Sécytana), is a Nelbec country in northwestern Europe. Bordering Alquiya, Trjebia, and New Svealand to the south, Seketan is comprised of the northern portion of Nelbecia. The majority of Seketese land is tundra with sprawling plains to the south and west points of the country. The country's climate is generally mild with severe winters seen in northern areas such as Ellinesa. The Fjoške mountains strike through the centre of the country bringing warm and wet conditions to central areas of the country. Seketan's population of 6.5 million (2016) is predominately urbanized within the country's 7 provinces. Conelibek is the largest and capital city of Seketan, and is home to most of the country's commercial and cultural activities. Other major cities include Loria, Winneston, Fyedor, and Porta.
Evidence of human activity in Seketan dates back to the Neolithic period. During the classical era, Seketan was inhabited by various North Nelbec groups and states. Classical societies declined where Seketan entered dark ages beginning in the 3rd century AD, whereafter the Secenic Empire arose and existed between the 4th and 6th centuries, although the extent of its grandeur is dubious and fabled. The Secenic Confederation succeeded the empire in the 6th century as a union of duchies whose borders inspire the provinces of Seketan. In the 9th century, the confederation was Christianized and Moress II declared himself King of Seketan. The kingdom emerged as a regional power, entering conflicts with the Trjebians, Alquiyans, Vikings and later Ny Svealanders. After a brief period of empire and dominance, the kingdom declined in influence.
Seketan entered into a personal union with Alquiya in 1765. The two countries were formally united into the Nelbec Empire in 1884, which was briefly considered a great power before its utter collapse following defeat in World War I. Following a revolution and civil war, the Second Seketese Republic was established and began the Kjedorate regime. Seketan defended itself during the Nelborne War and was reorganized into the Third Republic following the Wilsk representation movement. The Zemasy period and the consequential Fjeskan conflict culminated into protests and revolution that ousted Kjedorate authoritarian rule and formed the present Fourth Republic.
Seketan is a unitary parliamentary republic since 1978, with the President acting as a ceremonial head of state and the Prime Minister acting as head of government. Legislation is delivered through the country's bicameral parliament called the Hérvynsken. Seketan is geographically divided into 7 provinces; the provinces of Fjeska and Wilskland have their own devolved administrations based in their capitals of Loria and Fyedor. The official language of Seketan is Seketese; Fjeskan and Wilsk are recognized national languages and are official in Fjeska and Wilskland respectively.
Seketan is a developing country with an upper-middle-income economy largely focused on services, followed by industry—especially energy and mining—and agriculture. Seketan ranks 48th on the Human Development Index. Seketan is a founding member of the Nelbec Council and the Nelborne Union and has played a large role in intergovernmental activities in the Nelborne region. Despite previous negotiations, Seketan is not part of the European Economic Area or the European Union, however, it is a member of the Council of Europe.
History
Prehistory
Human settlement of what is today Seketan occurred during the Last glacial period where homo sapiens migrated from Europe into the Nelborne. Due to the lack of writing and evidence, it is unknown when Proto-Nelbec cultures came into existence, but it is often dated to originate from the Neolithic period. A large southern migration of Proto-Nelbecs took place, and those who stayed up north in what is today Seketan became the North Nelbec peoples. Proto-Secenic and Proto-Winnic cultures likely formed during Antiquity, eventually becoming the Sekens or Fjeskans and Wilsks respectively.
Although shrouded in fable and myth, it is likely that a large pan-Secenic empire existed in Late Antiquity, historiographically known as the Secenic Empire. This empire collapsed into 8 breakaway states which were later united in the Secenic Confederation led by the Conils and the Duchy of Conelibek. In the 9th century (traditionally in 867), Moress II of the Conils proclaimed himself King of Seketan, effectively establishing the Kingdom of Seketan as the successor state to the confederation. Around this time, the Christianization of Seketan occurred and written records in Latin began, marking the beginning of written history in Seketan.
Middle ages
The Kingdom of Seketan beginning with Moress II under the Coþepag dynasty embraced the Roman Catholic Church. Saint Gjenor was commonly accepted as the patron saint of Seketan; his influence established Medieval Seketese literature which was predominately produced by literate Seketese Christian bishops and priests. The church became central to Seketan's culture and politics and is often cited as a stabilizing force in uniting the Secenic states into Seketan. As part of its divine mission, the Kingdom of Seketan waged wars against neighbouring pagan states. Seketan conquered lands from the Kingdom of Trjebia during the Seco-Trjebian wars, and the Wilsks were subjugated where the Duchy of Wilskland as a client state.
The viking invasions during the early Middle Ages was the major crisis for medieval Seketan. Norse settlements were established on the western shores of Seketan, most successfully in the southeast. Seketese lands south of Fjeska were consistently pillaged and later abandoned due to their low economic output and stability caused by Norse expansion. These lands were claimed as overseas possessions of the Norwegian Empire, which resulted in numerous disputes and conflicts between Seketan and Norway. The Seco-Norwegian War from 1120 to 1128 resulted in Seketan's recognition of Norway's sovereignty over the Norse settlements whose land would later form New Svealand. Conflicts with Nordic powers over New Svealand, Iceland, Ellinesa, and other territories became commonplace in the Seketese Middle Ages.
The Black Death arrived in Seketan in 1352. Approximately a third of the population died during the outbreak. Despite the devastation, overall economic inequality was lowered as a result of the large population loss. King Enri III's long reign endured the Black Death, but his rule was characterized as a change in Seketese politics where adherence to the Roman Catholic Church became less of a priority. During the plague, Seketan accented Jewish refugees who were being persecuted by the South Nelbecs.
Across Europe, disagreements with the Catholic Church resulted in the Reformation. Lutheranism became fairly popular within Seketan and was not persecuted by Seketese monarchs. Giorgi IV established the Church of Seketan in 1531, marking the official split from the Catholic Church. Seketan maintained its religious stance through isolation as an island and solidarity with other Protestant seafaring kingdoms such as England and the Nordic countries. Seketan benefited economically and literacy, innovation, and education all benefited from the liberalized religion.
Seketese Empire

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed malesuada iaculis massa vel lacinia. Suspendisse commodo dui id justo vehicula, et ornare felis mattis. Praesent et dapibus ex. Aenean eu tellus cursus, luctus diam rhoncus, mollis orci. Duis et tortor quis nibh malesuada iaculis. Integer elementum urna a augue tincidunt pharetra. Pellentesque porta vulputate nisi, id maximus felis sagittis ut. Nam id euismod quam, eu elementum nibh. Suspendisse efficitur vitae quam ac mattis. Mauris a quam nec nisl mollis dignissim non quis nisi. Suspendisse mollis, erat vitae porttitor porttitor, massa ex aliquet justo, porttitor mattis arcu massa at augue. Aenean viverra nisi ac ullamcorper posuere. Maecenas rhoncus nec dolor sed porttitor. Nullam et erat leo. Aliquam vitae scelerisque mi.
Orci varius natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. Nulla sapien quam, vestibulum sed suscipit non, ultricies quis quam. Praesent dictum leo tincidunt nunc mollis, non mollis arcu congue. Vivamus luctus odio et ante facilisis condimentum. Morbi purus risus, ornare at pellentesque quis, tincidunt nec mi. Phasellus id ante justo. Praesent vitae quam nulla. Mauris augue quam, suscipit sit amet sapien ac, placerat tincidunt mi.
Sed eu ultricies tellus. Sed facilisis, leo quis accumsan dapibus, turpis sapien lobortis libero, id sodales lectus diam vitae mauris. Donec lacinia dolor sed enim lacinia, eu rhoncus sapien pharetra. Donec sed laoreet erat, sed dignissim justo. Class aptent taciti sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. Nullam id urna suscipit diam volutpat vehicula. Praesent vestibulum eros eleifend, rhoncus augue at, elementum ligula. Integer blandit molestie est, porta porttitor libero sagittis tristique. Vivamus condimentum, libero sit amet volutpat pretium, nunc lacus consectetur eros, a faucibus diam augue ut quam. Nulla vulputate diam dapibus hendrerit ultricies. Suspendisse ullamcorper urna ipsum, id elementum risus dictum eu.
Union with Alquiya
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed purus metus, laoreet id congue vel, feugiat quis arcu. Integer at ante a mi placerat porta vitae non nisl. Cras volutpat lectus vel leo imperdiet laoreet. Nulla consequat luctus ullamcorper. Nam magna mi, vulputate sit amet felis ac, sodales mattis ipsum. Curabitur vel metus cursus nunc cursus tincidunt vehicula non ipsum. Pellentesque rutrum elit risus, eu elementum risus hendrerit et. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Suspendisse potenti. Curabitur efficitur nisi sit amet posuere tempus. Donec in nisl eu quam pulvinar varius. Sed nec consequat dui, quis tempor ante.
Maecenas bibendum ex et elit suscipit, ut aliquam nibh vulputate. Integer fermentum diam quis auctor fringilla. Pellentesque a risus quis magna rutrum feugiat. Curabitur ultricies a nibh eget maximus. Vestibulum ac nibh ut ligula pulvinar suscipit quis egestas nisi. In tempus mattis enim sit amet egestas. Fusce sit amet lorem eget leo hendrerit dapibus sed condimentum arcu.
Sed at magna in nulla maximus aliquam. Aliquam nec sollicitudin magna. Aliquam venenatis nisl ipsum, ut faucibus velit condimentum ac. Pellentesque tincidunt dui sed nunc congue egestas. Ut eu est risus. Donec et lorem ac arcu lacinia egestas eget quis mauris. Sed at velit porttitor, scelerisque nulla vel, aliquet magna. Curabitur faucibus mi at ullamcorper semper. Cras bibendum dui nec ipsum mattis, ac euismod massa congue. Praesent id elementum ante, euismod varius orci. Curabitur ut leo faucibus, finibus dui congue, semper neque.
Republic
In concert with the collapse of the Nelbec Empire, two competing factions declared independence for Seketan, the Hervynsken backed and right-wing Kjedorates and the Djenibek based and left-wing Sosymets, resulting in the Seketese Civil War. The ensuing war was fought largely in Eastern and Southern Seketan, as well as around the Lake Region. Initially the Sosymets had the upper hand, catching the unprepared Kjedorates of guard in the Battle of Fjedor and the Battle of Loria, but gradual factionalism and infighting amoungst the various Sosymet militias allowed for a Kjedorate counter offensive and the eventual defeat of the Sosymets in the Battle of Sjon.
Upon victory in the civil war in 1923, the Kjedorates under Loren Allis declared a republic after reintigrating Free Conelibek and set out on reuniting Seketan under it's previous Kingdom borders. In 1924 an agreement was met with the breakaway Wilsk Republic to federate under the Federal Republic of Seketan and Wilskland, which would later be renamed as the Federal Republic of Seketan.
Loren Allis was reelected in the first free presidential election in 1925. Seketan experienced immense economic growth during the Roaring Twenties, and the period gave birth to modern Seketese art and culture. After the Wall Street Crash of 1929, reforms ordered by Allis personally resulted in the republic becoming a de facto rule by decree dictatorship, with Kjedorate Party symbols being incorporated into national flags and symbols.
Land disputes over the Rynedan peninsula with Alquiya escalated in the Nelborne War in 1933. New Svealand, allied with Seketan, declared war on Alquiya. Seketan was successful in defending its territory but failed to make any successful offensives. Lomortia entered the war in 1934 against Seketan. The war was won in 1937 with British and Danish support and resulted in the territorial status quo.
In the early 1970s, Seketan endured a banking crisis which later transformed into a currency crisis where the government attempted to pay back loans by printing more money. This period from 1970s Seketese history is referred to as the Zemasy period. This period resulted in unemployment in Seketan skyrocketing, along with rising ethnic tensions between the Sekens, Fjeskans, and Wilsks. Fjeskan insurgents, citing repression of their language rights and nonrecognition of the Fjeskan nation, began a low level insurgency in Fjeska. The FOD rose as the main Fjeskan insurgent group and was a key player in the resulting Fjeska conflict.
After a decade of financial crises and increasing political tension, the 1978 Seketese revolution came into force which resulted in Pesan being ousted from power and a constitutional referendum which birthed the Fourth Seketese Republic, where the president's role would be purely ceremonial, free and fair elections for the Commons Council were to be held, and where Fjeska would enjoy its own devolved parliament similar to Wilskland. The Kjedorate Party would contest Seketans first open election, but would eventually dissolve in 1988 after lacklustre results. Kjedorate imagery in national flags and symbols would be mostly phased out by 1981.
Geography
Geology
Climate
Politics
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Seketan |
The current system of government in Seketan is labelled as the Fourth Seketese Republic. The current republican system was established in 1978 after the Seketese constitutional referendum. Seketan is a parliamentary constitutional republic. The President of Seketan, currently Fjedor Alesk, is the head of state and is elected every six years; the president is largely a figurehead.
The Hérvynsken is made up of two chambers, the Commons Council, which represents the people of Seketan, and the State Council which represents the provincial administrations. The Prime Minister of Seketan, a title currently held by Simy Brasa, is the head of government and is confirmed by the Commons Council by a simple majority vote.
The province of Wilskland is constitutionally recognized as an independent state and retains significant autonomy from the national government. The province of Fjeska is specified in the constitution as autonomous.
Law
The Constitution of Seketan is the supreme law in contemporary Seketan, this version is written and applied in 1978 after the birth of the current Fourth Republic. The law according to the constitution is meant to vest government power to the Seketese people. Human rights in Seketan are upheld by the Declaration of Rights and Freedoms in our Republic of Seketan.
Foreign relations
Since the birth of the Seketese fourth republic in 1978, Seketan has adopted a foreign policy based on the principle of neutrality and independence. Cooperation and peaceful coexistence with other states in the Nelborne have been an important tenant to Seketese foreign policy ever since the end of the Nelborne War. Seketan generally maintains a policy of extending diplomatic reach to as many entities as possible, whilst still remaining neutral in international conflicts and disputes. Maintaining independence from politically and economically binding organizations continues to be an important aspect of Seketan's foreign policy.
Seketan is a member state of the United Nations, Council of Europe, OECD, Nelborne Union, and the Nelbec Council. Seketan is a neutral state, but maintains close ties to other states in the Nelborne. Seketan is not a member of the EFTA or the European Single Market, despite previous negotiations. The majority of political parties elected in the Hervynsken harbour neutral or opposing views to Seketan joining the European Union with polls revealing that a majority of Seketese people would oppose EU membership.
Seketan has aligned itself with different leagues and alliances throughout history. After Seketan embraced the Protestant Reformation, it aligned itself with the reformed countries of New Svealand, Trjebia, and Denmark. With the rise of nationalism and Pan-Nelbecism in the 17th and 18th centuries, Seketan was pulled into union with Alquiya. Beginning in the 20th century, Seketese nationalism and irredentism caused tensions with neighbouring countries. When the Great Nelborne War ended in 1937, Seketese imperialism and nationalism weakened, marking a beginning of neutrality in Seketese foreign policy.
Seketan maintains close ties with the Kingdom of Trjebia (F.K.T.) due to their historical ties as Protestant countries and a large Northern Trjebian population located in Bynan. Seketan is the only country that fully sides with the F.K.T. on the Trjebian dispute against Alquiya.
Seketan maintains close ties with its fellow Nelbec countries. Lormotia and Seketan have historically supported each other against Alquiya, and today they maintain close ties with a large Seketese-speaking minority located south of the country. Alquiya and Seketan maintain good relations with both countries being founding members of several Nelborne organizations; tensions arise with their disagreements on the Trjebia dispute. Seketan and New Svealand hold good relations and share membership in multiple organizations. Iceland and Seketan maintain relations, but disputes in water and fishing territory remain unresolved.
Military
The military branch of the Seketese government is known as the Seketese Armed Forces, further divided into the Seketese Land Army, Seketese Navy, and Seketese Air Force.
Administrative divisions
Seketan is divided into administrative divisions called provinces. The seven provinces of Seketan upkeep the responsibility for matters of subnational and regional importance. Each province has its own official flag, language, and capital. The provinces Fjeska and Wilskland have their own devolved administrations and have a significant level of autonomy from the Hervynsken.
Provinces are further subdivided into municipalities. Several municipalities in Seketan like Conelibek or Winneston are labelled as "cities" because of their high population and density. Municipalities are governed by municipal/city councils which are made up of elected members. Mayors are elected for leadership in municipalities.
Seketan is divided into regions both officially and unofficially for various purposes. The Seketese government defines six official statistical regions: Central, Western, Southern, Northern, Eastern Seketan, and Wilskland.
| Flag | Province | Population | Largest city | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gjenor | 1,141,500 | Conelibek | Seketese | |
| Wilskland | 1,079,393 | Fyedor | Wilsk | |
| Nelderjen | 988,047 | Winneston | Seketese | |
| Fjeska | 912,250 | Loria | Seketese, Fjeskan | |
| Bynan | 752,608 | Fevilla | Seketese, Trjeban | |
| Ellinesa | 604,095 | Porta | Seketese | |
| Giorgi-Alesk | 94,850 | Alitz | Seketese, Wilsk |
Economy
The economy of Seketan is an upper-middle-income economy, with approximately half of the gross domestic product (GDP) based in services, supported by strong sectors in energy and resource exploitation. Other important sectors in the economy of Seketan include agriculture and industry.
Corporations
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Duis molestie dui purus, sit amet accumsan enim feugiat eu. Sed neque ligula, blandit vel gravida pretium, pellentesque sit amet diam. Nullam odio mauris, ullamcorper at mauris id, varius viverra massa. Phasellus efficitur nibh convallis hendrerit pharetra. Donec non tellus et nisi venenatis ultricies a id diam. Sed non blandit eros. Aliquam aliquam eu libero in pulvinar. Integer non dui elementum, molestie nibh ut, hendrerit quam. Donec in nulla mi. Etiam nec erat vestibulum, posuere quam ut, finibus ante. Donec blandit massa lorem, sed placerat massa malesuada vitae. Fusce nisi odio, gravida in lectus eu, ultrices blandit magna.
Aliquam ante ex, vulputate interdum rutrum vel, convallis vitae neque. Nunc vitae tortor porta, porta leo sed, ornare turpis. Mauris gravida tellus orci, eu aliquam ante elementum eget. Interdum et malesuada fames ac ante ipsum primis in faucibus. Sed eu mi a tellus consequat convallis. Etiam ut viverra tellus, vel pretium velit. Integer a erat malesuada leo tincidunt rhoncus. Suspendisse non sapien aliquam libero placerat interdum varius non neque. Ut non-volutpat dui. Aenean molestie eu elit id luctus.
In tristique accumsan lobortis. Sed quis mauris mi. Nunc semper ipsum sit amet orci hendrerit posuere. Donec accumsan velit tellus, id euismod tellus finibus vitae. Ut bibendum euismod felis eu sollicitudin. Praesent non purus justo. Integer non urna vulputate, tristique quam eget, consequat est. Cras tempor laoreet tempor. Orci varius natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. In auctor vitae mi molestie pulvinar. Fusce sed quam iaculis, mattis arcu quis, semper est. Fusce et mattis nibh. Quisque sed ligula sit amet purus tempor pulvinar. Proin mattis lorem at dui efficitur placerat. Aliquam mollis mauris risus, a vulputate erat ornare et. Aenean imperdiet arcu non massa mattis fringilla.
Industry
Seketan's industrial sector plays a significant role in the country's economic development. Manufacturing industries, such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and food processing, contribute to job creation and export revenue. The government has encouraged industrial development through incentives, infrastructure development, and the establishment of industrial zones, attracting both domestic and foreign investments. Seketan's industrial sector continues to evolve, adapting to changing market demands and incorporating advanced technologies for increased productivity and competitiveness.
Tourism
Proin sed viverra est. Morbi vitae tempus nisi, sit amet semper diam. In hac habitasse platea dictumst. Donec ut libero cursus, congue augue rutrum, dignissim sapien. Donec mattis ultrices velit, eu tristique ex sollicitudin ac. Vivamus auctor eros id mauris dignissim pulvinar. Pellentesque vitae dolor nibh. Morbi in nulla tincidunt, euismod lorem at, egestas sem. Proin eu purus rutrum, luctus est at, volutpat dolor. Fusce fringilla iaculis massa, a mollis est malesuada et. Integer porttitor congue nisi, ac pharetra diam posuere eget. Morbi in libero eget elit posuere pellentesque et non nibh. Curabitur vel eros ante. Maecenas faucibus lorem sed mauris imperdiet, sit amet tincidunt augue blandit. Ut maximus erat ante, non egestas tellus lobortis ut. Ut sodales, ante et tristique tristique, enim elit ornare velit, a lacinia quam lectus sit amet quam.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. In hac habitasse platea dictumst. Etiam neque leo, ultrices in mollis vel, congue sed urna. Aliquam bibendum consequat ipsum eu feugiat. Fusce eget molestie lectus. Aenean hendrerit tristique velit. Aliquam eget tortor vitae arcu laoreet pulvinar. Vestibulum vestibulum erat nisl, in placerat risus vestibulum id.
Transport
Seketan has a developed road, rail, and water transport system. Seketan's controlled-access highway (Autyroute) network is principally centred on Central Seketan with the network extending to every province and major settlements. Intercity transport by rail is provided by SecRail, a state-owned enterprise. Provincial roadways are maintained and planned by provincial assemblies. In the province of Ellinesa, ferries serve island-to-island travel.
Conelibek is serviced by the Conelibek Metro. Loria, Winneston, Fyedor and Fevilla have tram networks.
Demographics
Education

Education in Seketan is administrated by the Ministry of Education. Seketese residents under the age of 16 are required by law to attend school in Seketan. Public education is delivered via primary schools, divided into Years 1 to 8, and secondary schools, divided into Years 9 to 12. Preschool in Seketan are usually private centres.
Language of insturction in Seketan varies by region. In most of the country, education is delivered in Seketese alongside a second language. In Fjeska and Wilskland, education is delivered in Fjeskan or Wilsk in areas where those languages are more commonly spoken. Until the age of 16, students in Seketan must enroll in second language classes. In predominately Seketese-speaking areas, French and English are the most commonly taught second languages with Alquiyan, Svealandic, Tvinan, Wilsk, and Fjeskan being regionally available. In non-Seketese speaking areas, students must take two-second language courses: one in Seketese and another from the list of languages Seketese speakers must learn such as French or English.
Seketan has 8 official universities:
- University of North Conelibek
- University of Djenibek
- Cjetor Mynseau University
- University of Winneston
- University of Fyedor
- University of Loria
- University of Bynan (multiple campuses)
- Syma Gjoske University
Languages
The official language of Seketan is Seketese. As of 2023, Fjeskan and Wilsk are recognized national languages. The Seketese language is a Nelbec language, and is closely related to Fjeskan and more distantly to Wilsk. Seketese (including Bynanese) is spoken by 84% of the population, Wilsk is spoken by 7.9% primarily in Wilskland, Fjeskan is spoken by 4.6% primarily in Fjeska, Trjebian is spoken by 2.4% primarily in southern Bynan, and the remaining 1% of languages spoken are a mix of Alquiyan, Icelandic, Tvinan, and Svealandic. English and French are commonly spoken a second languages.
The Christianization of Seketan and the translation of the Holy Bible contributed to the development of the Seketese, Fjeskan, and Wilsk languages. The printing press of the three versions of the Bible contributed to the centralization and standardization of all three languages.
The Fjeskan and Wilsk languages are used in their own devolved parliaments for regional decision-making.
Religion
Religious belief in Seketan (2010 census)
The Secens originally held polytheistic beliefs originating from Nelbec mythology. The Secenic Confederation became a Christian kingdom in the 9th century. The Protestant Reformation was embraced in Seketan and the state religion changed into Seketese Lutheranism. Ever since the First Seketese Republic, Seketan has been a secular state and currently has no state religion. The current Fourth Seketese Republic is a largely irreligious state; its constitution written in 1919 defines Seketan as a secular republic guaranteeing citizens the freedom of religion, and its fourth revision removed any mentions of God blessing the President of Seketan.
The majority of the Seketese population are defined as irreligious, including agnostic beliefs, athiesm, and undeclared religious beliefs. Protestantism is the leading religion in Seketan, mainly the Church of Seketan. Roman Catholicism remains a minority, most prelevant in Wilskland and Nelderjen. Seketan is home to a small community of Jews, including the Nelvojish.
According to the 2010 Seketan census, 57% of the population identifies as irreligious, 32% as Protestant, 9% as Catholic, and the remaining 2% being several other religions.
Largest municipalities
| Municipality | Province | Population | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conelibek | Gjenor | 827,193 | Conelibek has special status as a city municipality. |
| Winneston | Nelderjen | 592,832 | Winneston has special status as a city municipality. |
| Loria | Fjeska | 528,275 | Loria has special status as a city municipality. |
| Fyedor | Wilskland | 402,872 | Fyedor has special status as a city municipality. |
| Porta | Ellinesa | 394,729 | |
| Walycesa | Wilskland | 205,926 | |
| Fevilla | Bynan | 201,822 | Fevilla has special status as a city municipality. |
| Becjonyn | Wilskland | 192,742 | |
| Amytan | Ellinesa | 182,798 | |
| Zynatan | Bynan | 145,283 |
Culture
Seketan shares deep historic roots with the rest of the Nelbec countries. Seketan's geography and Secen heritage has played a major role in shaping its culture with tundras, glaciers, mountains, and the wildlife playing a large role in Seketese mythology, folklore, and celebrations. Germanic culture has also influenced Seketese culture by "westernizing" it, with the Christianization of Seketan playing a large role.
Regionalism plays a large role in Seketese society. Fjeskans and Wilsks often assert an independent or coexistent national identity in relation to Seketan.
Literature
Seketese literature first appeared with the emergence of Secenic political entities, such as the Secenic Confederation and eventually the Kingdom of Seketan. The Seketese language and its writing system was heavily influenced by early but influential poets and writers. The spread of Christianity resulted in the adoption of the Latin alphabet in Nelbec languages, with the translation of the bible influencing the Seketese language.
Early literature revolved around Seketese mythology and folklore. Svac én Þynad (English: literally With them and Die; translated Follow and Die) is one of the most famous Seketese myths that tell the tale of woodland creatures all competing against one another for a treasure that doesn't exist.
Literature "boomed" during the interwar period of the 20th century. Major events that shaped Seketan's history such as World War I, the Seketese Revolution and Civil War, the Great Nelborne War, and World War II were key themes explored by authors at the time. Seketese literature during the period was often cynical and sometimes nihilistic, reflective of the large amounts of atrocities that occurred in Seketan during the early 20th century. Dystonian novel The Greater Republic written by Martin Gev and published in 1940 is cited as the most influential of these works; the novel was a best-seller domestically and in foreign countries.
Celebrated modern Seketese poets and authors include Martin Gev, Sjédymaleþen Lyjonskn, Šema Linda, Pierre Wern, and Fjedor Ésyšji, among others.
Music
Visual arts
Cjetor Dasen was a Romantic nationalist painter during the 19th century who created various masterpieces during the Seketese National Awakening.
Amvel Elisen was a popular visual artist in post-revolution Seketan.
Cuisine
The cuisine of Seketan reflects the agriculture of the country. In Seketese culinary tradition, one is served an entée of rye bread with cašo, followed by a main course of seafood—usually cod or salmon—alongside side dishes consisting of cold salads. Pickled and smoked seafoods are staples of Seketese cuisine. The national dish of Seketan is cašo, a potato-meat dish.
Today's Seketese cuisine was heavily influenced by the industrial revolution and the need for quick and cheap meals; restaraunts and steet vendors sold quickly made quick cašo and Seketese style sandwiches. Mass produced food was introduced to Seketan in the 20th century, bringing it the advent of Seketese food and beverage brands such as Gyenor Soda and Dalijec. Imports and globalization have influenced Seketan into adopting culinary styles from around the world, further diversifying the cuisine of the country.
Seketan produces and exports several alcoholic drinks. Seketese vodka, locally known as celim, is mass produced by dozens of distilleries, with popular brands including Cajic, Bynanéça, and Celim á Rynedan. Seketese beer is typically dark or stout, with major brands including Nébyça, Bejond, and Demani. Winemaking in Seketan is done mainly in Fjeska. Celim or vodka has been a traditional Seketese alcoholic beverage for thousands of years, with beer and ale being introduced in the early modern period. The legal purchasing age in Seketan is 18 but there are no regulations for consumption.
Coffee culture and coffeehouses are popular in Seketan, with the most popular coffeehouse-chains being McCafé (211 locations), CoffeePlace (190 locations), and Costa (58 locations).
Cinema
The most renowned figures of Seketese cinema are Rividje Alité, Gima Çanjor, Sjedymaleþen Djenor, Vyoléta Cores, and Sjedor Çašé.
Sport
Seketese teams participate in a wide variety of sports, including the Nelbec Hockey League and the Nelborne Football Premier League
Notes
- 1.^ Other regional or alternative spellings, including Républyc á Sécytana, are also considered correct by the Secéteça Académie but are generally not used in official writings.