Brown Sea Community: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
Member states share rights and responsibilities, such as economic mutual aid, disaster relief, military defence, the settlement of border disputes between themselves, sharing scientific and diplomatic information, and issuing joint statements. The Brown Sea Community Council is the governing body, with its members being appointed by its member states' legislatures, and the working language is [[Ziba]]. | Member states share rights and responsibilities, such as economic mutual aid, disaster relief, military defence, the settlement of border disputes between themselves, sharing scientific and diplomatic information, and issuing joint statements. The Brown Sea Community Council is the governing body, with its members being appointed by its member states' legislatures, and the working language is [[Ziba]]. | ||
With a land area of nearly 3 million square kilometres and a population of nearly 300 million, the Brown Sea Community has a major presence on the international stage. Its demography and geography are diverse, with ethnic groups such as [[Dezevauni people|Dezevauni]], {{wp|Lao people|Kachai}}, [[Pelangi people|Pelangi]], Kabuese, languages such as Ziba, {{wp|Lao language| | With a land area of nearly 3 million square kilometres and a population of nearly 300 million, the Brown Sea Community has a major presence on the international stage. Its demography and geography are diverse, with ethnic groups such as [[Dezevauni people|Dezevauni]], {{wp|Lao people|Kachai}}, [[Pelangi people|Pelangi]], Kabuese, languages such as Ziba, {{wp|Lao language|Kachai}}, {{wp|Javanese language|Kabuese}} and belief systems such as {{wp|irreligion}}, [[Badi]] and [[Solarian Catholic Church|Solarian Catholicism]]. Its combined GDP PPP is worth nearly $5 trillion, and nominal near $3 trillion. While its members are part of the Global South, they are broadly wealthier, healthier and stabler than neighbours in [[Bahia]], [[Southeast Coius]] or on the [[Great Steppe]], giving the organisation comparative regional influence and autarky. | ||
=== History === | === History === | ||
[[File:Cement Road Base Working in Rainbow Riverside Park 20141022b.JPG|thumb|right|BSC funded construction work in South Kabu]] | [[File:Cement Road Base Working in Rainbow Riverside Park 20141022b.JPG|thumb|right|BSC funded construction work in South Kabu]] | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| {{wp|Lao_language| | | {{wp|Lao_language|Kachai}}, [[Ziba]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| {{Flag|South Kabu}} | | {{Flag|South Kabu}} | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 20 September 2022
|
Flag | |
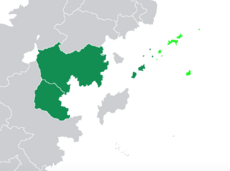 Location of the Brown Sea Community (dark green) in Coius, light green are claimed territories of member states. | |
| Type | Regional organisation |
| Membership | Expand
3 states |
| Establishment | |
• Establishment | 19th of September 1975 |
| Area | |
• | 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 285,000,000 |
• Density | 100/km2 (259.0/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2.5 (DST) |
The Brown Sea Community is a regional organisation composed of three states located around the Brown Sea in Southeast Coius. It is an organisation for coordinating and relating the socialist states of the region; all its three member states are also members of the larger Association for International Socialism. Brown Sea Community members work together widely on military, cultural, scientific, diplomatic and economic matters.
The organisation was established in 1975, as the Association of Emerging Socialist Economies had shown itself to be ideologically heterodox and incoherent, and incapable of judicious action. It is closely associated with the AIS, both as a matter of principle, and operating to coordinate its members more tightly at a smaller scale; it has been compared in its functionality to the Euclean Community, the Mutual Assistance Organisation, or the Asteria Inferior Common Market.
Member states share rights and responsibilities, such as economic mutual aid, disaster relief, military defence, the settlement of border disputes between themselves, sharing scientific and diplomatic information, and issuing joint statements. The Brown Sea Community Council is the governing body, with its members being appointed by its member states' legislatures, and the working language is Ziba.
With a land area of nearly 3 million square kilometres and a population of nearly 300 million, the Brown Sea Community has a major presence on the international stage. Its demography and geography are diverse, with ethnic groups such as Dezevauni, Kachai, Pelangi, Kabuese, languages such as Ziba, Kachai, Kabuese and belief systems such as irreligion, Badi and Solarian Catholicism. Its combined GDP PPP is worth nearly $5 trillion, and nominal near $3 trillion. While its members are part of the Global South, they are broadly wealthier, healthier and stabler than neighbours in Bahia, Southeast Coius or on the Great Steppe, giving the organisation comparative regional influence and autarky.
History
Formed in 1975.
Member states
| Name | Capital | Accession | Population | Area (km2) | GDP (Int$ bn) |
GDP per capita (Int$) |
GDP PPP (Int$ bn) |
GDP PPP per capita (Int$) |
Gini | HDI | Languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bazadavo | 1975 | 190,902,213 | 2,000,000 | 2,328 | 12,194 | 3,990 | 20,899 | 20.4 | 0.850 | Ziba | |
| Pers | 1975 | 86,842,742 | 713,879 | 640,292 | 7,373 | Kachai, Ziba | |||||
| Ayukarta | 1975 | 7,841,984 | 44,154 | 45 | 5,773 | 101 | 12,938 | 23.1 | 0.736 | Kabuese |

