Novus Natum Galaxy: Difference between revisions
m (Layfet moved page AAS09282022-1 to Novus Natum Galaxy: name change) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The Novus Natum Galaxy is one of the furthest known objects to mankind. It is a collisional ring galaxy that was formed in the early stages of the universe. It was discovered by the Mount Nebula National Observatory Team using the Extremely Distant Discovery Infrared Exploration System (EDDIES) developed by [[The Vanna]]'s National Astronomical Sciences and Observation Department. The object was discovered on accident during a test of the EDDIES. The EDDIES won't be fully operational until September, 2023. Currently little is known about the object. Upon discovery, the galaxy was given the [[Aldeve Astronomical Survey]] designation AAS09282022-1. In December 2022, NASOD proposed renaming AAS09282022-1 to the Newborn Galaxy or Novus Natum Galaxy to the International Astronomical Commission's Naming Board. It was approve the next day. | |||
{{Template:Tendor system table}} | {{Template:Tendor system table}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:47, 30 December 2022
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| AAS09282022-1 | |
|---|---|
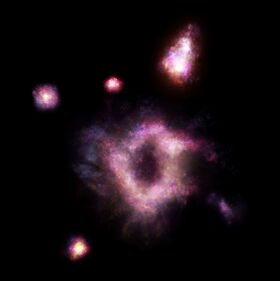 AAS09282022-1 collated photograph by the Extremely Distant Discovery Infrared Exploration System (EDDIES) | |
| Observation data (Epoch A2000) | |
| Constellation | TBA |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | collisional ring galaxy |
| Notable features | TBA |
| Other designations | |
| Newborn Galaxy (not official), Novus Natum Galaxy (not official) | |
The Novus Natum Galaxy is one of the furthest known objects to mankind. It is a collisional ring galaxy that was formed in the early stages of the universe. It was discovered by the Mount Nebula National Observatory Team using the Extremely Distant Discovery Infrared Exploration System (EDDIES) developed by The Vanna's National Astronomical Sciences and Observation Department. The object was discovered on accident during a test of the EDDIES. The EDDIES won't be fully operational until September, 2023. Currently little is known about the object. Upon discovery, the galaxy was given the Aldeve Astronomical Survey designation AAS09282022-1. In December 2022, NASOD proposed renaming AAS09282022-1 to the Newborn Galaxy or Novus Natum Galaxy to the International Astronomical Commission's Naming Board. It was approve the next day.

